BMS 595 Human Phys: Organization of the Nervous System
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
How many neurons are contained in the CNS?
More than 100 billion
What type of neurons take nerve impulses from the CNS to muscles or glands?
Motor Neurons
What type of neurons take nerve impulses from sensory receptors in muscles, glands, and tissues and send it to the CNS?
Sensory Neurons
What type of neurons are considered association neurons and occur entirely within the CNS? They also convey nerve impulses between various parts of the CNS.
Interneurons
What is the CNS composed of?
Brain and Spinal Cord
What is the PNS composed of?
cranial nerves and spinal nerves
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there in the PNS?
31 Pairs
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there in the PNS?
12 Pairs
What are the three major areas of the brain?
1. Cerebrum
2. Cerebellum
3. Brain stem
What major area of the brain is composed of the telencephalon and diencephalon?
Cerebrum
What are the 4 major lobes of the cerebrum?
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital
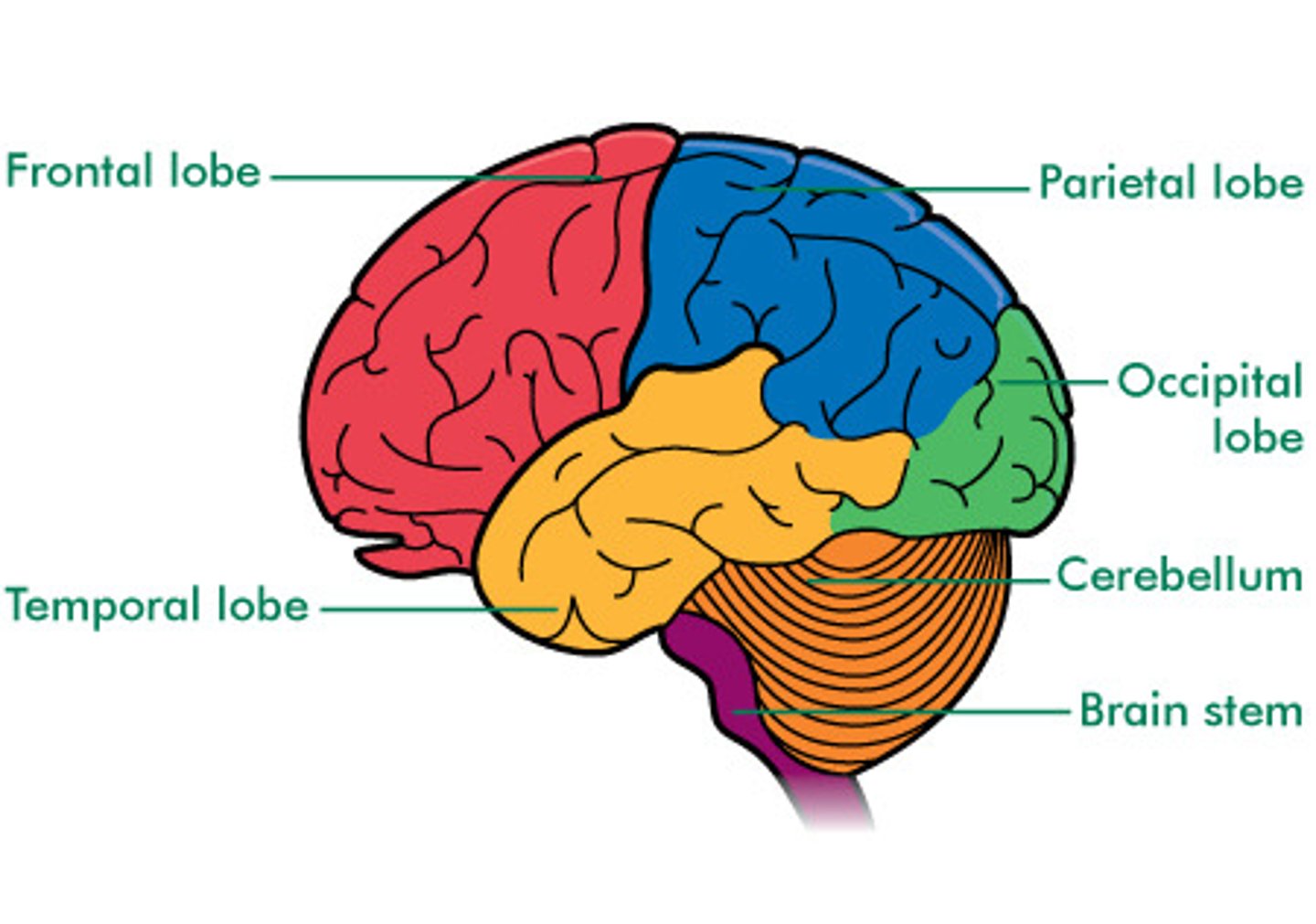
What major area of the brain functions in intellectual processes and sensory information processing?
Cerebrum
What are the two major parts of the diencephalon?
thalamus and hypothalamus
What area of the diencephalon relays stimuli and signals for processing and interpretation?
Thalamus
What area of the diencephalon monitors temp, blood glucose levels, hormone levels and helps maintain homeostasis?
Hypothalamus
What major area of the brain is located behind the brainstem, helps monitor and regulate movement, and integrates postural adjustments and equilibrium?
Cerebellum
What major area of the brain is composed of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata?
Brainstem
What major area of the brain controls respiratory and cardiovascular centers?
Brainstem
What part of the somatic nervous system carries sensations from the periphery (muscles, tissues, etc.) to the spinal cord?
