gms 200 midterm
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
intellectual capital
the combined brainpower and shared knowledge of an organizations employees
what is intellectual capital used for?
continuously used to transform human creativity, insight and decision making
intellectual capital equation
intellectual capital = competency x commitment
competency
represents your personal talents or job-related capabilities
commitment
represents how hard you work to apply your talents and capabilities to job-related tasks
tech iq
a persons ability to use current technologies at work and in personal life, while always keeping yourself updated as it evolves
globalization
the worldwide interdependence of resource flows, product markets, and business competition that characterize our economy
job migration
the shifting of jobs from one country to another
reshoring
the shift of manufacturing and jobs back home overseas
what is reshoring often prompted by?
rising global manufacturing costs or labour costs
ethics
code of moral principles that set standards of conduct of what is “good/right” and what is “wrong/bad”
role of board of directors and the 3 factors
to hold top management responsible for organizational performance. 3 factors: financial performance, ethical performance, sustainability.
workplace diversity
differences with respect to gender, age, race, ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, and able-bodiedness
3 ways diversity bias occurs in the workpace
1) prejudice, 2) discrimination, 3) glass ceiling effect
prejudice
the display of negative, irrational opinions and attitudes
discrimination
unfairly treating members of some groups
glass ceiling effect
an invisible barrier of ceiling
free-agent economy
an economy where people change jobs more often and work on flexible contracts with a mixing shift of employers overtime
organizations
a collection of people working together to achieve a common purpose
how do organizations serve society?
providing goods and services
how do organizations as an open system interact with their environments?
the environment supplies (resource inputs) —> the organization creates value (transformation process) —> the environment consumes (product outputs)
define management
the process of planning, organizing, leading and controlling the use of resources to accomplish performance goals
how is value created
when an organizations operations ass value to the original cost of resource inputs
productivity
an overall measure of the quantity and quality of work performance with resource utilization taken into account
performance effectiveness
an output measure of task or goal accomplishment
performance efficiency
an input measure of the resource costs associated with goal accomplishment
describe an organization with high goal attainment but poor resource utilization
effective but not efficient - goals achieved but resources wasted
describe an organization with high goal attainment and good resource utilization
effective and efficient - goals achieved and no wasted resources *high productivity
describe an organization with low goal attainment and poor resource utilization
neither effective nor efficient - goals not achieved and resources wasted
describe an organization with low goal attainment and high resource utilization
not effective but efficient - goals not achieved but no wasted resources
what is the role of managers?
to directly support, supervise, and help to activate the work efforts of others
role of board of directors?
makes sure the organization is run well and managed in a lawful and ethical way
role of top managers?
responsible for performance of an organization as a whole, or for one of its major parts
define CEO, COO, CFO, CIO, CDO
chief executive officer (CEO), chief operating officer (COO), chief financial officer (CFO), chief information officer (CIO), chief diversity officer (CDO)
what are the management levels in both a typical business and non-profit business?
1) top managers 2) middle managers 3) first line managers 4) non-managerial workers
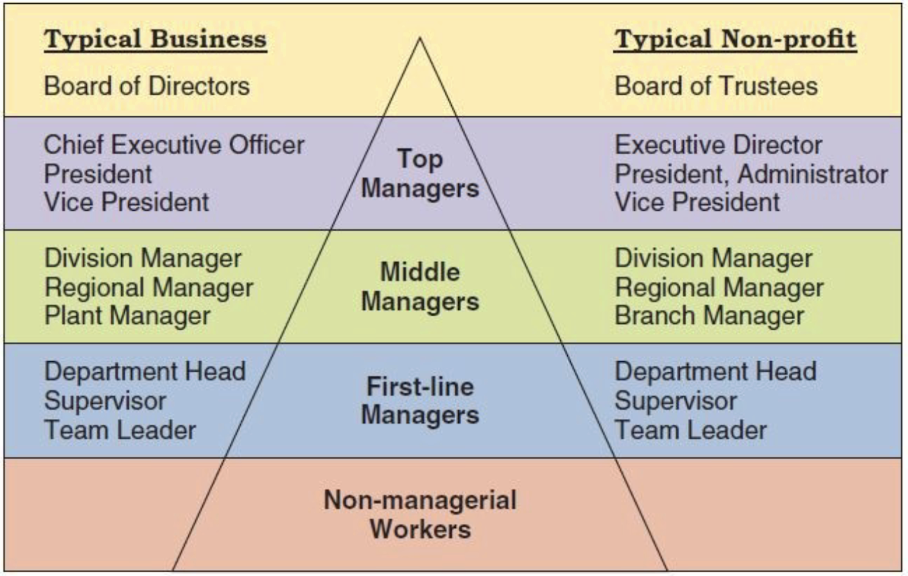
role of middle managers?
