9521 Lecture 16- Homelessness
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is the definition of homelessness?
“Homelessness describes the situation of an individual or family without stable, permanent, appropriate housing, or the immediate prospect, means and ability of acquiring it. It is the result of systemic or societal barriers, a lack of affordable and appropriate housing, the individual / household’s financial, mental, cognitive, behavioural or physical challenges, and/or racism and discrimination. Most people do not choose to be homeless, and the experience is generally negative, unpleasant, stressful and distressing.”
What is part of the taxonomy of homelessness?
Transitional→ housed then unhoused for a few weeks and then housed again
Episodic→ in and out of homelessness
Chronic→ lasts longer than 6 months, one year continuously or 4 times within 3 years
What stage of homelessness should treatment begin in?
Transitional to prevent ongoing homelessness
What is the affordable housing timeline?
WWII: Federal investments in social housing, government insured mortgages, subsidies for rental housing
1980’s: Brian Mulrouny, Ronald Regan and Thatcher said we shouldn’t put money into social housing and tax payers shouldn’t pay for this. Poverty rates begin to rise, need for social housing increases
1980s/1990s: Liberal government didn’t do anything about housing, funding lost, social housing decreased and we lost many social housing units across the country
2000s: Increased use of food banks. Increased waitlists for social housing- 10 years
2008 to Present: Increased homelessness, responses to homelessness develop
What is the homelessness in Canada?
At least 235,000 individuals are unhoused annually (Gaetz et al., 2016)
Not everyone unhoused looked unhoused
Some used a by name list for those connected with services, but not everyone seeks services or consents to services
Costs over 10 billion dollars per annum
Unhoused persons cost 6 times more in healthcare when compared with housed individuals (Richard et al., 2024)
Since they’re interacting so often
Some come to the ER to be warm for a little while
Chronic homelessness is a growing problem
When people become unhoused they’re unhoused for longer
What is the prevalence of global homelessness?
150 million people are unhoused internationally
2 million forcefully evicted from their homes each year
1.8 billion people living in inadequate housing conditions
What are chronic health conditions among homeless persons?
Mental Illness (MI)
76.2% persons experiencing homelessness
Sexually assaulted, being told you aren’t eligible for certain things
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) 45-53%
65% of Persons with TBI have been diagnosed with MI
What is the prevalence of neuropsychiatric disorders in homeless people?
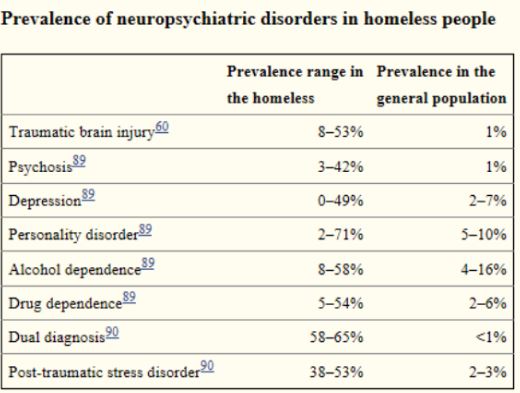
What is the treatment first/staircase model basic tenets and what does it emphasize?
Basic Tenets: Treatment for addictions, mental health problems, and physical health problems must precede the security of housing
Emphasizes: Transitional housing; Shelter use; Medical mode
What is the housing first support model basic tenets and what does it emphasize?
To help a person become housed and keep housing for longer we need to help them overcome their challenges
Find housing and help them keep it for longer
Basic Tenets: Housing should be accessed regardless of mental/physical health or addictions problems
Emphasizes: Supportive housing (scatter); Permanent housing; Recovery orientation
Inhumane, provide people with housing first and then ask them what they need to keep housing and the you support them
Don’t say that they’re too ill, move the individual into housing to get all basic needs met
What issues have bee challenging to address with existing approaches?
Symptoms of mental illness
Substance misuse
Community integration
Employment
Engagement in meaningful activity . . . during and following homelessness
What is the clinical role in homelessness for OT’s?
Housing First ACT Teams → only work with those who experience homelessness, OT needs to be on the team or they don’t receive funding
Supportive Housing
Transitional Housing
Mental Health Services—ACT, Crisis, Acute/Tertiary Psychiatric Units
Pilot Projects
What is the non-clinical role for OT’s in homelessness?
Research
Community Development
What is at the centre of bridging the transition to housing: A Social Justice Framework for Homelessness Prevention?
At its centre is relationship as foundation, relationship needs to be developed before anything else can occur
What are the four processes of leaving homelessness?
Survival, Adaptation (secured housing), Integration, Precarity (at risk of losing their housing)
What is the most favourable outcome in the Bridging the Transition to Housing: A Social Justice Framework for Homelessness Prevention?
Community integration is the most favourable outcome
What are strategies in the Bridging the Transition to Housing: A Social Justice Framework for Homelessness Prevention?
1. Performance of meaningful activity
2. Engagement in meaningful activity
3. Use of activity for well-being
What are the levels of interventions in the Bridging the Transition to Housing: A Social Justice Framework for Homelessness Prevention?
1. Individual
2. Community
3. Population
What are the 6 guiding principles of the Bridging the Transition to Housing: A Social Justice Framework for Homelessness Prevention?
1. Social Justice
2. Housing First
3. Recovery
4. Harm Reduction
5. Trauma and Violence Informed Care
6. Intersectionality