Inheritance Patterns
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are these symptoms of?
Short, webbed neck
Decreased range of motion in the cervical spine
Low-set hairline
Klippel-Feil Syndrome
What Klippel-Feil Syndrome characterised by
congenital fusion of any 2 of the 7 cervical vertebrae
What causes Klippel-Feil Syndrome
Mutations in the GDF6, GDF3, or MEOX1 genes
Is Huntington Disease inherited in an autosomal dominant/recessive pattern
Dominant
Huntington Disease Symptoms
Progressive neuronal loss - disease onset usually occurs in 30’s or 40’s
Huntington Disease cause
mutation in the HTT gene (a repeat - the more repeats, the earlier the onset or more severe phenotype)
27-35 premutation (risk for children)
36-39 at risk (incomplete penetrance)
40+ = HD
Select the non-hereditary, congenital diseases from the following list:
• Cystic Fibrosis
• Toxoplasmosis
• Sickle Cell Anaemia
• Cerebral Palsy
• Type 1 Diabetes
Toxoplasmosis
Cerebral Palsy
Rank these concepts in order of first appearance
• The concept of DNA
• The concept of genes
• The concept of inheritance
The concept of inheritance
The concept of genes
The concept of DNA
Autosomal inheritance
Not sex dependent
(Allele located on one of the 22 autosomes)
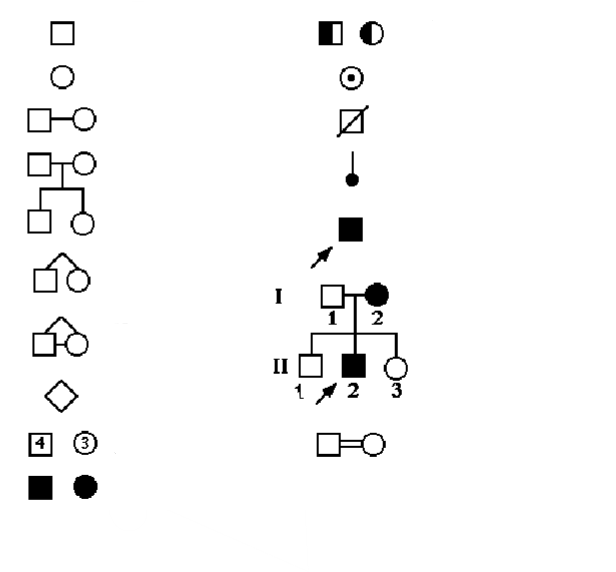
What does each symbol mean on a pedigree chart
Finding out the pattern of inheritance, what 2 questions must you ask?
Are the parents affected/carriers?
Does it affect both genders?
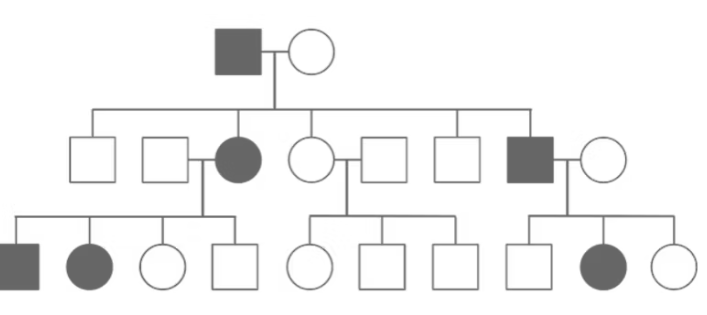
What pattern of Mendelian Inheritance is this?
Autosomal Dominant
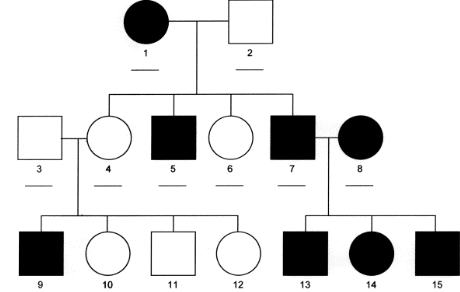
What pattern of Mendelian Inheritance is this?