Somatic Afferent (Sensory)
What part of the somatic nervous system communicates from the spinal cord to skeletal muscles?
Somatic Efferent (Motor)
What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
1. Sympathetic Division
2. Parasympathetic Division
What division of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for increasing activity in most systems and adrenergic fibers release epinephrine?
Sympathetic division
What division of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for slowing activity in most systems and cholinergic fibers release acetylcholine?
Parasympathetic division
where do parasympathetic fibers arise from?
neurons in the brainstem and sacral region
Where do parasympathetic fibers leave the CNS?
Through cranial nerves 3, 7, 9, and 10
The knee jerk response is what type of reflex?
Autonomic Reflex
The crossed extensor reflex is what type of reflex?
Complex Reflex
A single motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates is called?
A motor unit
What are the two basic types of neurons?
Motor and Sensory
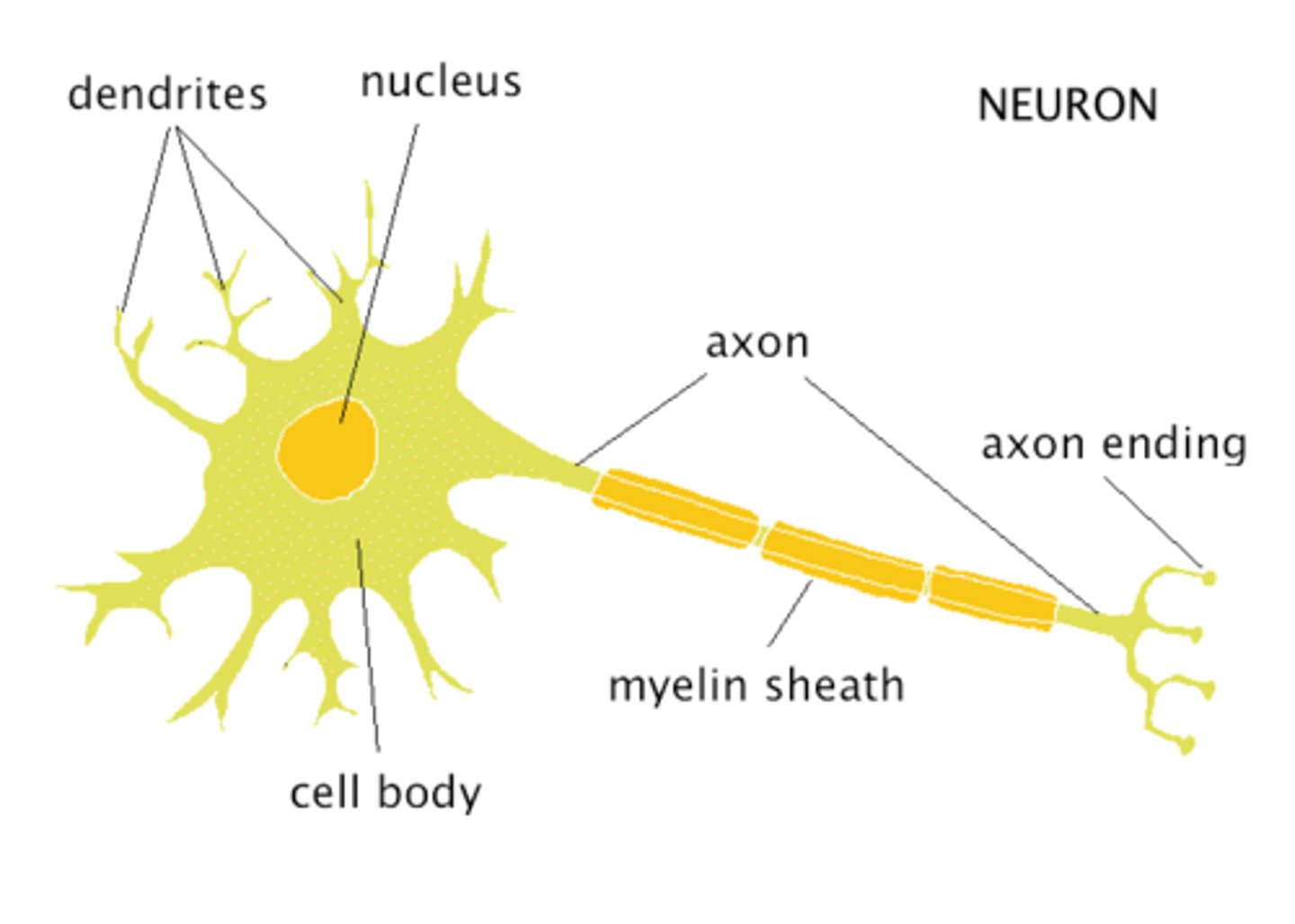
What are the three basic parts of a neuron?
Axons, Dendrites, and Cell Body
What side of the spinal cord do sensory nerves enter?
Dorsal Side of the Spinal Cord
Where do the cell bodies for sensory nerves lie?
Outside the spinal cord in the dorsal root ganglia
What side of the spinal cord do motor nerves exit?
The ventral side
What part of the neuron receives stimuli and carries it to the cell body?
Dendrites
What part of the neuron is the site of cellular activity?
Cell Body
What type of motor nerves have larger fibers, conduct impulses faster, and innervate regular muscle fibers?
Alpha Motor Nerves
What type of motor nerves have smaller fibers, conduct impulses more slowly, and innervate proprioceptors such as muscle spindles?
Gamma Motor Nerves
Muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, pacinian corpuscles, and ruffini endings are all _________________________.
Proprioceptors