Curved Gram Negative Rods (Exam 2)
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
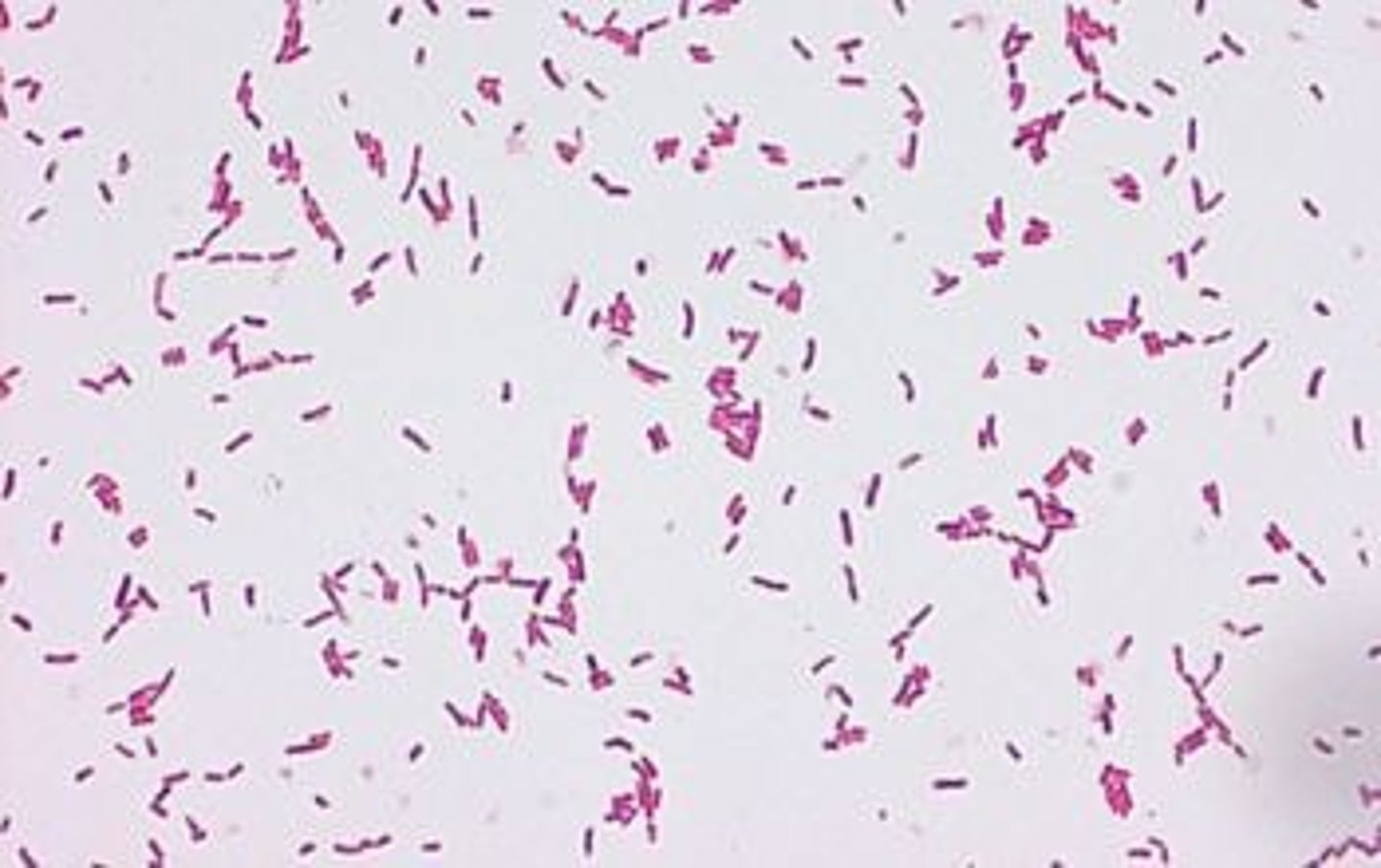
Campylobacter Gram Stain
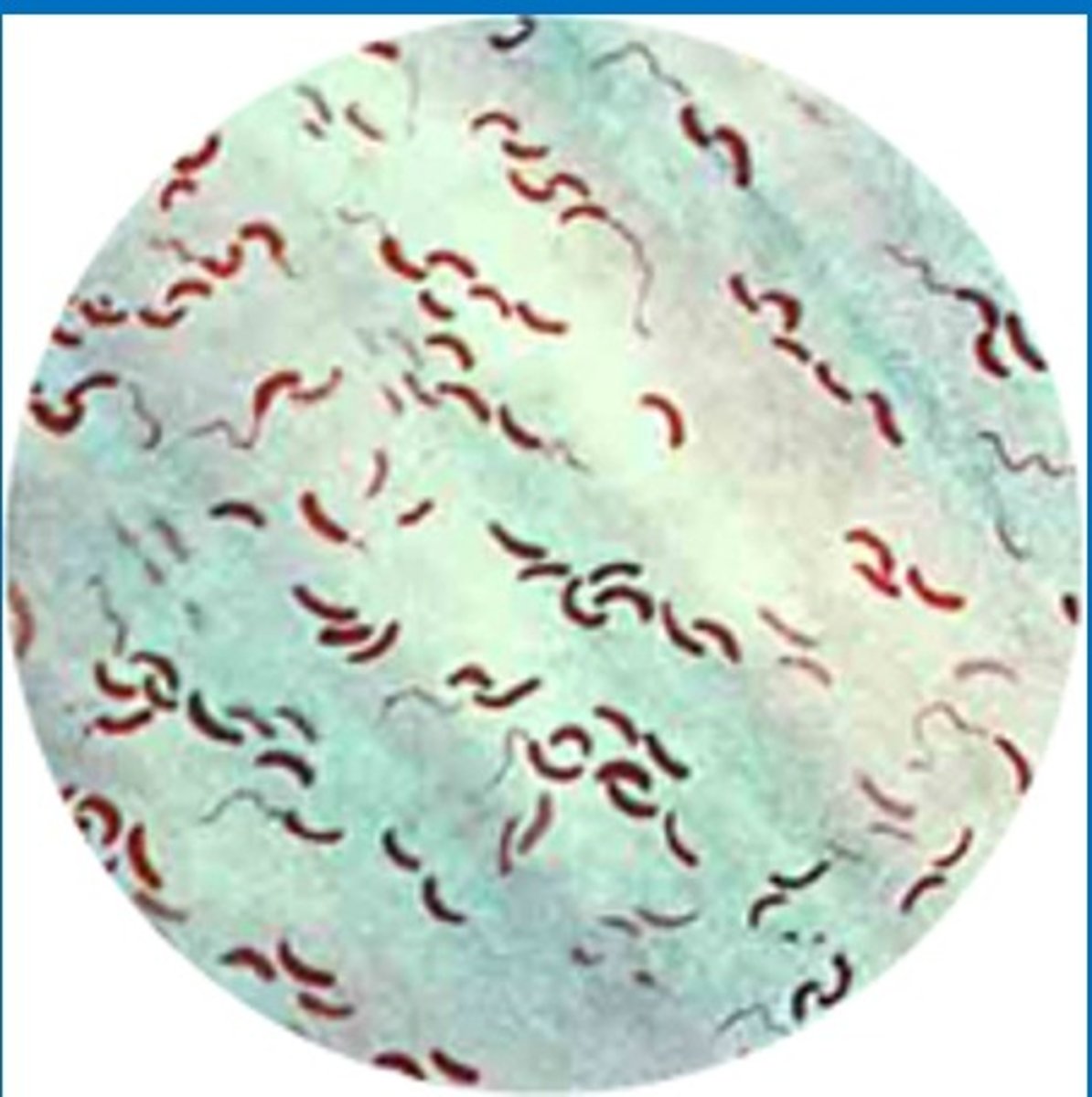
Campylobacter colonies
What kind of agar can be used to culture Campylobacter?
- CAMPY-BAP
- CAMPY- CVA
- CAMPY-Charcoal
Campylobacter must be incubated on its own selective media at ______C.