oversee large departments or divisions
role of team leaders?
supervise non-managerial workers
role of line managers?
responsible for work that makes a direct contribution to the organizations outputs
role of staff managers?
use special technical expertise to advise and support the efforts of line workers
role of functional managers?
responsible for a single area of activity such as finance, marketing, production, human resources, accounting, or sales
role of general managers?
responsible for activities covering multiple functional areas
define accountability
the requirement of one person to answer to a higher authority for performance results —> accountability flows upwards in the traditional organizational structure
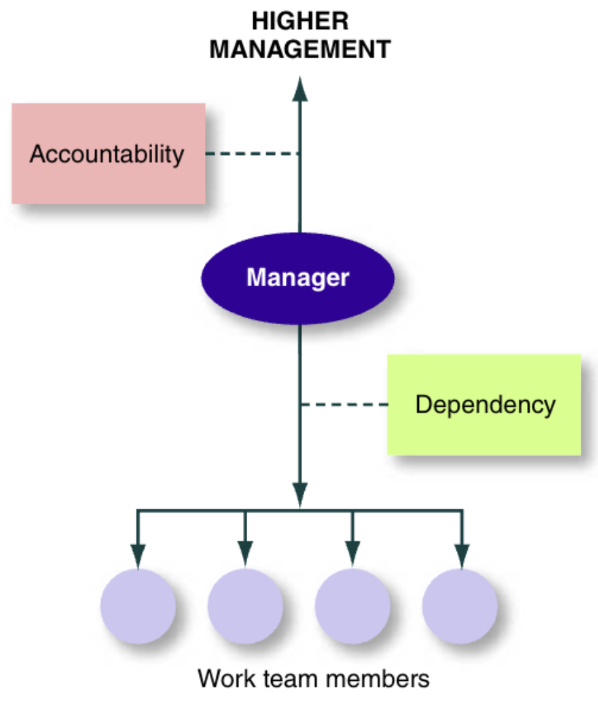
define quality of work life (QWL)
an indicator of the overall quality of human experiences in the workplace
what are the 6 QWL indicators?
1) respect 2) fair pay 3) safe working conditions 4) opportunities to learn and use new skills 5) room to grow and progress in a career 6) protection of individual rights
what are the 4 functions of management?
planning, controlling, organizing, and leading
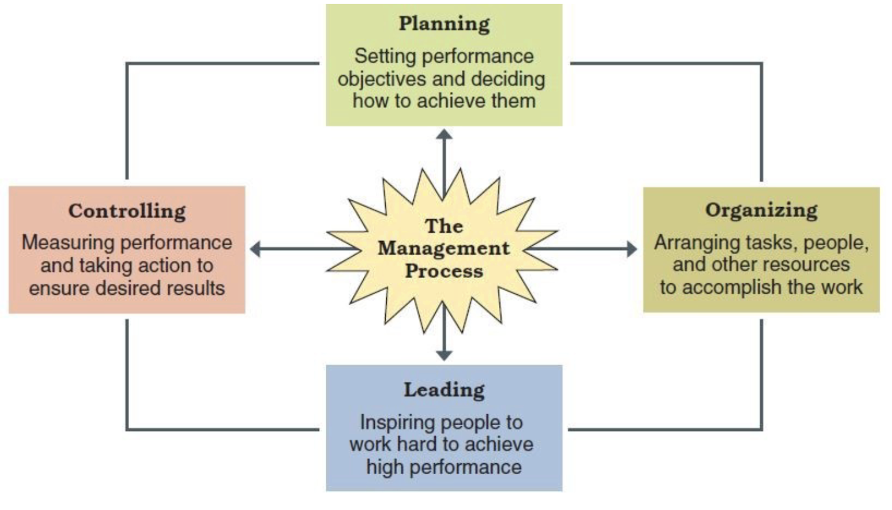
describe the planning function
the process of setting objectives and determining what actions should be taken to accomplish them
describe the organizing function
the process of defining tasks, allocating resources, and coordinating work activities
describe the leading function
the process of arousing people’s enthusiasm and inspiring then to work hard to achieve goals
describe the controlling function
the process of measuring work performance, comparing results and taking corrective action
what are the 5 characteristics of managerial work?
