Introduction to Genetic Algorithms + Knapsack
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
what is a genetic algorithm?
algorithms inspired by evolutionary biology
2
New cards
when are genetic algorithms helpful?
helpful for areas where no solution seems available - GAs can find partial answer (near optimal solution) but other methods might be better
3
New cards
what features of genetic algorithms mimic evolution?
evolution process
gene
chromosomes
gene pool
adaptation
gene
chromosomes
gene pool
adaptation
4
New cards
what is the evolution process?
the change in the gene pool over time
* genes mutate randomly which introduces variation to gene pool
* individuals survive through natural selection
* populations evolve and breed via recombination
* genes mutate randomly which introduces variation to gene pool
* individuals survive through natural selection
* populations evolve and breed via recombination
5
New cards
what is a gene?
biological hereditary unit passed on for generations
6
New cards
what is a chromosome?
cells where the nucleus contains multiple genes
7
New cards
what is a gene pool?
set of genes for a species
8
New cards
what is adaptation?
change in environment causes change in gene pool for survival
9
New cards
what is the representation for a genetic algorithm?
* each gene is a binary digit
* a chromosome is a single string of genes (digits)
* a solution to a problem is encoded as a chromosome
* a chromosome is a single string of genes (digits)
* a solution to a problem is encoded as a chromosome
10
New cards
how are the components for heuristic algorithms similar to genetic algorithms?
* encoding = **representation**
* encoding must cover whole **search space (gene pool)**
* **fitness function** uses to rate the solution the chromosome represents
* encoding must cover whole **search space (gene pool)**
* **fitness function** uses to rate the solution the chromosome represents
11
New cards
what is the knapsack problem?
* NP-complete problem
* given n items, each with a weight and value, determine the items to include in the knapsack so that the total weight is less than or equal to a given limit and the total value is as large as possible
* given n items, each with a weight and value, determine the items to include in the knapsack so that the total weight is less than or equal to a given limit and the total value is as large as possible
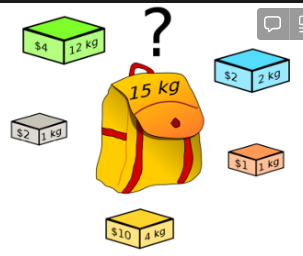
12
New cards
what is the representation of the knapsack problem using genetic algorithms?
eg. binary encoding where 1 - take item, 0 - don’t take the item and length - number of items we have to consider
invalid solution could be all 1s, means the weight limitation stated in the problem brief would be invalid
to deal with them
* create only valid chromosomes from start by catering to conditions
* create any solution and deal with validity afterwards
consider this when we create a representation
invalid solution could be all 1s, means the weight limitation stated in the problem brief would be invalid
to deal with them
* create only valid chromosomes from start by catering to conditions
* create any solution and deal with validity afterwards
consider this when we create a representation
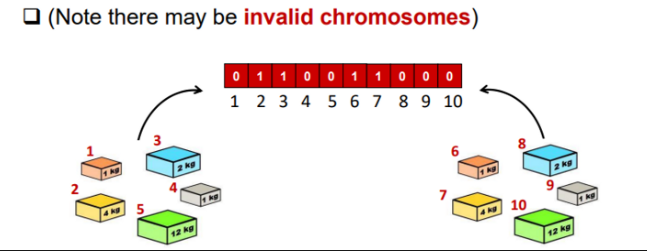
13
New cards
what is the fitness function for the knapsack problem?
* total value
* low value = bad, high value - good, easy-to-compare solutions
* invalid solutions can be given the total value = 0
* low value = bad, high value - good, easy-to-compare solutions
* invalid solutions can be given the total value = 0
14
New cards
what is a population?
the number of chromosomes alive at any time
15
New cards
what are the generations?
the number of times breeding has occurred, aka. the number of times a population is created (older generation produces new generation)
16
New cards
how does a genetic algorithm work \[informal\] ?
* create @@population@@ of random @@chromosomes@@
* each chromosome scored with @@fitness function@@
* create a new @@generation@@ through @@genetic operators@@ - selection/ crossover/ mutation
* @@repeat@@ until complete - best solution found
* each chromosome scored with @@fitness function@@
* create a new @@generation@@ through @@genetic operators@@ - selection/ crossover/ mutation
* @@repeat@@ until complete - best solution found
17
New cards
what are the 3 genetic operators for Holland’s genetic algorithms?
crossover
mutation
selection
mutation
selection
18
New cards
what is crossover?
breeding, passing genes of 2 parents to create children
19
New cards
what crossover operators are there?