42C
Campylobacter is ______ (aerophilic/etc.).
microaerophilic
Campylobacter is oxidase and catalase ______.
positive
What are the strains of Campylobacter?
- C. jejuni
- C. coli
- C. fetus
What test should be used to differentiate C. jejuni from C. coli?
Hippurate
C. jejuni is hippurate ______, while C. coli is hippurate ______.
positive, negative
C. jejuni and C. coli are both susceptible to ______ and resistant to ______.
nalidixic acid, cephalothin
Campylobacter can cause gastroenteritis with exposure to ______ or ingestion of contaminated ...
farm animals, water/dairy/poultry
Campylobacter can be transmitted ______, person-to-person.
sexually
Campylobacter gastroenteritis has an incubation period of ______ days after ingestion.
2-10 days
What are the S/Sx of Campylobacter gastroenteritis?
Cramps, bloody diarrhea, fever, chills
Self-limiting, resolves in 2-6 days
C. fetus is hippurate ______.
negative
C. fetus is resistant to ______ and susceptible to ______.
nalidixic acid, cephalothin
Helicobacter pylori is associated with gastric, peptic and duodenal ______.
ulcers
Helicobacter pylori may have ______ transmission.
human-to-human
Helicobacter pylori may be found in ______.
fresh ground water
Helicobacter pylori presence increases the risk of gastric ______.
cancer
Helicobacter pylori can be detected via gastric ______.
biopsy
Helicobacter pylori can be tested via ______ test or ______ test.
urea (2 hour)/CLO
Helicobacter pylori can be detected via a urea ______ test.
breath
Helicobacter pylori antigen can be detected in ______ samples.
stool
Helicobacter pylori can also be detected via ______.
PCR
Enterobacterales and Vibrionaceae can be differentiated with a ______ test.
oxidase
Enterobacterales are oxidase ______, while Vibrionaceae are oxidase ______.
negative, positive
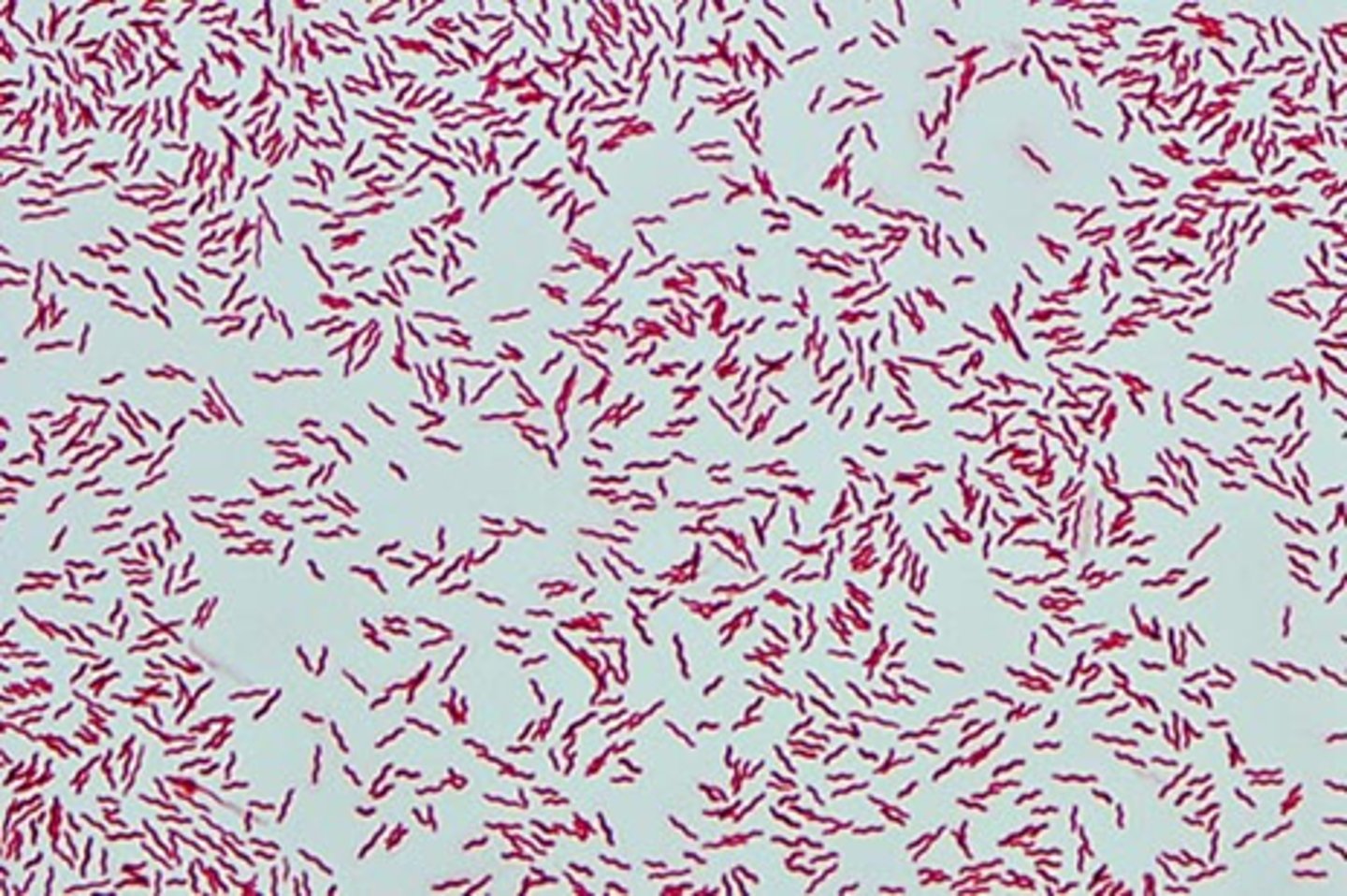
