Lecture 21 - Mechanical Ventilation
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation
What does IPPV stand for? This is when airway pressure is maintained above atmospheric pressure during inspiration and then falls to atmospheric pressure, allowing passive expiration. A ventilator can be used to provide repeated controlled breath, or it can be done using a reservoir bag manually.
Anesthesia
What use of mechanical ventilation is done for a limited period of time (hours), in healthy lungs, and uses controlled ventilatory modes?
ICU
What use of mechanical ventilation is done over long periods (days), is done when there is an underlying disease that impairs the ventilation, and uses assisted ventilatory modes?
Tidal Volume
What is the term for the amount of air moved in or out of the lungs with each respiratory cycle?
Peak Inspiratory Pressure
What is the term for the highest pressure measured during the respiratory cycle? If it is too high, then barotrauma can occur. It is commonly abbreviated PIP.
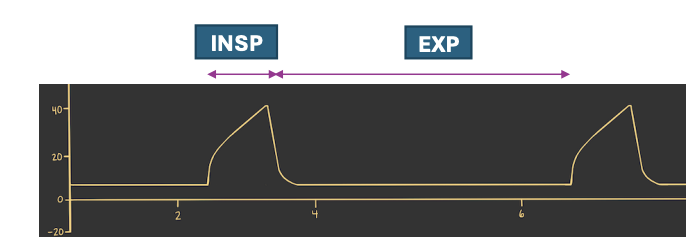
I:E
What term represents the inspiratory to expiratory ratio, and refers to the ratio of the duration of the inspiratory and expiratory phases? Normally it is 1:2.
1:2
What is the normal inspiratory:expiratory ratio?
Resistance
What is the term for the pressure difference per unit flow across the airway? It is not a constant, but increases as flow increases.
Compliance
What is the term for a measure of the distensibility of the lungs and of the restriction to expansion imposed by the surrounding structures, and is also defined as the ratio of change in volume for a given change in pressure?
Spontaneous
In what type of ventilation, inspiration involves a decrease in interpleural pressure and drawing of gasses into the lungs? This is followed by a passive return of interpleural pressure to a baseline, towards atmospheric pressure.
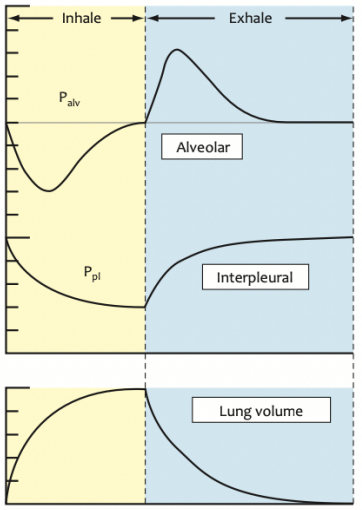
IPPV
In what type of ventilation (abbreviated) inspiration involves an increase in interpleural pressure and expiration is when interpleural pressure returns to atmospheric pressure at the end of expiration?
Negative
What type of intrathoracic pressure is found in spontaneous ventilation, involving reduction of pressure to sub-atmospheric levels and flow of gas down a concentration gradient into the lungs?
Positive
What type of intrathoracic pressure is found in mechanical/IPPV, involving ventilators driving gas into the lungs by creating a pressure within a breathing system that is above atmospheric pressure?
Anesthetized
In which patients is IPPV done to counteract the effect of anesthetic drugs and to ensure proper ventilation and oxygenation of obese patients?
ICU
In which patients is IPPV done to provide oxygenation and ventilatory support, to prevent hypoxemia and hypoventilation, especially in cases of sepsis, intoxication, CNS depression, and muscle respiratory fatigue?
Hypercapnia
What clinical sign/condition results from alveolar hypoventilation and produces effects such as acidemia, hyperkalemia, reduced contractility, ventricular tachyarrhythmias, increased vagal tone, and CNS depression/narcosis?
35-45
What is the normal range, in mmHg, of PaCO2 in dogs?
33-38
What is the normal range in mmHg, of PaCO2, in cats?
Yes
If there is severe hypoxemia despite oxygen supplementation, severe hypoventilation despite therapy, excessive respiratory effort with impending respiratory failure/fatigue, and severe hemodynamic compromise refractory to therapy, should you start ICU IPPV?
Stopped
If there is open thorax, neuromuscular blockade, phrenic nerve paralysis, neuromuscular disease, decreased lung/chest wall compliance, pneumonia, or diaphragmatic hernia, is ventilation stopped or decreased?
Decreased
If there is anesthesia, increased intracranial pressure, CNS disease, hypothermia, or severe hypoxemia, will ventilation be stopped or decreased?
Ventilator-induced lung injury
What consequence of IPPV on the respiratory system is abbreviated VILI, and occurs due to wrong settings being used, is more likely to occur with prolonged mechanical ventilation and lung disease (barotrauma, biotrauma, volutrauma, atelectrauma), and produces effects on alveolar ventilation and lung perfusion?
Preload
One consequence of IPPV on the CVS is a decrease in venous return, which will decrease what component of blood pressure? This will lead to hypotension. IPPV should be used carefully in hypovolemic patients and patients with cardiac conditions depending on adequate levels of this factor. Venous return will also be worsened by long inspiratory times, high PIP, and PEEP.
Kidney
Consequences of IPPV on what organ involve decreased blood flow, increased sympathetic tone, release of antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin), and stimulation of the RAAS, increasing reabsorption of Na and water?
Liver
Consequences of IPPV on what organ result in reduced MAP, reducing hepatic arterial flow, and increased thoracic pressure, reducing portal blood flow and causing hepatic venous congestion?
Intracranial
Mechanical ventilation, like IPPV and PEEP, can increase what pressure due to increased spinal pressure, reduced CSF outflow, increased central venous pressure, and reduced cerebral venous outflow? It also reduces MAP, which can result in cerebral vasodilation. Hypercapnia will also cause vasodilation, which will increase this pressure, but too much reduction of PaCO2 will cause vasoconstriction of CNS arteries and brain hypoxia. The aim is to keep PaCO2 at 35 mmHg.
35
For optimal intracranial pressure, the aim of IPPV is to keep PaCO2 around what value in mmHg?
APL
Manual PPV in small animal can be done by closing what valve and squeezing the reservoir bag? The cuff is inflated, a quick one second breath is usually sufficient, observe chest inflation, and ensure PIP doesn’t exceed 10 cmH2O. The valve should then be re-opened.
No
While manual PPV in foals, small ruminants, and swine is done similar to in small animals, is it practical to do it in adult horses and cattle?
Yes
While manual ventilation is good for freeing anesthetists to do other monitoring, decreases fatigue from continuous breaths, delivers more consistent inhalant anesthetic gases, and delivers more even respiratory rate and volume, does it also lead to loss of contact between patient-anesthetist, difficulty recognizing ventilator malfunctions, require expensive equipment/training, changes in VR and hypotension, possibility for trauma, and can be difficult to clean?
Major Control
What variable in a mechanical ventilator can be either the pressure or volume control, and is the target or limiting variable used to determine tidal volume delivered by the ventilator?
Power Source
Which part of the mechanical ventilator can be either compressed gas, electricity, or both, and is required to operate it?
Dual-circuit
What type of ventilators use compressed gas, and have one part for the ventilator and one for the patient?
Single-circuit
What type of ventilators do not use gas to power them and are electronically driven?
Cycling
What mechanism in a ventilator can use time, pressure, and volume, and controls how a ventilator moves from inspiration to expiration and back?
Bellow
Which part of a ventilator is an accordion style device that can collapse on inspiration or expiration, depending on the type? It is moved by gas compressed in a cylinder.
Ascending
What type of bellows move upward during the expiratory phase of breathing?

