AC STRUCTURES. WELDING PROCESSES
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
The two most prominent methods of welding aircraft structures and components are ____ and _____
fusion
non-fusion
The blending of compatible molten metals into one common part or joint
Fusion Welding
Fusing of metals is accomplished by producing sufficient ____ for the metals to melt, flow together and mix
heat
The heat is then removed to allow the fused joint to ____
solidify
Is the joining of metals by adhesion of one metal to another
Non-fusion Welding
The most prominent non-fusion welding processes used on aircraft are ____ AND ____.
brazing
soldering
IS THE SINGLE MOST IMPORTANT CHARACTERISTIC OF A GOOD WELD
PROPER PENETRATION
2 TYPES OF FUSION WELDING PROCESSES
• Gas Welding
• Electric Arc Welding
Often referred to as oxyacetylene welding, gets its name from the two gases, oxygen and acetylene, that are used to produce a flame
Gas Welding
______ is the fuel for the flame and _____ supports combustion and makes the flame hotter
The combination of these two gases results in sufficient heat to produce molten metal
Acetylene
oxygen
The temperature of the oxyacetylene flame ranges from _____ TO ______
5,600 to 6,300F
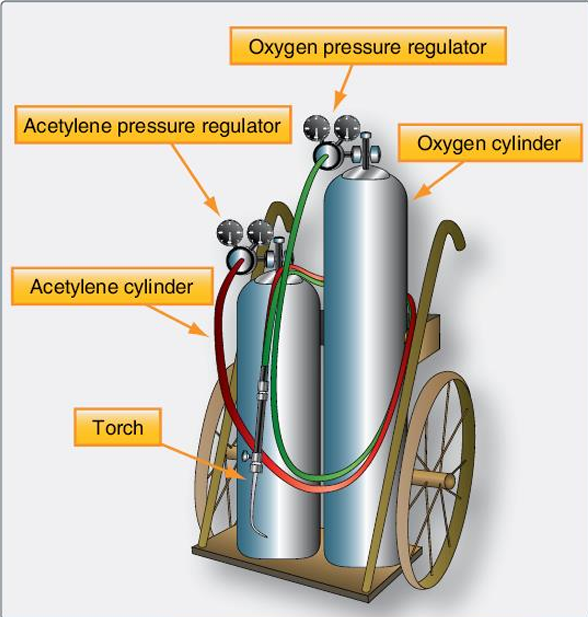
