Anxiety and Eyewitness Testimony (Booklet 8)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Outline the effects of anxiety on eyewitness testimony
Many events witnessed by eyewitnesses can cause them anxiety
Sometimes anxiety seems to improve memory and at other times it makes memory less accurate and/or detailed
Define anxiety
A state of emotional and physical arousal which has a number of physiological and psychological effects
Describe the Procedure and Findings of Johnson and Scott’s study
Participants sat in a waiting room and made to believe they were waiting to take part in a laboratory study. There were 2 conditions:
Group 1 overheard a heated argument in an adjoining room and then a man exited the room carrying a pen with grease on his hands (low anxiety condition)
Group 2 overheard the same heated argument, but accompanied by the sound of breaking glass. A man walked out of the room holding a paper knife that was covered in blood (high anxiety condition)
Participants had to pick the man from 50 photos.
Results:
49% of group 1 (low anxiety) could identify the man
33% of group 2 (high anxiety) could identify the man
What does Johnson and Scott’s study show about the effects of anxiety on eyewitness testimony?
Suggests anxiety has a negative effect on recall for eyewitness testimony
Supports the “tunnel theory” which argues that a witness’s attention narrows to focus on a weapon, because it is a source of anxiety (reducing recall accuracy of surroundings)
How does the findings of Pickel’s study challenge Johnson and Scott’s interpretation?
Participants watched a video of a man holding an object in a hairdressing salon who demanded money from receptionist. Participants then had to select the photo of the man carrying the object.
This was repeated using different objects:
Wallet (low anxiety, usual)
Raw chicken (low anxiety, unusual)
Handgun (high anxiety, unusual)
Scissors (high anxiety, usual)
The recall was worst in the handgun and raw chicken conditions. This suggests the unusualness of the object causes decreases recall accuracy, not anxiety (opposing Johnson and Scott’s findings which suggested anxiety causes decrease in recall)
What did Yuille and Cutshall find about the effects of anxiety on eyewitness testimony in their study?
Asked real life witnesses to gun shop robbery to rate how stressed they felt at the time of the incident on a 7 point scale.
Findings:
Witnesses were able to recall the incident in detail, even after 5 months.
There was a high level of agreement between witnesses.
The accounts did not alter in response to leading questions
Those who reported highest level of stress were more accurate than those who were less stressed (suggesting anxiety improves accuracy)
Describe the Yerkes-Dodson Law (U-curve)
States that arousal increases performance (including memory) up to a certain level and then, after a certain point (past optimum level), increased arousal decreases performance
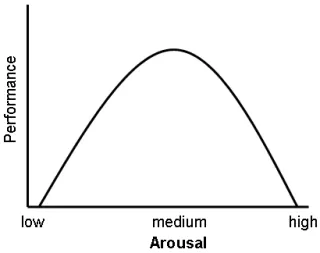
How does the Yerkes-Dodson Law explain the contradictory findings of the effects of anxiety on eyewitness testimony?
Johnson and Scott found in a low anxiety condition recall was better. This could be due to anxiety (caused by knife) being above optimal level
Yuille and Cutshall found that those who reported the highest level of stress had more accurate recall than those who were less stressed
The Yerkes-Dodson Law suggests that there is an optimum anxiety level for recall in between the two anxiety extremes
How can the flight or fight response be used to explain the findings of research into eyewitness testimony?
Increases anxiety levels causing recall accuracy to either increase or decrease depending on whether anxiety levels surpass optimum level of anxiety.
Why might research into factors affecting EWT have limited application to real life?
Large proportion of research is attained through lab studies (which have low external validity)
In lab study participants will not have same levels of emotions (e.g: anxiety levels) as real life witnesses
In real life events, the consequences of witness’s recall are higher, so may be more considerate when recalling event
In real life events participants will likely be paying less initial attention to the event than in a lab study (due to it being unexpected)