* one point crossover - Holland original
* uniform crossover - improvement
* uniform crossover - improvement
20
New cards
what is CP/ P - crossover point?
a random number up to the size of the chromosome generated, in order to split both parent chromosomes into 2 sections
21
New cards
what is one point crossover?
chromosomes \[with n genes\] move to the crossover pool with CP chance
\
1. each chromosome is randomly paired with another chromosome (A and B)
2. for each pair, a crossover point P is randomly generated with a value between 2 and n-1
3. to create 2 children (C and D),
1. all genes from 1 → P from parent A are given to child C
2. all genes from 1 → P from parent B are given to child D
3. all genes from P+1 → n from parent A are given to child C
4. all genes from P+1 → n from parent B are given to child D
4. the children are added to the population
\
1. each chromosome is randomly paired with another chromosome (A and B)
2. for each pair, a crossover point P is randomly generated with a value between 2 and n-1
3. to create 2 children (C and D),
1. all genes from 1 → P from parent A are given to child C
2. all genes from 1 → P from parent B are given to child D
3. all genes from P+1 → n from parent A are given to child C
4. all genes from P+1 → n from parent B are given to child D
4. the children are added to the population
![chromosomes \[with n genes\] move to the crossover pool with CP chance
\
1. each chromosome is randomly paired with another chromosome (A and B)
2. for each pair, a crossover point P is randomly generated with a value between 2 and n-1
3. to create 2 children (C and D),
1. all genes from 1 → P from parent A are given to child C
2. all genes from 1 → P from parent B are given to child D
3. all genes from P+1 → n from parent A are given to child C
4. all genes from P+1 → n from parent B are given to child D
4. the children are added to the population](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/96de1369839f456aa71c14c375c7872d.jpeg)
22
New cards
what is uniform crossover?
more powerful crossover where for each gene there is a 50% chance the child C will get the gene from parent A and 50% chance child C will get the gene from parent B. child D will get the gene from the opposing parent
* each bit is treated separately instead of separating the whole chromosome into only 2 chunks.
\
eg. for parent 1, P1 has 50/50 chance to be for child 1 or 2
* if it goes to child 1, child 2 gets the corresponding gene in parent 2
* and vice versa