AIRCRAFT STEEL TUBINGS ARE WELDED USING WHAT TYPE OF WELDING
GAS WELDING
is used extensively by the aircraft industry in both the manufacture and repair of aircraft.
It can be used satisfactorily to join all weldable metals, provided that the proper processes and materials are used
Electric Arc Welding
When electricity has sufficient voltage to ___ across the space between an electrode to an area of different electrical potential, heat is produced from the movement of electrons
arc
The amount of heat is predominantly determined by the amount of ____ flowing across the gap
current
For all types of arc welding, a ____ OR _____ unit is used to produce and control electrical power
transformer/rectifier
this welding produces a blinding light, with infrared and ultraviolet rays, which can burn both skin andeyes
Electric Arc Welding
ELECTRIC ARC WELDING
3 types of electric arc welding
• Shielded Metal Arc Welding
• Gas Metal Arc Welding
• Tungsten Inert Gas Welding
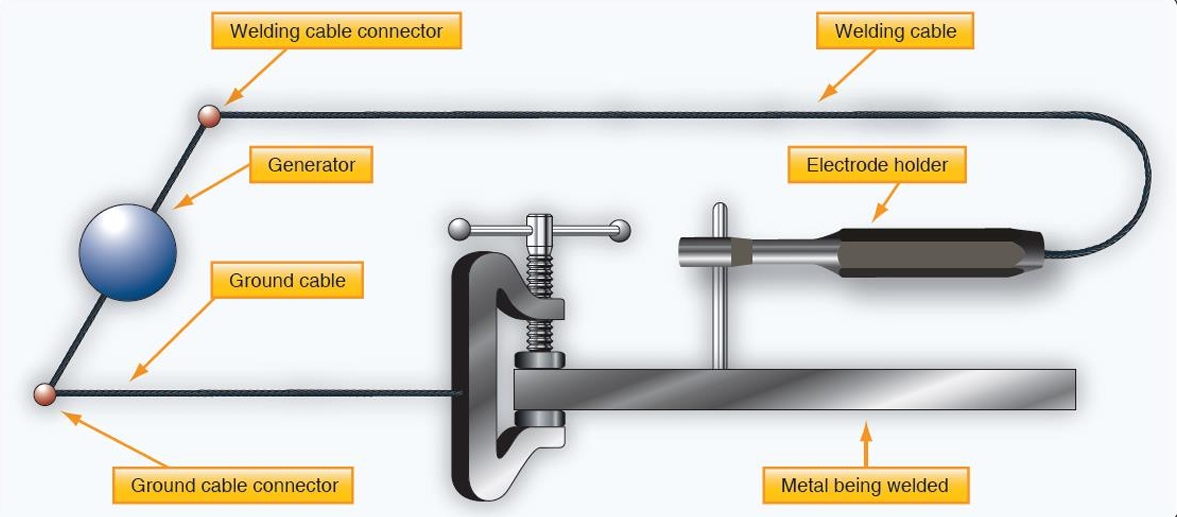
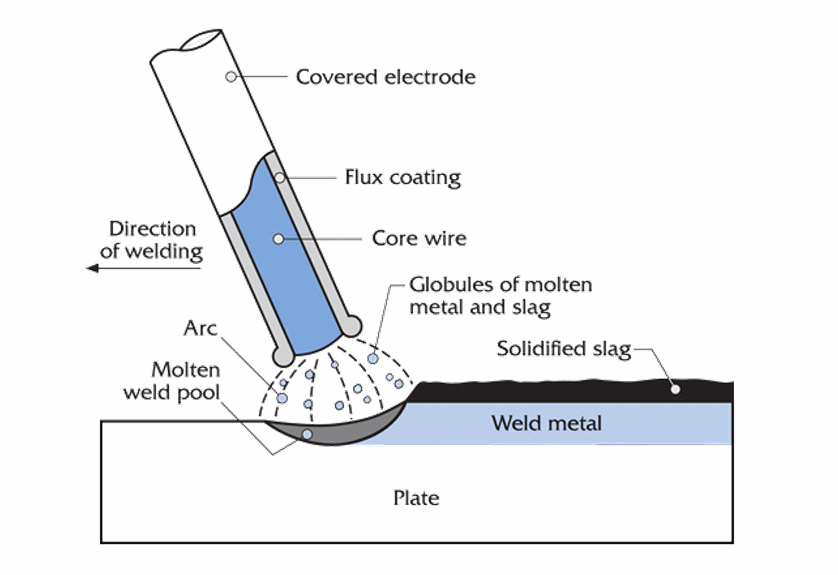
Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), or_____, is the most common type of arc welding.
You may find stick welding useful for fabricating tools and shop equipment, but it is not generally used for the fabrication or repair of aircraft
