BIO 233 Unit 7 (Set # 2) Lecture Exam Material
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
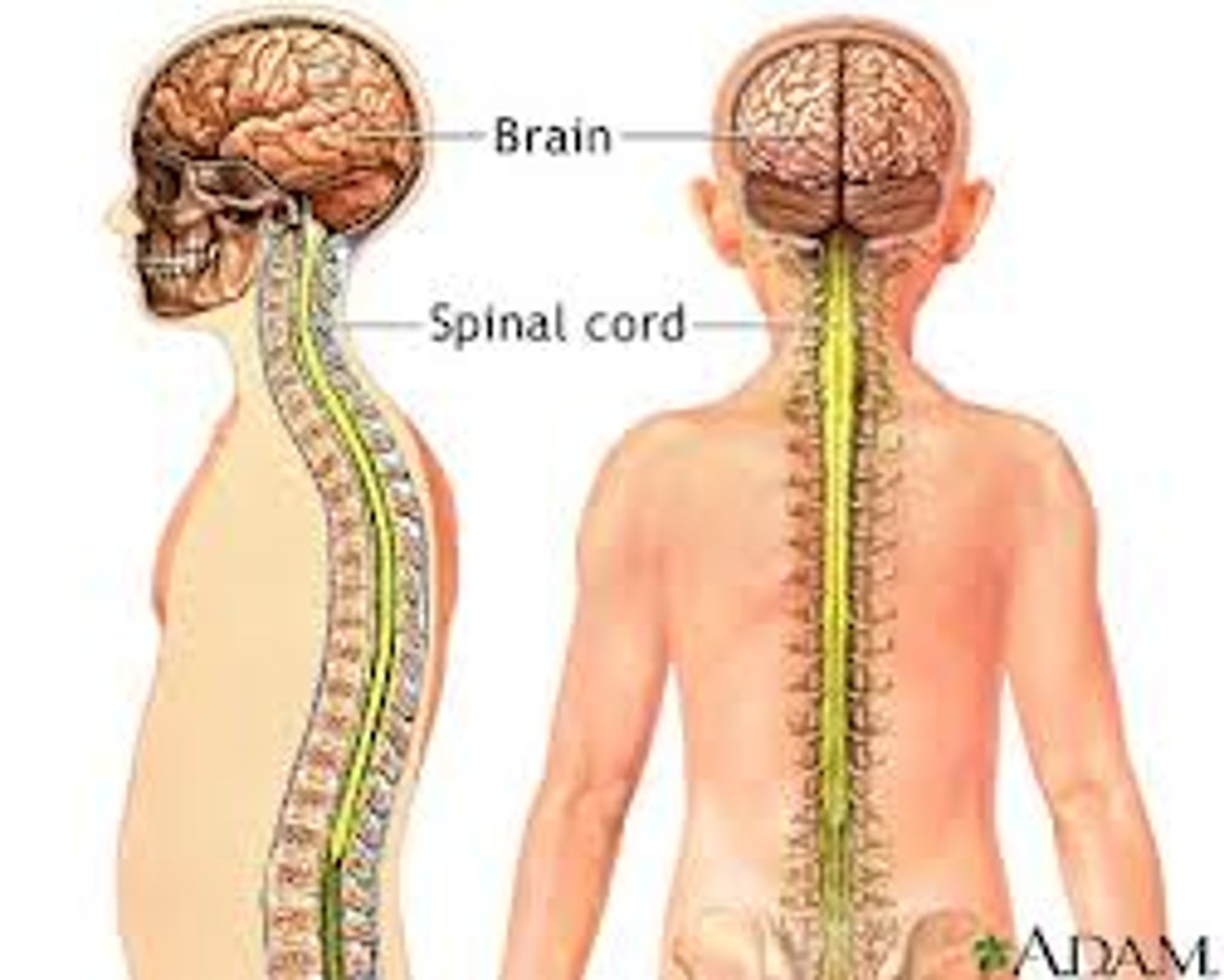
Central Nervous System (CNS)
consists of the brain and spinal cord
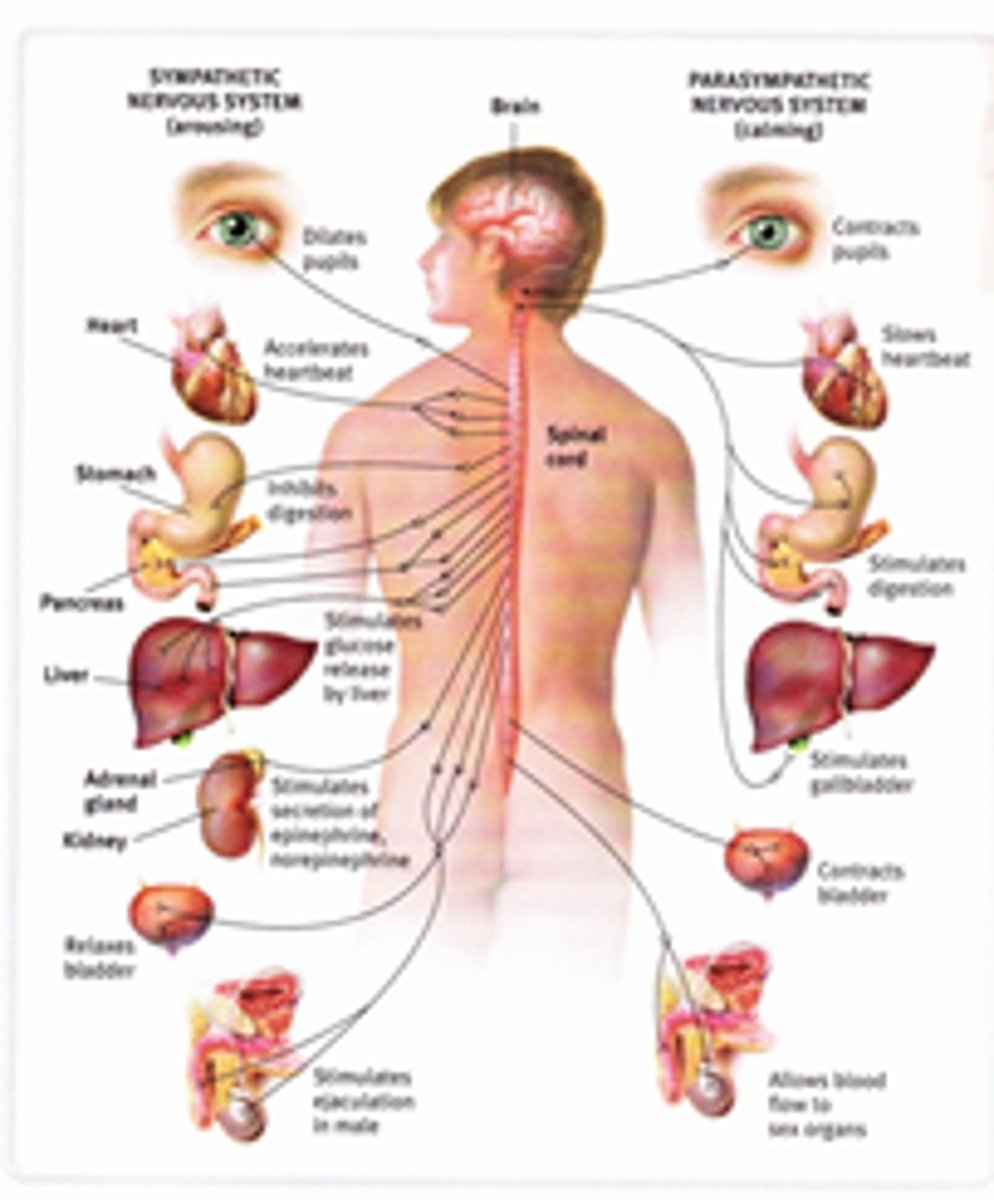
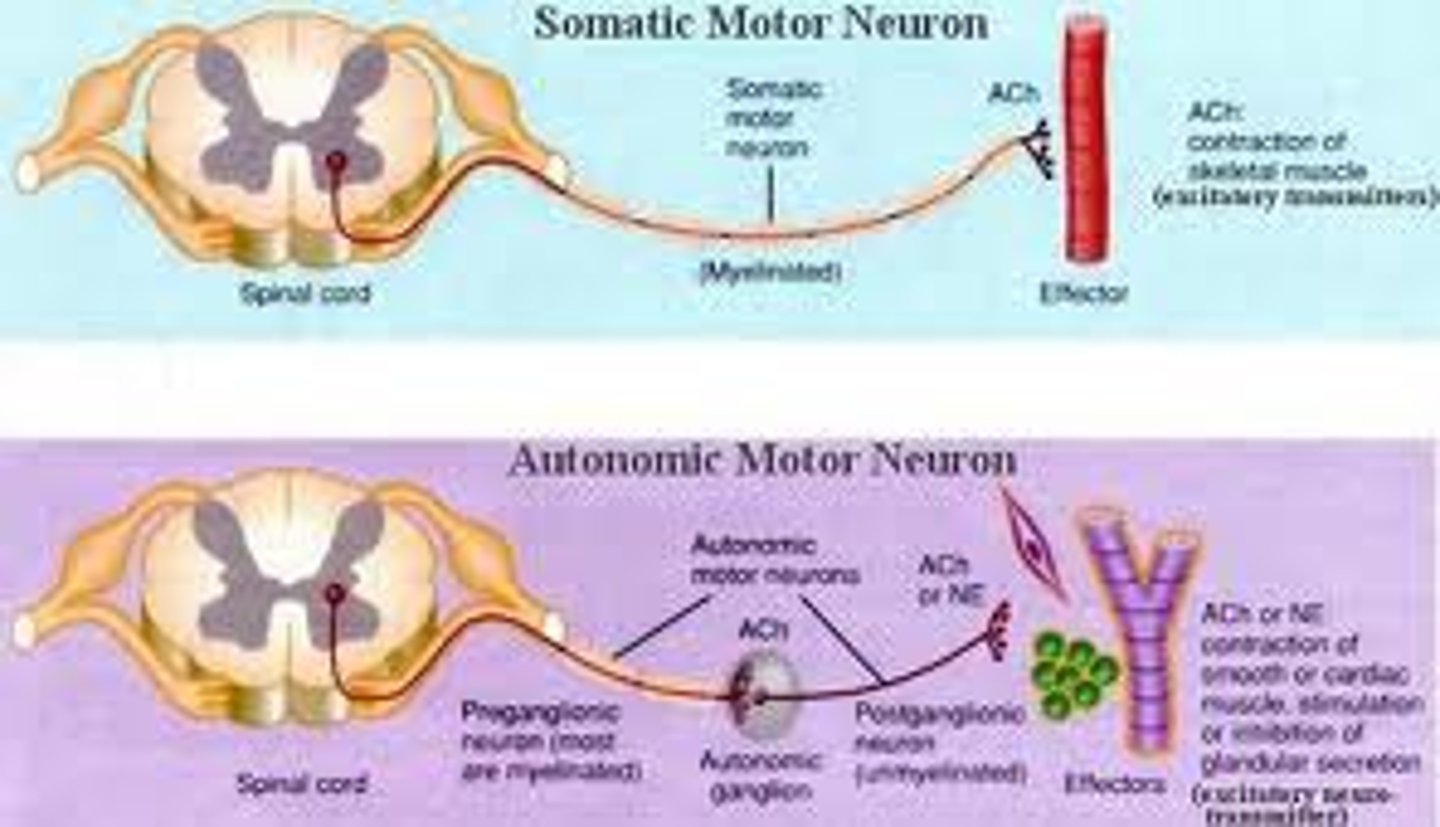
autonomic nervous system
Controls involuntary activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
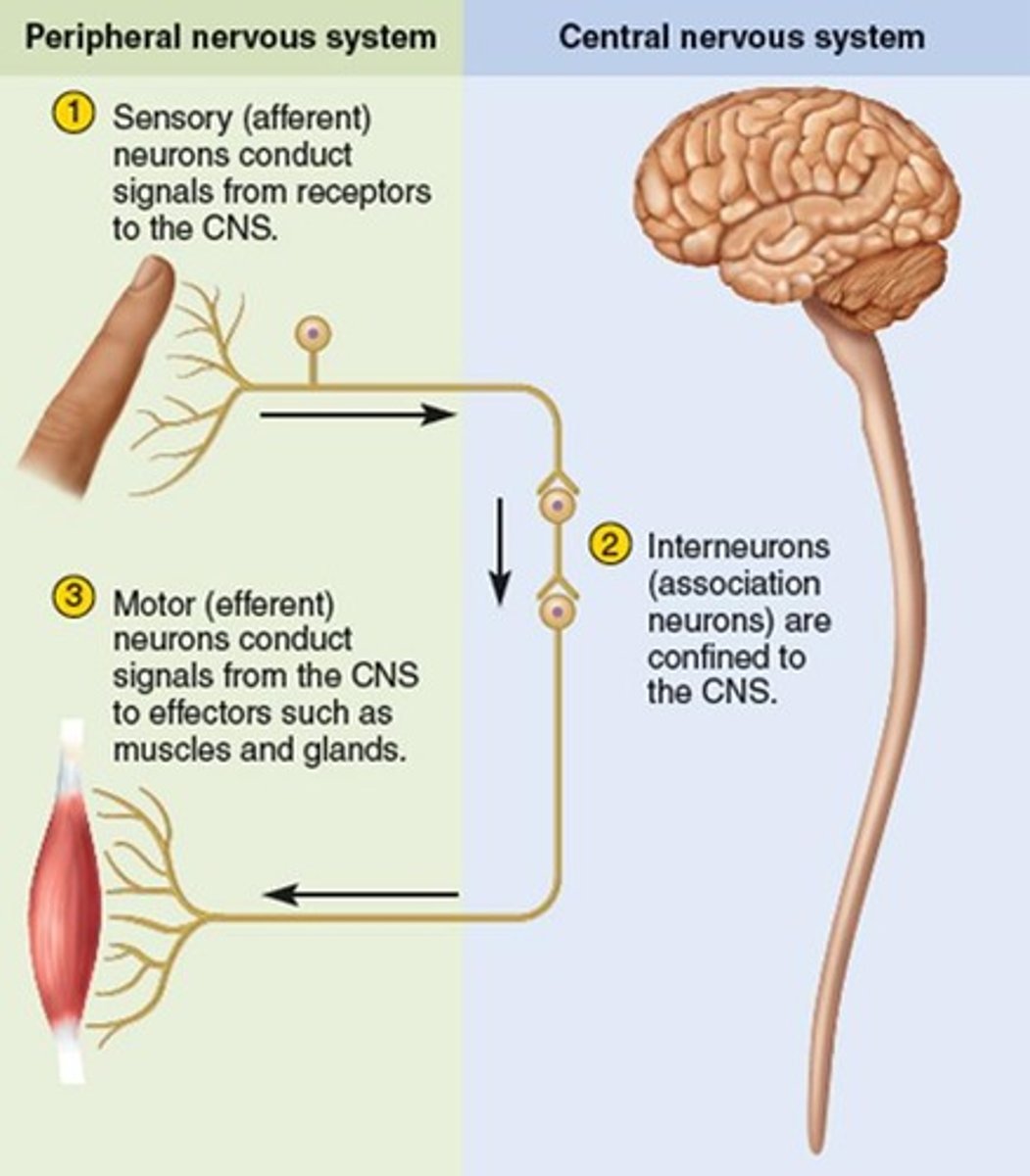
afferent neurons
carry sensory information to CNS
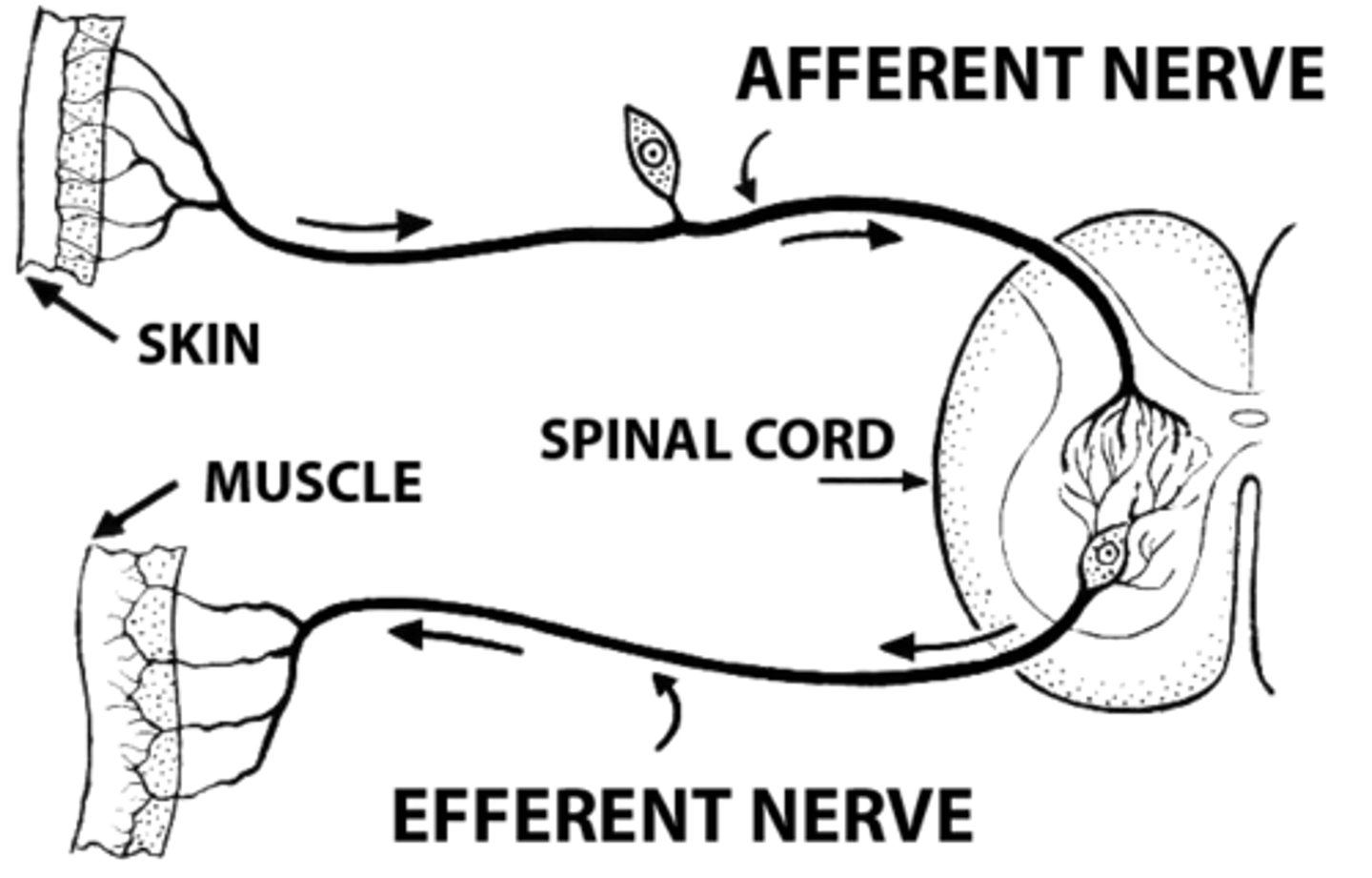
efferent neurons
Nerve cells that conduct impulses away from the central nervous system
Interneurons
these process sensory and motor impulses--only within brain and spinal cord (CNS)
