1 Cell Theory
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Define Cell
The smallest, basic membrane bound unit of life, responsible for all of life's processes.
for a cell to continue living it requires:
1. metabolic machinery to obtain energy from the environment
2. ability to use this energy
3. a set of genes to control synthesis of cell components
4. cell membrane
what are the 2 types of cells?
prokaryotic: bacteria
eukaryotic: animal, plant, fungi
what are the main components a virus consists of?
DNA/RNA
capsid (protein coat)
some have a lipid envelope
define Bacteriophage
a type of virus that infects bacteria.
bacteriophage = 'bacteria eater'
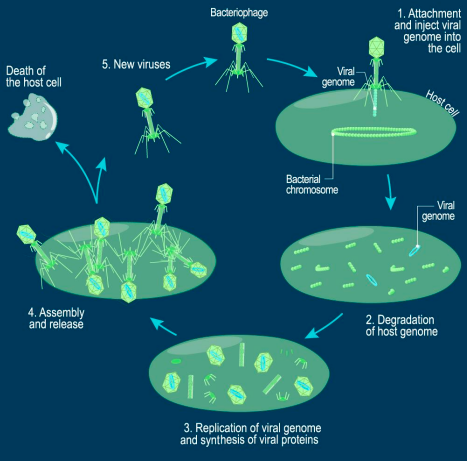
how does a bacteriophage infect a host cell?
bacteriophage attaches & injects viral genome into cell
breakdown of host genome
viral genome replicated & synthesis of viral proteins
assembly & release
define genome
the complete set of genes in a cell
why are viruses not considered living?
they are acellular (not made up of cells) & can only replicate by using the biochemical machinery of a host cell
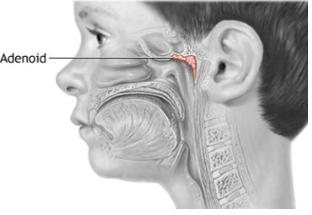
define adenovirus
group of DNA viruses discovered in adenoid tissue (found between the back of the nose & throat).
what illnesses to adenoviruses cause?
adenoviruses cause a wide range of illnesses:
cold or flu like symptoms
fever
sore throat
bronchitis
pneumonia.
how can adenoviruses be transmitted?
in droplets or secretions
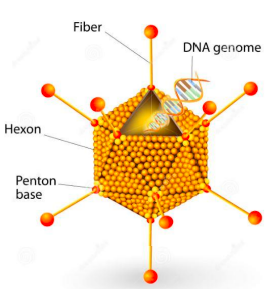
describe the shape of adenoviruses
medium sized with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing double-stranded DNA.
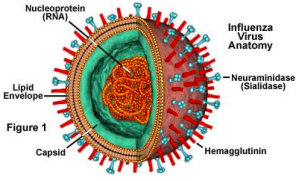
describe the shape of influenza virus
spherical shape
2 glycoproteins: hemagglutinin (HA) & neuraminidase (NA)
why is a new flu vaccine required each year?
Due to antigenic drift. mutations occur in the HA & NA antigens, causing them to change in shape so that theyre no longer recognised by the immune system.
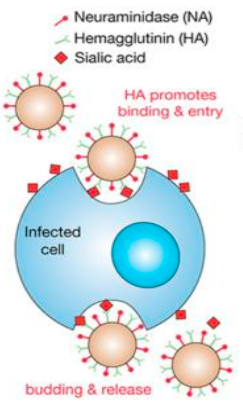
How does influenza virus affect a cell?
Influenza virus binds to _____ ___ _________ through its surface glycoprotein _____________ (HA).
Endocytosis (ingestion & uptake of macromolecules in small vesicles) of the virus occurs.
Vesicle fuses with a lysosome (organelle containing digestive enzymes).
Acidity breaks down coating of the virus, HA structurally changes & is inserted into cell membrane.
Membrane fuses, RNA released into host cell.
Intracellular replication (virus replicates using host cell machinery)
Neuraminidase cleaves (seperates) sialic acid from cell membrane allowing viral escape.
sialic acid receptors
hemagglutinin (HA)
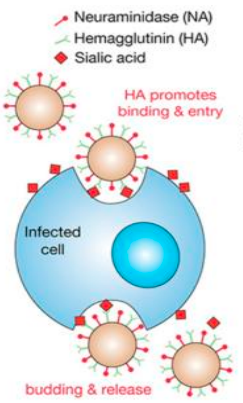
How does influenza virus affect a cell?
Influenza virus binds sialic acid receptors through its surface glycoprotein hemagglutinin (HA).
___________ (ingestion & uptake of macromolecules in small vesicles) of the virus occurs.
Vesicle fuses with a lysosome (organelle containing digestive enzymes).
Acidity breaks down coating of the virus, HA structurally changes & is inserted into cell membrane.
Membrane fuses, RNA released into host cell.
Intracellular replication (virus replicates using host cell machinery.
Neuraminidase (NA) cleaves (seperates) sialic acid from cell membrane allowing viral escape.
endocytosis
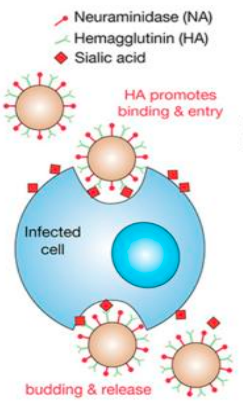
How does influenza virus affect a cell?
Influenza virus binds sialic acid receptors through its surface glycoprotein hemagglutinin (HA).
endocytosis (ingestion & uptake of macromolecules in small vesicles) of the virus occurs.
Vesicle fuses with a lysosome (organelle containing digestive enzymes).
Acidity breaks down coating of the virus, HA structurally changes & is inserted into cell membrane.
Membrane fuses, ___ released into host cell.
Intracellular replication (virus replicates using host cell machinery)
Neuraminidase (NA) cleaves (seperates) sialic acid from cell membrane allowing viral escape.
RNA
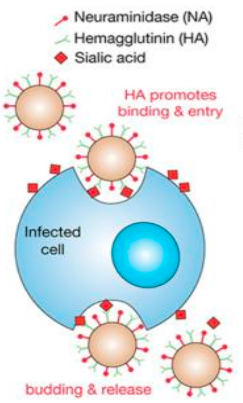
How does influenza virus affect a cell?
Influenza virus binds sialic acid receptors through its surface glycoprotein hemagglutinin (HA).
endocytosis (ingestion & uptake of macromolecules in small vesicles) of the virus occurs.
Vesicle fuses with a lysosome (organelle containing digestive enzymes).
Acidity breaks down coating of the virus, HA structurally changes & is inserted into cell membrane.
Membrane fuses, RNA released into host cell.
Intracellular replication (virus replicates using host cell machinery)
_____________ cleaves (seperates) sialic acid from cell membrane allowing viral escape.
Neuraminidase (NA)
what are antiviral drugs?
Drugs that inhibit or disable viral proteins that are part of the cell entry mechanism or the viral replication and release process.