Bio topic 1 PPQ wrong
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
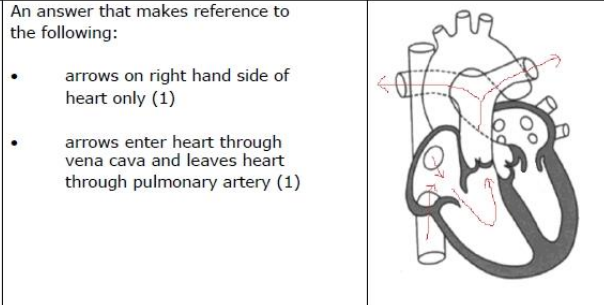
Explain why a mammal born with a hole in their heart will be easily tired due to lack of energy (3)
Less oxygen available for aerobic respiration
Deoxygenated blood mixes with oxygenated blood
Therefore reducing concentration of oxygen in blood circulating the body
Because some deoxygenated blood does not leave the right ventricle/ is transferred to left ventricle/does not go to lungs/ goes to repairing tissue
Diet is one factor that affects the development of CVD. Explain how the diet of a person could affect the development of CVD. (4)
higher salt intake
increases blood pressure
high blood pressure causes damage to endothelium (of artery)
high intake of cholesterol/saturated fat
high (LDL’s/saturated fat) linked to (athreoma/plaque formation)
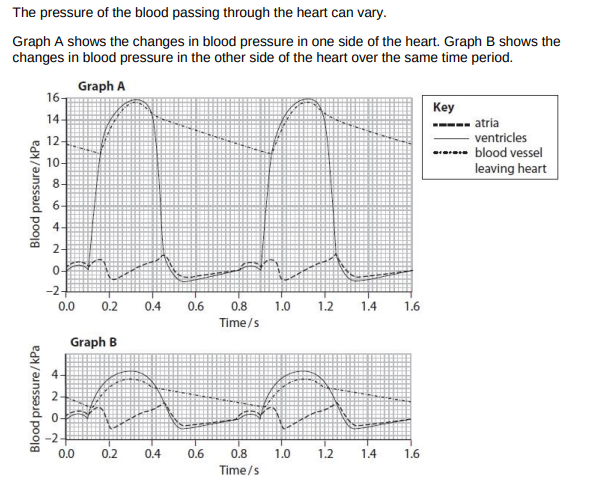
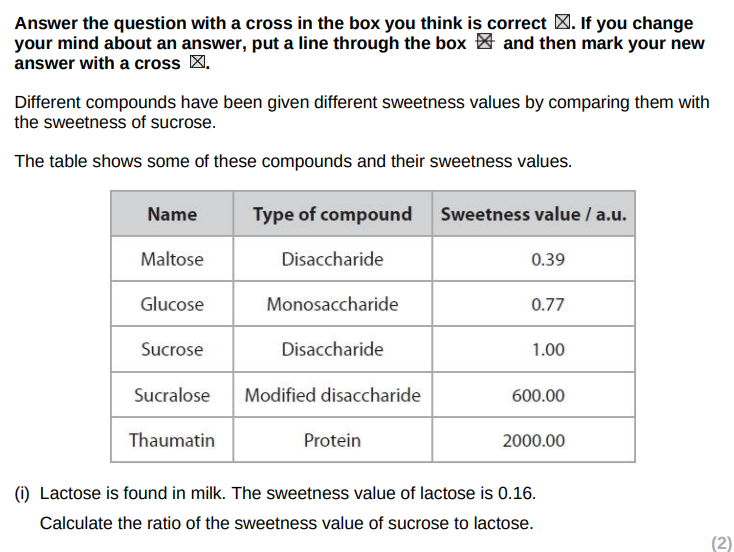
Calculate heart rate from this graph (2)

Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a major cause of death and disability in the UK. It has been suggested that magnesium ions are involved in regulating the ratio of HDL to LDL in the blood. (i) Describe the role of LDLs in the development of atherosclerosis. (3)
(LDL/lipoproteins carry) cholesterol in the blood
Cholesterol is deposited to form atheroma
in the edothelium of an artery
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a major cause of death and disability in the UK. It has been suggested that magnesium ions are involved in regulating the ratio of HDL to LDL in the blood. (ii) explain how astherocsclerosis can cause damage to heart muscle (3)
Narrowing of (lumen of ) coronary artereis
reduces blood flow/oxygen to the cardiac muscle
which reduces aerobic respiration
Thrombophilia is a condition that increases the risk of blood clots forming. This condition increases the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), a condition where a blood clot forms in a vein. Thrombophilia due to the production of overactive factor V can be inherited. Factor V is involved in the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. (i) Describe the role of thrombin in blood clotting (3)
thrombin is an enzyme
which catalyses the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin
a mesh of fibrin traps platelets/red blood cells to form a clot
Thrombophilia is a condition that increases the risk of blood clots forming. This condition increases the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), a condition where a blood clot forms in a vein. Thrombophilia due to the production of overactive factor V can be inherited. Factor V is involved in the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. (i) Explain why a mutation in the gene coding for the protein factor V may increase the risk of VTE (3)
mutation in the gene changes the sequence of the amino acids in the factor V molecule
Overactive factor V will increase the production of thrombin
increases blood clotting
An ischaemic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain is blocked by a blood clot. Explain how a blood clot could form in a blood vessel. (4)
collagen is exposed when a wall of blood vessel is damaged
leading to the release of thromboplastin
thromboplastin catalyses conversion of prothrombin to thrombin
thrombin catalyses conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin
fibrin forms a mesh of fibres and traps red blood cells to form a clot
fibrin forms a mesh that collects platelets/ RBCs
Tranexamic acid prevents plasmin digesting fibrin/ stops breakdown of fibrin
allowing clots to remain in place
Describe how very high blood pressure could result in atherosclerosis.
high blood pressure damages endothelium of artery
causing an inflammatory response
white blood cells/cholesterol accumulate/atheroma forms
calcium salts and fibrous tissue build up/ formation of a plaque
What is an anticoagulent?
Medication that prevents blood clots
A heart attack may occur when a coronary artery is blocked with a blood clot. The risk of this can be reduced by treatment with platelet inhibitors. Explain why platelet inhibitors would reduce the risk of a heart attack. (2)
platelet inhibitors reduce the risk of blood clots forming
therefore less likely that coronary arteries/ blood flow to heart muscle will be blocked
What are the 2 methods for determining is a person is obese?
If BMI is over 30
Waist to hip ratio
Describe how high blood pressure could be reduced by medication and lifestyle changes.