stick welding
In SMAW welding, a metal wire rod, which is composed of approximately the same ______ as the metal to be welded
chemical composition
is normally used for welding heavy gauge steel
it is seldom used in aircraft construction or repair
SMAW
SMAW
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) AKA
Metal Inert Gas (MIG)
Used primarily in large volume production work.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
GMAW
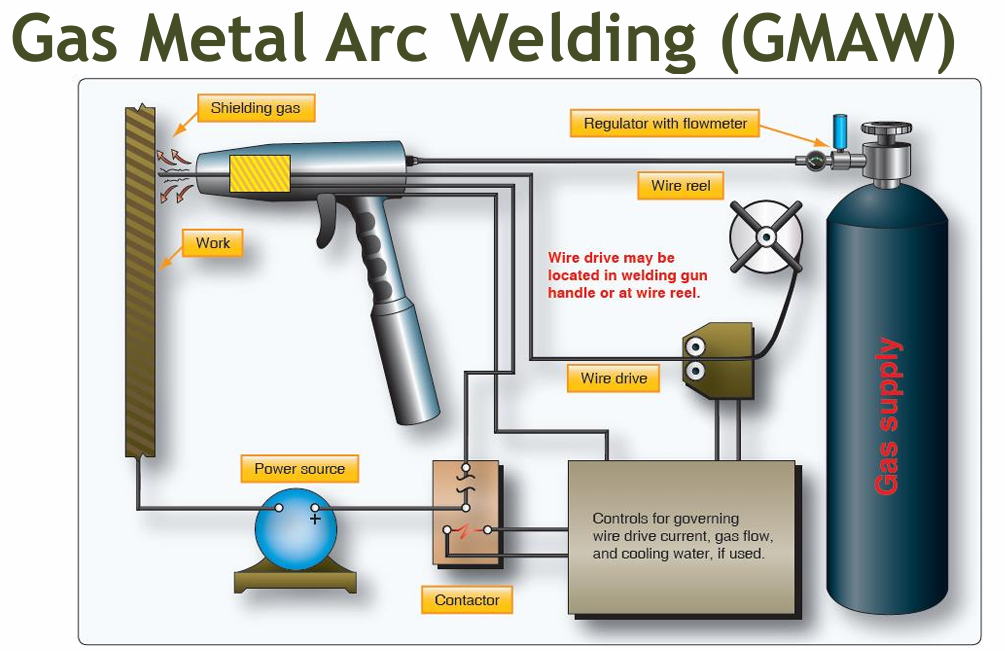
WHAT IS THE ADVANTAGE OF GMAW TO SMAW
no slag is deposited on the weld bead
An ______ acts as the electrode.
uncoated filler wire
An inert gas such as ____, ______ or ______ flows out around the wire to protect the weld zone from oxygen
argon
helium
carbon dioxide
When power is supplied to the electrode, and it is brought into contact with the work, it produces an arc, which melts the ____ and the _____
metal
filler wire
Tungsten Inert Gas Welding (TIG) IS ALSO KNOWN AS
gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW)
TIG
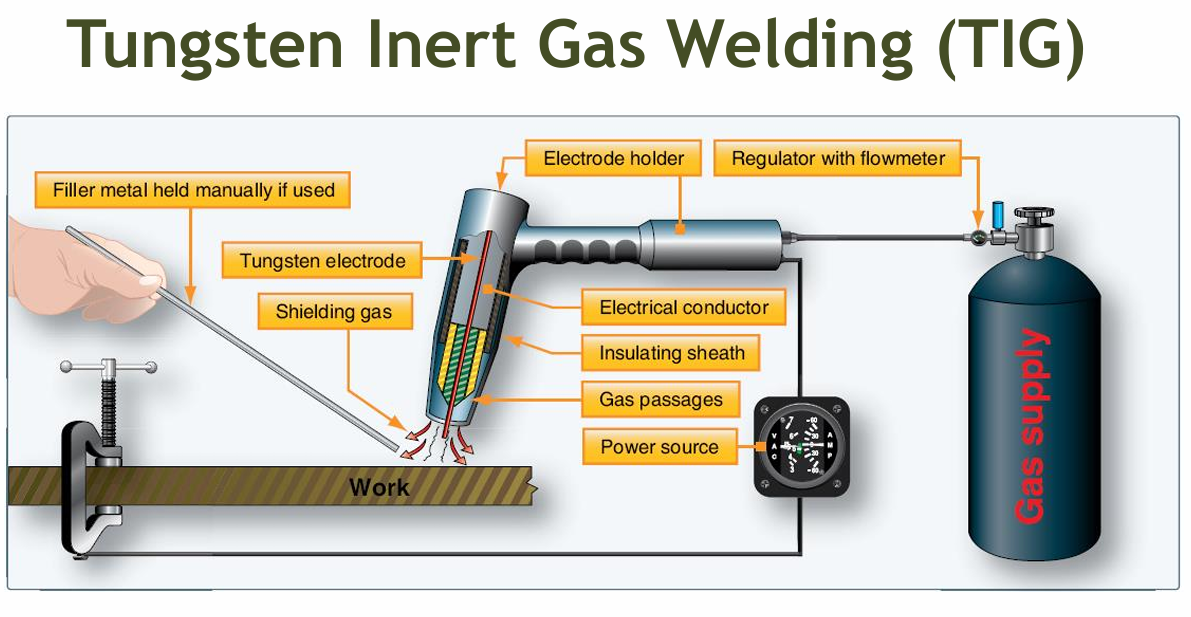
2 TRADE NAMES OF TIG WELDING.
These trade names were derived from the fact that the inert gas originally used was helium
Heliarc
Heliweld
TIG is the preferred method to use on______, ______, and most forms of thick ______.
