Transcription and Translation
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
First half only transcription and second half only translation =
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Describe RNA polymerases
Do not require primer nad lack 3-5 exonuclease
Syn RNA in the 5 to 3 direcction
Need ATP, GTP, CTP and UTP
Why do we need tranascitption?
Cell only has one or several copies —> not enough for cell meta
Protect a genomic DNA from cytoplasmic envrion (Euks only)
Reg the rate of protein syn via number of nRNA, life time of mRNA(degrade) and RNA binding factors (translation)
What is the difference between RNA poly in Euks vs Proks?
Proks - Single RNA poly for all RNA, E coli had 4 subs (sigma facotr —> promoter sigma 70
Euks - Have 3 types
I - prod rRNA
II - prod mRNA
III - prod tRNA and 5S rRNA
***Same mech for all 3 but diff types of promoters
Describe the strucutre of a gene.
Reg sequences: promoter —>binding for RNA poly and trans factors
…………………Promoter proximal elements and enhancers bind nuclear rep, co act, and co repressors
***Start + terminaiton seq needed
Describe the template and coding strand using their specific terms
Template - made via Rna poly, Comp and antiparrallel to coding strand and RNA
Coding - Analogus to produced RNA (Can be used to determine AA seq of protein)
How do we started transcription? What is the regulation?
AT rich seqeunces
E coli TATAAT - pribnow box (PROKS)
Euks have TATA(A/T)A - TATA box
Also can have CAAT boxes, GC rich seq, and enchanters in EUKS
How is enlongation stopped?
Termination seq via
Rho independent - formation of hairpin loop —> release of RNA polu and transcript
Rhi dep - binding of rho causes release of poly and transcript
AHHour DNA is way too coiled what do we use to prevent this?
DNA topoisomerase
Describe binding of RNA poly in bacteria
Recog and binds to promoter
Unwinds and separates DNA
Sigma factor dissaociates from DNA
RNA poly transcribes DNA
What is a cistron?
Region of DAN that encodes for single polypeptide chain
***Relates to prok mRNA s which are ususal polycistronic transcripts
*8Proks lack of nucleus allows for coupling of transcription and translation
AHH patient Ivy Sharer has a positive sputum stain whihc reveals that she has TB, what will we treat her with?
Multidrug regimen inclduing rifampin (Abx of the rifamycin family)
Inh bacteria RNA poly however can also inhibit micro RNA polymerase (TB dosage below needed amount for inhibition)
What are the differences when comparing EUK transcription vs PROK counterpart?
Occurs in Nuc and in chromatin
More reg: Nucleosome mod enzymes (histone acetytransferases), chromatin remodeling
3 polymerases
More processing :mod of RNA and splciing
nMRNA = only one polypeptide
What do general transcription factors interact with?
GTFs interact with polymerase II —> initiate trans
Enhancers —>up or down stream to stim transctiption initiation, can bind to trans factors or activators.
What is thalassemias?
Group of hereditary anemias —> most common gene disorder
Affects subunits of adult hemoglobin—>anemia
Mutations with Beta + phenotype are withint he TATA box
Messes with start point and red beta globin by 75%
Describe the synthesis of EUK tRNA.
tRNA synthesized by RNA poly III (Poly III)
mature tRNA is made from precurosors via cleavge of 5 and 3 ends, splciing to remove introns, replacement of 3 termineal UU with CCA, or multiple mods of bases
Describe the syn and processing of EUK mRNA.
RNA Poly II syn primary transcript
capped at 5 end during trans - 5 capm (recognition for ribosome binding + decreases degradation)
Poly A tail at 3 end once released from RNA poly
Introns spliced out
—>cytoplasm once mature RNA done
Describe the synthesis of EUK rRNA
Via RNA poly I
From repeating genes
Mult RNA poly I can transcript from a single gene
rRNAs for thje ribonucleoprotein complex ie ribosome
What kind of mutation causes sickle cell anemia
Missense mutation
Single base change in each allele for B globin DNA ie GTG (Val) replaces normal GAG (Glu)
- Oxygenated molescules (soluble) however upon deoxygenation then aggreattion to insluble fibers
Defroms RBC into spiny and sickle shaped
What are the componenets needed for translation
template ie mRNA
ribosomes
tRNA
AAs
Translation factors
ATP and GTP - used to attach AA to tRNA, binding of aminoacyl tRNA to A site and trasnslocation
mRNA syn from 5 end producing a polypeptide syn from its amino terminal end
Describe the formation of aminoacyl tRNA
Attachemnt of AA to tRNA cat via aminoacyl tRNA synthetases
AA atttachmed to 3 end of tRNA
Req ATP
Respon for specifcity and proofreading and high fidelity of translation
each memeber recognizes specidc AA with corresponding tRNA
Describe the sites associated with ribosomes and where they are located?
APE sites
A binds incoming aminoacyl tRNA and directs next AA added
P occupied by peptidyl tRNA —>carries syn peptide’
E - empty tRNA about to exit
Can be free or bound to the rough ER
Describe the initation of translation.
