Hip and Thigh Disorders
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
MVA, ring, avulsion
Pelvic Fratures: Background
-Can be life threatening
-Anatomy
Sacrum, coccyx, ilium, ischium, pubis
Contains viscera, extensive vascular system, and neural network
-Mechanism of Injury
___, falls
-Types
____ disruptions (“open book” fracture)
Sacral fractures
Acetabular fractures
_________ fractures → more common in younger athletes
stabilize, bleeding, urethra, rectal/vaginal, compression, CT
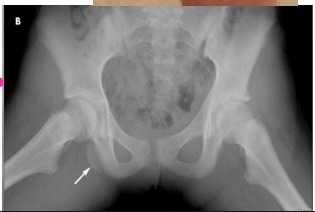
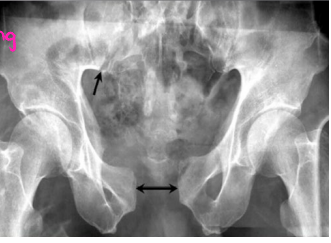
Pelvic Fractures: Physical Exam and Diagnosis
-PE
______ first!
Look for → external ________, ecchymosis, blood at _______, vaginal/rectal bleeding, position of LE and iliac crest
Full ______/_________ exam to look for blood and bruising
____________ of pelvic to check for instability
-Diagnosis
X-ray is the textbook initial test, while __ is the essential test for diagnosis
Possibly vascular and/or urologic imaging
wrapping, hemorrhage, gluteal, iliac, bladder
Pelvic Fractures: Treatment and Complications
-Treatment
Pelvic ___________ to reduce the amount of blood loss and stabilize bone fragments
Definitive treatment depends on fracture type
-Complications
_______________ → veins or superior _______/internal pudendal/internal ______ arteries
Neurologic injury → do thorough lower body neuro exam
Urogenital injury → _______, urethra, vagina, and rectum
intracapsular, intertrochanteric, elderly, trauma
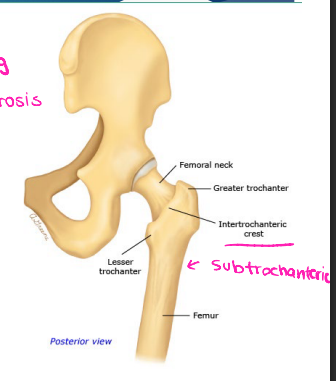
Hip Fractures: Background
-Fracture Classification
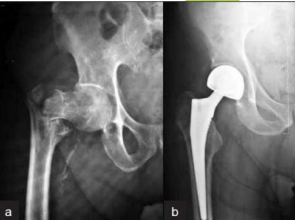
_______________ → femoral head or neck. Higher rate of nonunion and avascular necrosis. Rarely presents with swelling or bruising.
Extracapsular → _______________ (between the trochanters) and subtrochanteric
-Mechanism of Injury
Fall in _______ is the most common, while ______ in younger patients is another potential cause
pain, internal rotation, refuse, shortened, externally, MRI
Hip Fractures: Symptoms and Diagnosis
-S/S