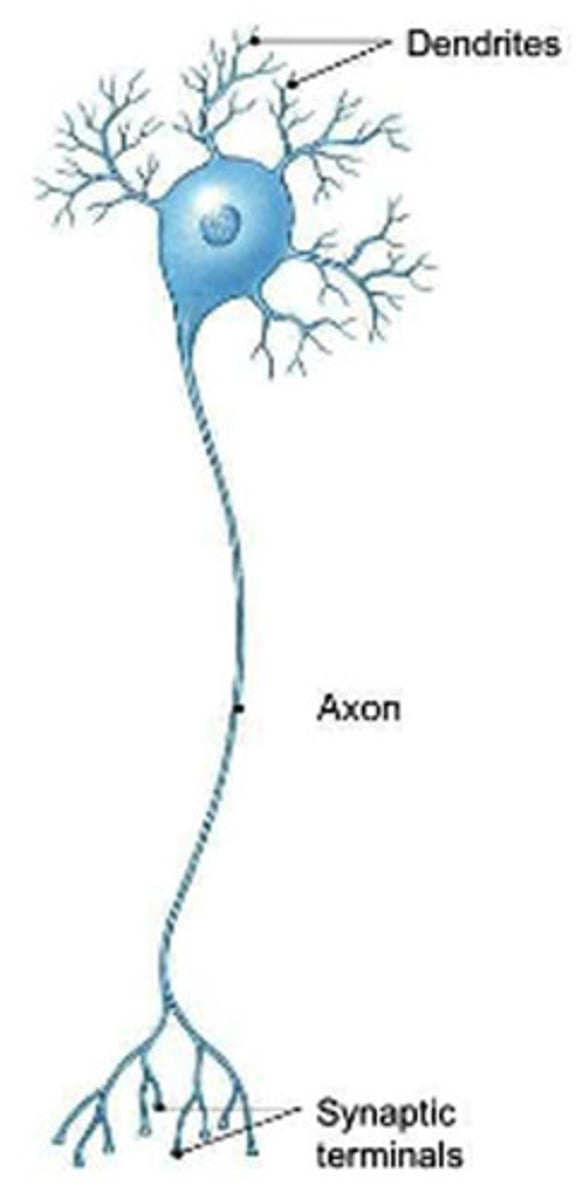
multipolar neuron
a nerve cell that has many dendrites and a single axon (most motor neurons and interneurons)
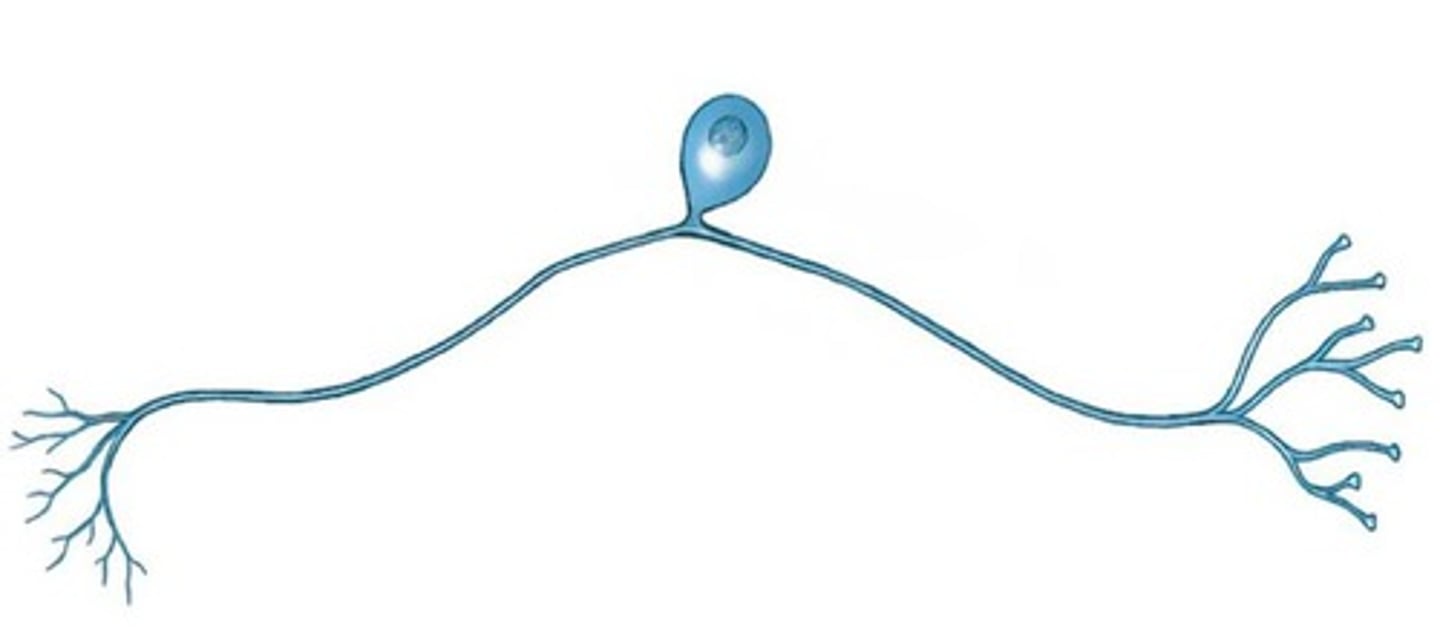
unipolar neuron
cell body located to side of axon--most afferent sensory neurons
Nissl bodies
Rough endoplasmic reticulum in neuron
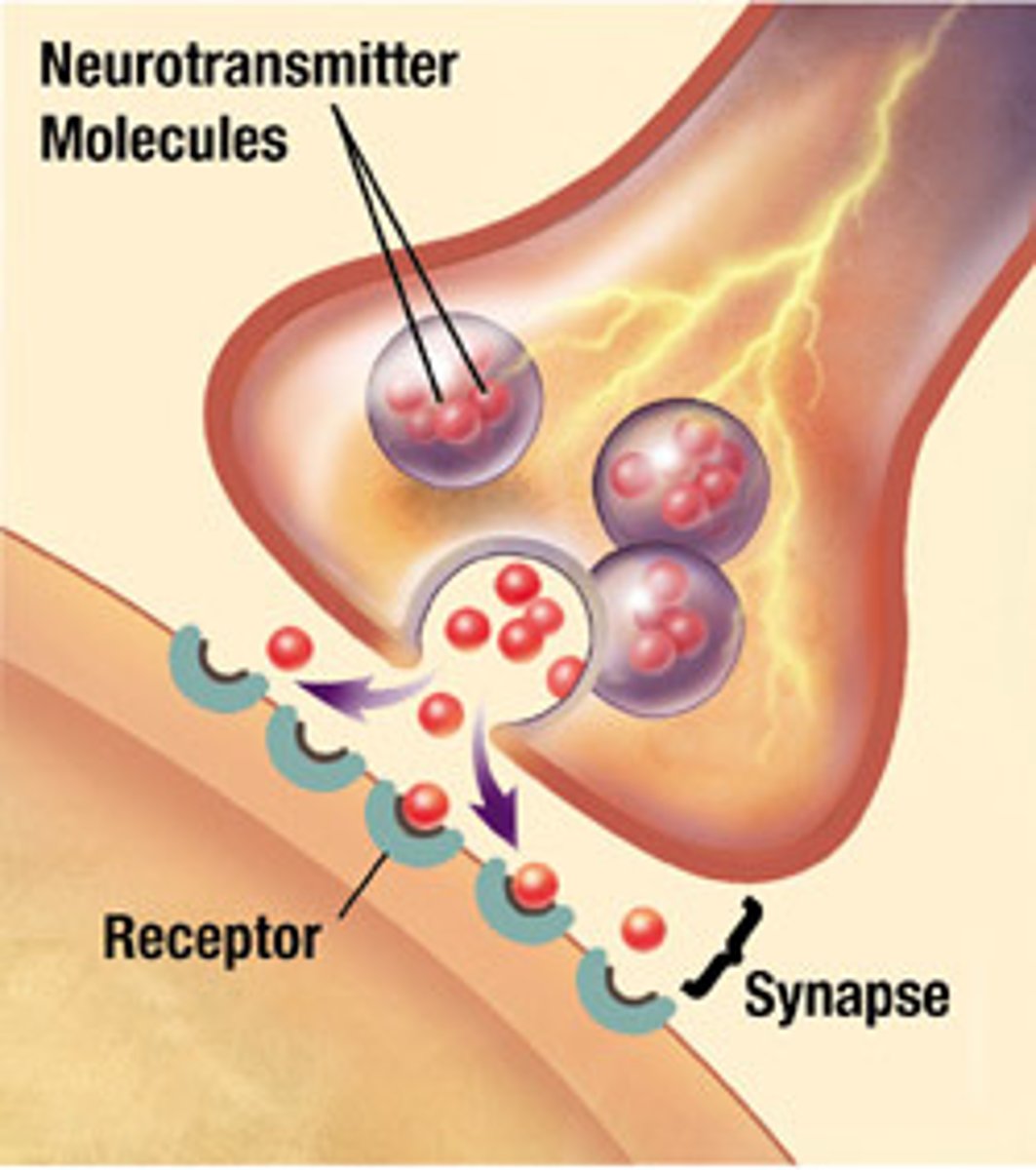
synapse
the site of intercellular communication between a neuron and another cell
Which type of neuron is most numerous in CNS?
Interneurons
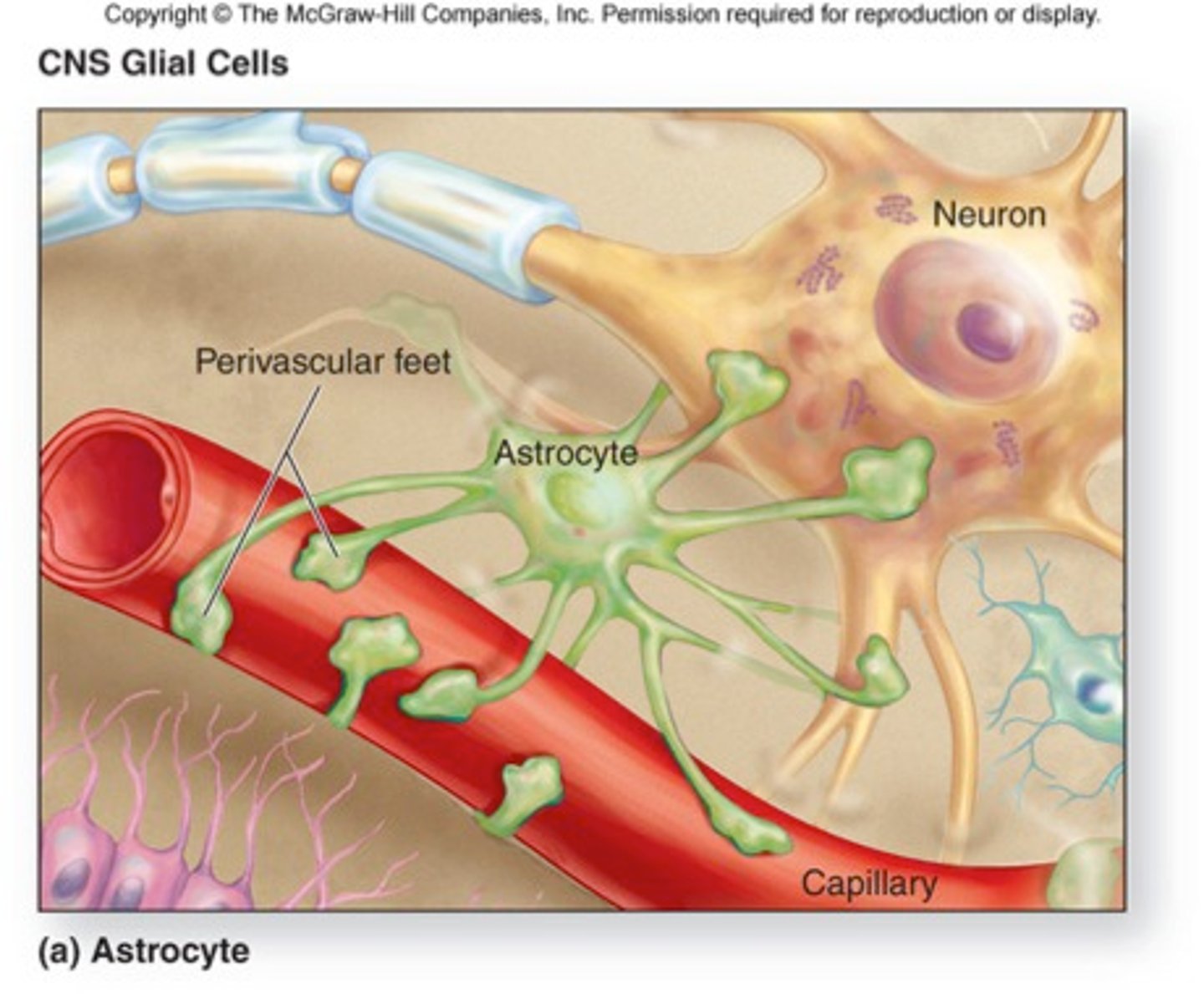
astrocytes
help form blood brain barrier
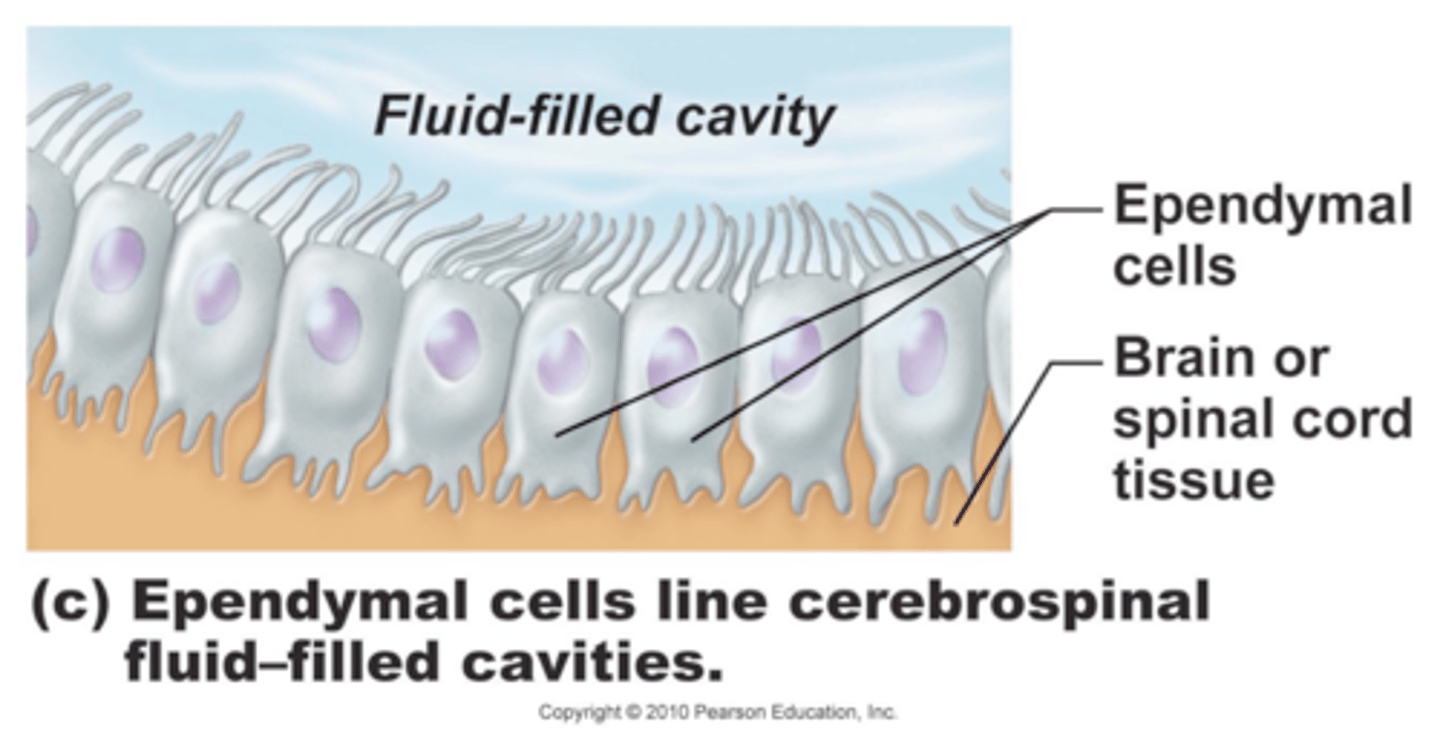
ependymal cells
