Hemoglobinopathies and elp
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Hemoglobinopathy
amino acid is substituted for another on the globin chain
Where do most hemoglobinopathies occur
Beta chain
Hemoglobinopathy is what kind of change in the chain
Qualitative
hgbc speed
crawl
hgbs speed
slow
hgbF speed
fast
HgbA
accelerate
HgbH
Hustle
Routine hgb elp is done at what PH
alkaline
What hgb comigrate together on alkaline elp
C,E,O,A2
S, D, G
mostly shows bars in A2, S, F, A1, F, H
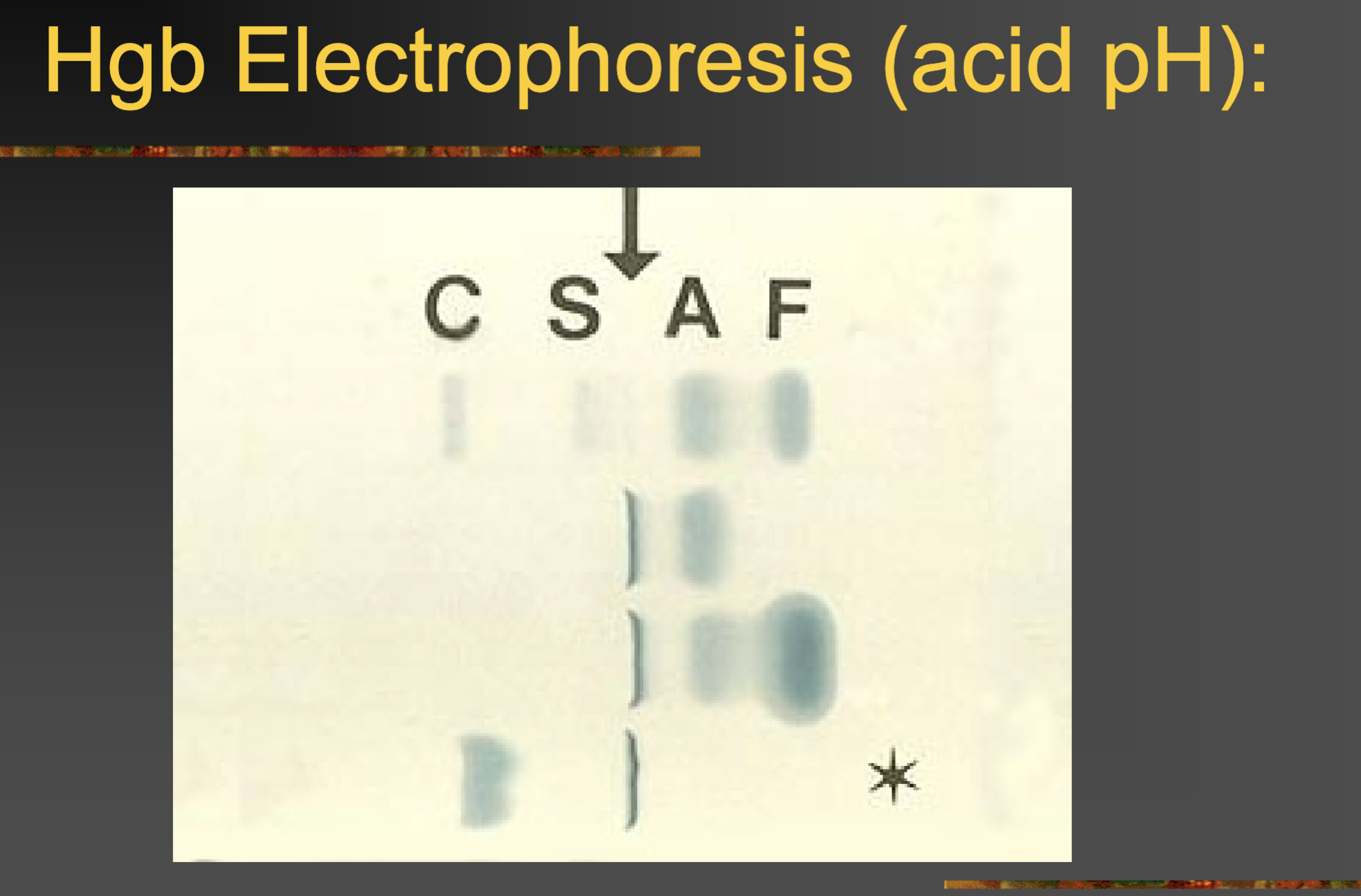
What Hgb comigrate together on acidic elp
A, D, G, E, O, A2, H, lepore, Barts
seperates C, S, F out
what Hemoglobinopathy has:
asymptomatic unless extreme hypoxia
no abnormal smear, No anemia
Normal CBC
Tube solubility +
A/S
What creates a false negative on a tube solubility
<7.5 gm/dL hgb
What creates a false negative on a tube solubility
Lipemia
HGb A/S electrophoresis %
60% A and 40% S
Why can’t you use Biorad HPLC of someone with A/S to measure A2
break down of S overlaps with A2
Hbg S/S
autosomal recessive Sickle cell anemia
S/S is mostly found in
What conditions cause Rbc to sickle