treatment with antihypertensive medication
reduce salt intake
stop smoking
increase excercise
reduce weight
Explain the effect that a diet high in salt could have on a person's risk of developing cardiovascular disease (5)
diet high in salt increases risk of CVD
high salt intake causes higher blood pressure
which increases risk of damage to endothelium of artery/ atherosclerossi
therefore increases risk inflammatory response
leading to increased risk of atheroma/plaque formation
narrowing of arteries increases risk of blood pressure/ reduces blood flow to cardiac muscle
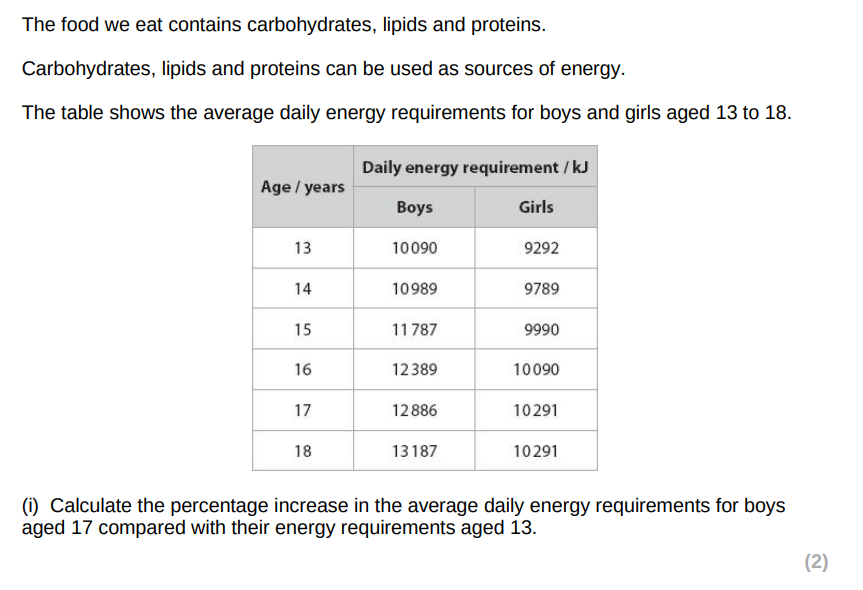
27.7%, 28%
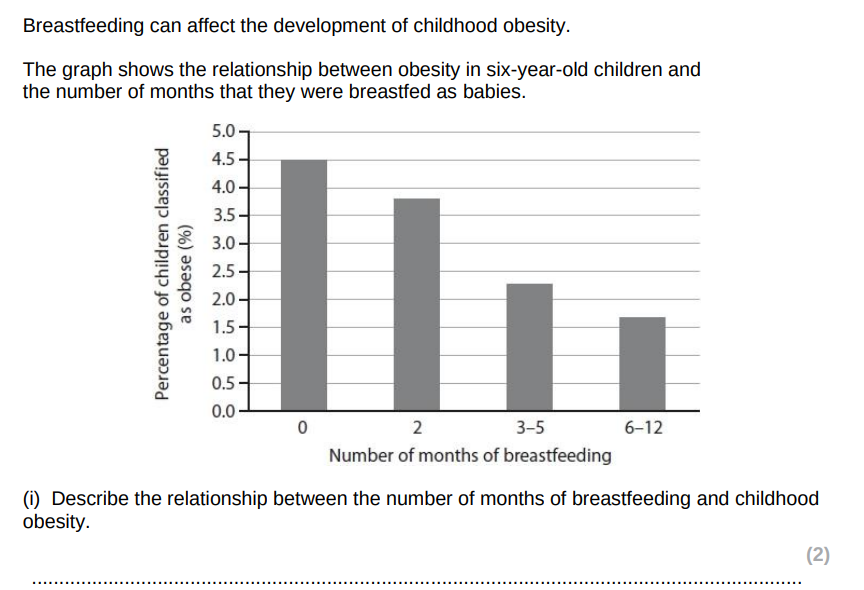
Increasing number of months of breastfeeding decreases the percentage of children with obesity
There is a large drop in obesity when children are breastfed for (3-5 months/ more than 2 months)
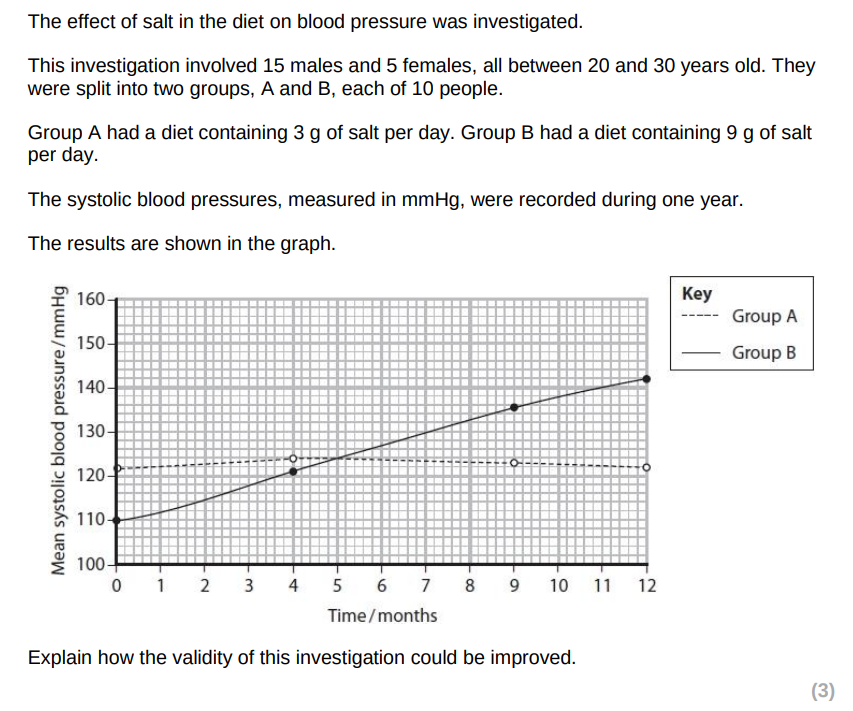
equal number of males and females
larger sample size
name a suitable controlled variable e.g. same starting blood pressure/ body mass/ diet/ exercise level
The incidence of obesity is increasing in some populations. High levels of sugars, such as fructose, in processed food could be contributing to this increase. Explain why high levels of sugars in a person's diet could lead to obesity
energy intake is higher than energy output
excess energy/sugars can be stored as/ converted to fat
leading to weight gain (greater than overweight)
obesity is indicated by a BMI above 30/ waist to hip ratio greater than 0.85 in women or 1 in men)
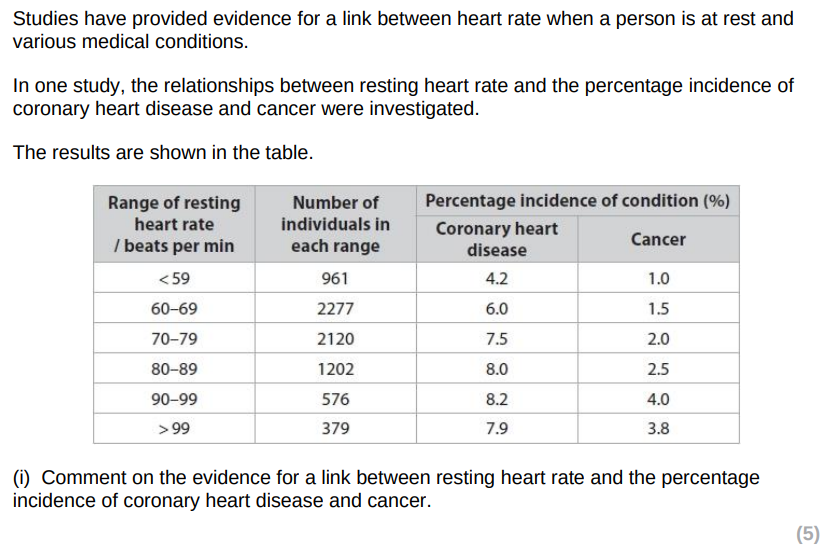
as heart rate increases, so does incidence of both conditions
relationship between heart rate and CHD quantified
relationship between heart rate and cancer quantified
greater increase in incidence of cancer with increased heart rate
at a heart rate >99bpm there is a reduction in incidence pf both conditions/plateaus/little difference
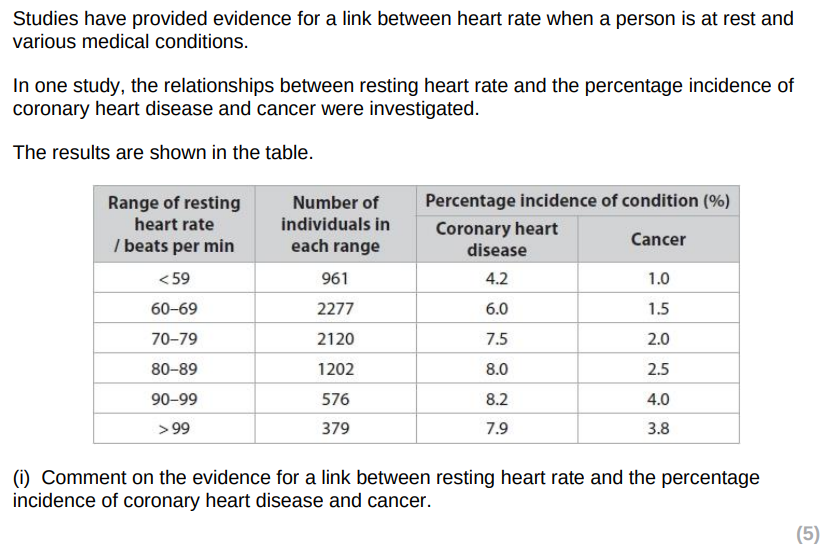
Give two reasons why there were different numbers of people in each resting heart rate group.