line cavities of the brain and spinal cord, circulate cerebrospinal fluid
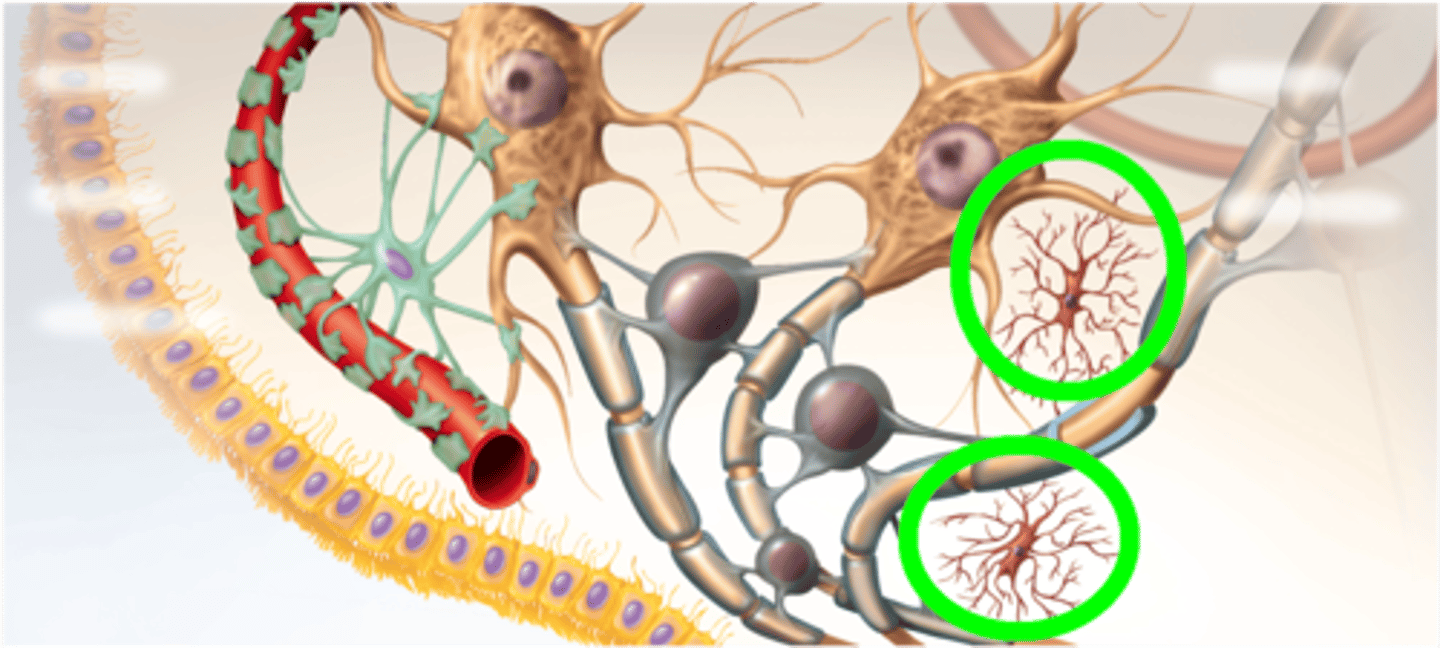
Microglia
Act as phagocytes, eating damaged cells and bacteria, act as the brains immune system
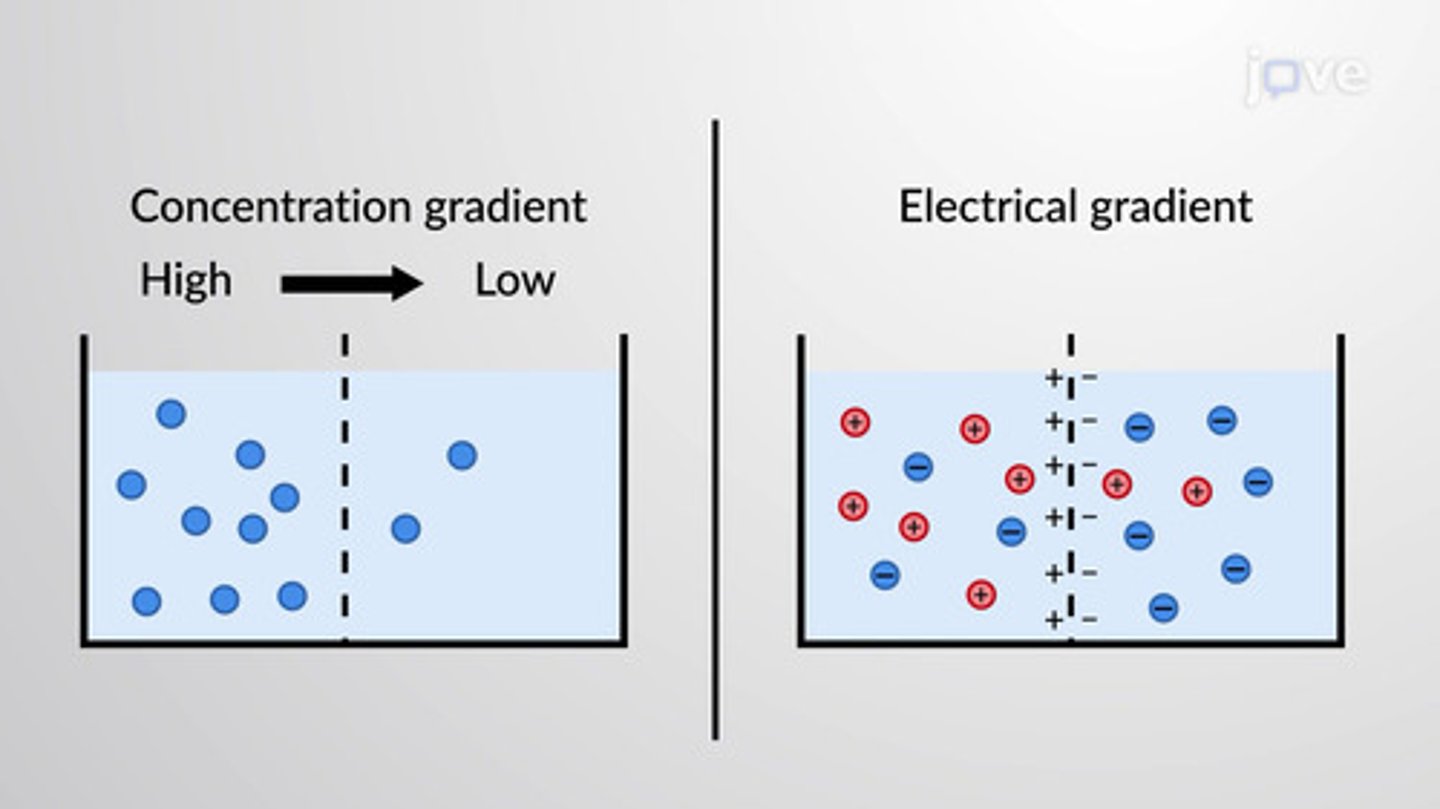
electrochemical gradient
The combination of forces that acts on membrane potential.
Voltage-gated sodium channels are located where on a neuron?
On the axon
Ligand -gated sodium channels are located where on a neuron?
On the dendrites
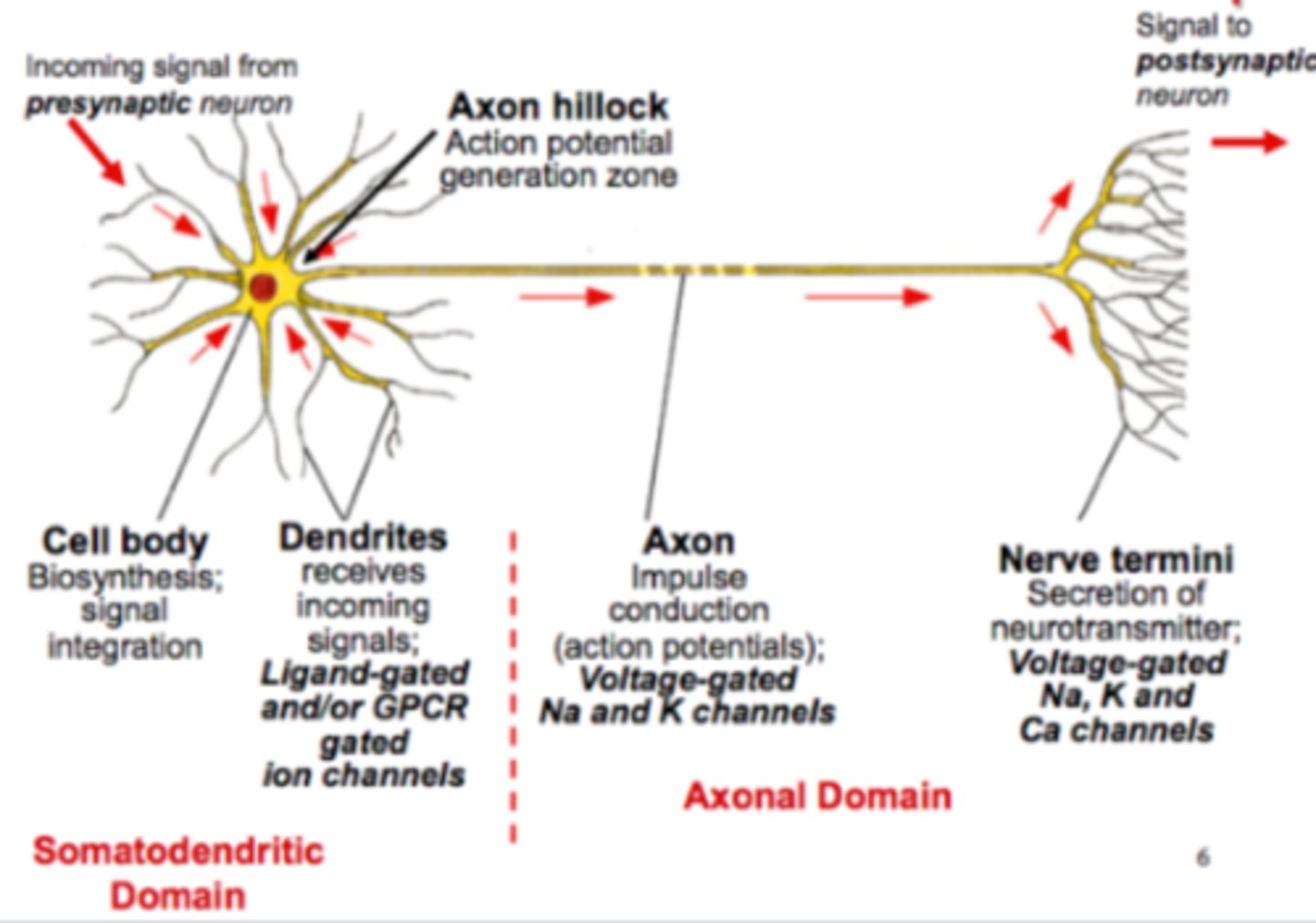
Ligand-gated channels on a neuron produce _________ potential/s.
graded
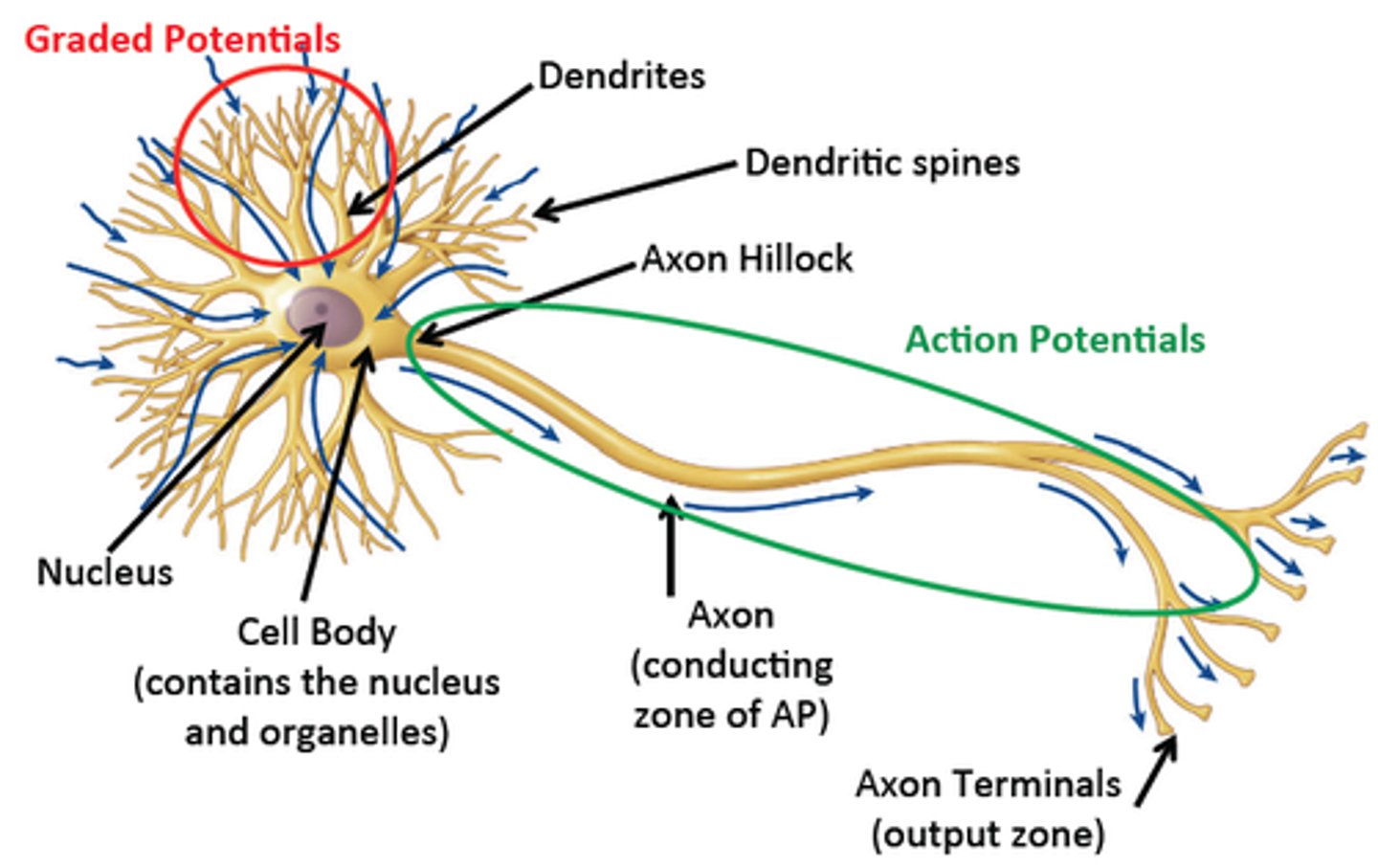
Voltage-gated channels on a neuron produce _________ potential/s.