____ in hip and groin
Pain with ROM (especially ________ _________)
______ to bear weight. Individuals with osteoporosis may still be able to bear weight
Leg ____________ and __________ rotated, if the bone is displaced
± swelling and ecchymosis
-Diagnosis
X-ray
___ is the preferred imaging modality. Bone scans or CT are also options for occult fractures
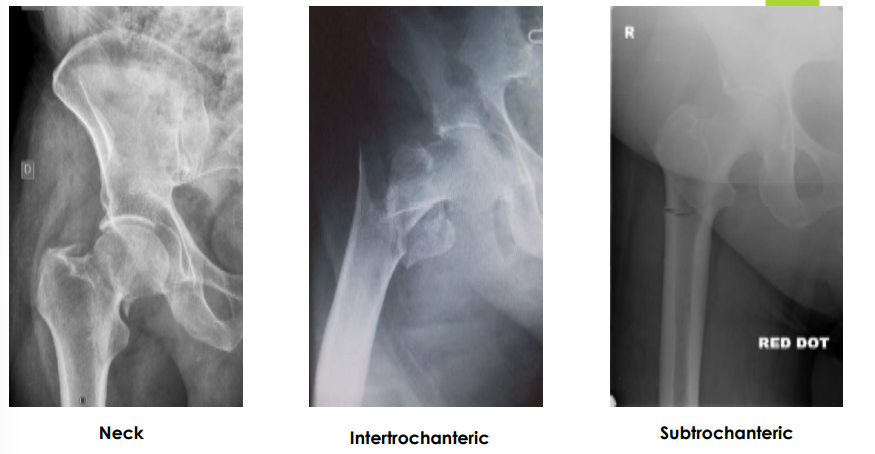
pain, ortho, arthroplasty, stress, non-weight
Hip Fractures: Treatment
-____ control → do this first
-_____ referral/consult (immediately)
-ORIF or ______________ for most hip fractures
_____ fractures may be treated with ___-______ bearing
Most neck fractures need screw fixation or a joint replacement
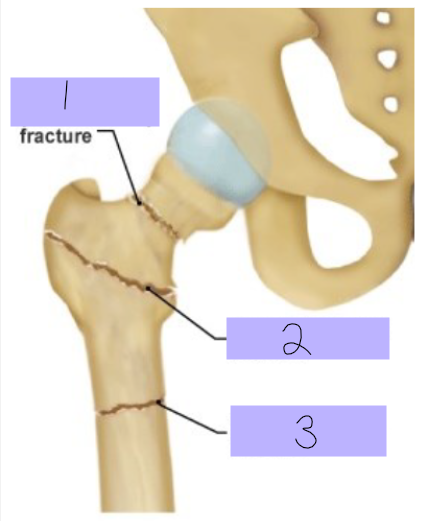
Intracapsular fracture
#1
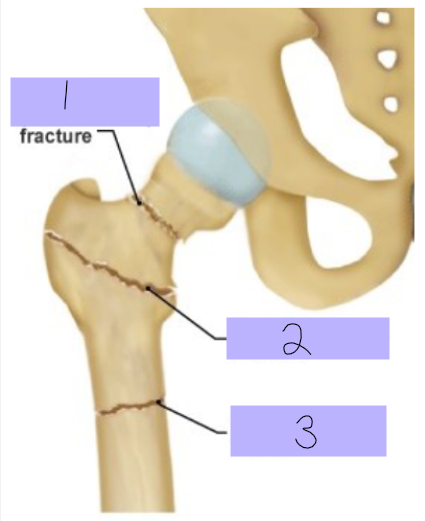
Intertrochanteric fracture
#2
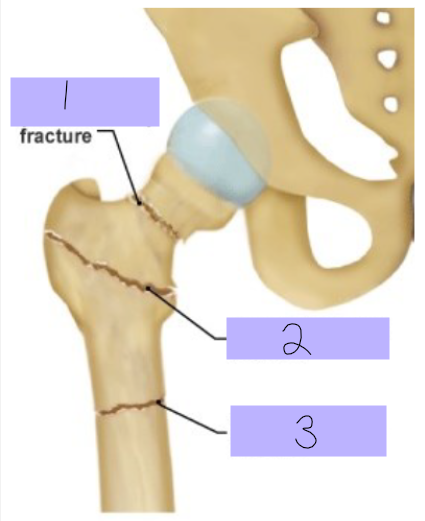
Subtrochanteric fracture
#3
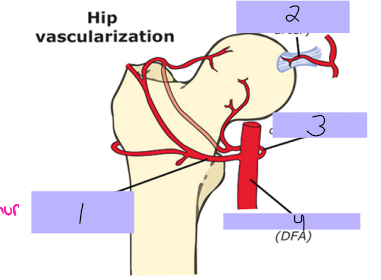
Lateral femoral circumflex artery
#1
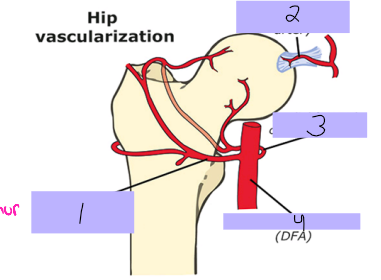
Round ligament artery
#2
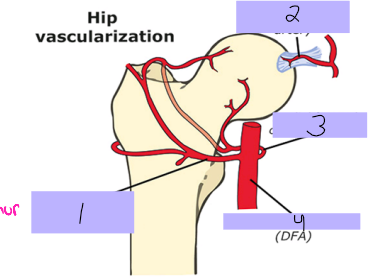
Medial femoral circumflex artery
#3
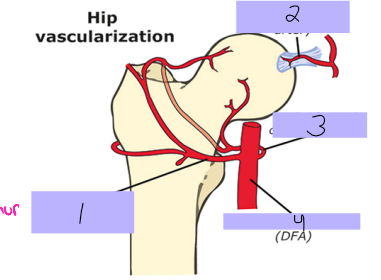
Deep femoral artery
#4
fractures, alcohol, sickle cell, disruption, ischemia, death
Avascular Necrosis (Aseptic Necrosis): Background
-Risk Factors
Trauma → __________ (femoral neck, scaphoid), dislocations (hip)
__________ use
Glucocorticoid use
_______ _____ disease
-Pathogenesis (trauma)
___________ of blood supply → _________ → ______ of bone and marrow cells
dull, groin, antalgic, decreased, xray, crescent, ortho
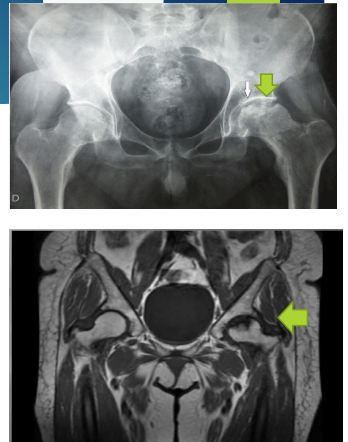
AVN: S/S, Diagnosis, and Treatment
-S/S
____, aching, ______ pain
Pain with weight bearing = _______ gait
Pain with hip ROM = ____________ ROM
-Diagnosis
_____ is the initial imaging of choice (mild density changes → sclerosis/cysts)
MRI → ________ sign
-Treatment
Refer to ______
energy, MVA, fall, sports, pain, shortening, bleeding
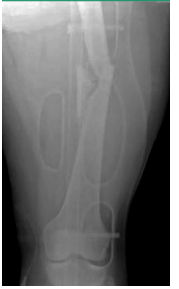
Femur Shaft Fracture: Background
-Mechanism of Injury
High _______ force → ___, being struck by car, fall from height, gunshot wound