1) long hours 2) intense pace 3) fragmented and varied tasks 4) many communication media 5) filled with interpersonal relationships
what are Mintzbergs 3 common roles filled by management?
Interpersonal roles, informational roles and decisional roles
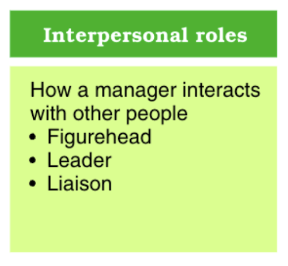
describe interpersonal roles (3 of them)
how a manager interacts with other people
figurehead: modeling and setting forth key principles and policies
leader: providing direction and insteilling enthusiasm
liaison: coordinating with others
describe informational roles (3 of them)
how a manager exchanges and processes information
monitor: scanning for information
disseminator: sharing information
spokesperson: acting as an official coordinator
describe decisional roles (4 of them)
how a manager uses information in decision making
entrepreneur: developing new initiatives'
disturbance handler: dealing with problems and conflicts
resource allocator: handling budgets and distributing resources
negotiator: making deals and forging agreements
social capital
the ability to attract support and help from others in order to get things done
networking
building and maintaining positive relationships with people whose help may be needed to implement those agendas
agenda setting
managers develop action priorities that include goals and plans spanning long and short time frames
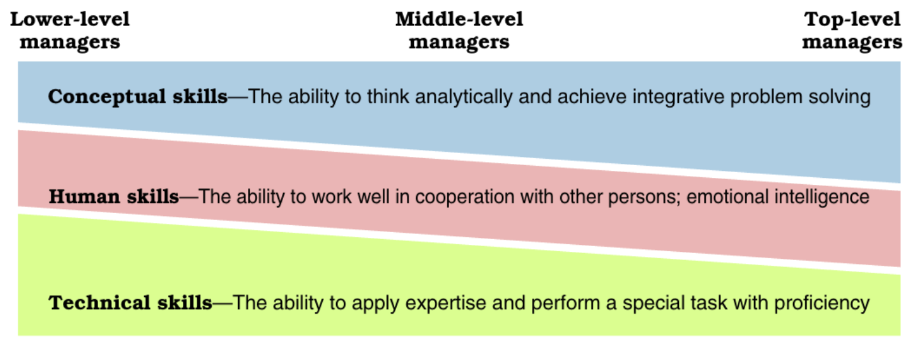
what are the 3 management skills? define them too
conceptual skills (the ability to think analytically and achieve integrative problem solving), human skills (the ability to work well in cooperation with other people), technical skills (the ability to apply expertise and perform tasks with proficiency)
what are Katz’s essential managerial skills chart?
define emotional intelligence
the ability to manage ourselves and our relationships effectively/understand and manage feelings when interacting and dealing with others
what are the 3 managerial competencies?
technological competency, informational competency, analytical competency
technological competency
ability to understand new technologies and to use them to their best advantage
informational competency
ability to locate, gather, organize, and display information for decision-making and problem solving
analytical competency
ability to evaluate and analyze information to make actual decisions and solve real problems
useful data