Action (if they add up to threshold)
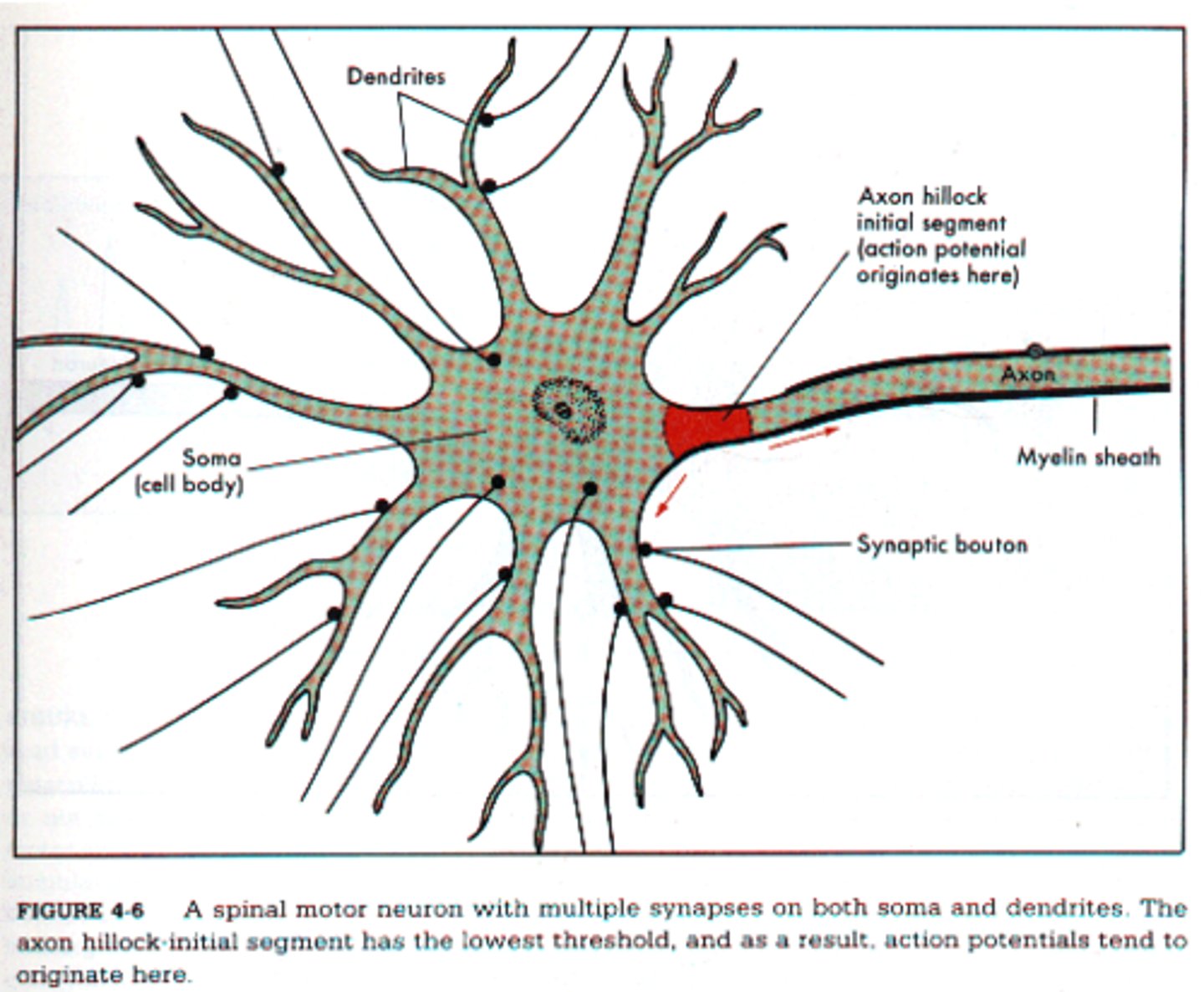
axon hillock
Cone shaped region of an axon where it joins the cell body--summation of potentials occurs here
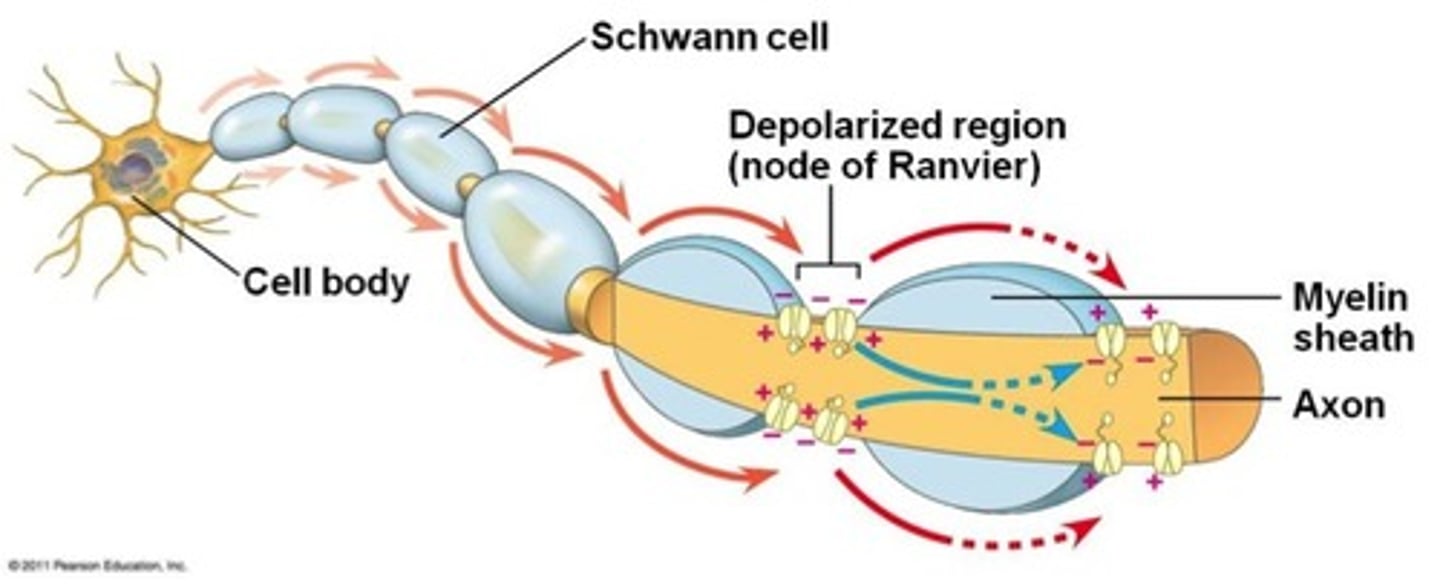
saltatory propagation
the movement of an action potential along a myelinated axon, "jumping" from node to node
Type A fibers
Myelinated
Large diameter
High speed (140 m/sec)
Carry rapid information to/from CNS
For example, position, balance, touch, and motor impulses
Type C nerve fibers
Unmyelinated
Small diameter
Slow speed (1 m/sec)
Carry slower information
For example, involuntary muscle, gland controls
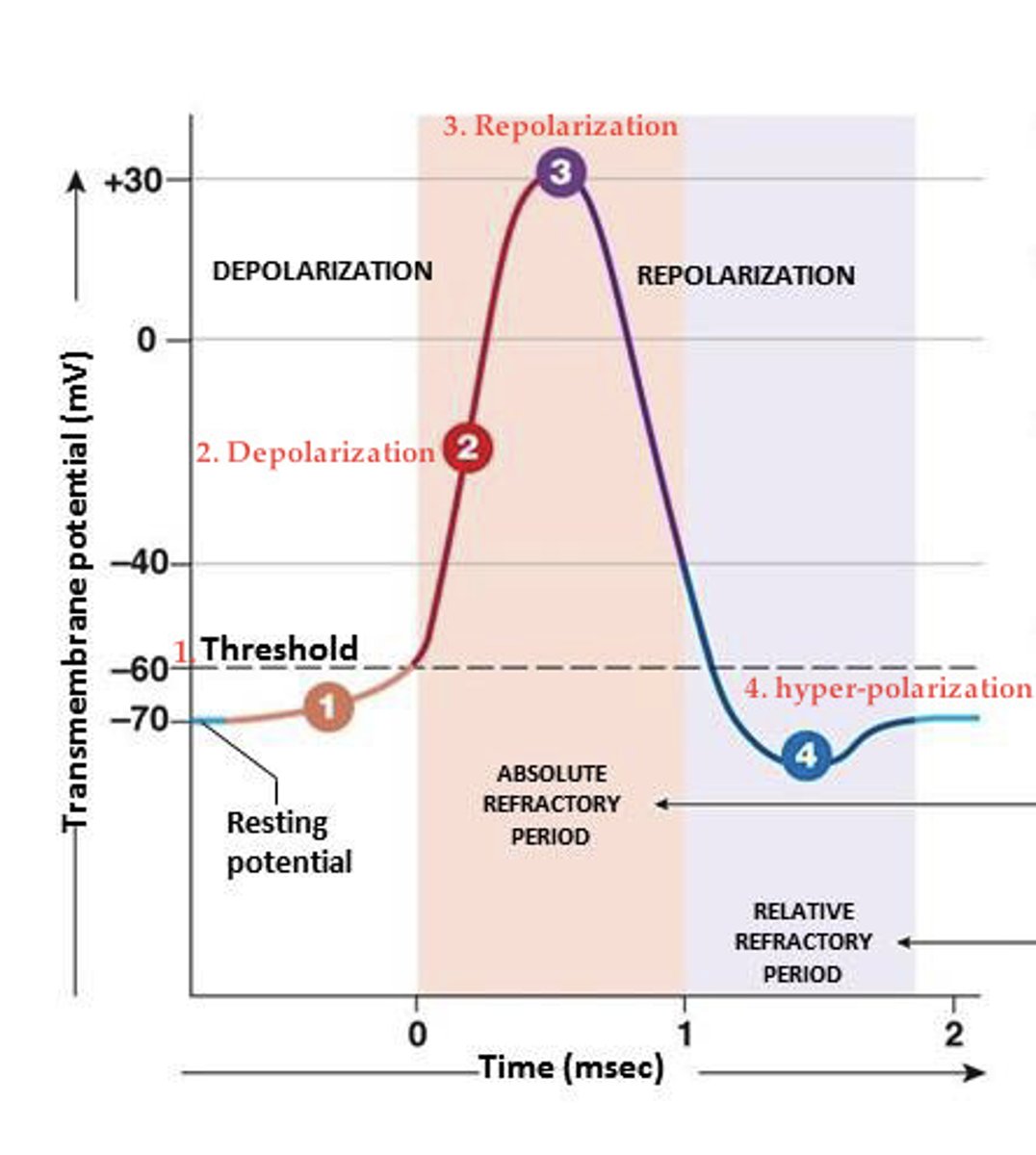
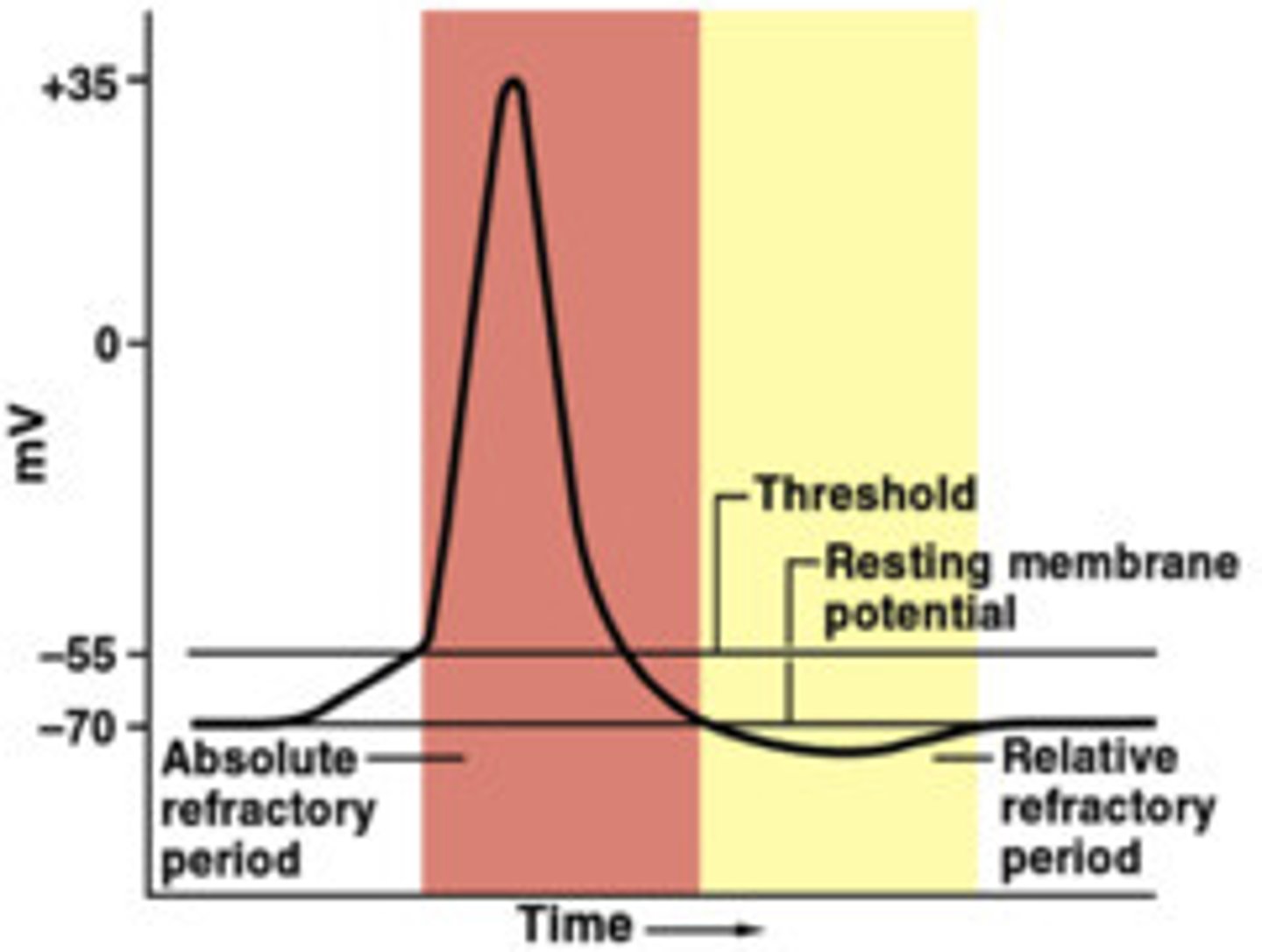
absolute refractory period
time during which another action potential is impossible; limits maximal firing rate
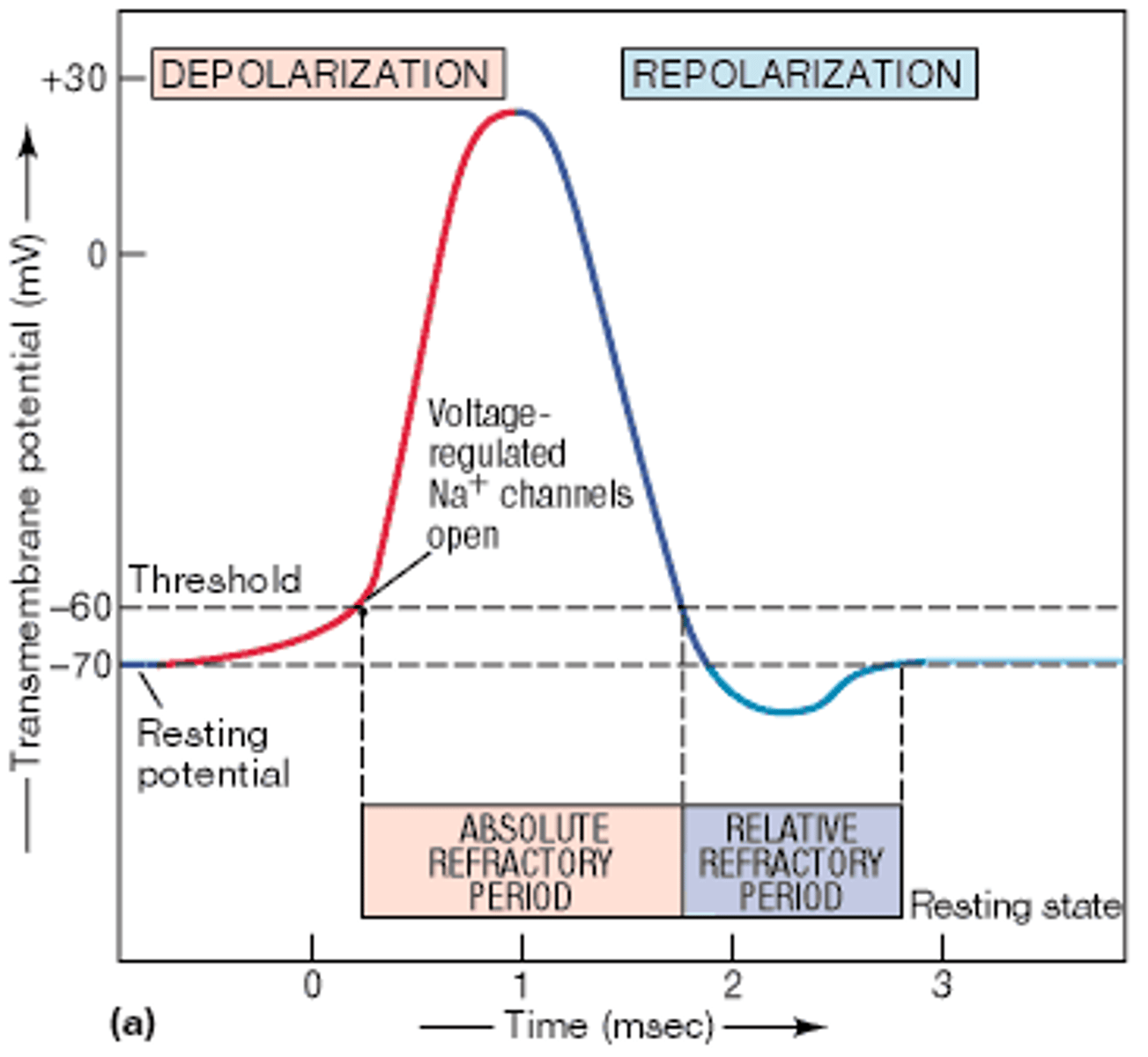
relative refractory period
a stronger than usual stimulus is necessary to initiate an action potential