Low energy force → ____ from stumbling or low height, ________
-S/S
____, swelling, deformity
____________ of thigh
Soft tissue injury and _________
-Diagnosis
X-ray → get other views to rule out other fractures
stabilization, tetanus, infection, nonunion, hemorrhage, compartment, fat emboli
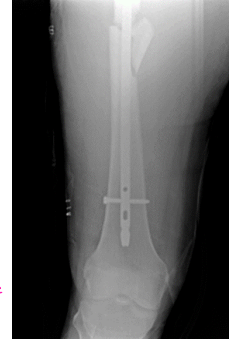
Femur Shaft Fracture: Treatment and Complications
-Treatment
Initial → __________ if unstable, pain control, immobilization
If open fracture, add antibiotics and ________ prophylaxis
Ortho consult
-Complications
___________, malunion, delayed union, __________, pain d/t ortho hardware
_____________, neurovascular injury, __________ syndrome, hardware failure, PE (DVT, ___ _______)
posterior, flexed, external, extended, acetabulum, knee
Hip Dislocation: Background
-Types
___________ is most common
Anterior
Inferior
-Mechanism of Injury
Posterior → significant force on ______ hip and knee
Anterior → forced ________ rotation of an __________ hip
-Commonly associated with fractures of the __________, femur, or ____
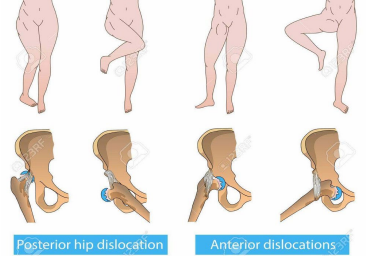
severe, decreased, shortened, internally, adducted, abducted, externally, CT/MRI
Hip Dislocation: S/S and Diagnosis
-S/S
_______ hip pain and __________ ROM
Posterior → _________, ________ rotated, ___________, flexed extremity
Anterior → ___________, _________ rotated, slightly flexed extremity
-Diagnosis
Xray is the initial imaging
__/___ are for definitive diagnosis
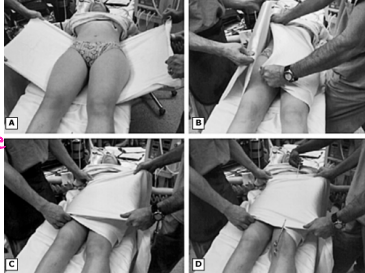
closed reduction, films, fracture, ortho, arthritis, femoral
Hip Dislocation
-Treatment
Immediate _______ ___________ with post-reduction _____
Be sure to rule out femoral __________ before attempting reduction
_____ consult
-Complications
__________ and AVN
Sciatic or ________ (anterior) nerve injury
gluteus, tendinopathy, female, scoliosis, repetitive, walking
Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome: Background
-________ medius or minimus _____________ with or without bursa involvement
-Risk Factors