Vibrio Gram Stain
Vibrio cause ______ or ______ infections, sometimes septicemia.
gastrointestinal, wound
Vibrio are ______ anaerobes.
facultative
Vibrio are oxidase _______ and ______ reducers.
positive, nitrate
Vibrio are susceptible to ______.
O/129
Vibrio are inositol ______.
negative
What are the Vibrio sucrose fermenters?
V. cholerae (also VP positive), V. alginolyticus
What are the Vibrio sucrose non-fermenters?
V. parahaemolyticus, V. vulnificus (lactose fermenter)
Vibrio require ______ to grow (except for V. cholerae and V. mimicus).
NaCl
Vibrio cholerae produces ______.
cholera toxin
The cholera toxin B subunit binds to ______ receptor.
GM1-ganglioside
The A2 subunit of the cholera toxin facilitates entry of ______ into the cell.
A1
Once in the cell, the A1 subunit of the cholera toxin stimulates production of ______.
adenylate cyclase
This increases the levels of ______.
cAMP
cAMP stimulates hypersecretion of ______ and ______ out of the cell, causing dehydration.
electrolytes, water
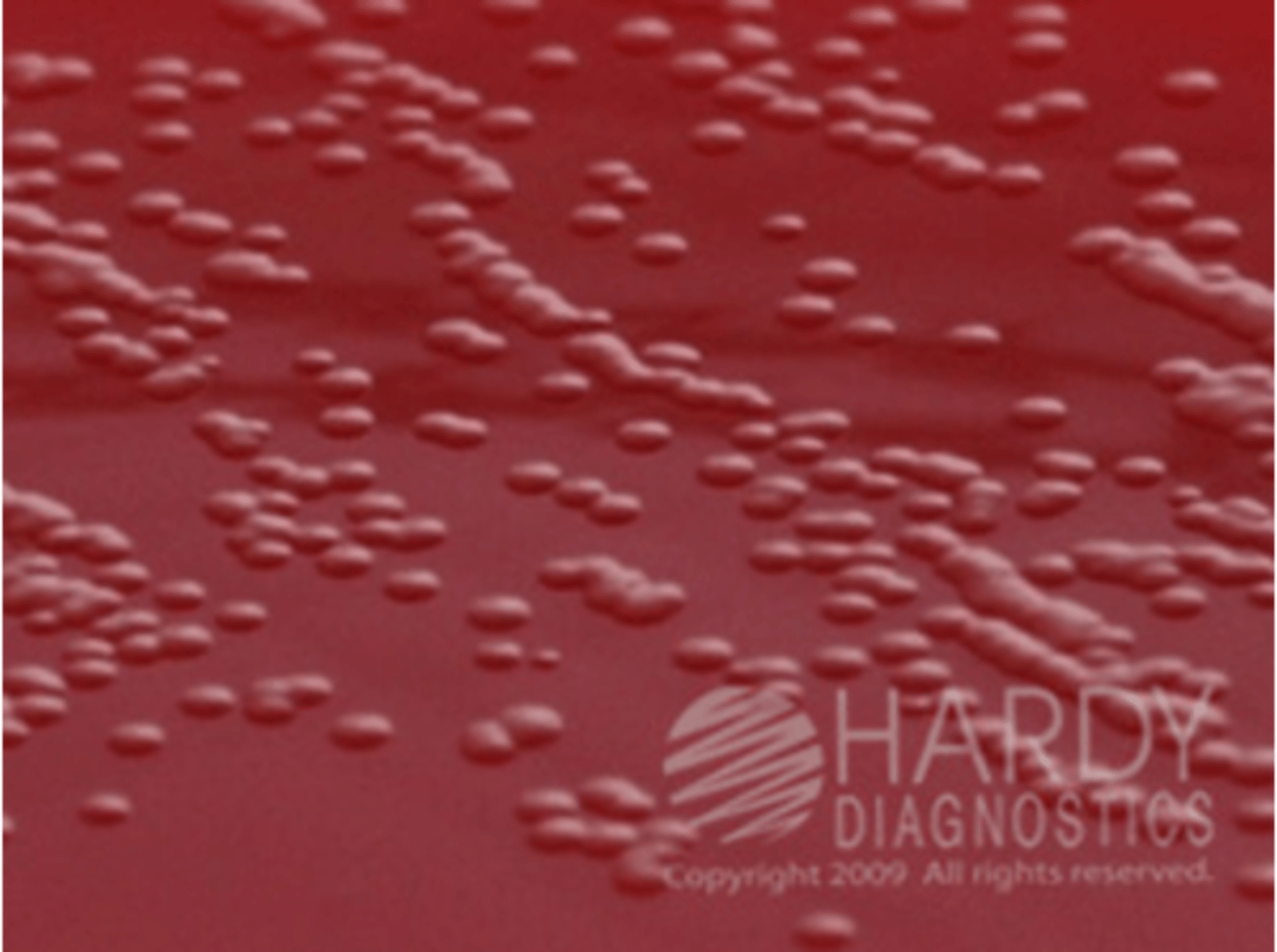
Vibrio cholerae colonies on blood agar
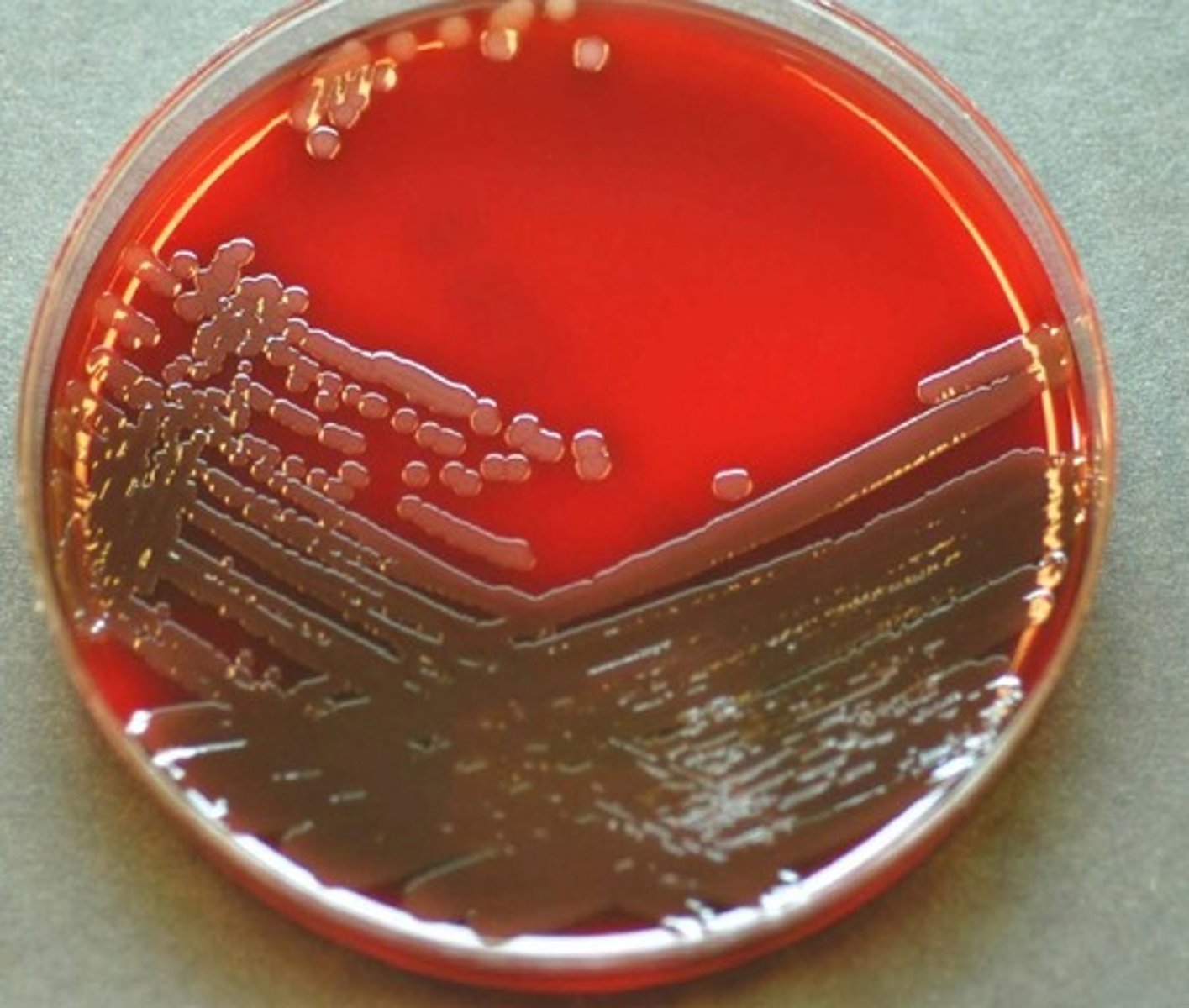
Vibrio cholerae is commonly ______ hemolytic.
beta
Vibrio cholerae on MacConkey agar is ______ fermenting.
non-lactose (no pink)
Vibrio cholerae on Hektoen agar is ______ fermenting.
sucrose (yellow colonies)
Vibrio cholerae on TCBS is ______ fermenting.
sucrose (yellow colonies)
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is associated with ______ and ______ infections.
gastroenteritis, wound
Vibrio parahaemolyticus requires 1-8% ______ for growth.
NaCl
Vibrio parahaemolyticus colonies on BAP are ______ in color.
gray/brown
Vibrio parahaemolyticus on Hektoen shows ______ and ______ fermenting.
non-sucrose, non-lactose
On Hektoen, Vibrio parahaemolyticus shows no ______ production, as well.