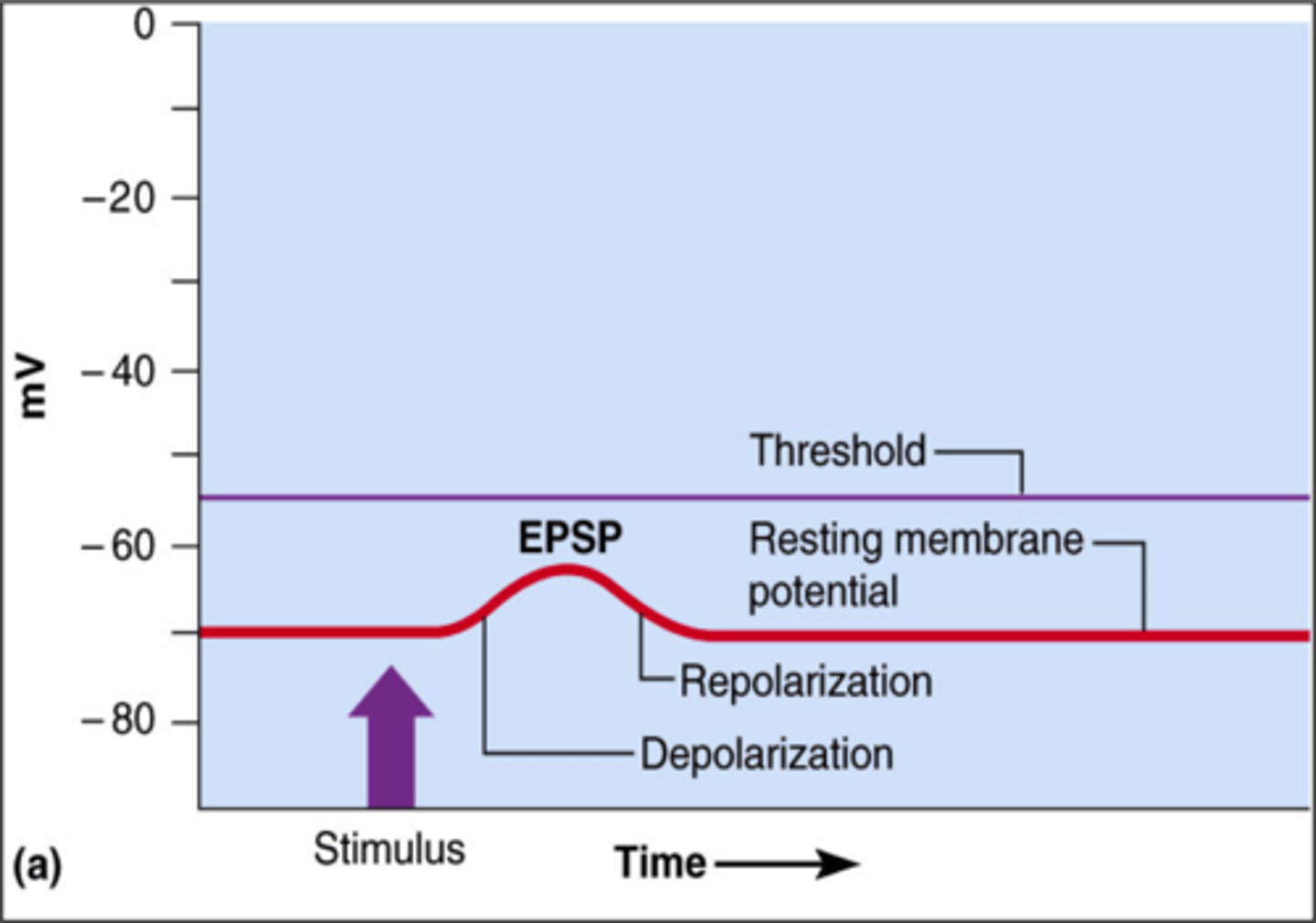
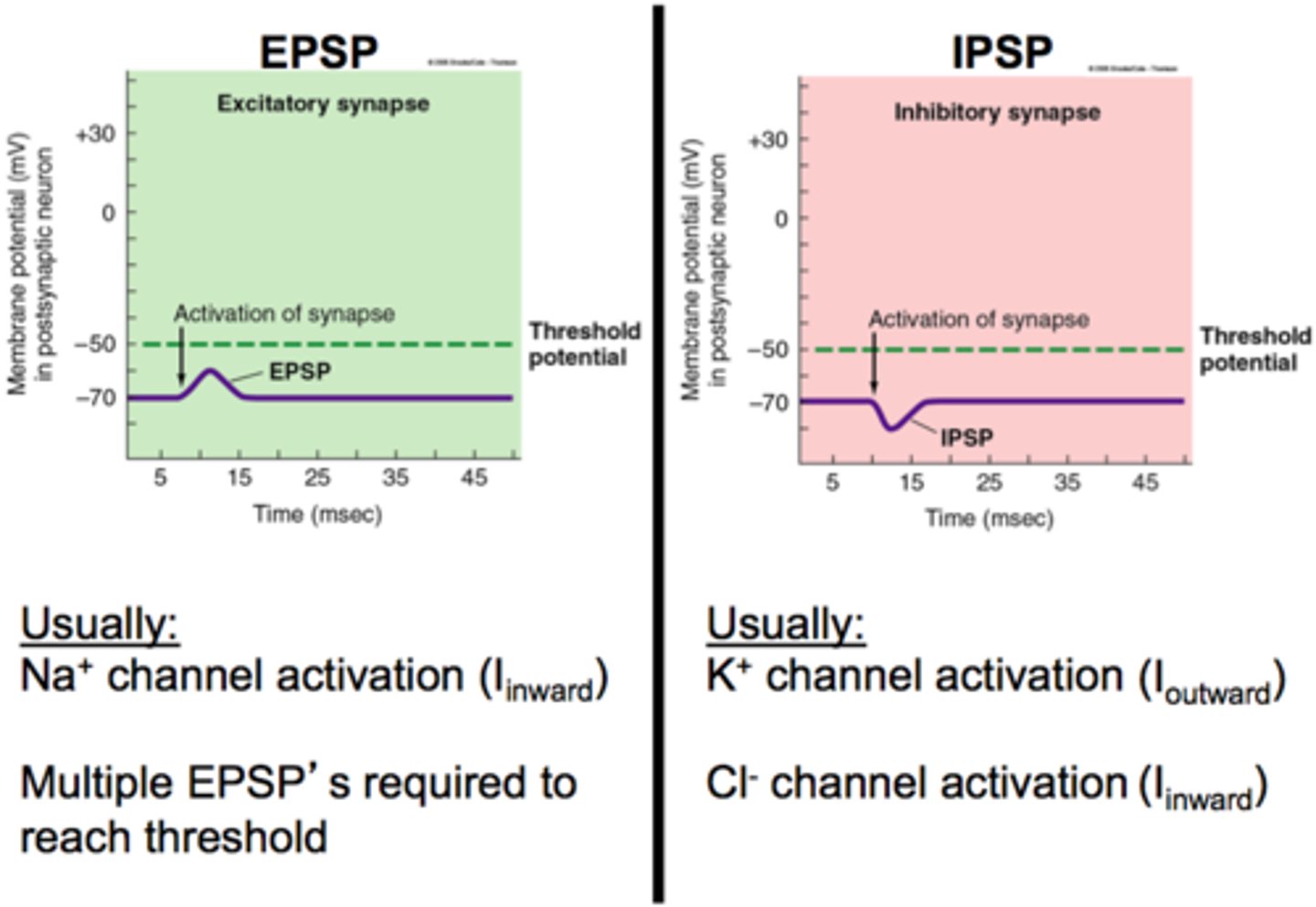
EPSP (excitatory postsynaptic potential)
Excitatory--makes cell more positive--Synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron more likely to generate an action potential
IPSP (inhibitory postsynaptic potential)
Inhibitory--makes cell more negative--synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron less likely to generate an action potential
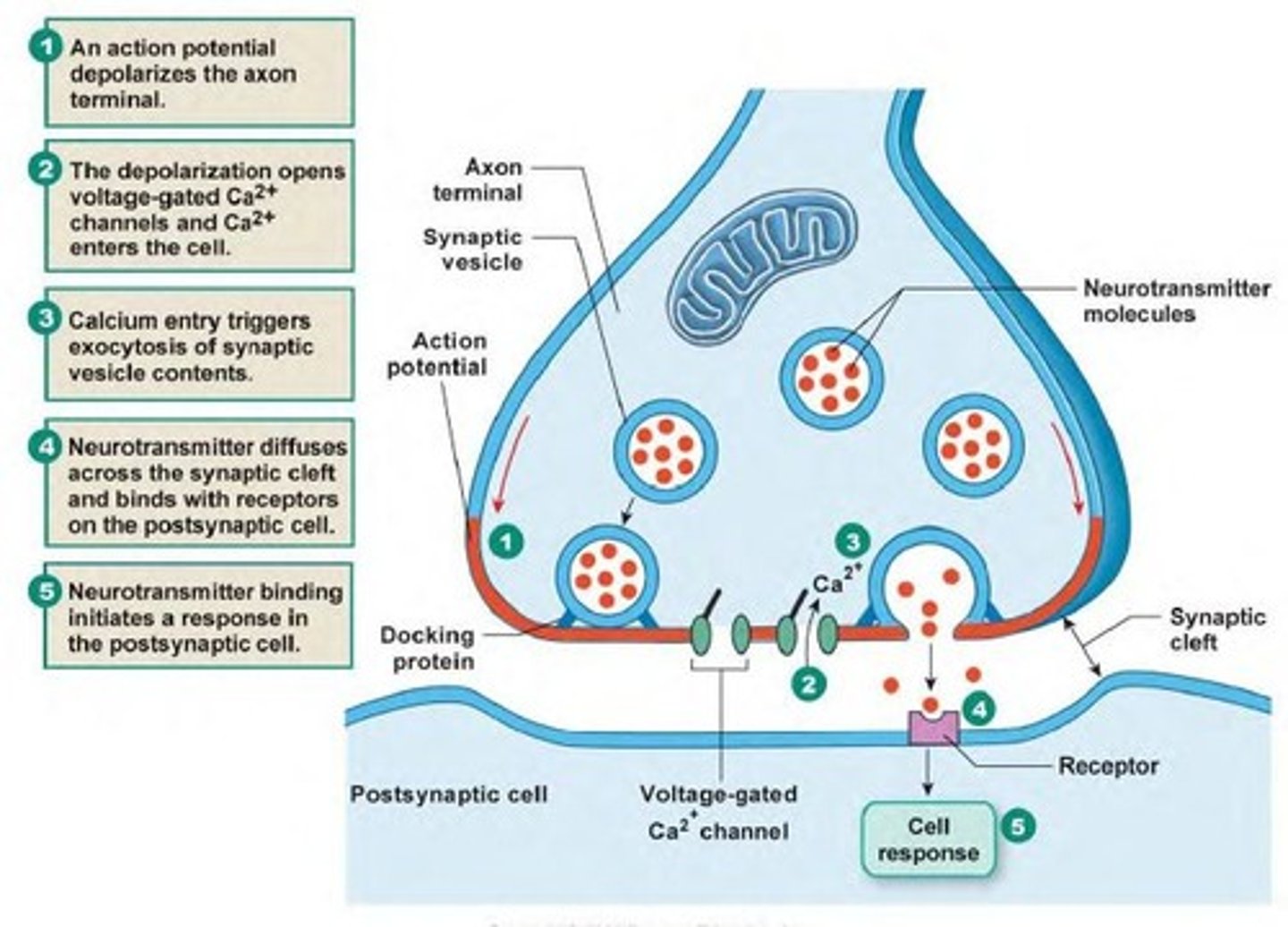
Synaptic delay is caused by
calcium influx (into pre-synaptic terminal bulb), and neurotransmitter release.
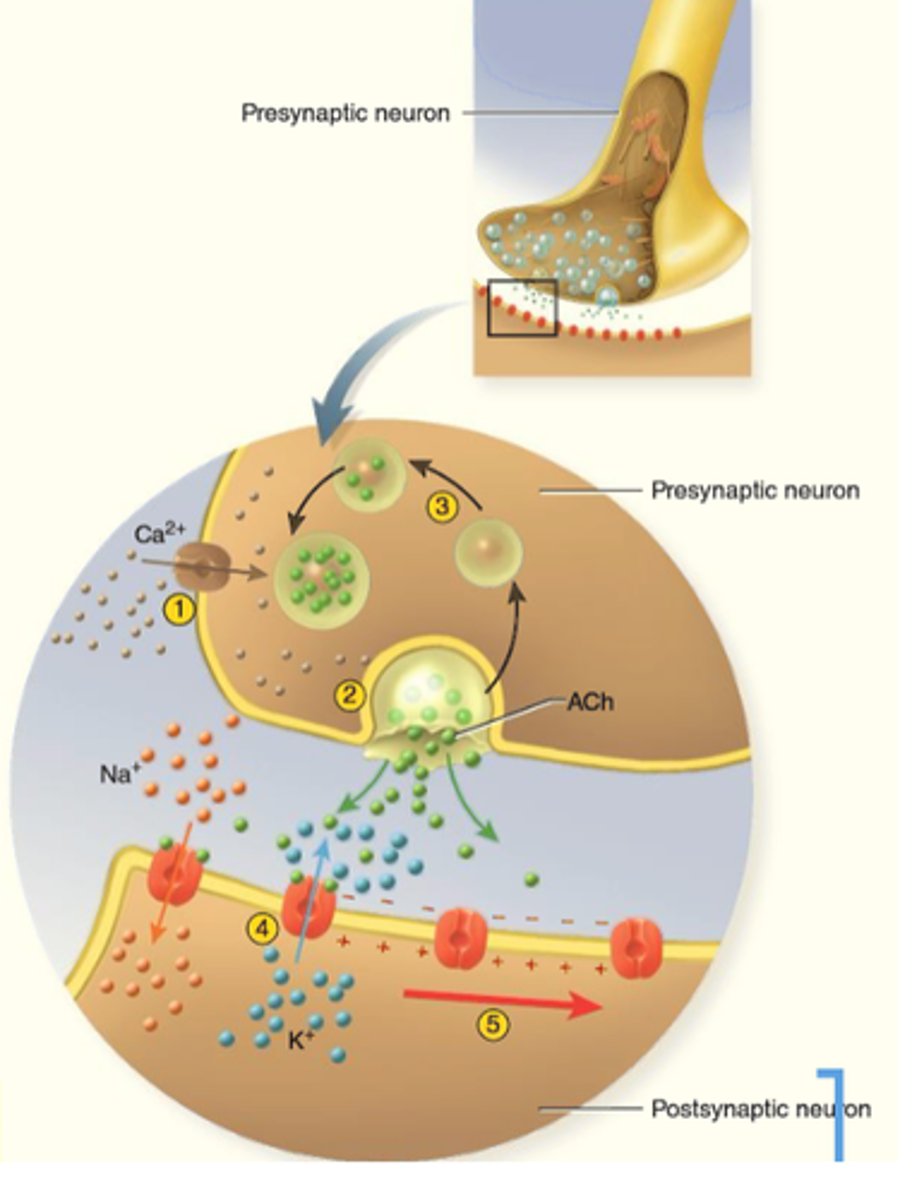
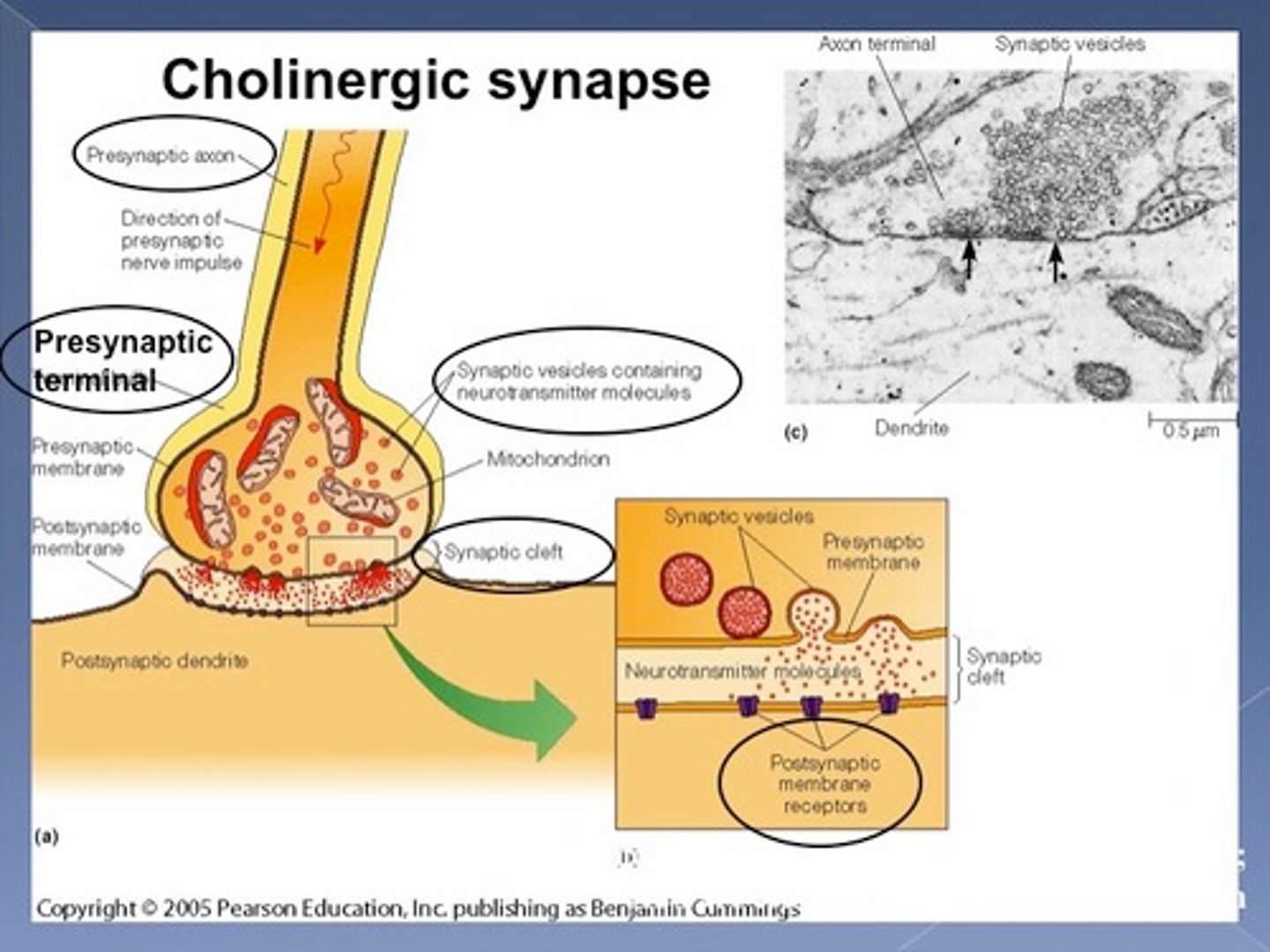
Steps at cholinergic synapse
1) action potential arrives
2) Ca2+ enters, triggers release of ACh
3) ACh released, binds to receptors
4) post synaptic cell depolarizes
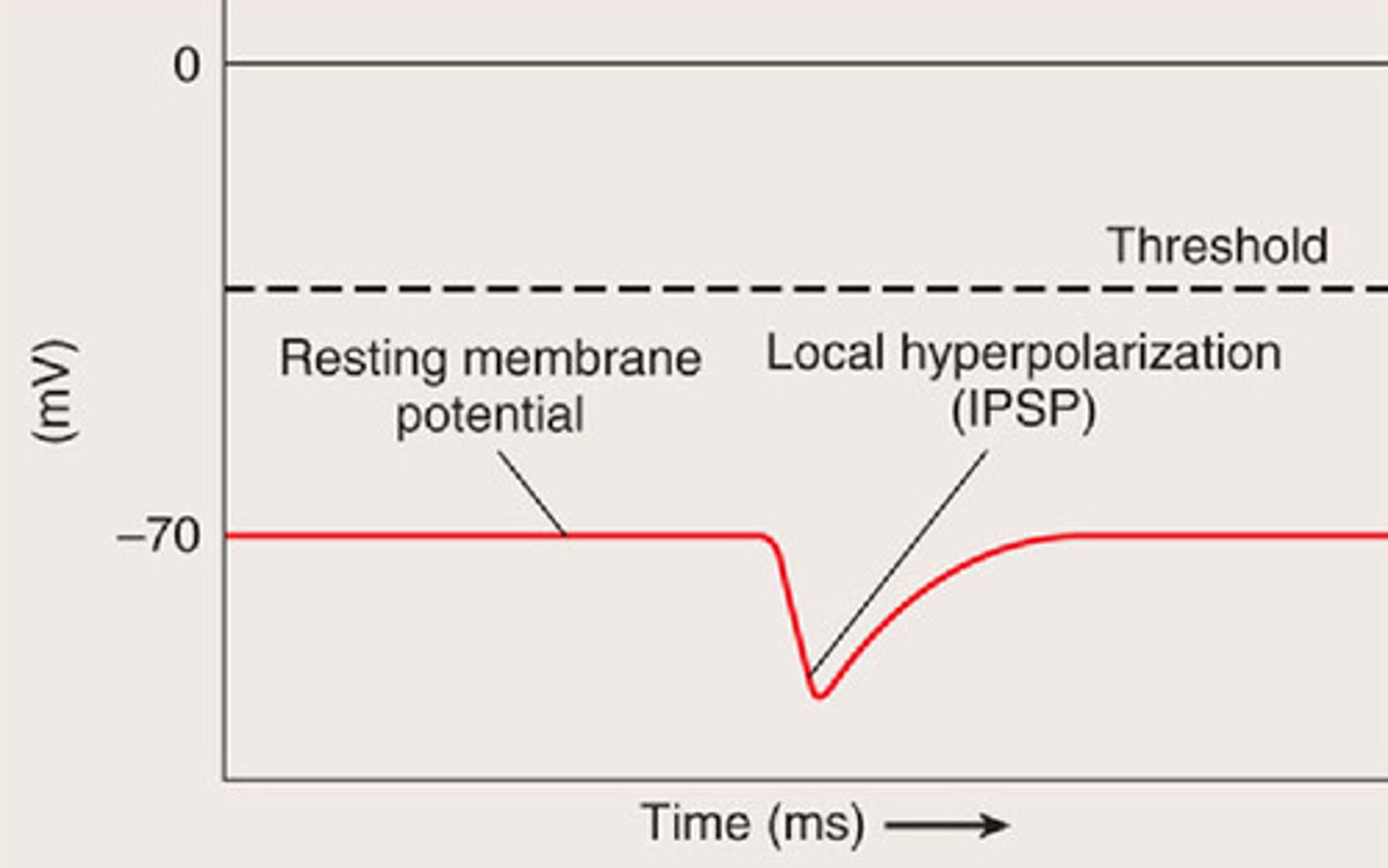
What is another name for IPSPs?