* each bit is treated separately instead of separating the whole chromosome into only 2 chunks.
\
eg. for parent 1, P1 has 50/50 chance to be for child 1 or 2
* if it goes to child 1, child 2 gets the corresponding gene in parent 2
* and vice versa
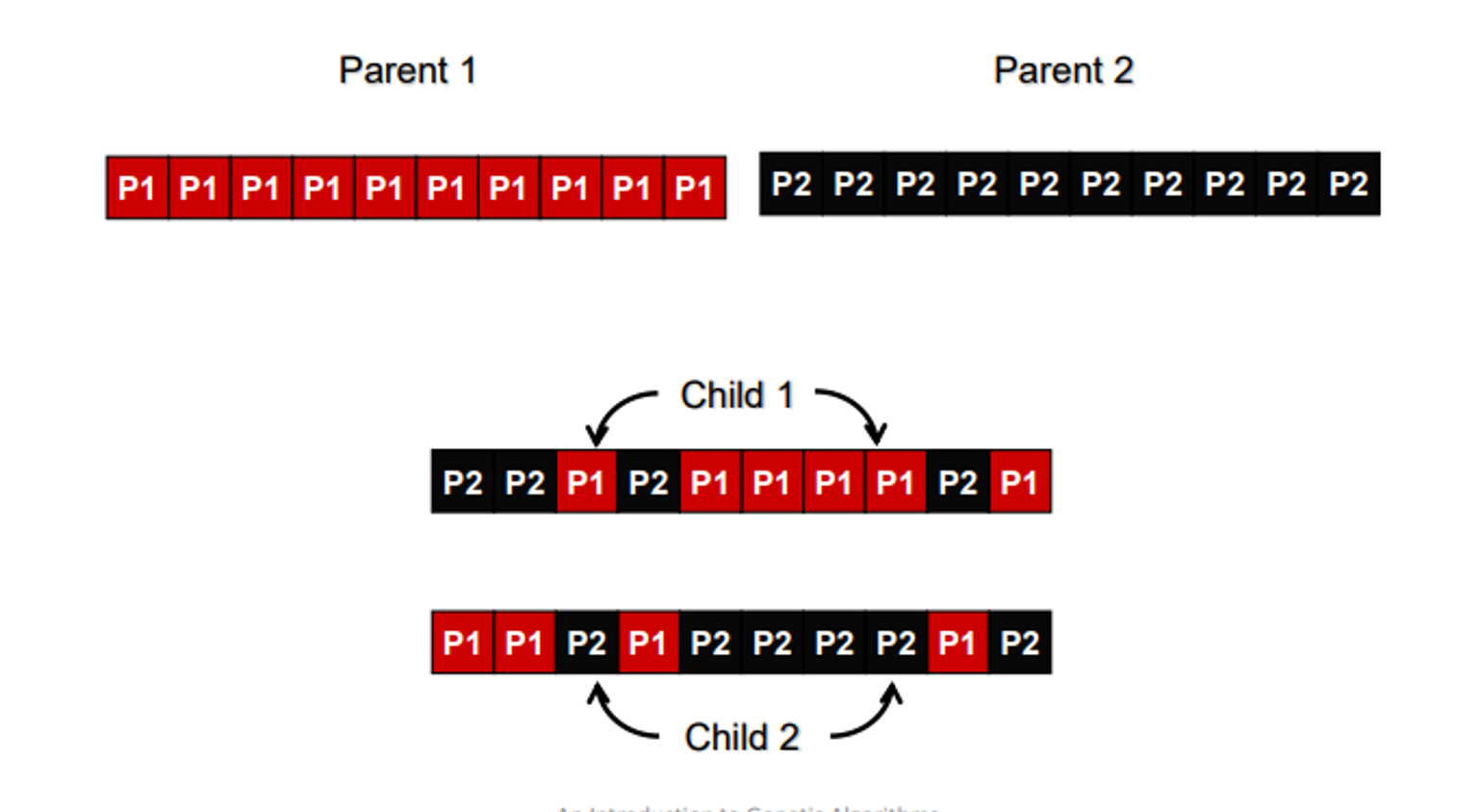
23
New cards
what is mutation?
small random change in gene to get a new solution
allows GA to explore more of search space and avoid falling into local optima
allows GA to explore more of search space and avoid falling into local optima
24
New cards
how does the mutation operator work?
each bit \[gene\] of a chromosome is given a probability MP of inverting.
\
eg.
1 turns into 0
0 turns into 1
\
eg.
1 turns into 0
0 turns into 1
25
New cards
what is selection?
keeping the chromosomes with the best fitness functions from one generation to the next generation where the new population formed is equal in size to the original population
26
New cards
how does the selection operator (roulette wheel) work?
the change of a chromosome surviving to the next generation is proportional to it’s fitness vs. the total fitness of others.
\
a roulette wheel is formed where chromosomes with better finesses have larger portions of the wheel and therefore once the wheel is spun, have a higher chance of being selected by the selection point to continue to the next generation
\
a roulette wheel is formed where chromosomes with better finesses have larger portions of the wheel and therefore once the wheel is spun, have a higher chance of being selected by the selection point to continue to the next generation
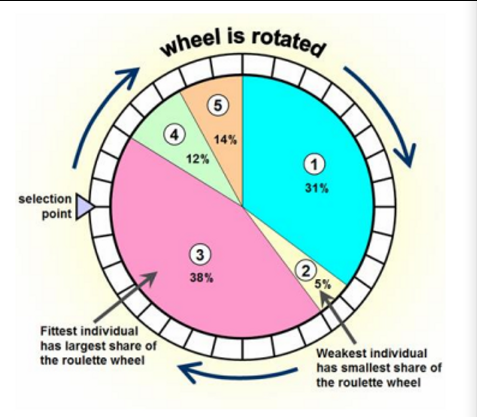
27
New cards
what parameters are needed for Holland’s Genetic Algorithm
NG - number of generations (iterations), how long it will take, how many populations will be created
PS - population size, how many chromosomes will be in population, will remain the same number in each generation?
CP - crossover probability
MP - mutation probability
n - length of a chromosome
PS - population size, how many chromosomes will be in population, will remain the same number in each generation?
CP - crossover probability
MP - mutation probability
n - length of a chromosome
28
New cards
what is the pseudocode for Holland’s Genetic Algorithm?

29
New cards
what are the recommended parameter values for Holland’s GA?

30
New cards
what are the applications of genetic algorithms?
Numerical optimisation
aircraft design
image processing
dna analysis
vehicle routing problems
Ai search
aircraft design
image processing
dna analysis
vehicle routing problems
Ai search