mid heart beat is more common in the general population/heart rate is normally distributed in the population
fewer people available at low and high rate because of other health risks
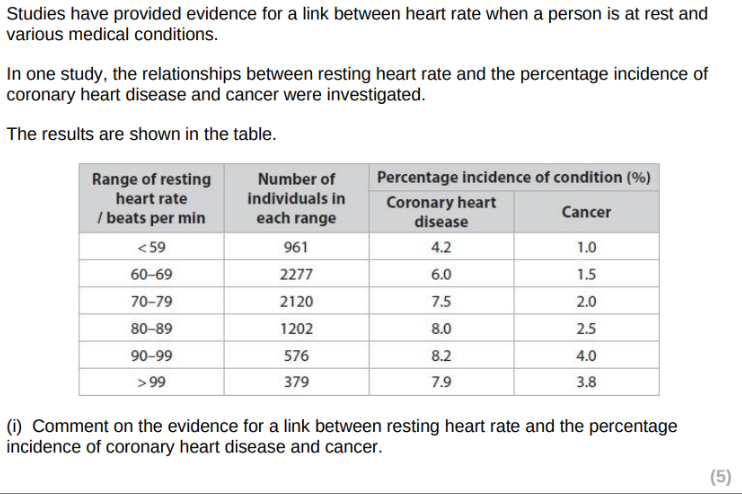
Give two reasons why the number of people in each resting heart rate group did not affect the validity of this investigation.
still statistically a large sample size
wide range of heart rate considered
percentage incidence used rather than numbers
blood test to measure (HDL and LDL/ cholesterol) levels
higher HDL:LDL decreases risk/high cholesterol increases risk
measurement of (height and mass/ waist and hip size)/ calculation of (BMI/wait:hip)
(BMI above 30/ waist:hip above 1) increases risk
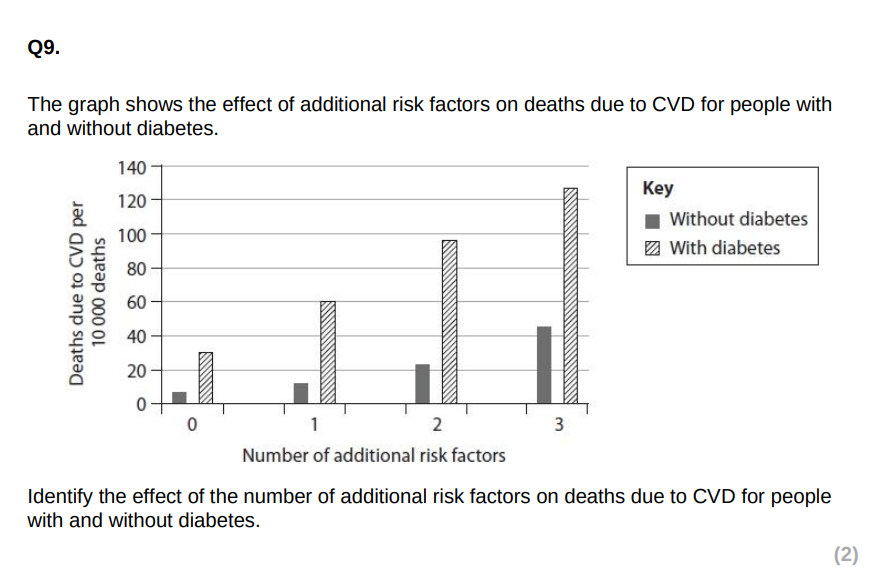
correlation between the number of risk factors and deaths due to CVD
deaths due to CVD is higher for diabetics than non-diabetics
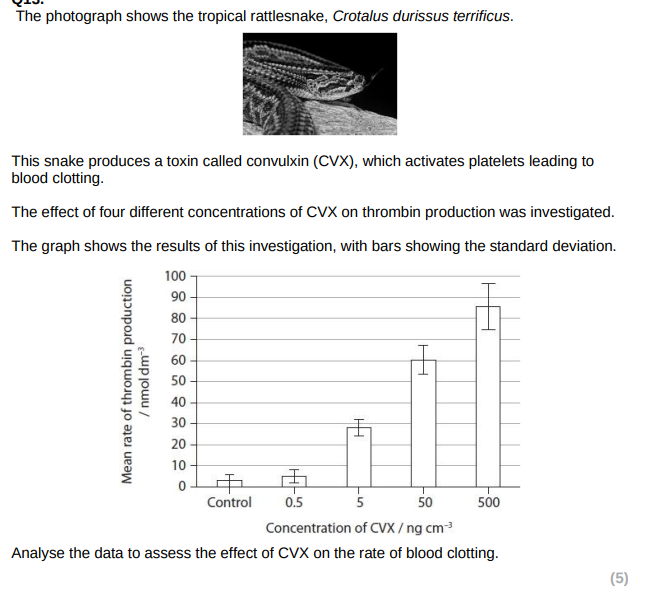
Increased thrombin production as CVX concentration increases
The relationship between CVX concentration and rate of thrombin production is not (directly proportional/linear)
Little difference between control and 0.5ngcm-3 (CVX)/greatet increase from 5ngcm-3 to 50ngcm-3
no significant difference/standard deviations overlap between control and 0.5
greater thrombin production leads to faster/increased conversion of firinogen to fibrin
greater thrombin production leads to faster/increased clotting of blood
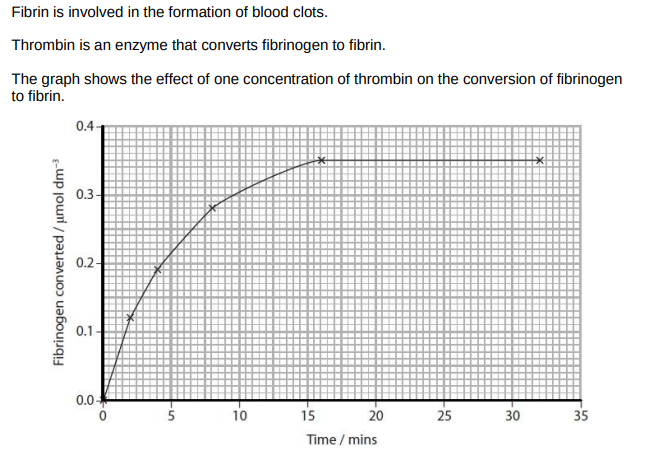
On the graph, draw a line to show the effect of halving the concentration of thrombin
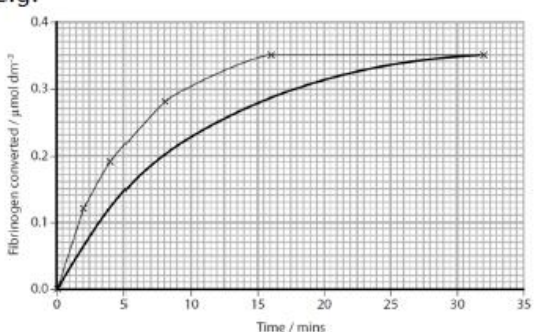

Explain the effect of changes in the initial rate of reaction on the time taken for a blood clot to form
the slower the initial rate of reaction the longer it will take for a clot to form
because fibrin will be produced more slowly
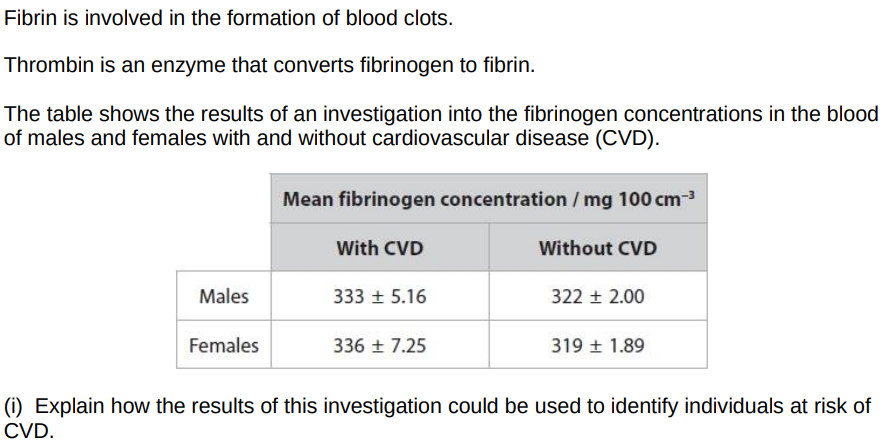
fibrinogen concentration is higher in individuals with CVD