Descending
What type of bellows move downward during expiration, are difficult to detect leaks or disconnections, have safety issues, and collect humidity, which adds weight to the system?

Expiration
The type of bellow is determined by which direction it moves during which phase of respiration?
Small
Closed chest PIP 10-15 cmH2O, open chest PIP involving expansion of the lung beyond wound limits, RR of 10-20 breaths/min, Vt of 10-15 ml/kg, and I:E of 1:2 are the basic settings of ventilators in which animals (large or small)?
Large
PIP not exceeding 20 cmH2O, RR of 6-8 breaths per minute, Vt of 10 ml/kg, and I:E ratio of 1:2 are the basic settings of ventilators in which animals (large or small)?
Merlin
What type of ventilator is shown?

VentiPAC
What type of ventilator is shown?

Drager
What type of ventilator is shown?

Tafonius
What type of ventilator is shown?
Pressure Triggering
Which type of ICU assisted ventilatory mode is when patient effort to breathe triggers positive-pressure breaths, RR is set by patient inspiratory effort, it is often used in ICU in patients with respiratory muscle paralysis, low Vt, and atelectasis, and the role of the ventilator is to do more than just correcting hypoventilation?
Flow Triggering
Which type of ICU assisted ventilation is similar to pressure triggering, involves changes in flow due to patient’s attempts to breathe, and involves less work of breathing compared to pressure triggering?
Positive End Expiratory Pressure
What does PEEP stand for? It is the positive pressure that the ventilator maintains within the breathing system after the end of each expiratory phase (between breaths). This prevents atelectasis of the alveoli and minimizes VILI. Most ventilators maintain it at 2-4 cmH2O, and if it is very high this can cause collapse of capillaries in the lung, exacerbating the preload and hypotension.
Yes
To “wean” a patient from IPPV, should you ensure the patient can ventilate, reduce anesthetic depth, let some CO2 accumulate, reduce RR, and possibly administer reversals to drugs like opioids and alpha 2 agonists?