Sex linked mendelian inheritance
What is a dichotomous trait
Yes/No - You have it or you don’t
What is a Polygenic/Multifactorial trait
Character is determined by a large number of genes and the interaction of expression of those genes with the environment (not Mendelian)
Give examples of dichotomous traits
Height
Shoe size
Eye colour
Intelligence
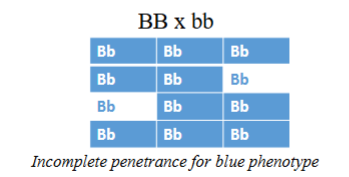
Incomplete penetrance
Penetrance = probability of a genotype/trait being expressed
Incomplete = phenotype only expressed in a fraction (%) of the population with the genotype
Variable expressivity
Variation in phenotypic expression when penetrance is complete
A range of symptoms displayed in individuals with the same fully penetrant genotype
Variable expressivity is the norm among genetic diseases and is particularly common for disorders that affect multiple organ systems

Clinical Case (Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI))
Rachel’s mother had 10 leg bone fractures as a child, is 4ft 11 inches tall, is very double-jointed and has had blue/grey sclera since birth
Rachel is 26, 5 ft 7, has never had a fracture and has normal colour eyes
Rachel’s daughter is 4, has already had 2 fractures, is slightly double-jointed and has normal colour eyes
All three females are heterozygous for the same dominant mutation in the COL1A1 gene.
What phenomenon best explains the genotype phenotype correlation seen in Rachel?
Incomplete penetrance
Clinical Case (Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI))
Rachel’s mother had 10 leg bone fractures as a child, is 4ft 11 inches tall, is very double-jointed and has had blue/grey sclera since birth
Rachel is 26, 5 ft 7, has never had a fracture and has normal colour eyes
Rachel’s daughter is 4, has already had 2 fractures, is slightly double-jointed and has normal colour eyes
All three females are heterozygous for the same dominant mutation in the COL1A1 gene.
What phenomenon best explains the genotype-phenotype correlation seen between Rachel’s child and her grandmother?
Variable expressivity
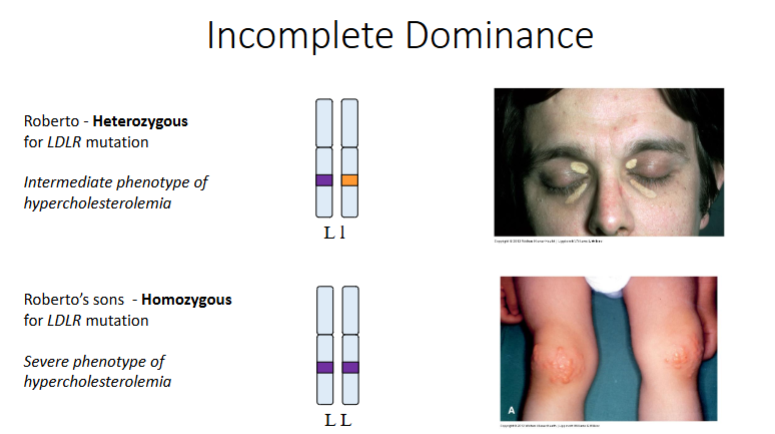
Familial Hypercholesterolemia, is a genetic disorder with a dominant pattern of inheritance that is associated with mutations in the LDLR gene on Chr19
Roberto 35 - Heterozygous for LDLR mutation
Elevated LDL cholesterol 350mg/dL
Skin lesions (xanthelasmata) present on eyelids and under the eyes
Recently had a mild MI
His twin sons (age 2) have symmetrical xanthomas on their knees and elbows
Blood LDL cholesterol level 1.2g/dL
Homozygous for LDLR mutation
What phenomenon of inheritance explains the phenotype of Roberto’s condition?
Congenital
Present at birth.
(Not necessarily hereditary)