compare an individual’s fibrinogen concentration with values in the table
no overlap between fibrinogen concentrations for those with CVD compared with those without CVD
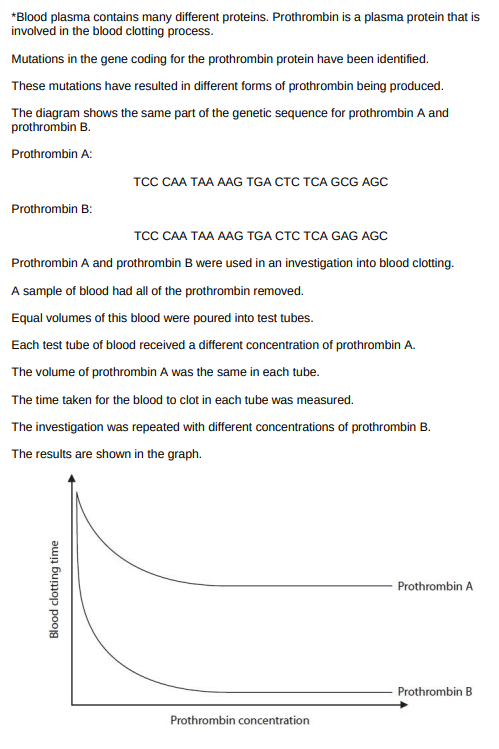
Explain the results of the investigation (6)
Lipids and carbohydrates are found in both plants and animals. The carbohydrate content of vegetables ranges from 3 to 35%. However, meat contains little to no carbohydrate. Milk is the only food source from animals that contains a significant amount of carbohydrate. Although plant material contains a higher proportion of carbohydrate than animal tissues, it has been claimed that carbohydrates are more important to animals than they are to plants. Assess the relative importance of carbohydrates to plants and animals. (9)

Explain how the structure of glycogen allows it to be an energy store. (3)
polymer of glucose
to provide glucose for respiration
branched/contains 1,6 glycosidic bonds/ has many terminal ends for rapid hydrolysis
compact to allow large amount of glucose/energy to be stored in a small space/insoluble therefore no osmotic effect on cells

Explain how the structures of amylopectin and glycogen make them suitable for storing energy.
branched therefore can be rapidly hydrolysed (to release glucose)
compact so more energy/glucose can be stored
insoluble therefore does not affect osmosis
molecules too large to diffuse across cell surface membrane
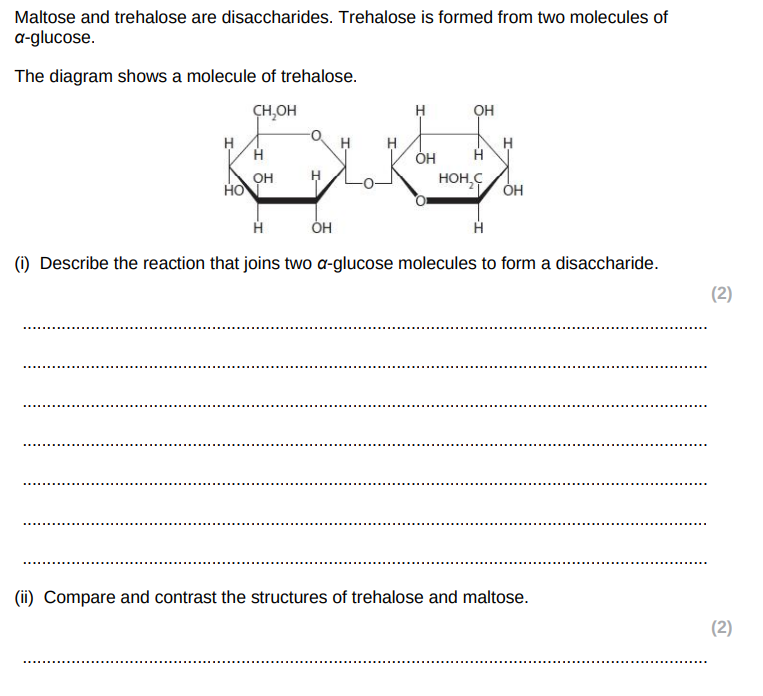
increases blood cholesterol
because triglyceride is saturated
lipoprotein is an LDL
lipoproteins transport cholesterol
LDL binds to receptors on cell surface membranes/ LDL accumulates in blood if receptors overloaded
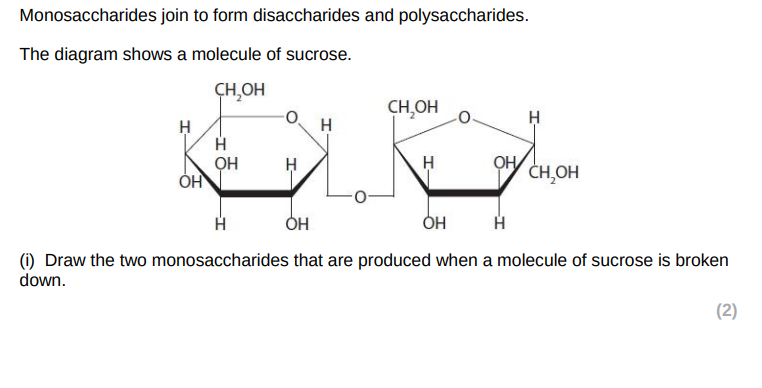
Name them
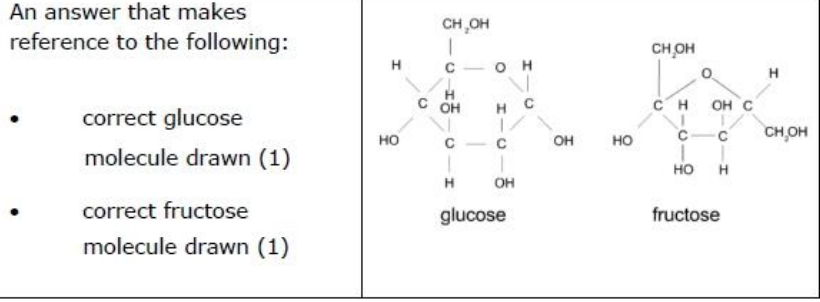
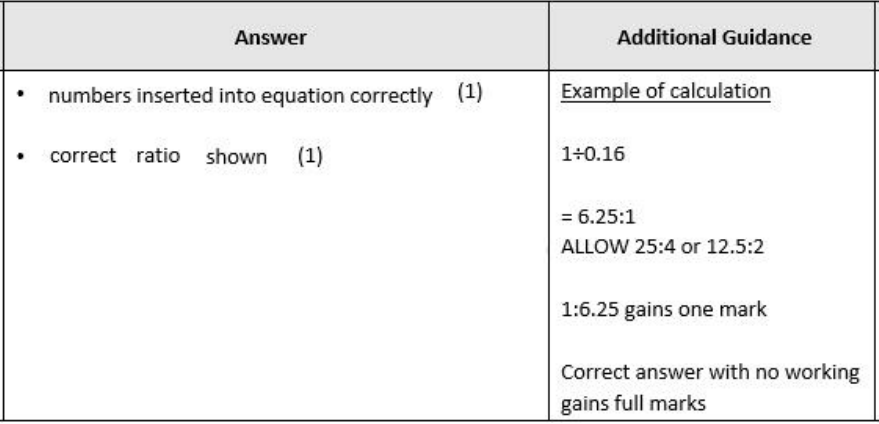
Monosaccharides join to form disaccharides and polysaccharides. Compare and contrast the structure of a disaccharide with glycogen.
