Lab 10: Retention (Clasps) and Support (Rests) - For removable dentures
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is a major and minor connector (for RPDs)?
Major connector
Main body of a denture which provides rigidity and unites all the denture parts
Minor connector
Connects all other parts of the denture to the major connector
Define: Direct retainer parts
Direct retainer
Parts of a denture that prevents it from dropping out of the mouth. Clasps are often used as a direct retainer
Define: Reciprocation/Bracing
Reciprocation/Bracing
Retentive factors preventing the denture moving horizontally
Define: Indirect retainer
Indirect retainer
Part of the denture preventing it rocking or sifting sideways or rotating during eating and talking e.g. Rests, connectors and acrylic
They prevent lever action of the fulcrum point
Define: Support (RPDs)
Support/ Rests in RPDs
Prevents the denture from sinking towards the soft tissues
Rest is a small projection of metal from the main frame
What is a reciprocating arm?
Reciprocating arm is something to provide opposite pressure from the clasp
Support on RPDs normally uses teeth as rests. However on edentulous you use mucosal support, what can this result in?
Mucosal support normally results faster resorption rate of the ridge
Tooth support in RPDs is often advised to share across 2 teeth or more, why?
To share the load between two teeth
What are the 4 main functions of the rests?
Rest functions
Transmit axial loads to natgural teeth (vertical)
Deflect food away (rounded)
Indirect retainer and support for major connector (limits soft tissues)
Main clasp-to-tooth relationship
What are the design criteria for a rest?
Rest criteria for design
Rigid
Don’t interfere with occlusion
Rounded to permit movement in function
Angle of less that 90o with minor connector (transmit vertical load to long axis)
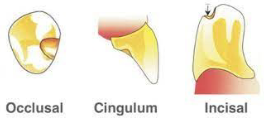
What are the 3 types of rest design (placement)?
Occlusal rest
Cingulum rest
Incisal rest
What are the keys to a successful Retention/Clasps selection?
Select a direct retainer that will control tipping and torquing forces to prevent dislodging
What are the materials used for clasps?
Chrome cobalt (0.25mm)
Gold (0.5mm)
Stainless steel wire (0.75mm)
Tooth colour resins
Flexible denture base
What is the gold standard material for RPDs clasps?
RPDs gold standard is Cast chrome cobalt
Good tensile strength, durability and accuracy
Either Occlusally or gingivally approaching
What are the reasons you would use stainless steel wires for clasps?
Stainless steel wire is used because
It’s the easiest and cheapest material to use
Well tolerated
Not aesthetically great
What are the reasons you would use Gold wires for clasps?
Gold clasps
Well tolerated and some like the aesthetic
Costly
What are the mm distances for flexible dentures and why there’s a safety issue?
Flexible dentures are Nylon based (Monomer free)
Major connector thickness: 1.5mm (allows flexibility)
Flexible clasps are 1mm above gingival necks
These clasps are close to the tissues and therefore a sharp safety risk
What is known about tooth shaded materials for claps?
Aesthetics meet patients demands
Scarce information on staining an stability
Other than clasps what are other forms of gaining retention?
Adhesion (e.g Fixident) / Cohesion (attraction between molecules and surfaces
Capillary attraction (space between denture and basal tissues)
Fluid viscosity
Post dam