Modeling With Rasters II: Intro to MCDA
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is MCDA?
a framework used to evaluate and prioritize multiple and often conflicting criteria to supports-decision making
has no priorities
Why do we use MCDA in GIS
Helps make complex spatial decisions more structured and transparent
integrates both qualitative and quantitative factor
combines spatial data with expert knowledge and stakeholder input
Components of an MCDA problem?
a goal or set of goals to achieve
multiple decisions makers involved in decisions making process
conflicting preferences among decisions maker
potentially many alternatives to evaluate
each alternative is evaluation based on multiple criteria
decisions are often made under uncertainty
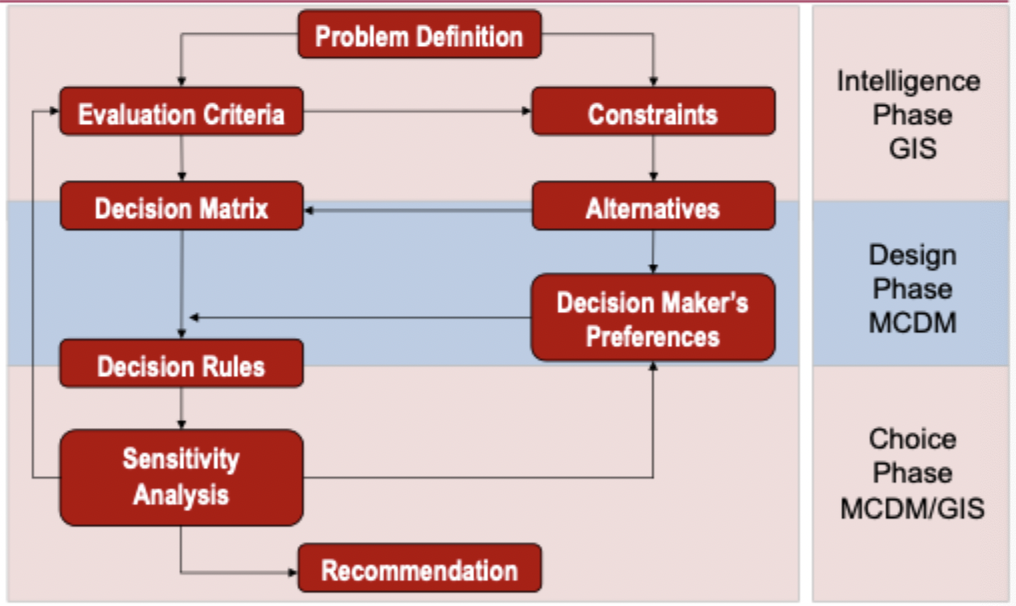
Steps for Spatial MCDA mapping
(1) define the goal
what is being mapped what information is needed(objectives: maximization, or minimization)
(2) Criterion Maps
will selected concurrent scale
What do Criterion maps do?