similarities
both contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
both contain glycosidic bonds
both contain glucose
Differences
glycogen contains 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds whereas disaccharides only contain one type of glycosidic bond
glycogen only contains glucose whereas disaccharides can contain glucose and other monosaccharides
Mucopolysaccharides are complex molecules found in the human body. Mucopolysaccharides can be broken down by enzymes. Describe how an enzyme could break down the polysaccharide component of mucopolysaccharides.
polysaccharide made up of many monosaccharide components
joined together by condensation reactions/glycosidic bonds
only 1,4 glycosidic bonds present/ no 1,6 glycosidic bonds present
Blood plasma contains glucose dissolved in water. Glucose is a polar molecule that is taken up by muscle cells and used in the synthesis of glycogen. Glucose is used in the synthesis of glycogen in muscle cells. (i) Describe the formation of glycogen from glucose.
joined together in a condensation reaction
forming 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
Describe how the structure of glycogen is related to its function as a storage molecule
branched molecule for more rapid hydrolysis
compact so more can be stored
Sweating is a thermoregulatory mechanism. A student stated that loss of heat when sweating is related to the dipole nature of water molecules. Justify this statement. (3)
the water has an uneven distribution of charge (making it a dipole)
so water forms hydrogen bonds with other water molecules
and it requires a lot of heat/thermal energy to break these bonds
and allow water to evaporate taking the heat energy with it high latent heat of evaporation
Explain how the properties of water make it an ideal transport medium.
water is a solvent
because water molecules surround polar molecules/ion/hydrogen bonds form between water molecules and solute molecules
water is liquid so has the ability to flow
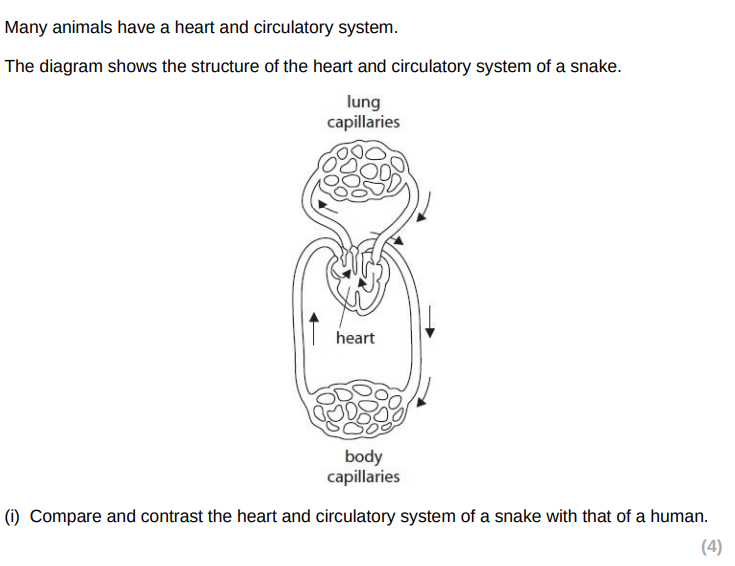
both have a double/closed circulatory system
both have 2 atria, arteries, veins and capillaries
Snake heart has only one ventricle whereas human heart has 2/snake heart does not have a complete septum/wall between the ventricles/sides of heart whereas human heart does
In snake heart the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood mix (in the ventricle) whereas they do not mix in a human heart
Explain why a snake needs a heart (2)
to pump blood to supply oxygen/glucose to body cells/to remove carbon dioxide/waste from the body
by mass transport
because a small surface area to volume ratio does not allow diffusion to occur at a sufficient rate
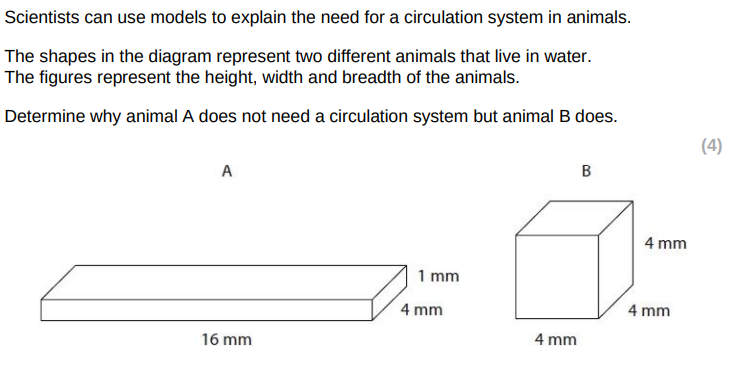
both have the same volume
animal a has a larger surface area
animal a has a larger surface area to volume ratio
so sufficient surface area in animal a for diffusion
distance to cells in centre of a is shorter than for b allowing quicker/sufficient diffusion/shorter diffusion distance

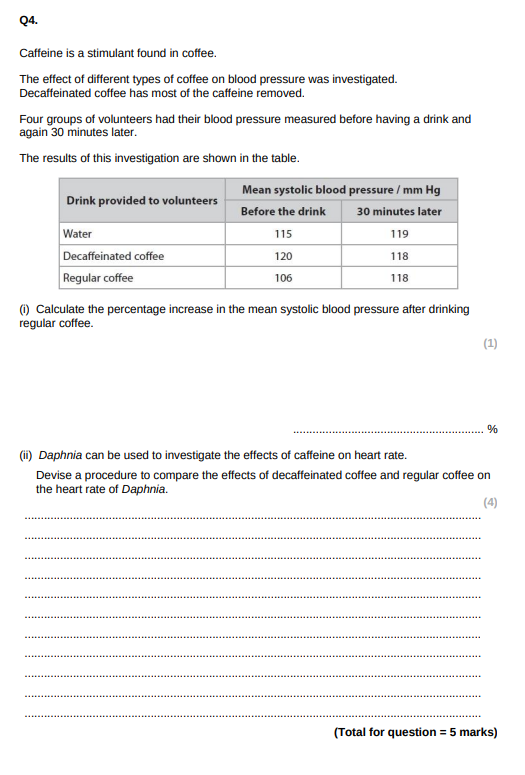
What would you use as a control for the daphnia experiment and why?
pond water to compare with the caffeine solutions/to show normal/resting heart rate
What are two variables that should be controlled for the daphnia practical?