data: raw facts and observations, information: data made useful and meaningful for decision-making
5 characteristics of useful information
timely, high-quality, complete, relevant, understandable
management information systems
using the latest technology to collect, organize and distribute data
data mining
the process of analyzing data to prodice useful information for decision makers
big data and the 5 V’s of big data
exist in huge quantities and are difficult to process without sophisticated mathematical and analytical techniques
→ 5 V’s: volume, variety, veracity, velocity, value
management analytics
involved the systemic evaluation and analysis of data to make informed decisions
business intelligence
taps information systems to extract and report data in organized ways that are useful to decision-makers
data visualization
Visually update and display key performance metrics and information on a real-time basis through executive dashboards
Information exchanges with the external environment
gather intelligence information
provide public information
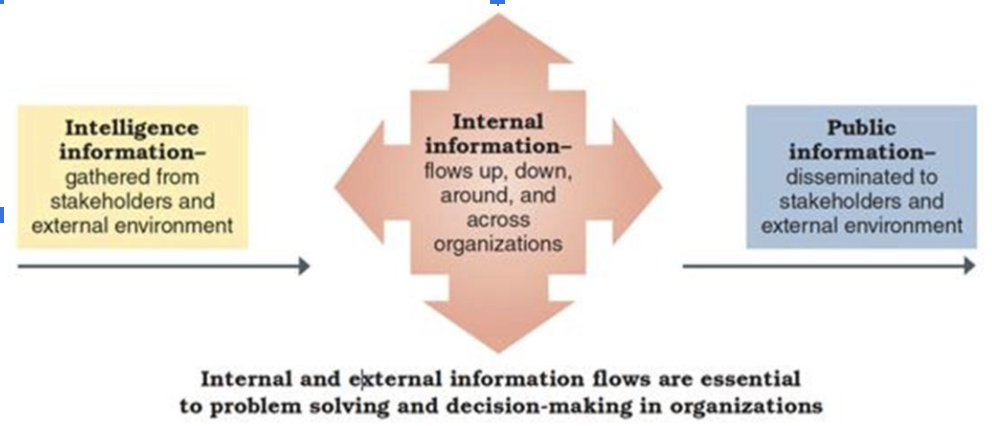
Information exchanges within the organization
facilitate decision-making
facilitate problem-solving
problem solving
the process of identifying a discrepancy between actual and desired performance and taking action to resolve it
performance threat
something is wrong or has the potential to go wrong
performance opportunity
situation offers the change for a better future if the right steps are taken
3 problem solving approaches/styles
problem avoiders: inactive in information gathering and solving problems
problem solvers: reactive in gathering information and solving problems
problem seekers: proactive in anticipating problems and opportunities and taking appropriate action to gain an advantage
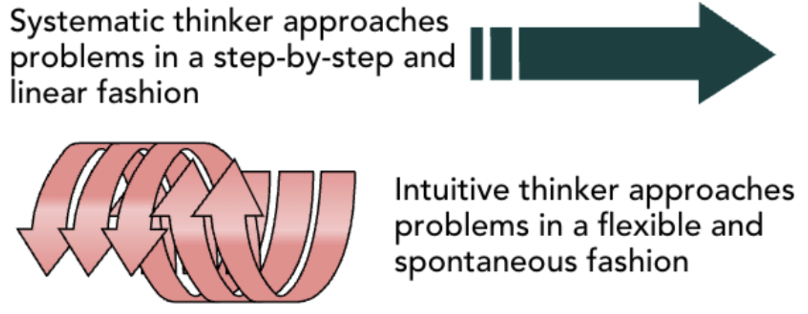
systematic thinking
approaches problems in a rational, step-by-step, and analytical fashion. This method is slow and methodical
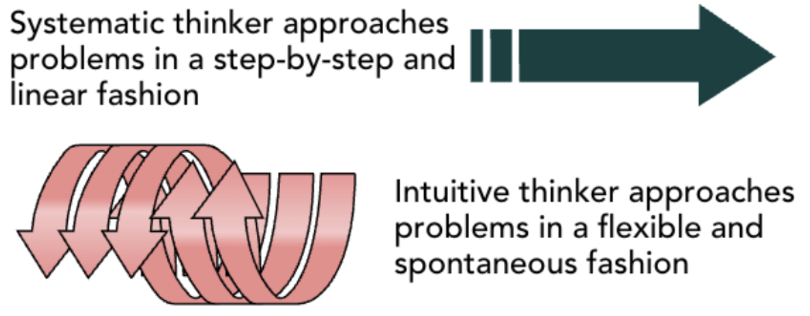
Intuitive thinking
approaches problems in a flexible and spontaneous fashion. This method is quick and broad
multi-dimensional thinking
combines both intuitive and systemic thinking, therefore allowing you to remain focused on long-term objectives, and be flexible to resolve short term problems
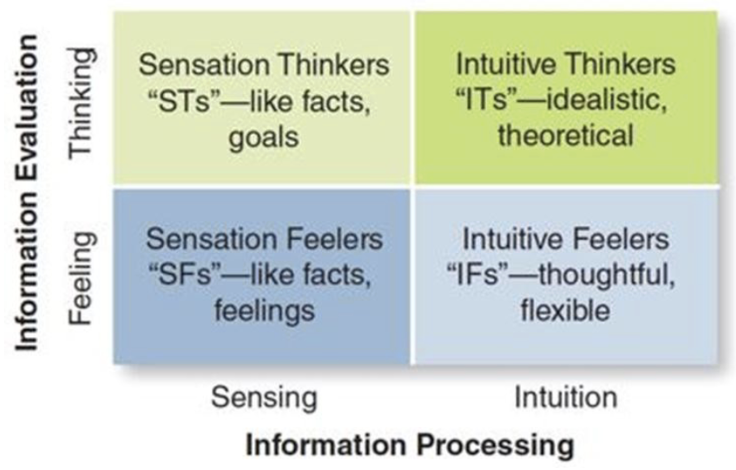
4 types of cognitive thinkers
sensation thinkers (ST’s) - like facts and goals