Graded hyperpolarizations
The effect that a neurotransmitter has on the postsynaptic membrane depends on the _______.
specific properties of the receptor proteins
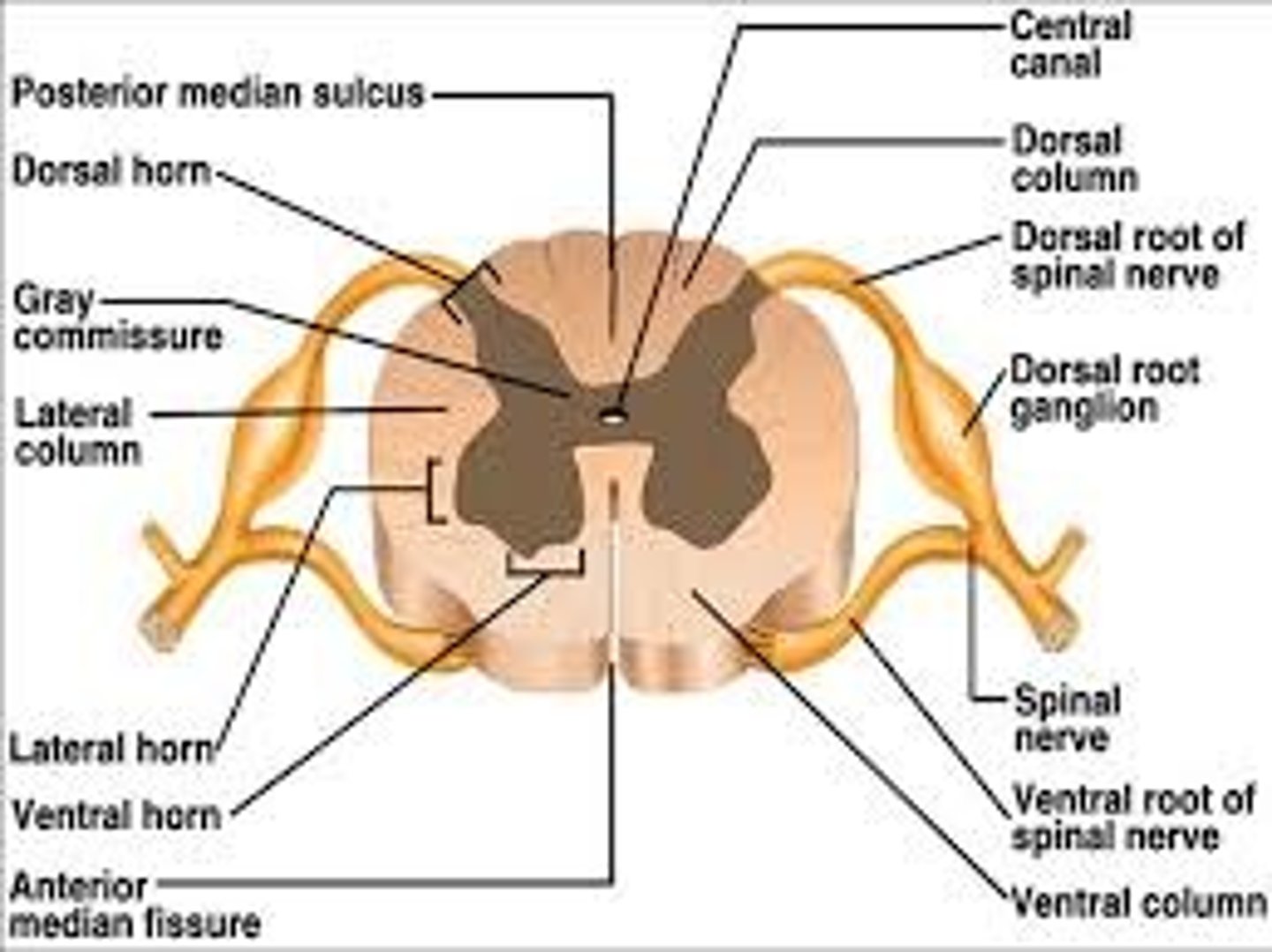
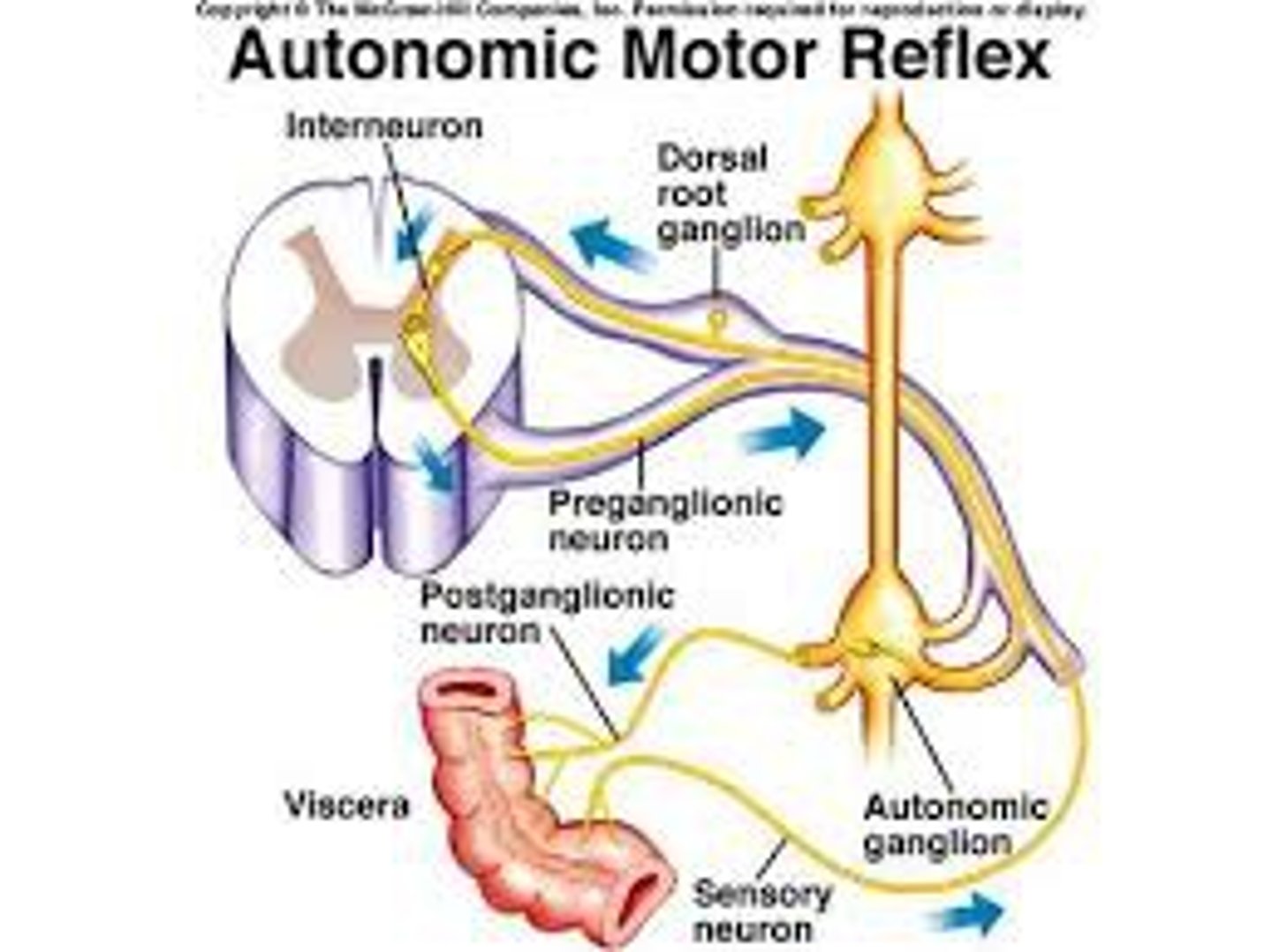
dorsal root ganglion
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons
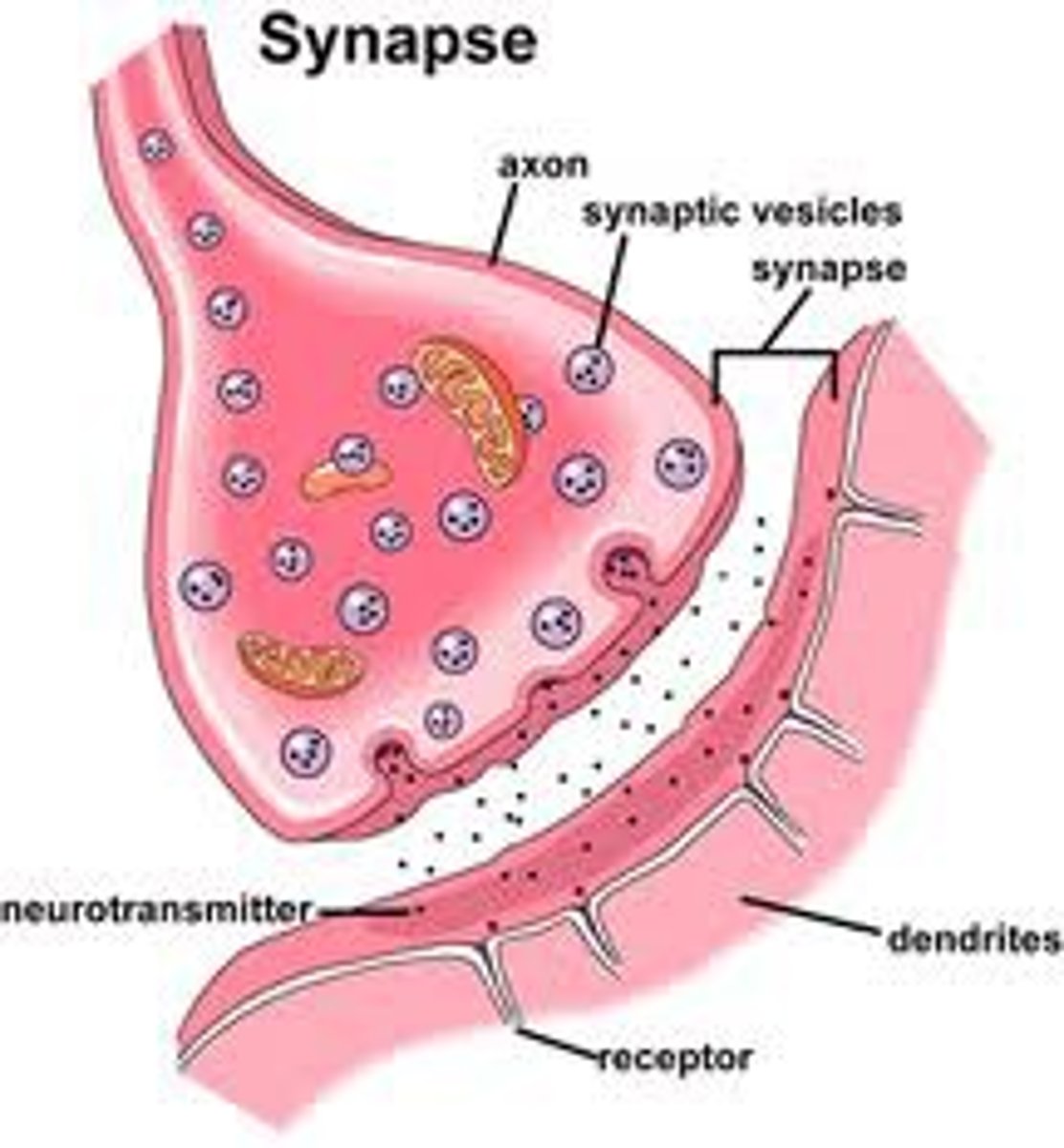
most common type of synapse in the body
chemical synapse
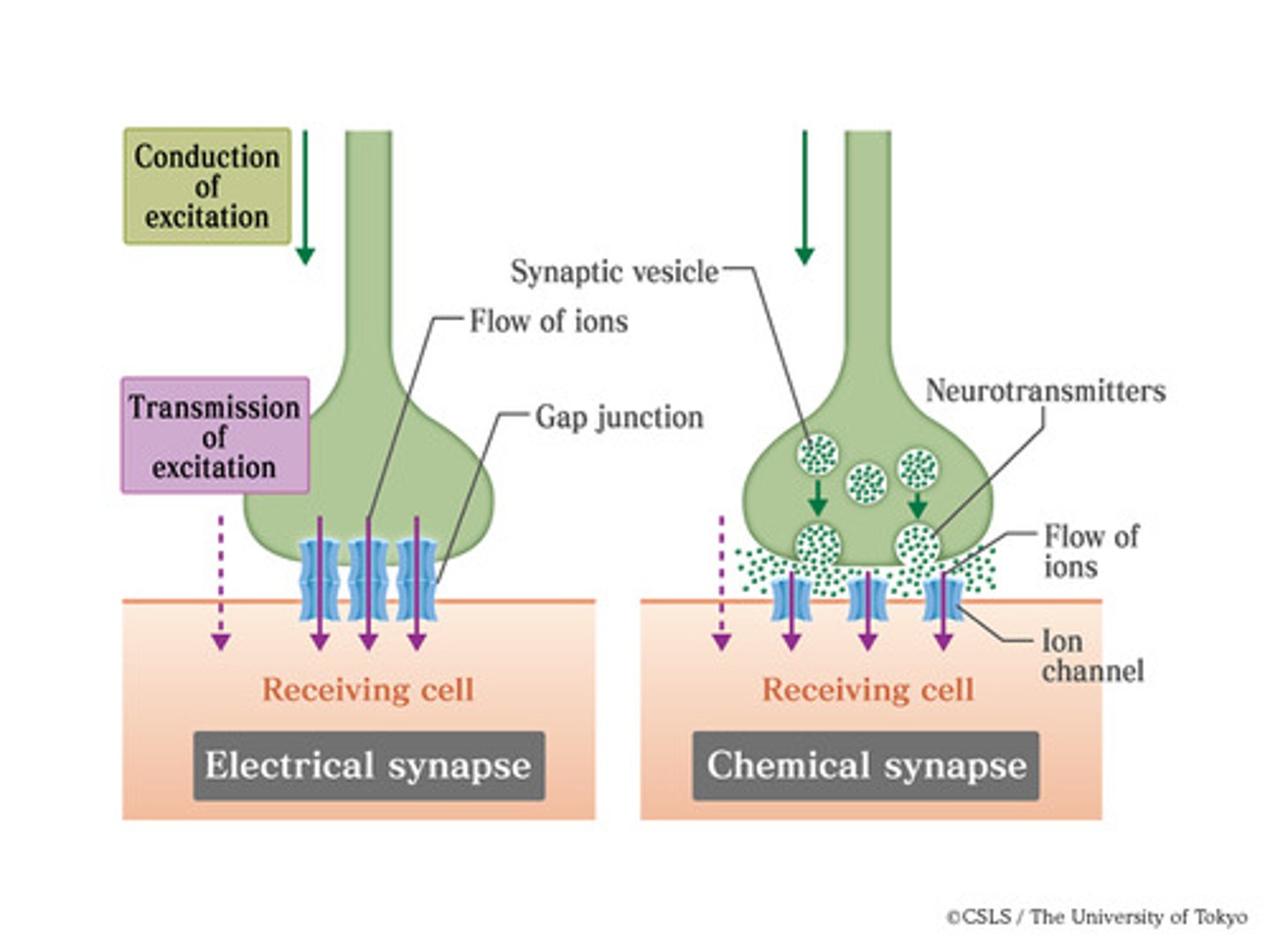
Least common type of synapse in the body
electrical synapse
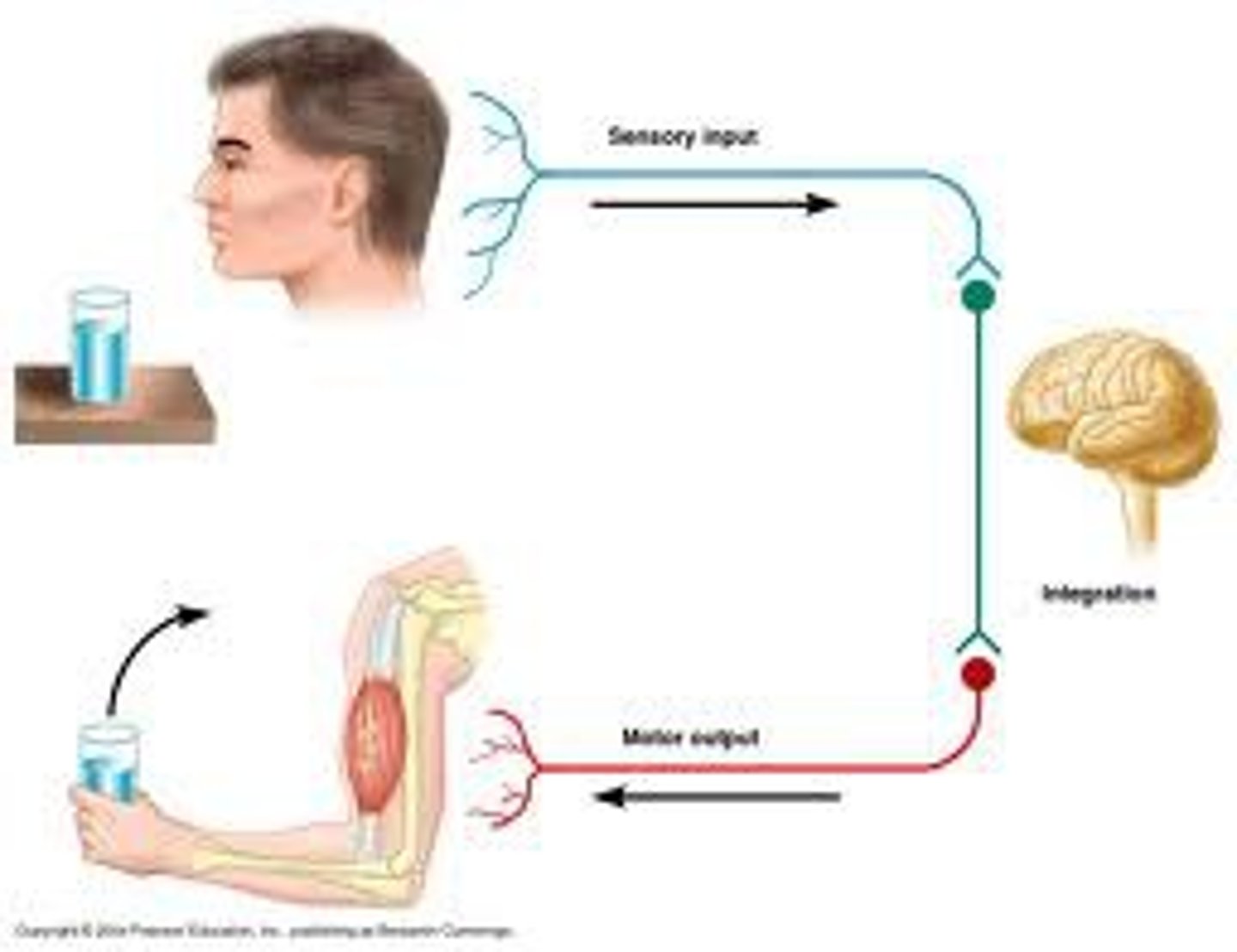
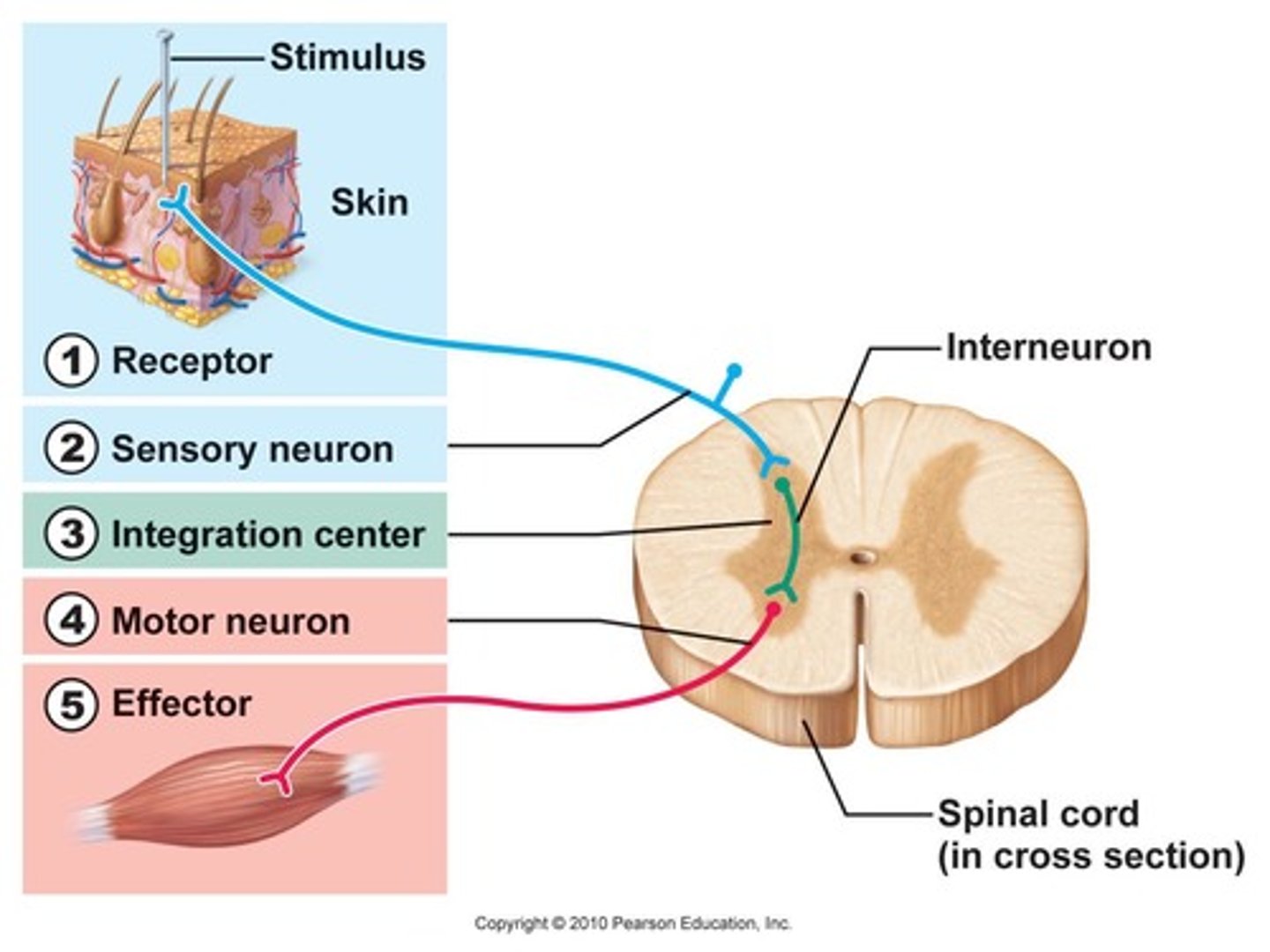