temperature of solution/ acclimatisation time - b/c e.g. cold temp decreases heart rate
same sex/size/age of ghost shrimp
so caffeine would affect ghost shrimp equally/to produce more valid results
IGNORE SPECIES
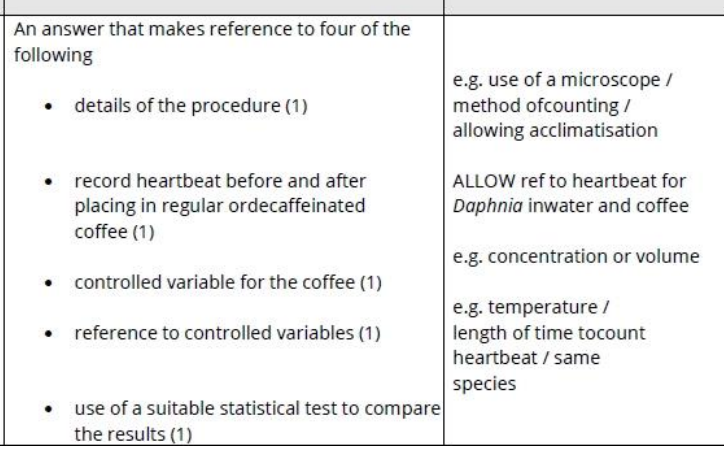
11.3/11.32%
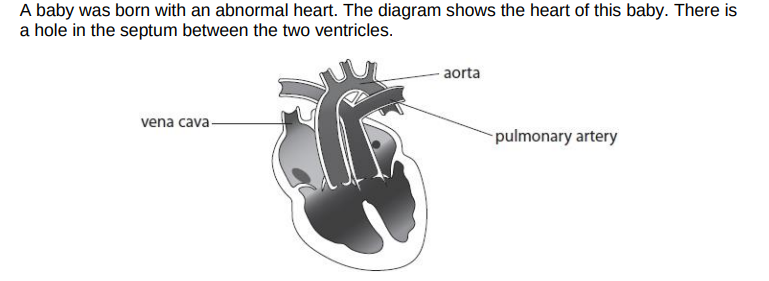
Problem with blood vessels
The baby survived because of the hole in the septum of the heart. Explain how the hole in the septum allowed this baby to survive.
the hole allows oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to mix (between the 2 ventricles)
oxygenated blood travels to the body/enters aorta/dexoygenated blood travels to the lungs/enters pulmonary artery
providing some oxygen for respiration
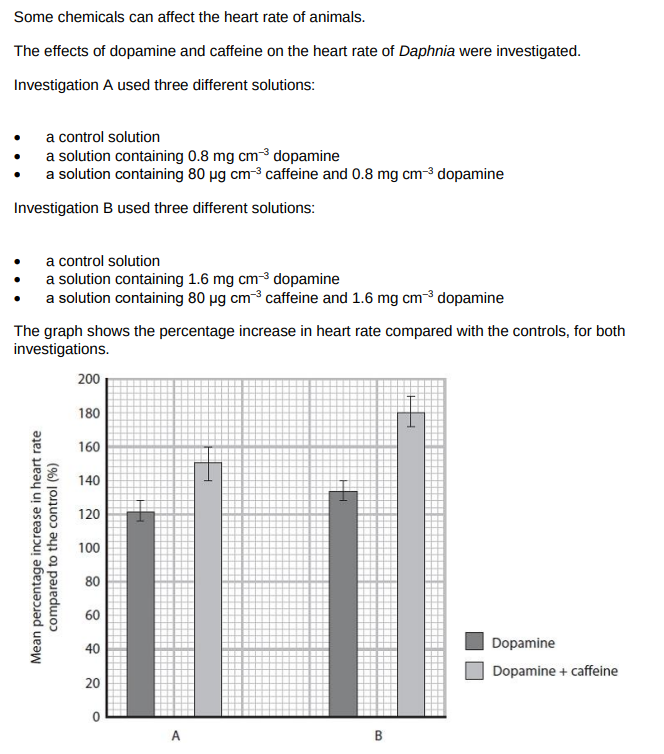
Comment on the effects of dopamine alone and dopamine with caffeine on the heart rate of Daphnia in this investigation.
adding caffeine to dopamine increases heart rate
adding/increasing the concentration of dopamine increases heart rate
larger increase when both are used together at a higher concentration
no overlap between error bars indicates significant difference between dopamine and dopamine with caffeine/overlap between error bars indicates no significant difference between dopamine concentrations
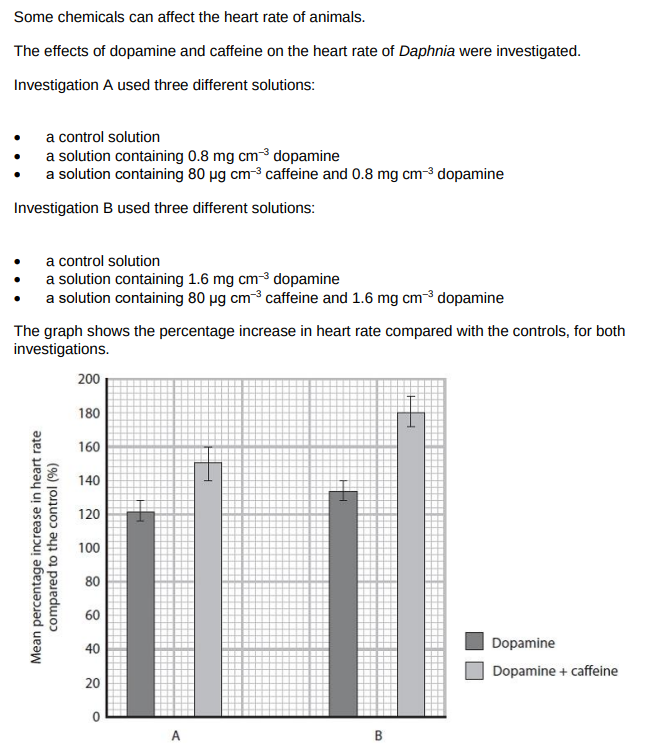

Devise a procedure that could have been used to produce the results shown in the graph. (5)
daphnia immobilised on cavity slide
acclimatisation time in (control/dopamine/dopamine and caffeine) solution
use of cocentration from graph
suitable method for counting and recording heart rate
use daphnia of same (species/age/sex/size)
repeats and calculation of mean/standard deviation
As levels of activity increase, the heart can respond to the changing demand for oxygen. During the cardiac cycle there are pressure changes in the chambers of the heart. Explain how pressure differences in the heart ensure efficient pumping of the blood into the arteries.