H2S
Vibrio parahaemolyticus on TCBS
Non-sucrose fermenting
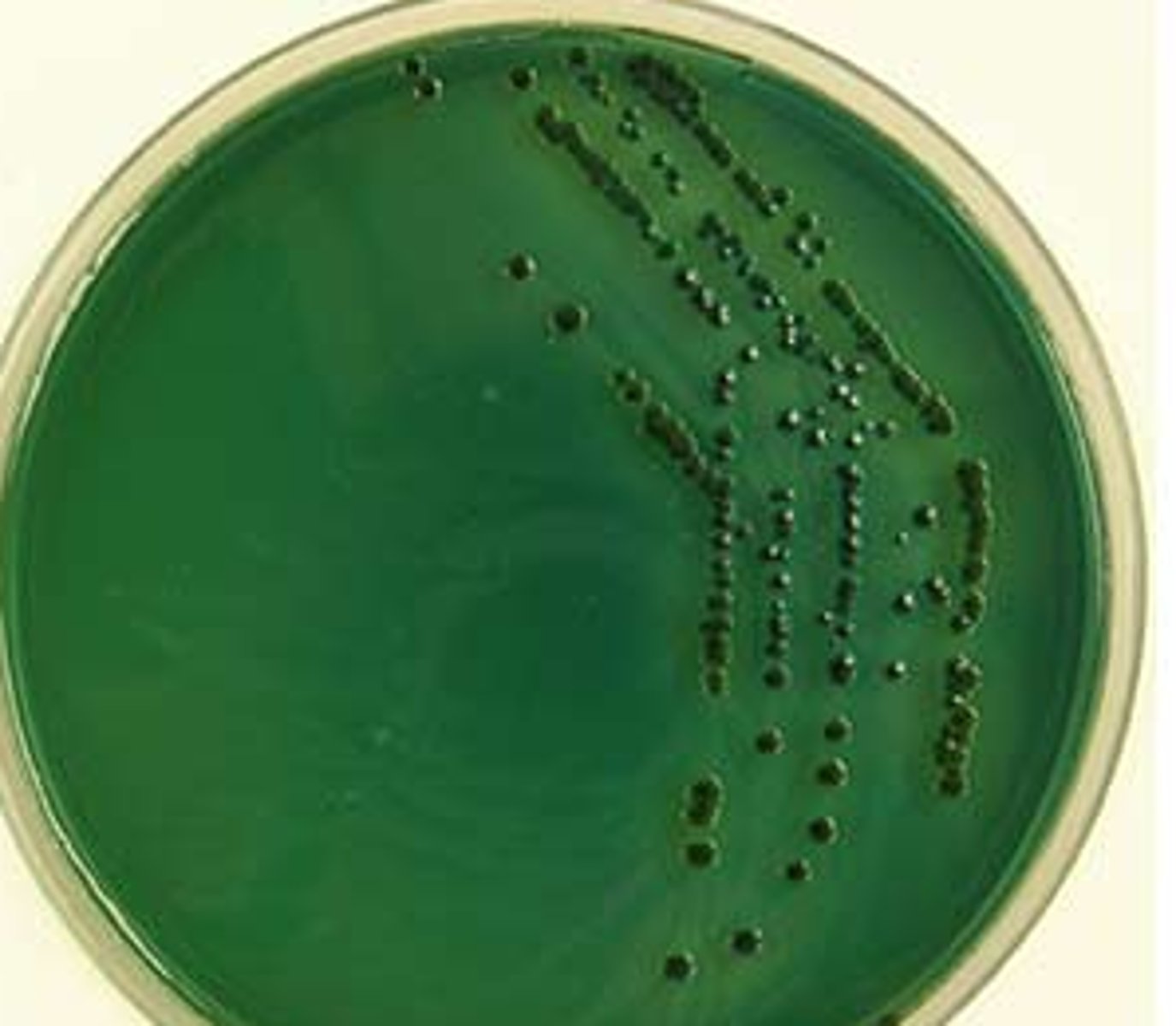
TCBS is selective for ______ and differentiates based on ______ fermentation.
Vibrios, sucrose
Vibrio require alkaline peptone water broth with 1% ______ for growth.