_________, obesity, back/knee/foot pain, ___________, and leg length discrepancy
-Mechanism of Injury
__________ overload from ________, stair climbing, or running
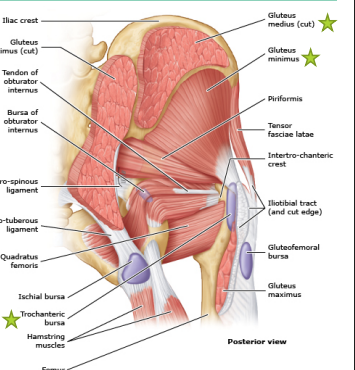
lateral, greater, activity, preserved, clinical, self limited, NSAIDs, PT
Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome: Treatment
-S/S
_______ hip pain
TTP over ________ trochanter
Pain increased with __________
ROM is ________
-Diagnosis
_______
Imaging is reserved for persistent sx or to r/o other conditions
-Treatment
Often ____ _________
Rest, ice, ________, stretching, __
Steroid injection
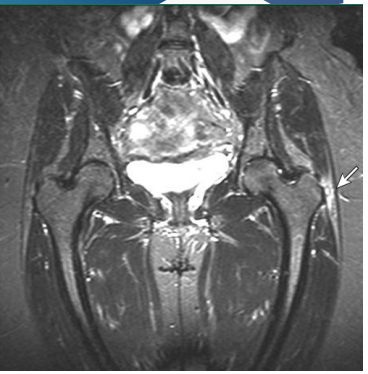
inflammation, viral infection, children, >, pain, absence, afebrile, aspiration, rest
Transient Hip Synovitis
-_____________ of the hip joint usually following a _____ __________ (URI/GI)
-Epidemiology
_________ (3-10 y/o)
M _ F
-S/S
Hip _____ in the __________ of injury/limited hip ROM
-Synovitis vs Septic Arthritis
WBC, ESR, CRP, usually normal; ________
MRI and/or synovial fluid __________ for definitive diagnosis
-Treatment
____ and NSAIDs, mostly self limiting
flex, extend, fatigue, instability, running, biceps femoris
Hamstring Strain: Background
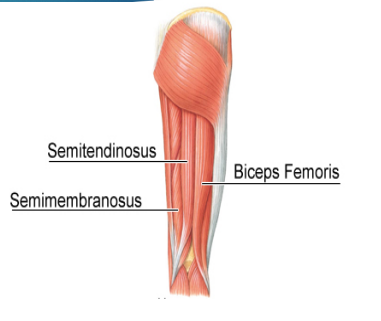
-Hamstrings
Biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus
____ knee and ______ hip; some internal/external rotation
-Risk Factors
Inadequate warm up, muscle _______, muscle weakness/________, poor biomechanics, and previous injury
-Mechanism of Injury
Most occur during high speed _________
_____ _______ is the most commonly injured
posterior, popping, straight leg raise, weakness, clinical, avulsion, compression, ortho
Hamstring Strain: S/S, Diagnosis, Treatment
-S/S
Sudden ___________ thigh pain
_______ sensation
TTP over hamstring
± swelling and ecchymosis
Pain with ________ ___ ______
± hip extension and knee flexion ___________
-Diagnosis
______, x-ray concerned for ________ fracture or US/MRI if concerned for tear
-Treatment
Rest, ice, _____________, NSAIDs, PT
_____ consult if there is a fracture or tear