determine the criteria for inclusion
should all be measureable
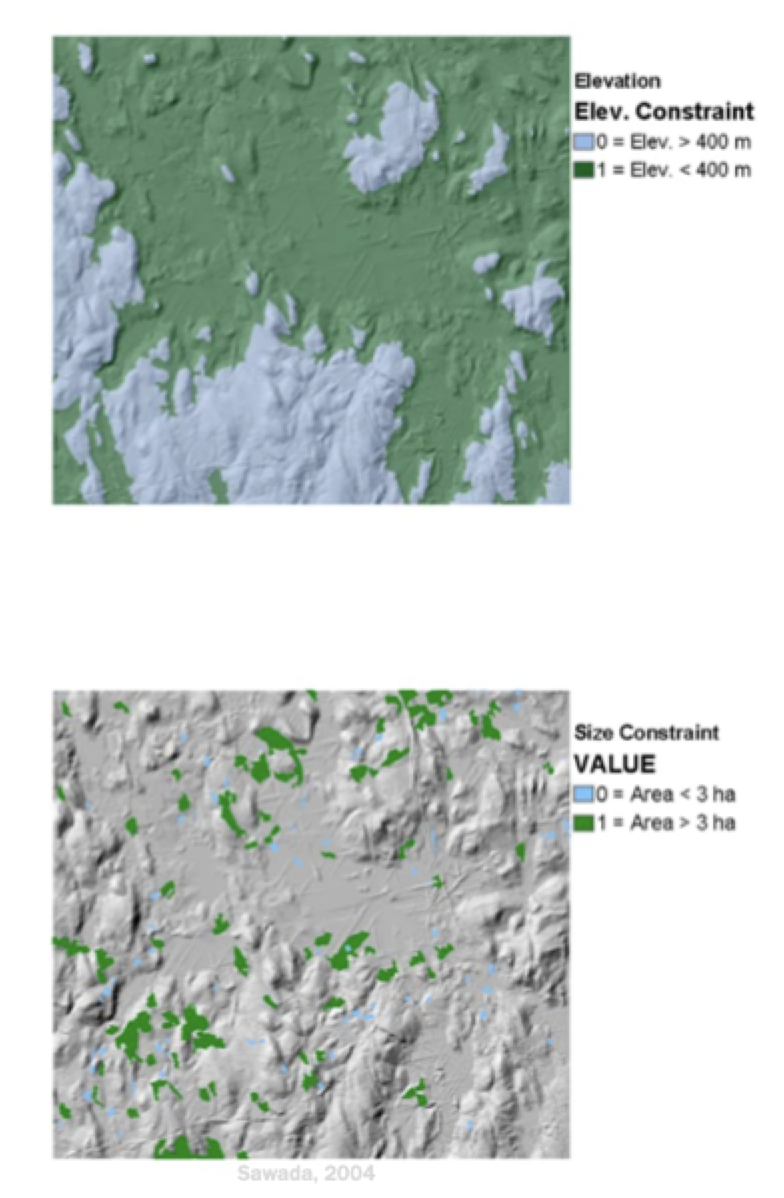
Constraint Maps
displays limitations on the values that the attribute may assume
limit the alternatives under consideration and are boolean in nautre(act as a mask)
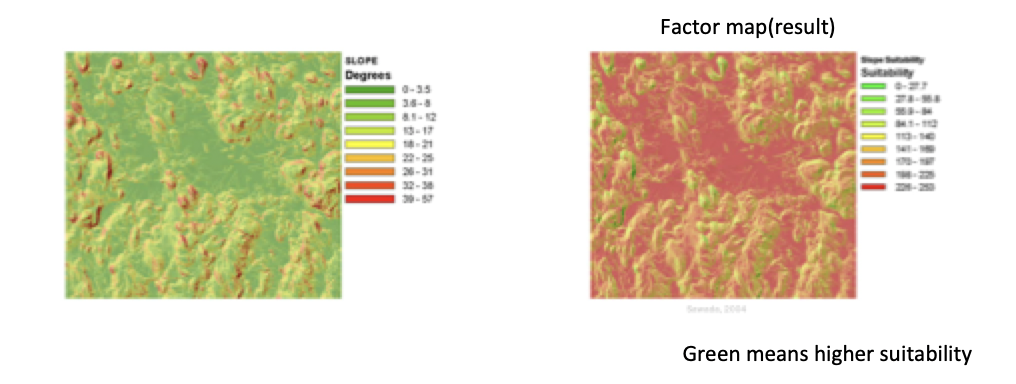
Factor Maps
enhance or detract from suitability of an alternative
Natural Scales
needed for constructing criterion maps
well established, common usage and interpretation
directly measurable, physical or observable data
Constructed Scales
subjective in nature, created by assigning values based on judgment, ranking on classification
for construction of criterion maps
Proxy Measures
mo obvious measures available to directly estimate an attribute/objective, so something stands in for it
for construction of criterion maps
Deterministic Scales
for construction of criterion maps
known with certainty or measured precisely
Fuzzy Scales
For construction of criterion maps
lacking a solid boundary, involves uncertainty or vagueness, with values assigned based on likelihood or membership to a group