stainless steel
magnesium
aluminum
The result of a weld is a
joint
5 Types of Welded Joints
BUTT JOINT
TEE JOINT
LAP JOINT
CORNER JOINT
EDGE JOINT
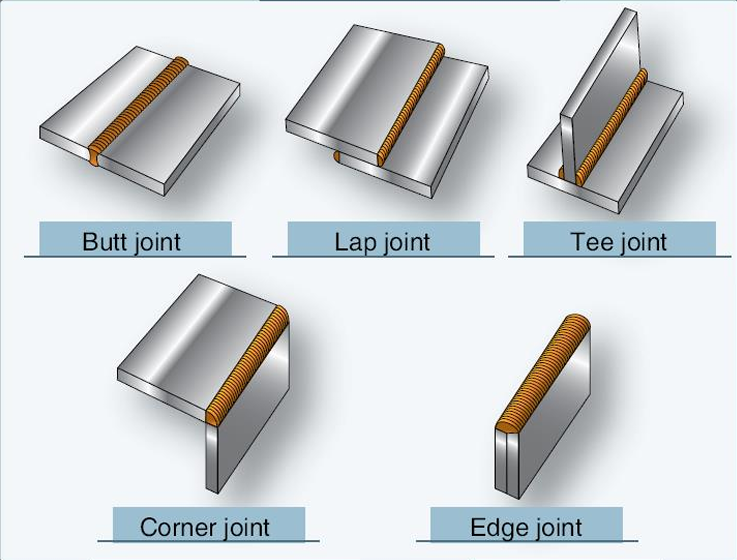
Made by placing two pieces of material edge to edge, without overlap, and then welding
Butt Joint
joints generally are not used for joining tubing because they are too weak for aircraft structures
Butt Joint
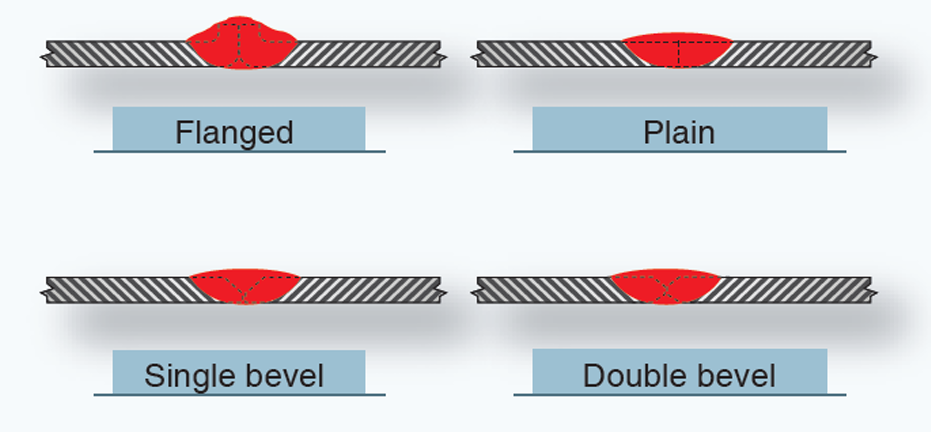
A plain butt joint is used for metals from ___ inch to ___-inch in thickness.
