LIFE 102 EXAM 2
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
The “fluid mosaic” model of the cell membrane proposes that membranes
Consiste of protein molecules embedded in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids
The movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration is called
Diffusion
Which of the following most accurately describes selective permeability?
Only certain molecules can pass through the cell membrane
The part of a membrane protein that extends through the phospholipid bilayer is primarily composed of amino acids that are
Non-polar
Certain molecules/atoms can diffuse directly through the phospholipid bilayer of a membrane (without the help of a transport protein). Which of the following types of molecules will diffuse most-easily directly through a membrane?
Small and hydrophobic
A scientist performs an experiment in which they create an artificial cell with a selectively permeable membrane through which only water can pass. They next a 5M solution of glucose into the cell and then place te cell into a beaker containing 10M glucose. What effect do you expect to observe?
Water moves out of the cell
A dehydrated runner drinks a lot of water after a race. They rehydrate because
The bloodstream is hypotonic compared to the stomach
A type of transport of a solute across a membrane, up its concentration gradient, using protein carriers driven by the expenditure of chemical energy is known as
Active transport
Which of the following processes includes all the others?
Passive transport
Ions diffuse across membranes through specific ion channels down
Their electrochemical gradients
Metabolic reaction fall under two general categories: anabolic and catabolic. What type of chemical reactions are these two classes of metabolic reactions?
Anabolic reactions are endergonic reactions, whereas catabolic reactions are exergonic
Why do we have storage macromolecules, such as fats, in our bodies?
We can break down these macromolecules to provide energy for the endergonic reactions in our bodies
You eat a bowl of beans as part of your dinner. As you digest the beans, the proteins that are present get broken to their component amino acids. As your body destroys the macromolecules that were present in the beans, is the energy present in those molecules destroyed?
No. The energy contained within these macromolecules is converted into other forms of chemical energy and kinetic energy, though some is lost as heat.
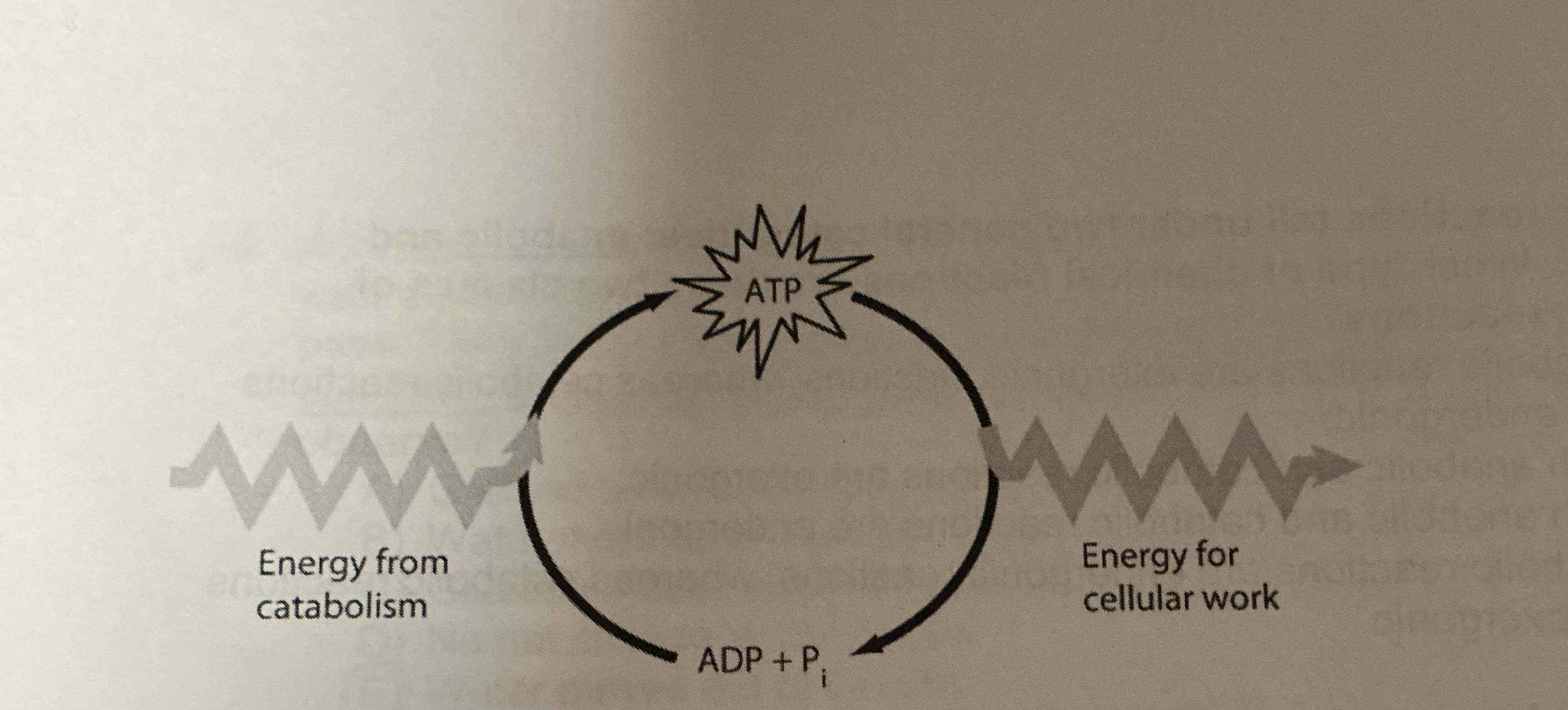
Which of the following is the most correct interpretation of the figure shown above?
ATP is a molecule that acts as an intermediary to store energy for cellular work
Which of the following is not true of enzymes?
Enzymes provide extra activation energy for the reaction they catalyze
The energy needed to destabilize existing chemical bonds and start a chemical reaction is called
Activation energy
The lock and key analogy for enzymes applies to the specificity of enzymes
Binding to their substrate