pressure increases in the ventricles
greater pressure in the ventricles than in the atria/arteries
causes the atrioventricular valves to close
causing the semilunar valves to open/forcing blood into the arteries
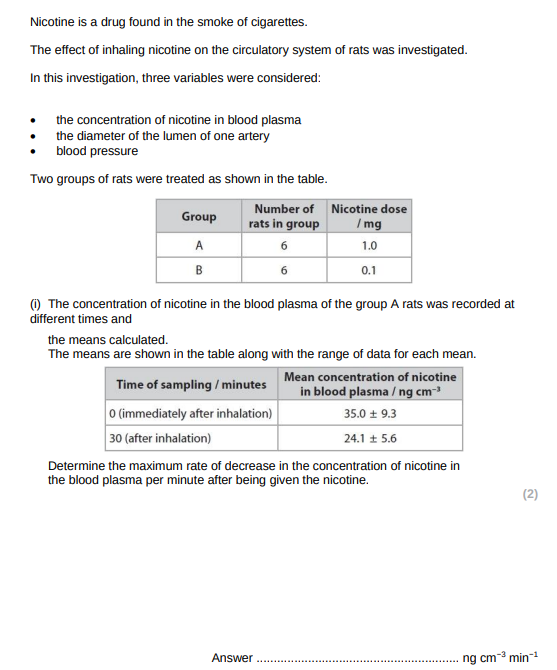
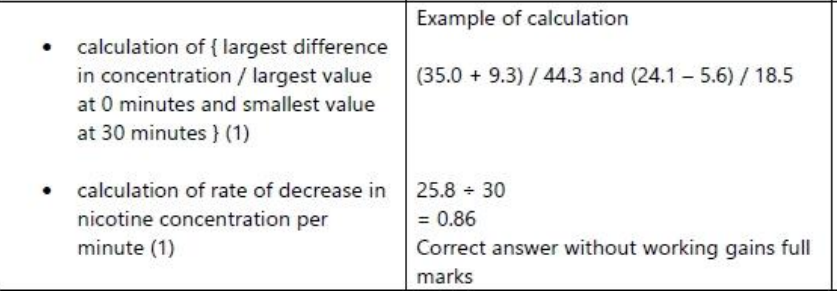
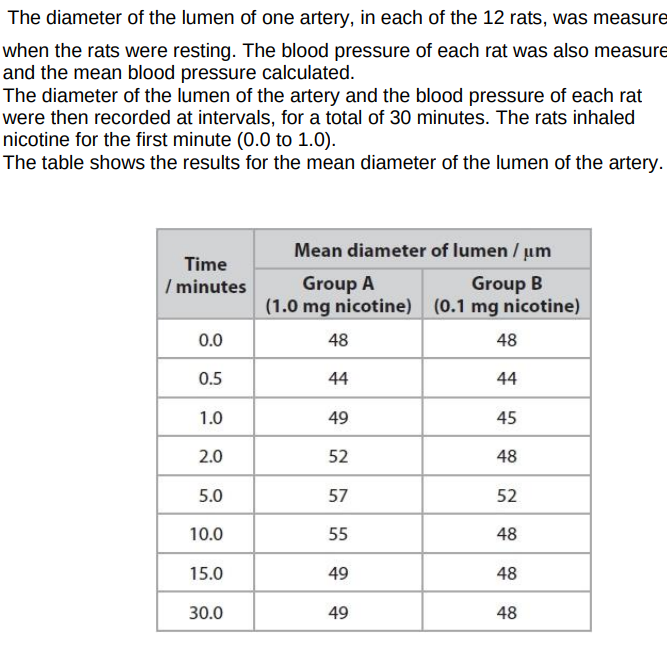
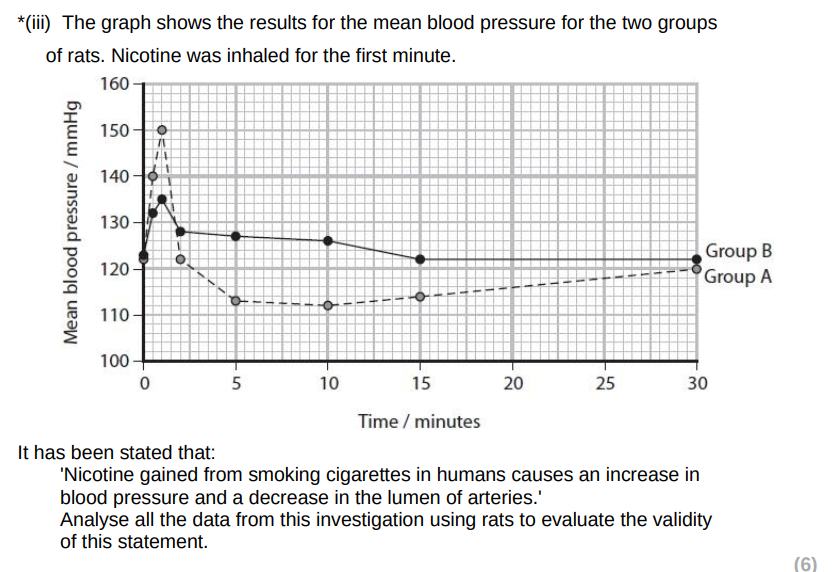
validating statement:
investigation involved rats inhaling nicotine which humans do during smoking
rats are mammals so can extrapolate to humans
Not validating the statement
nicotine inhaled (for both conc) leads to vasocontriction and then vasodilation and then returns to original diameter
blood pressure for 1mg nicotine concentration increases and decreases but drops below original value
presence of nicotine leads to no adrenaline release which increases heart rate
blood pressure for both nicotine concentrations increases and decreases
no referenece to rats inhaling smoke only nicotine
rats are not the same as humans
sample size is too small to make a valid statment
comment whether you agree or disagree with statement
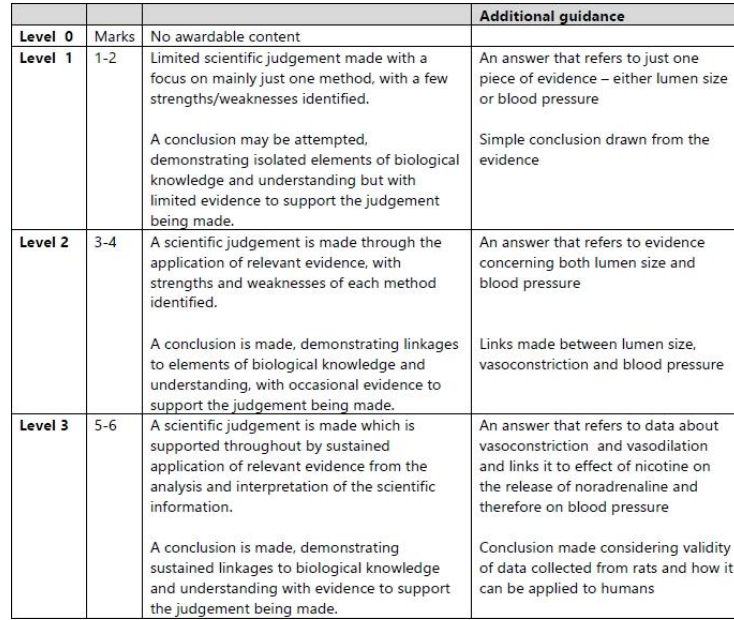
Atrial systole
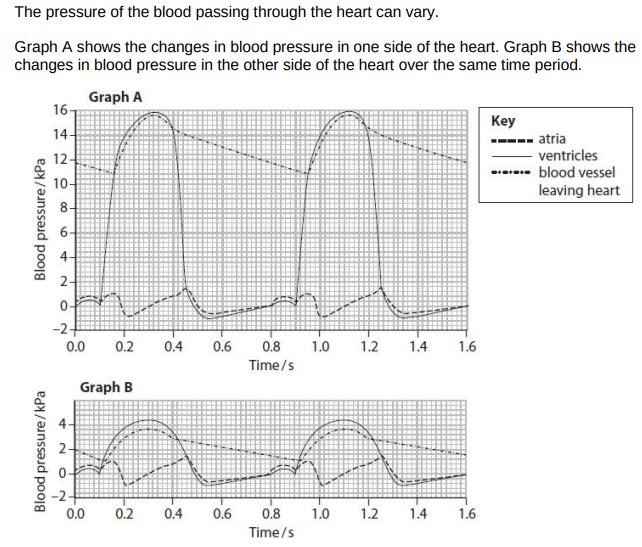
In graph A, the blood pressure inside the ventricle changes between 0.0 and 0.45 seconds. Explain how these changes in blood pressure occur in this part of the cardiac cycle. (4)
from 0s (to 0.05s) pressure increases due to atrial systole
ventricle fills with blood (from the atrium/due to atrial systole
after atrial systole finishes (from 0.05s to 0.1s) there is a fall in ventricular pressure
from 0.1s to (0.32s) there is an increase in pressure due to ventricular systole
(from 0.32) ventricular pressure decreases due to ventricular diastole
Explain the term causal relationship (1)
The idea that a change in one variable will directly result in the change of another variable
Lipoproteins are composed of phospholipids, cholesterol and proteins. (i) Proteins are made up of amino acids. Describe how amino acids join together to form the three-dimensional structure of a protein. (4)
reference to peptide bonds (joining amino acids)
between amino group (of one amino acid) and carboxyl group (of another)
the sequence of amino acids is the primary structure of the protein
reference to folding (of primary structure) held together by bonds
disulfide bridges/ hydrogen bonds / ionic bonds / Van Der Waals forces
between the R groups
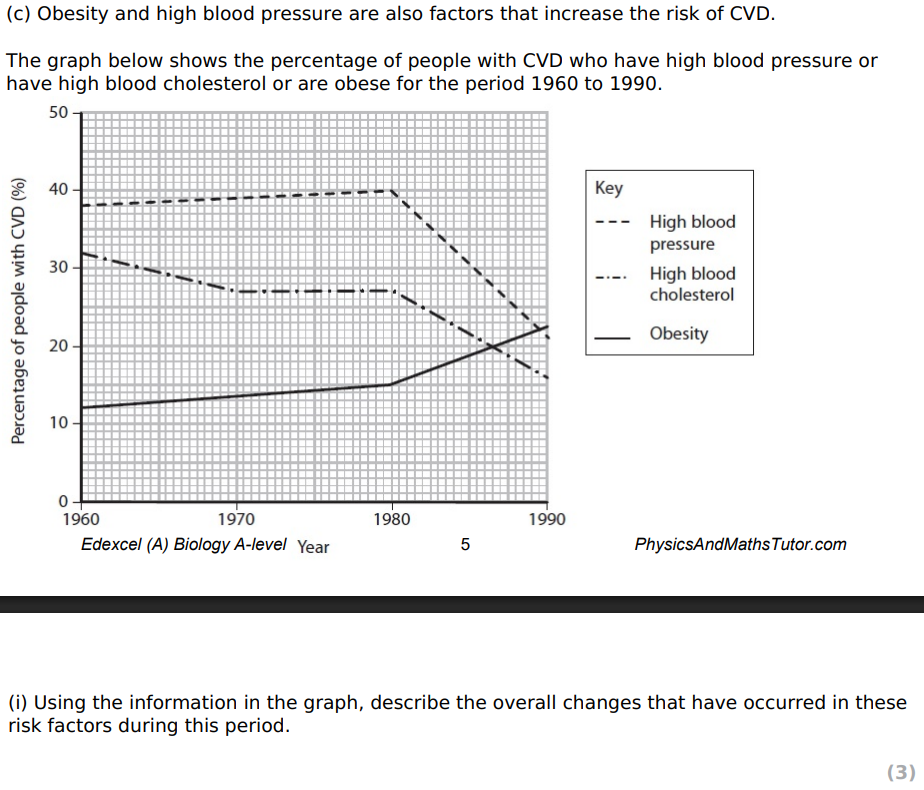
high blood pressure has fallen overall
high blood cholesterol has fallen overall
obesity has risen overall
obesity was the lowest risk factor but is now the highest
credit use of manipulated figures (ONLY CREDIT OVERALL CHANGE FIGURES)
Other than obesity, high blood pressure and high blood cholesterol what are the factors which increase the risks of CVD?
being male
increase in age
lack of exercise / inactivity
smoking
genetics
high alcohol consumption
high salt diet
high saturated fat intake
stress
diabetes
Describe how glucose moves into cells by facilitated diffusion (2)
carrier protein (in cell surface membrane)
(glucose moves from) high to low concentration
glucose binds to (carrier) protein / (Carrier) protein changes shape to move glucose (across the membrane)
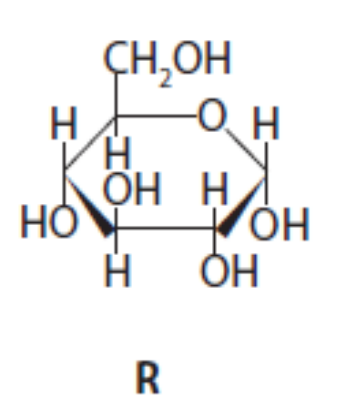
Draw a diagram to show the molecules produced when two molecules of R join together during a condensation reaction.