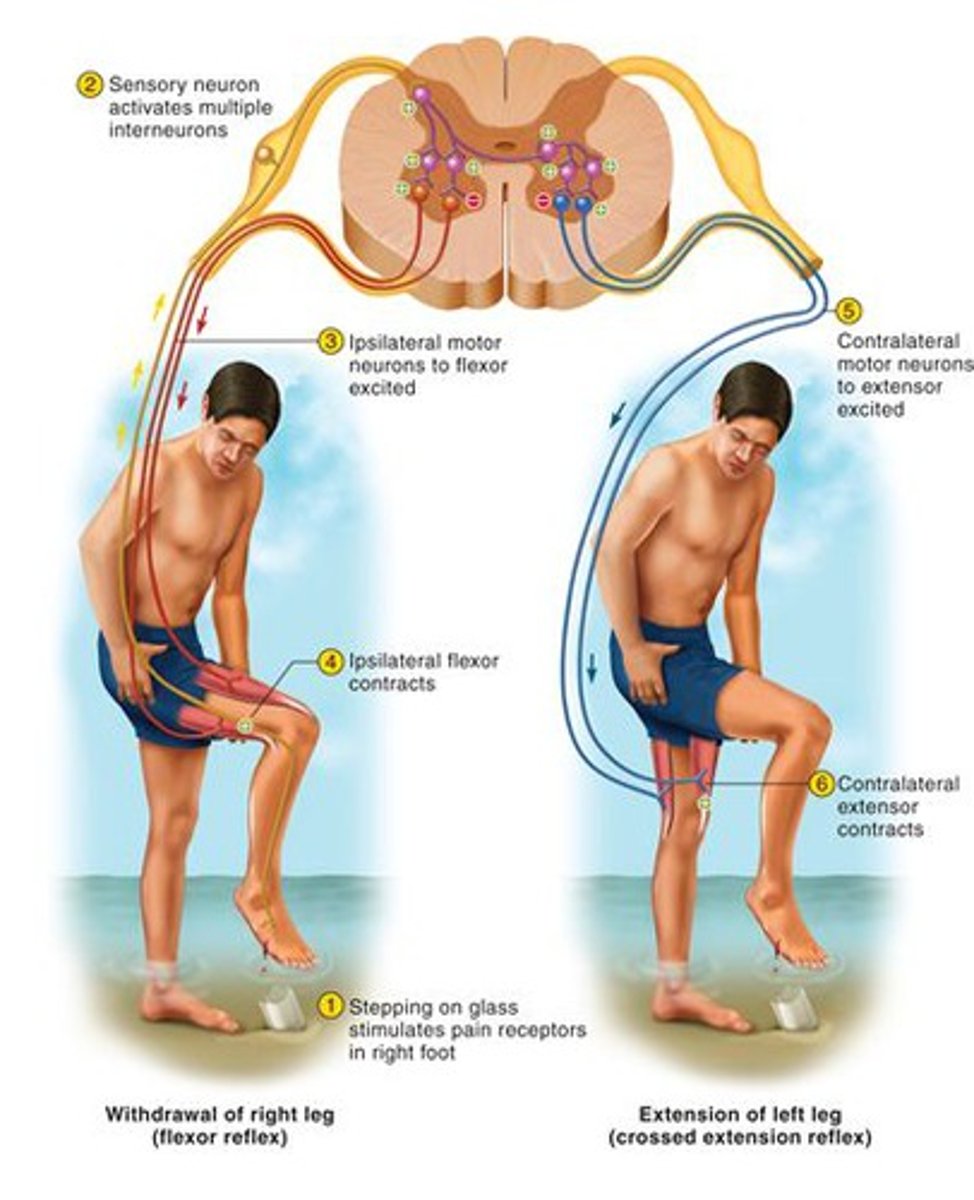
Steps of Reflex Arc in order:
1. Arrival of stimulus and activation of receptor
2. Activation of a sensory neuron (Afferent)
3. Information processing in CNS (Interneurons)
4. Activation of a motor neuron (Efferent)
5. Response by effector
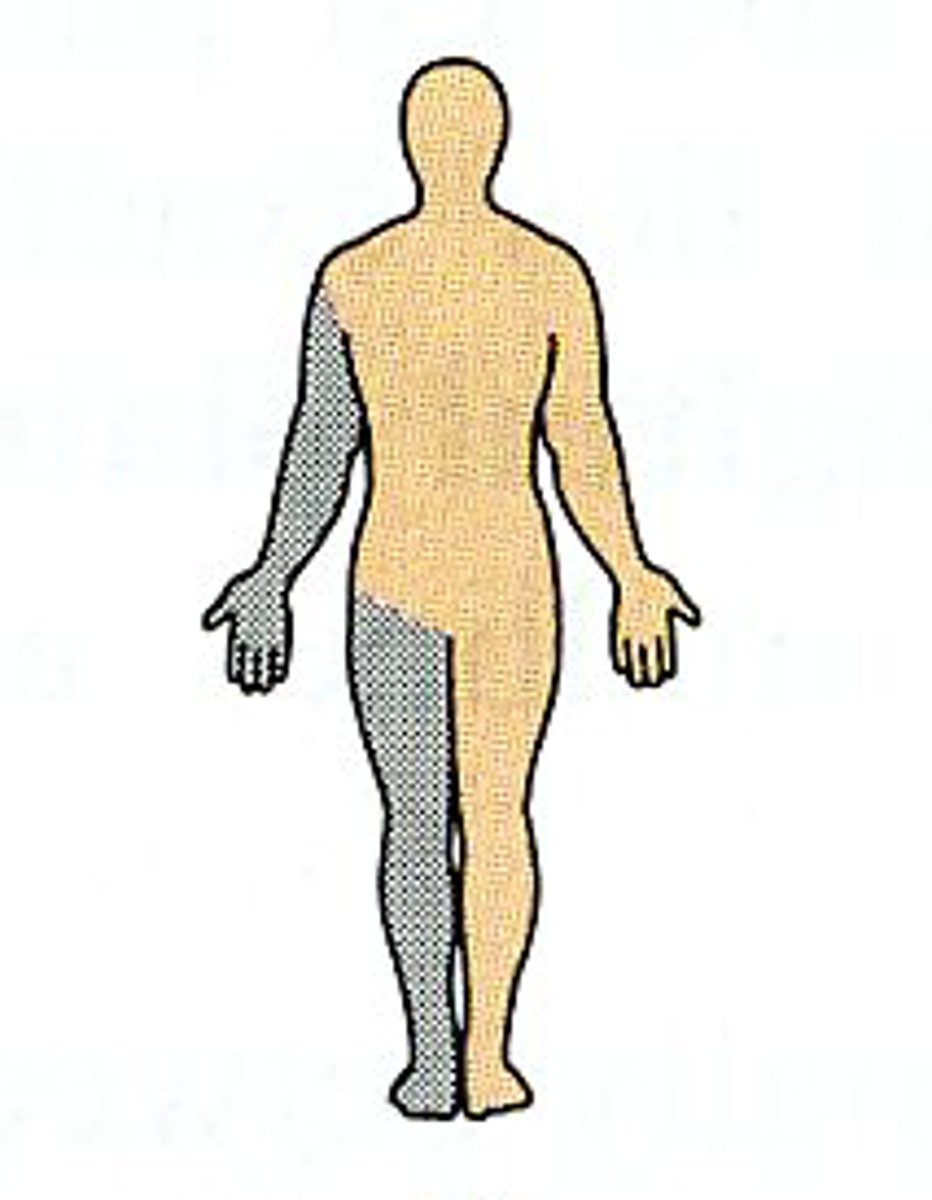
Contralateral
on the opposite side of the body
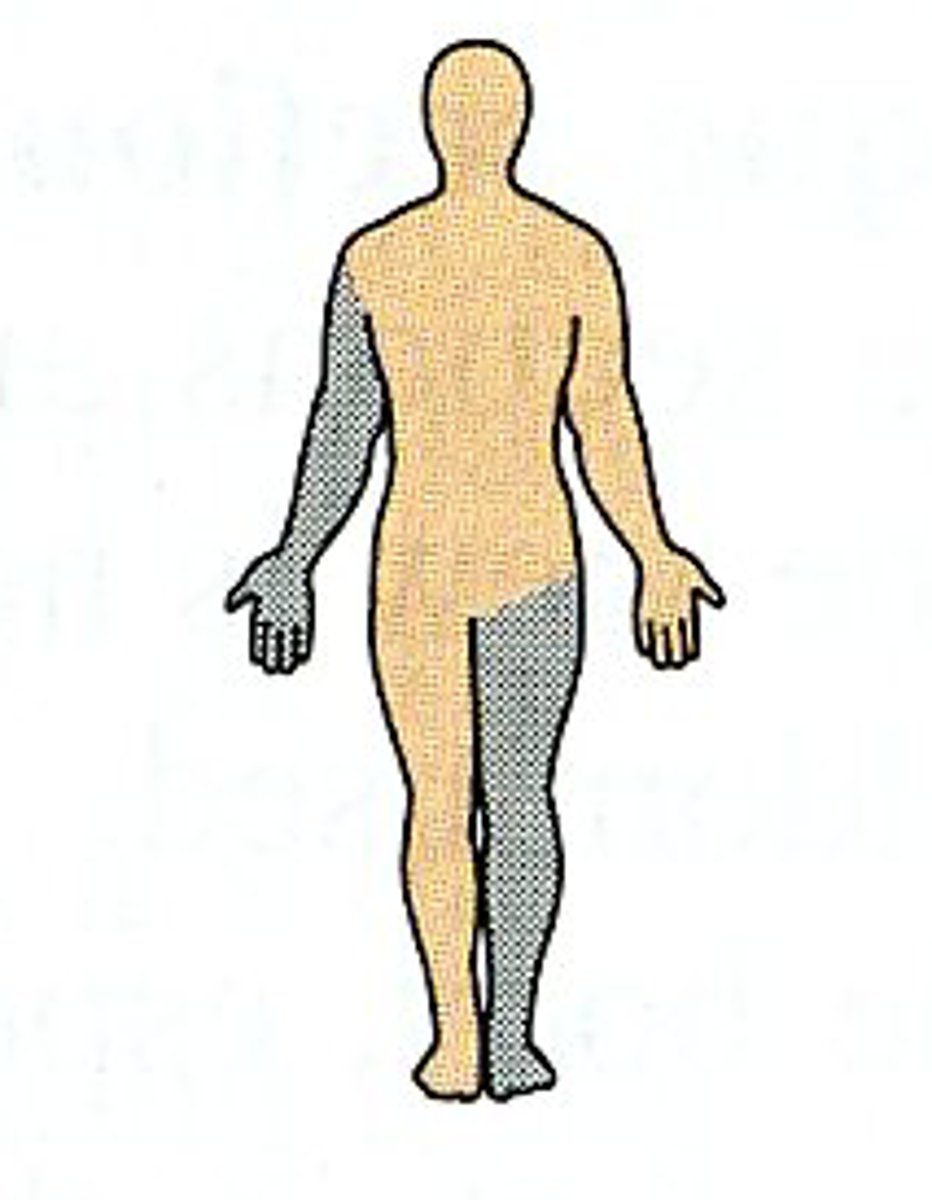
Ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
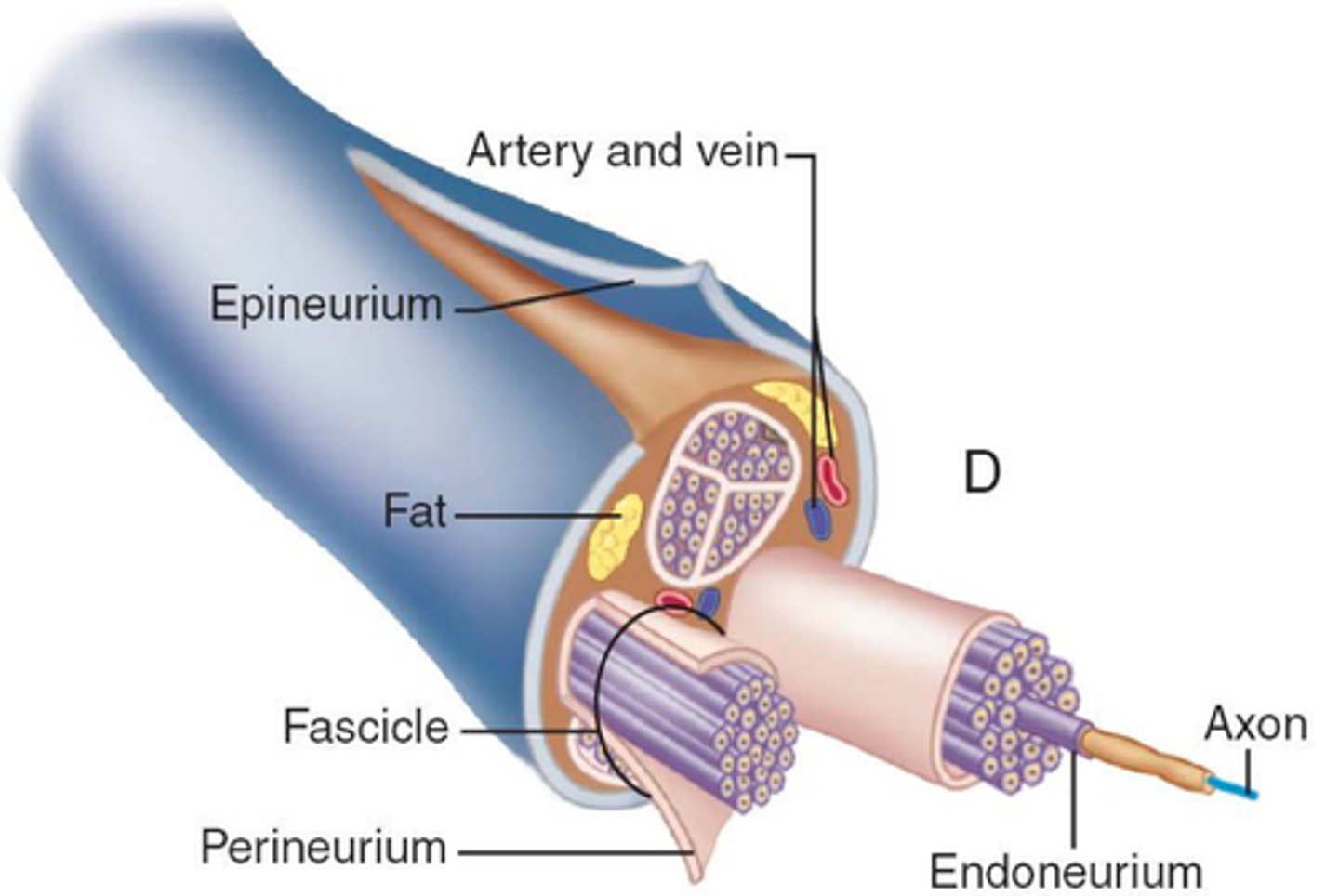
endoneurium, perineurium, epineurium
Layers of connective tissue of a nerve from interior to exterior