Based on the graph, what are the optimal temperatures for the human enzyme and hot springs prokaryote enzyme?
The optimal temperature for the human enzyme is 40 degrees C. The optimal temperature for the hot springs prokaryote enzyme is 72 degrees C.
How does a non-competitive inhibitor decrease the rate of an enzyme reaction?
By changing the shape of the enzyme’s active site

Characterize this reaction: (picture)
Catabolic; G<0; Exergonic; NADH intermediate; ATP is produced
In animals that take in oxygen from their environment, glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water in a process called
Aerobic respiration

Which of the listed statements describes the results of the reaction shown below?
C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced
Your friend is having difficulty keeping track of the energy flow from glucose through glycolysis, the Krebs cycle and electron transport. Your best advice would be to
Follow the electrons
In glycolysis, a major portion of the energy remains in the final product, which is called
Pyruvate
All of the reactions of cellular respiration that occur after glycolysis take place in what part of the eukaryotic cell?
The mitochondria
As electrons move along the electron transport chain, they lose potential energy. How is the energy that is released used by the cell?
The energy is used to transport H+ ions against their concentration gradient
What happens to the oxygen that is used in aerobic respiration?
It is reduced to form water
During aerobic respiration, electrons travel “downhill” in which sequence?
Glucose- NADH - Electron transport chain - Oxygen
The oxygen (O2) consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
Accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
High levels of ATP inhibit the enzyme phosphofructokinase (a key enzyme in glycolysis). As a result, glycolysis slows down, and lower amounts of ATP are produced. This is an example of
Feedback inhibition
The synthesis of sugar molecules through the process of photosynthesis required energy absorbed from sunlight. bearing this in mind, what kind of reaction is photosynthesis?
Endergonic
Most atmospheric oxygen comes from photosynthesis. From which of the following molecules is the oxygen derived
Water
Where do the carbon atoms in glucose come from
Carbon dioxide
The Calvin cycle of a plant exposed to light during the day that is suddenly put in the dark
Can still run as long as there is ATP, CO2, and NADPH present
What color of light is not strongly absorbed by chlorophyll
Green
What is a photosystem?
A cluster of pigments and proteins that work together to capture light energy
In the thylakoid membranes, what is the main role of the pigment molecules in the light harvesting complexes?
Absorb photons and transfer light energy to the reaction-center chlorophylls
NADPH is made by
The passing of electrons from photosystem I to an electron transport chain
Photosynthetic reactions that require the input of CO2 occur in
The Calvin cycle alone