16s rRNA contains seq comp to shine dalgarno seq
Posititons mRNA on 30s subunit
in EUKS, 40S sub binds to cap strucutre of mRNA
AUG is recognized via initator tRNA —> enters P site
Reg via IF2 in E coli and several eIF in humans
Proks + mitro iniator tRNA carries N formylated methionine
***IN EUK not formylated
***AA attacched to carbonxyl end via peptidyltransferase
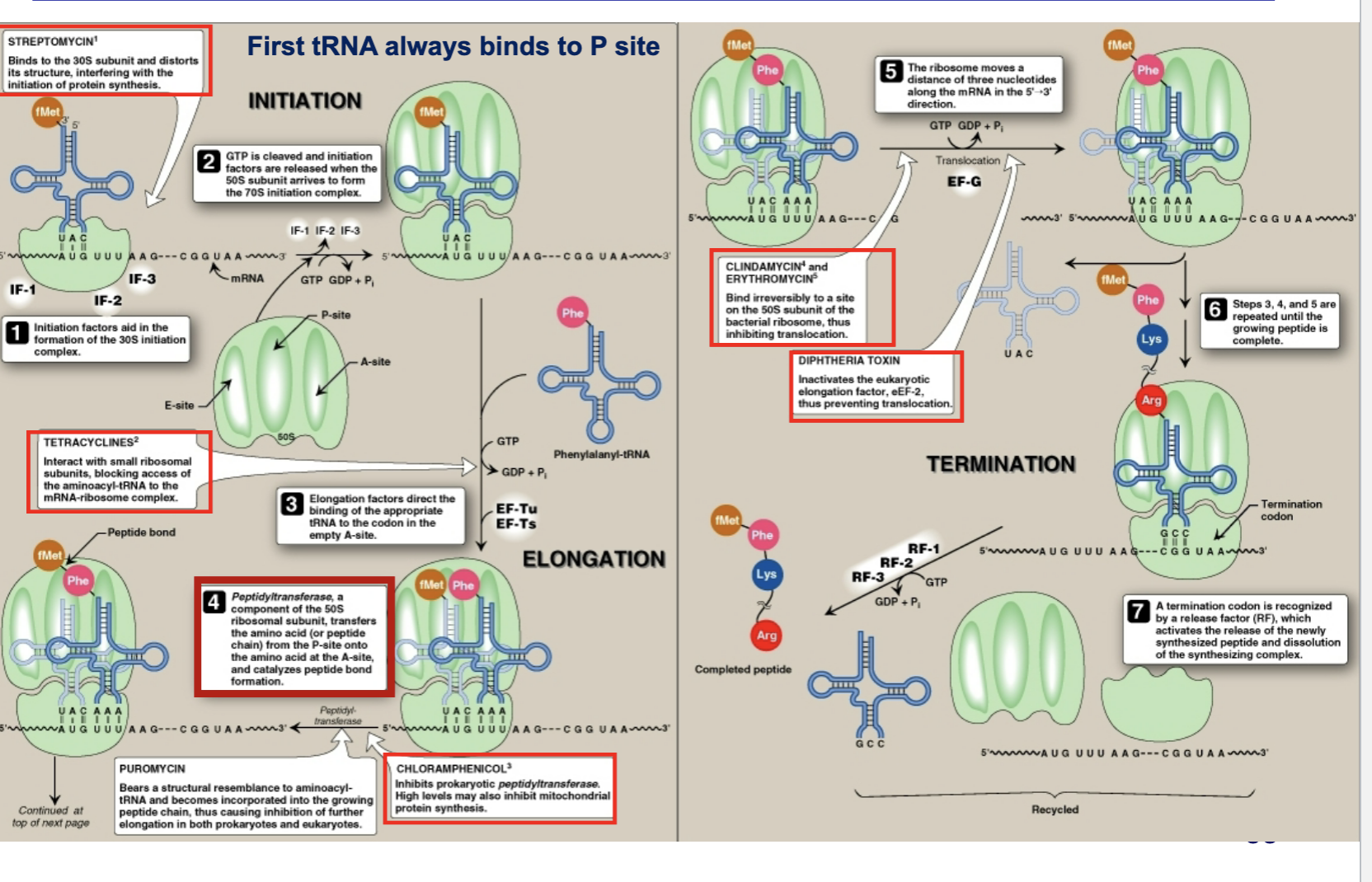
What are some medications that take use of the translation system and where do they act? Ex clindamycin, diphtheria toxin. tetracycline
What happens when we do a shitty job and need to degrade our misfolded proteins?
Misfolded proteins labeled for degradation by polyubiq
Polyubiq proteins degraded by 26S proteosome
What assists in folding these newly synthesized proteins? What do they do and what family are these apart of?
Chaperones - HSP60 or 70 family, disulfide bonds cat via protein disulfide isomerase (PDI)
Describe termination of translation?
Moves until a termination codon goes into the A site
Release factor binds to A site —>triggers hydrolyses of teh bond bertweenpeptide and tRNA by a peptidyltransferase —>released from ribosome—>ribosome dissoasited into subunits
What are some regulation of translation
regulatory proteins - either stabalize or prevent binding
rare codons - fewer tRNA, slow down, translation, usually at the beg of mRNA
Small interfering RNA
AHAH somes has been exposed to streptomycin, what subunit does this affect and what are the effects?
AHAH somes has been exposed to tetracycline, what subunit does this affect and what are the effects?
AHAH somes has been exposed to chloramphenicol, what subunit does this affect and what are the effects?
AHAH somes has been exposed to ricin, what subunit does this affect and what are the effects?