intuitive thinkers (IT’s) - idealistic, theoretical
sensation feelers (SF’s) - like facts, feelings
intuitive feelers (IF’s) - thoughtful, flexible
types of problems and decisions
structured problems:
programmed decisions
unstructured problems
non-programmed decisions
structured problems
are ones that are familiar, straightforward, and clear with respect to information needs - uses programmed decisions
programmed decisions
apply solutions that are readily available from past experiences to solve structured problems - used for structured problems
unstructured problems
are the ones that are full of ambiguities and information deficiencies - use non-programmed decisions
non-programmed decisions
apply a specific solution solution to meet the demand of a unique problem, commonly faced by higher-level management - used for unstructured problems
crisis decision-making
a crisis involved an unexpected problem that can lead to disaster if not resolved quickly and appropriately
6 rules for crisis management and descriptions
Figure out what is going on → Take the time to understand what’s happening and the conditions under which the crisis must be resolved.
Remember that speed matters → Attack the crisis as quickly as possible, trying to catch it when it is still easily managed.
Remember that slow counts, too → Know when to back off and wait for a better opportunity to make progress with the crisis.
Respect the danger of the unfamiliar → Understand the danger of all-new territory where you and others have never been before.
Value the skeptic → Don’t look for and get too comfortable with agreement; appreciate skeptics and let them help you see things differently
Be ready to “fight fire with fire” → When things are going wrong, you may have get imaginative to solve the crises, like building a backfire to stop a raging forest fire
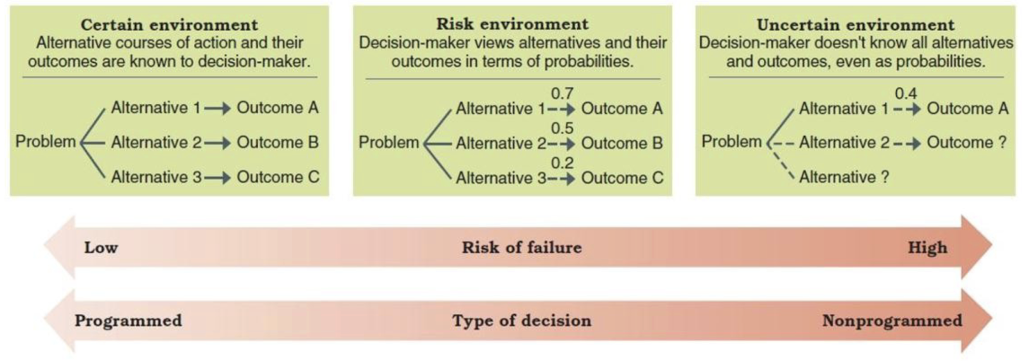
3 environments for making decisions with various amounts of information
Certain environment: offers complete factual information on possible action alternatives and their consequences. This is the ideal!
Risk environment: lacks complete information but offers probabilities of the likely outcomes for possible action alternatives
Uncertain environment: lacks so much information that it is difficult to assign probabilities to the likely outcomes of alternatives
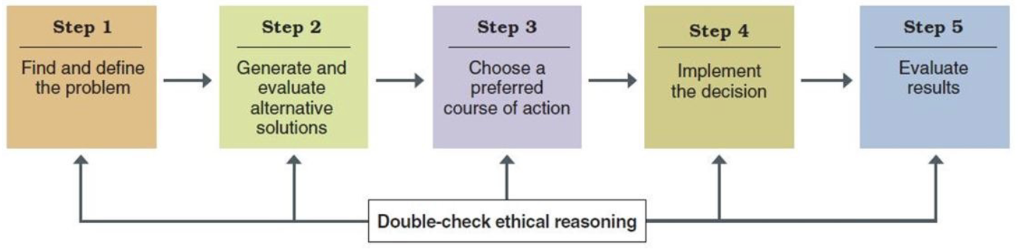
5 steps in the decision making process