Low O2
What is the mechanism of S/S defect
pluggs cappilaries
impeded blood flow
splenic infarction
What is protective in S/S
HbgF
Vaso-occlusive crisis
sickle crisis
Infectious crisis
abnormal spleen function
Aplastic crisis
Panytopenia follows an infection and requires transfusion and hositalization
Dactylitis in S/S
painful asymmetrical swelling of the hands and feet along with uneven growth
Slow blood flow and blockages from S/S can cause
DVT, stroke
liver issues
blindness
kidney disease and diabetes
chronic leg ulcers
CBC shows:
WBC normal to slight increase
hgb= 5-9 gm/dl
indices are normal
Plt usually increased and there may be giant ones
retic counts 10-20%
S/S
Dif shows
sickle cells
targets, ovals, frags
polychromasia
few nrbc
baso stippling
HJ bodies
Pappenheimer bodies
Hgb elp shows pt #4
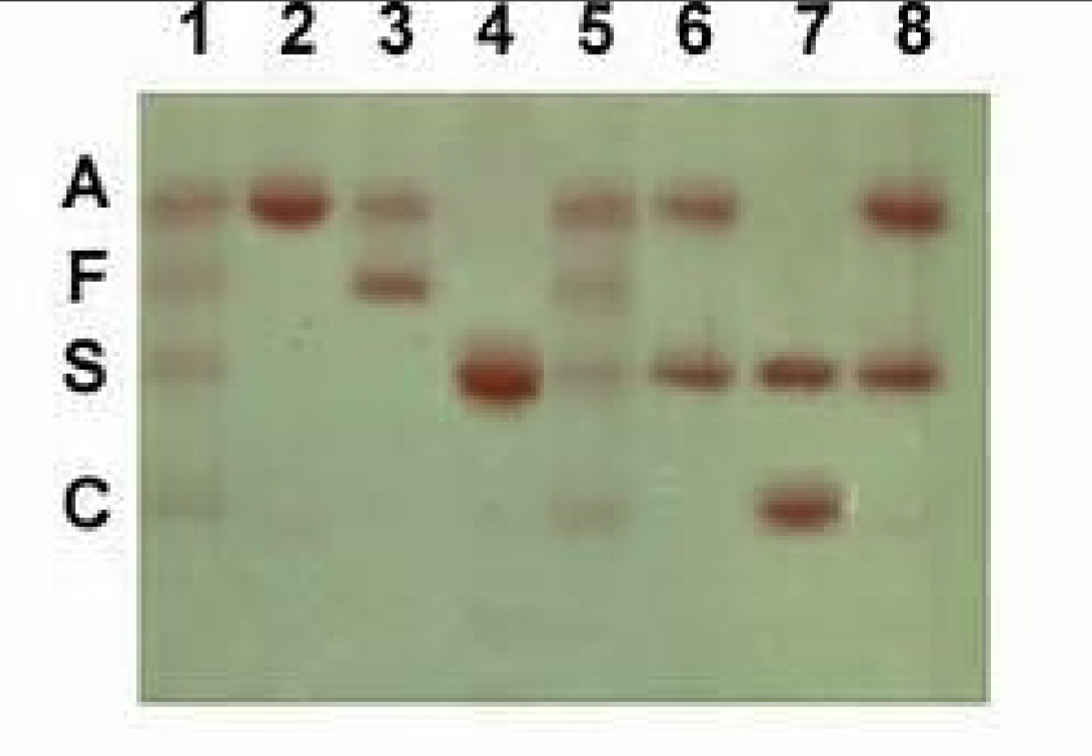
S/S
Pt 6
S/A
iron stores of S/S patients have
increased iron stores
Treatment of S/S
preventing crisis
prompt antibiotic treatment
avoid extreme heat and cold
Hydroxyurea to stimulat hgb F
gene therapy: Casgevy and Lyfgenia
Hbg C is associated with what pop.