1/16
1/8
The flanged butt joint can be used in welding thin sheets, _____
1/16- inch or less
Abevel butt joint is used for metals thicker than ___-inch
1/8
4 TYPES OF BUTT JOINT
Seldom used in aircraft structures when welding with oxy-acetylene, but is commonly used and joined by spot welding
Lap Joint
joint has very little resistance to bending, and cannot withstand the shearing stress to which the weld may be subjected under tension or compression loads
SINGLE LAP JOINT
2 TYPES OF LAP JOINT

Formed when the edge or end of one piece is welded to the surface of another
Tee Joint
These joints are quite common in aircraft construction, particularly structures
Tee Joint
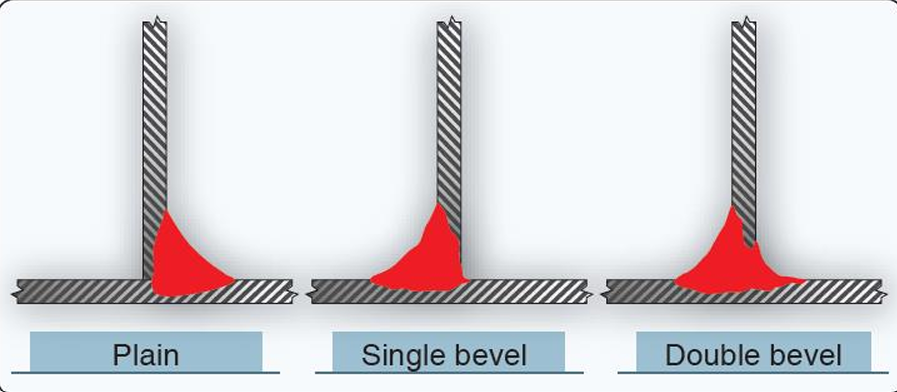
The______ is suitable for most thicknesses of metal used in aircraft, but heavier thicknesses require the vertical member to be either ___ or ____ to permit the heat to penetrate deeply enough
plain tee joint
single OR double beveled
3 TYPES OF TEE JOINT
Made when twopieces of metal are brought together so that their edges form a corner of a box or enclosure
Corner Joint
3 TYPES OF CORNER JOINT
Figure 5-44A used where the load stress is not important
The type shown in Figure 5-44B is used on heavier metals, and filler rod is added for roundness and strength
If a higher stress is to be placed on the corner, the inside is reinforced with another weld bead. Figure 5-44C]
![<p>Figure 5-44A used where the load stress is not important</p><p></p><p>The type shown in Figure 5-44B is used on heavier metals, and filler rod is added for roundness and strength</p><p></p><p>If a higher stress is to be placed on the corner, the inside is reinforced with another weld bead. Figure 5-44C]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bbe7b24f-2bfe-4693-b33c-0ba360a1f38f.png)
Used when two pieces of sheet metal must be fastened together and load stresses are not important
Edge Joint
are usually made by bending the edges of one or both parts upward, placing the two ends parallel to each other, and welding along the outside of the seam formed by the two joined edges
Edge Joint
2 TYPES OF EDGE JOINT
The joint shown in Figure 5-43A requires no filler rod since the edges can be melted down to fill the seam.
The joint shown in Figure 5-43B, being thicker material, must be beveled for heat penetration; filler rod is added for reinforcement
IS THE METAL THAT IS DEPOSITED AS THE WELD IS MADE
BEAD
IS THE EXPOSED SURFACE OF THE WELD
FACE
IS THE DEPTH THAT FUSION PENETRATES INTO THE BASE METAL
ROOT
IS THE DISTANCE THROUGH THE CENTER FROM THE ROOT TO THE FACE
THROAT
IS THE EDGE FORMED WHERE THE FACE OF THE WELD MEETS THE BASE METAL
TOE
IS THE QUANTITY OF THE WELD METAL ADDED ABOVE THE SURFACE OF THE BASE METAL
REINFORCEMENT
Parts of Welded Joints
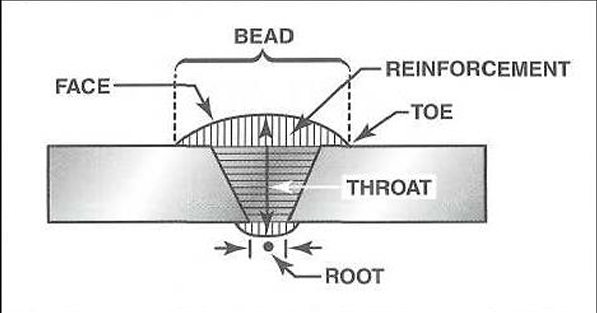
IS THE QUANTITY OF WELD METAL ADDED ABOVE THE SURFACE OF THE BASE METAL
REINFORCEMENT