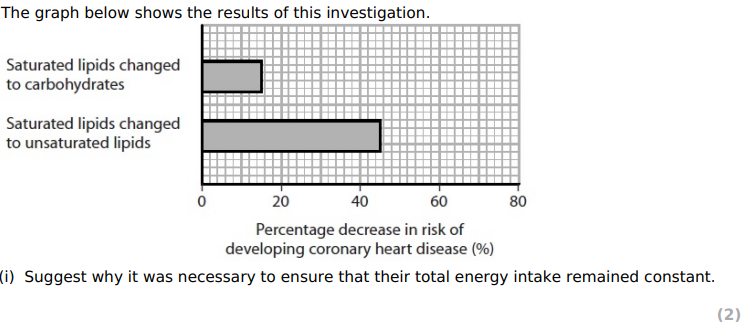
(i)
idea that on;y one factor has changed
if intake went up, increase risk obesity a risk factor / if intake went down could decrease CHD risk
(ii)
both diets decrease the risk
both diets have less saturated fats
saturated fat associated with heart disease
idea that changing to unsaturated lipids has the greater effect
idea that excess carbohydrates may be stored as saturated lipids
idea that unsaturated lipids change HDL/LDL ratio
Explain how the structure of the aorta relates to its function (3)
idea that there is a thick wall / lots of collagen / thick layers / thick tunica media
idea that it needs to avoid rupture / to withstand high pressure
elastic / muscular / layer / fibres / wall
control flow of blood / maintain blood pressure / elastic recoil
smooth endothelial wall
to reduce friction / resistance
semi lunar valave present
to prevent backflow (during diastole)
large lumen
idea of accommodating large volumes of blood
branches
to supply blood to different parts of the body including the coronary arteries
A stroke can be caused by cardiovascular disease (CVD) affecting arteries leading to the brain. Callum's family has a history of strokes. (i) Explain why a blood clot in an artery leading to the brain could cause a stroke. (3)
idea of reduced blood flow / bleeding
less / no oxygen / glucose reaches brain
idea of less / no areabic respiration
idea of less / no ATP produced
idea that brain needs lots of energy / ATP to function
lactic acid produced from anaerobic respiration
lactic acid inhibits enzymes / toxic
Some foods and drinks contain plant statins. Explain the benefits of plant statins to human health (2)
lower blood cholesterol
idea of inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in liver
reduce risk of CVD
Explain how the dipolar nature of water is essential for living organisms (2)
water can form hydrogen bonds
Any one from
water is a solvent / ions / polar molecules can dissolve / be transported / in water
reference to cohesion / adhesion
idea of hydrogen bonds holding water together as a liquid so that it can move in mass flow systems
suitable reference to specific heat capacity
idea of distribution of thermal energy around body
reference to high latent heat of vaporisation
Explain why any small animals such as daphnia have a heart (3)
reference to mass flow
name a suitable substance transported e.g. oxygen
comment on blood pressure / fast movement of blood to cells
idea of increased concentration gradient of solutes e.g. oxygen
idea that diffusion alone would be too slow
has high metabolic rate
Explain why the atrioventricular valves need to close (2)
ventricle needs to contract and force blood into the aorta / pulmonary artery / arteries
so valves need to close to prevent backflow into the atria on contraction
Explain how the structure of an artery is related to its functions (3)
reference to elastic fibres
allow stretching to accommodate high pressure / allow recoil to maintain high pressure
reference to folded endothelium
allow stretching to accomodate higher pressure
reference to smooth muscle
idea that muscle can contract / exert pressure
reference to smooth lining / endothelium
reduce friction / resistance to blood flow
reference to narrow lumen
to maintain high blood pressure
reference to collagen
idea that it avoids rupture / damage