black population
Hgb C disease is caused by
Lysine substituted for glutamic acid in the 6th positon of the beta chain
Hgb S/S is caused by
glutamine for valine sunstitution in the 6th position of the beta chain
Hbg c disease symptoms
mostly asymptomatic
some splenomegaly
mild to moderate anemia
How is Hgb C diagnosis made
elp at both alkaline and acidic ph
CBC
WBC and PLT normal
indices are N/N
Hgb 8-12gm/dl
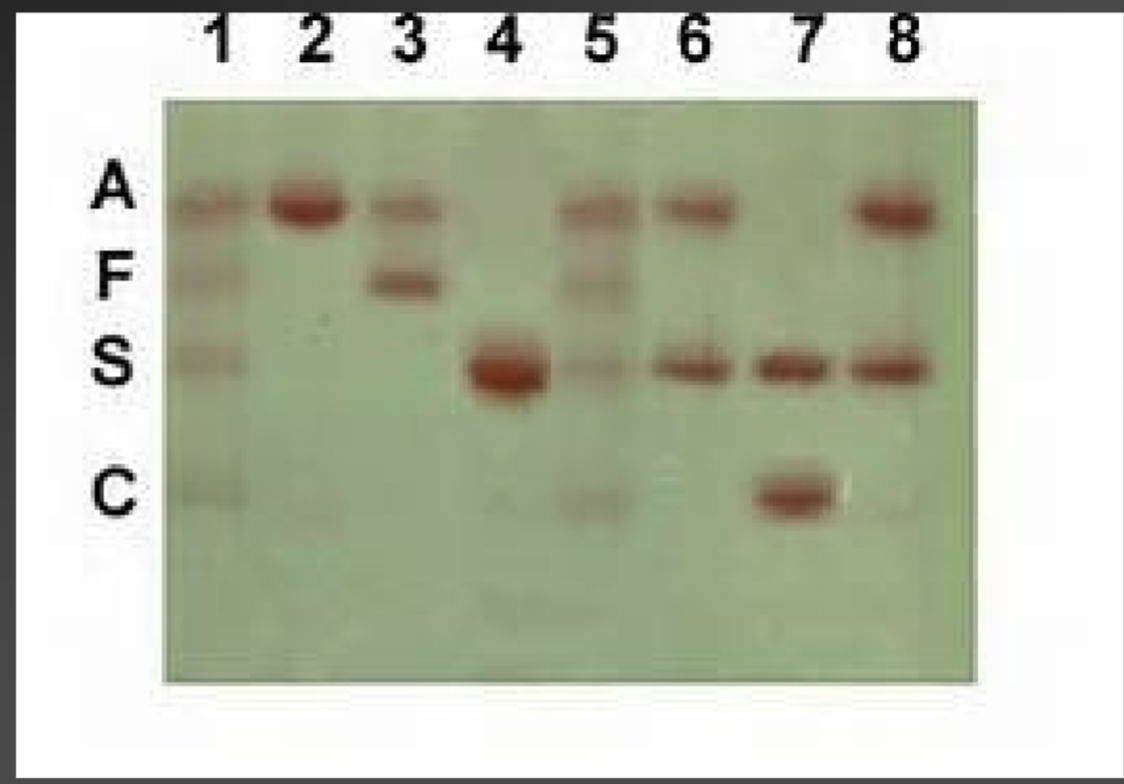
HgbC disease
diff:
2+- 3+ targets
occasional hgbC
folded pocket book or envelope cells
occ. sphere or frag
HgbC disease

HgbC disease
Hbg C train symptoms (A/C)
no symptoms
no anemia
maybe a few targets on diff
Hgb S/C symptoms
enlarged spleen but no incapacitation
mild anemia
CBC shows:
Hgb 10-14
Hct >25%
mild N/N anemia
S/C
Diff shows:
targets, occ. sphere
pocket book cells
rare sickle
S/C crystals
S/C
Hemoglobin E is found in what population
SE asian
What are the symptoms of A/E and E/E
no symptoms
What causes Hgb E
Substitution of lysine for glutamic acid at the 26 position on the beta chain
Hgb E does what to the indices of the person
Micro/hypo
What is high in the CBC of someone with E trait
RBC
A/E has what % in elp
30% E and 70% A
Sickle and Beta thal cause S trait to be
Worse
Sickle and alpha thal cause S trait to be
better
Amino acid substitution results in a chain that has weak points at critical internal portions what does this cause
Heinz bodies
Heinz bodies cause
decreased flexibility → extravascular hemolysis
In babies with S/S why dont they get sickle cell crisis
Levels of Hgb S not at full amount until 6 months of age
They have Hgb F which is protective
CBC:
no anemia
indices are micro/hypo
targets
RBC is high
Hgb E
Heinz body anemia have what happen to the oxygen curve
left shift, it looks the same as normal hgb on elp too
decreased oxygen affinity hgb is
mthhgb
increased oxygen affinity hgb is caused by what and causes what
amino acid subt. giving altered binding or release of 2,3 DPG
increased RBC mass
Polycythemia
What test do you use for unstable hgb like E
Isopropanol solvents (polar) causes hgb E to precipitate
heat denaturation, buffer solution is added to washed rbc hemolyzed with water, heated for a long time