NaCl
Aeromonas
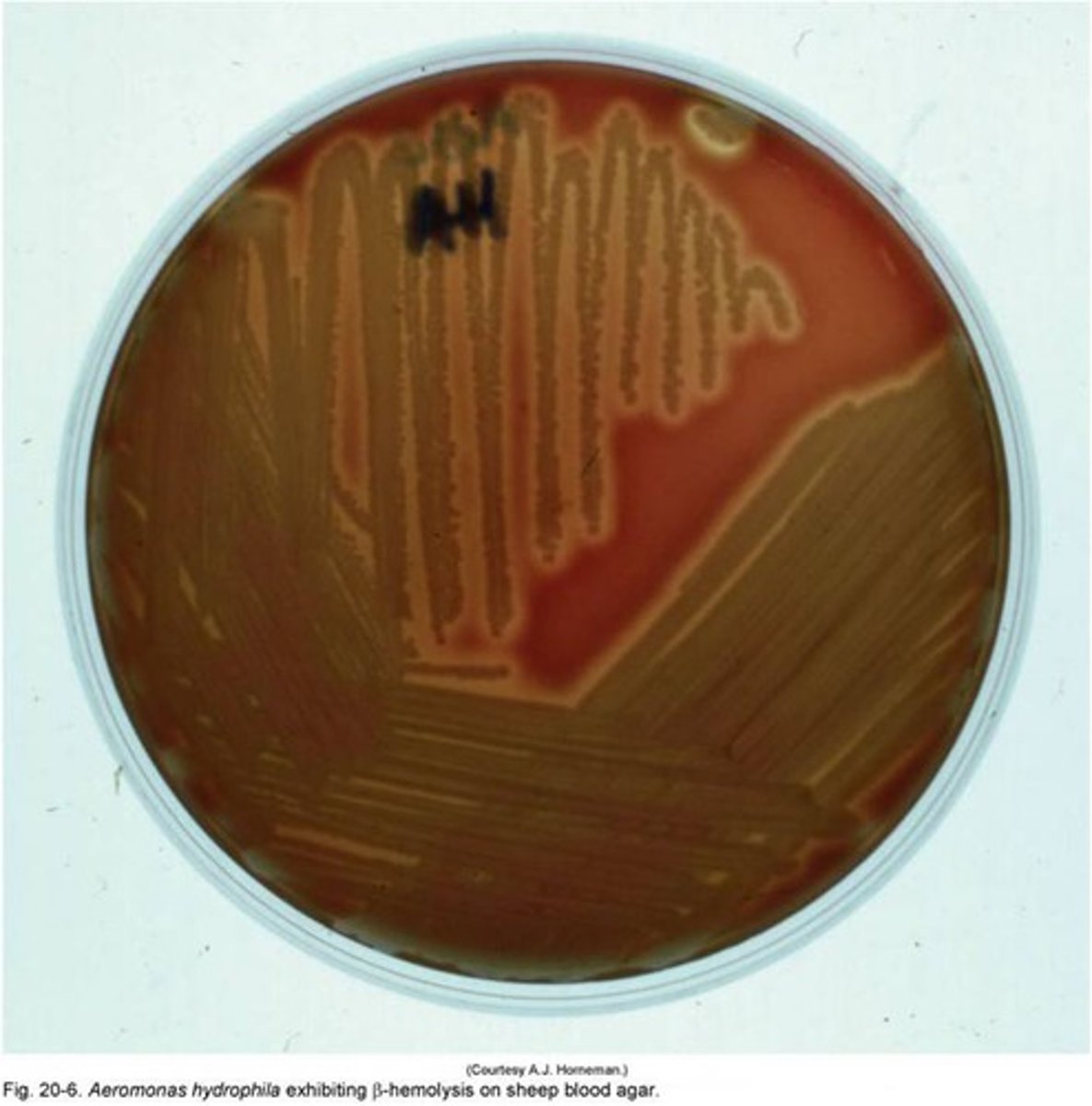
Aeromonas causes what diseases?
Gastroenteritis, septicemia and wound infections
Aeromonas colonies
Most are beta-hemolytic
Aeromonas on MacConkey agar shows ______ fermentation.
lactose (most)
On CIN, Aeromonas shows ______ colonies.
pink
Aeromonas are oxidase ______ and glucose ______.
positive, non-fermenters
Most Aeromonas are indole ______.
positive
Aeromonas are ______ to O/129.
resistant
Plesiomonas shigelloides causes ______ and ______ infections.
gastroenteritis, wound
Plesiomonas shigelloides don't grow in increased ______.
NaCl
Plesiomonas shigelloides require at least ______C temperature for growth.
8C
Most Plesiomonas are lactose ______.
fermenters (might be slow)
Plesiomonas are oxidase ______.
positive
Plesiomonas is ______ to O/129.
sensitive
Plesiomonas ferments ______.
inositol
Plesiomonas