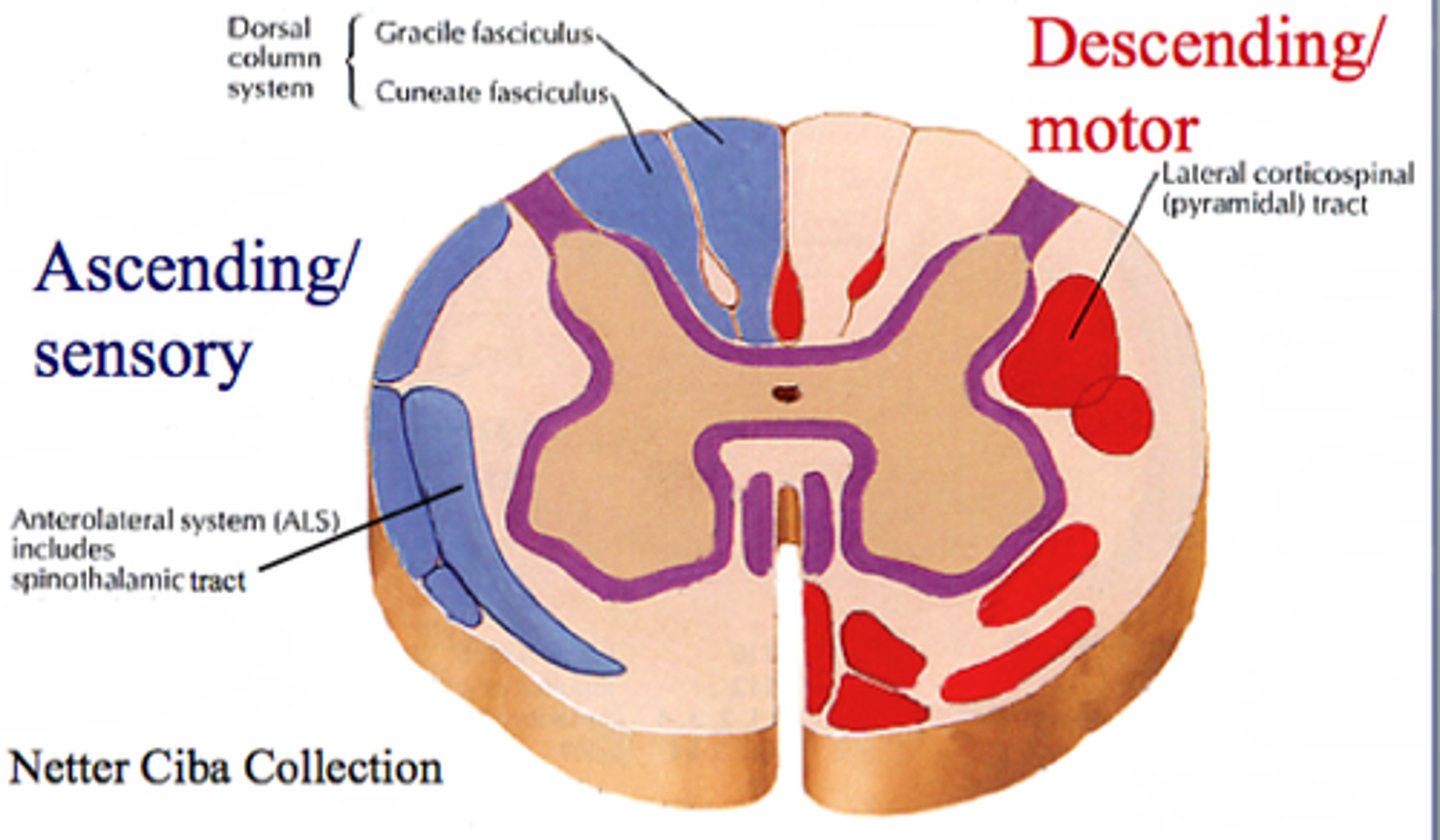
ascending white columns
carry sensory information up to brain (consist of myelinated axons)
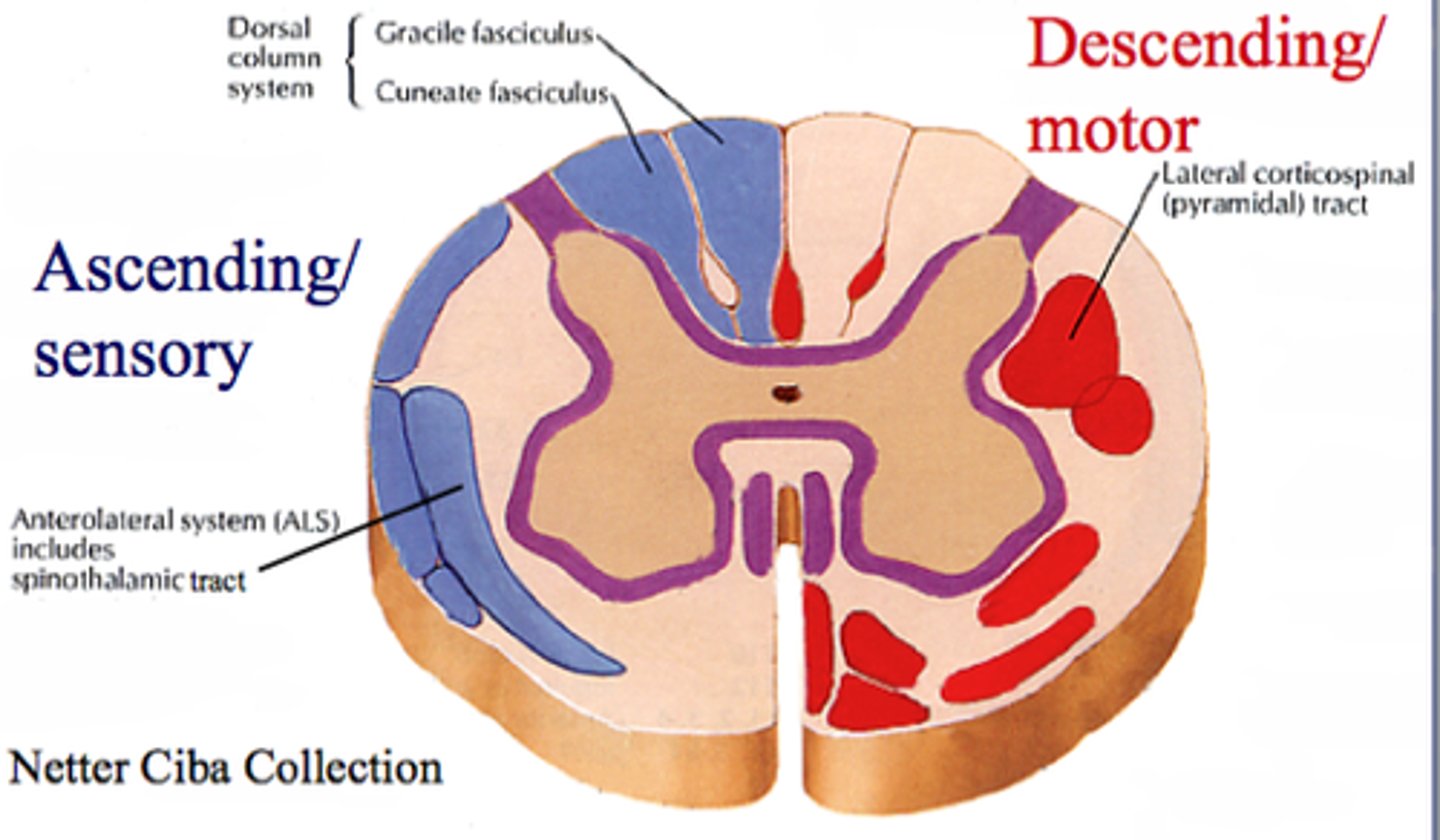
descending white columns
carry motor information from brain to motor neurons in PNS (consist of myelinated axons)
Spinal nerves contain
both sensory and motor fibers
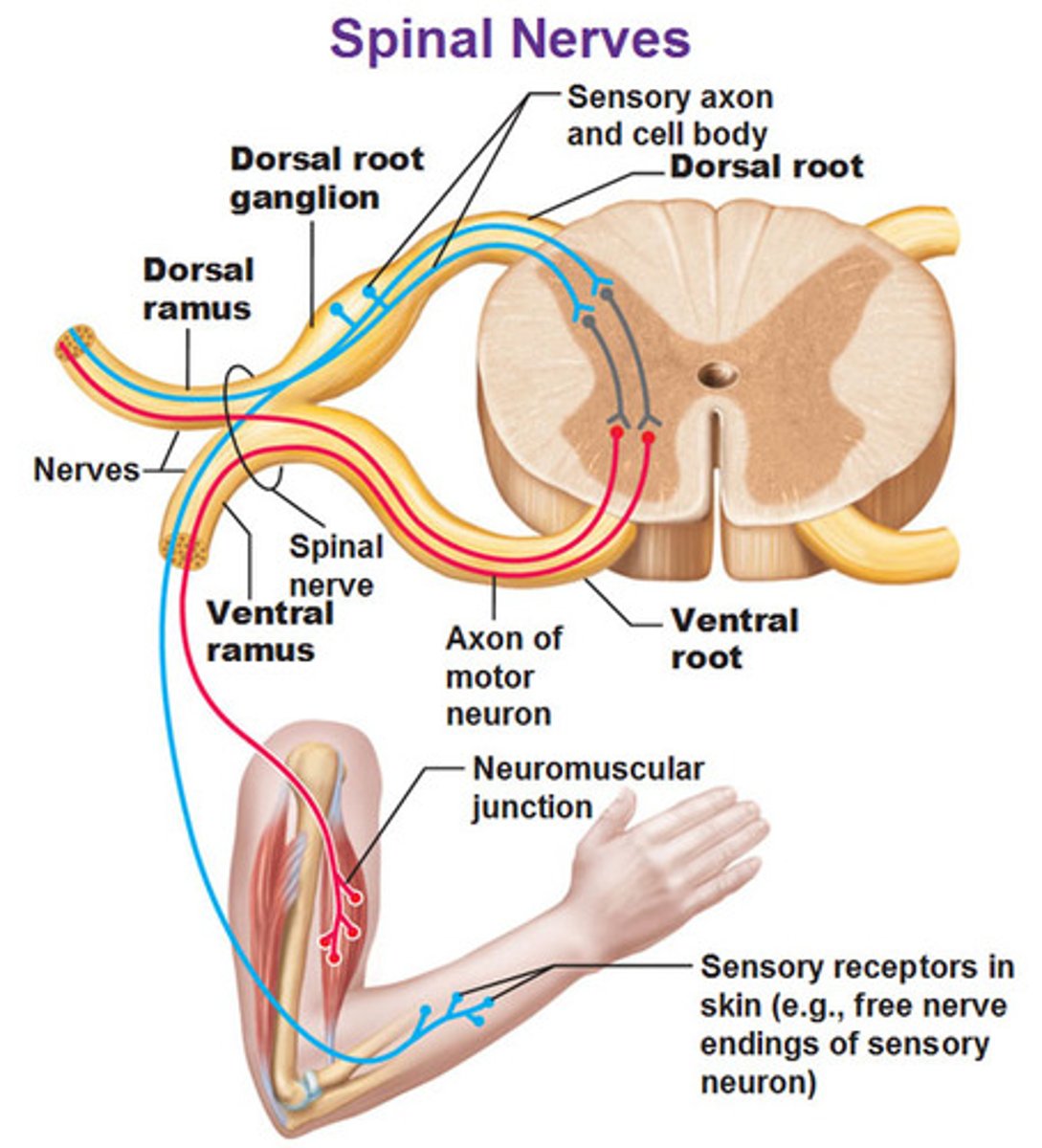
dorsal root
the sensory branch of each spinal nerve
ventral root
contains axons of motor neurons
somatic nervous system
Division of the PNS that controls skeletal muscles.
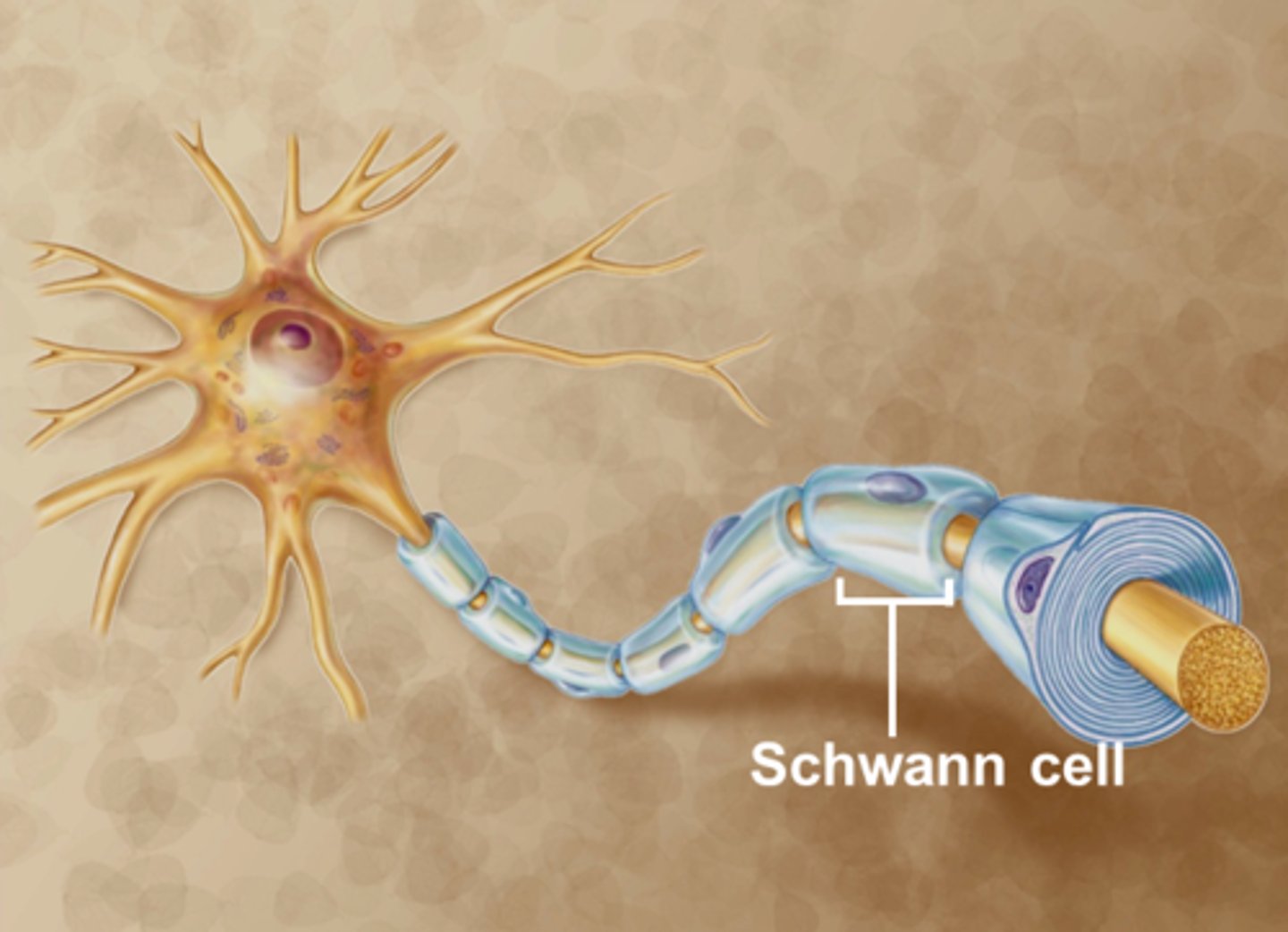
Schwann cells
produce myelin in PNS
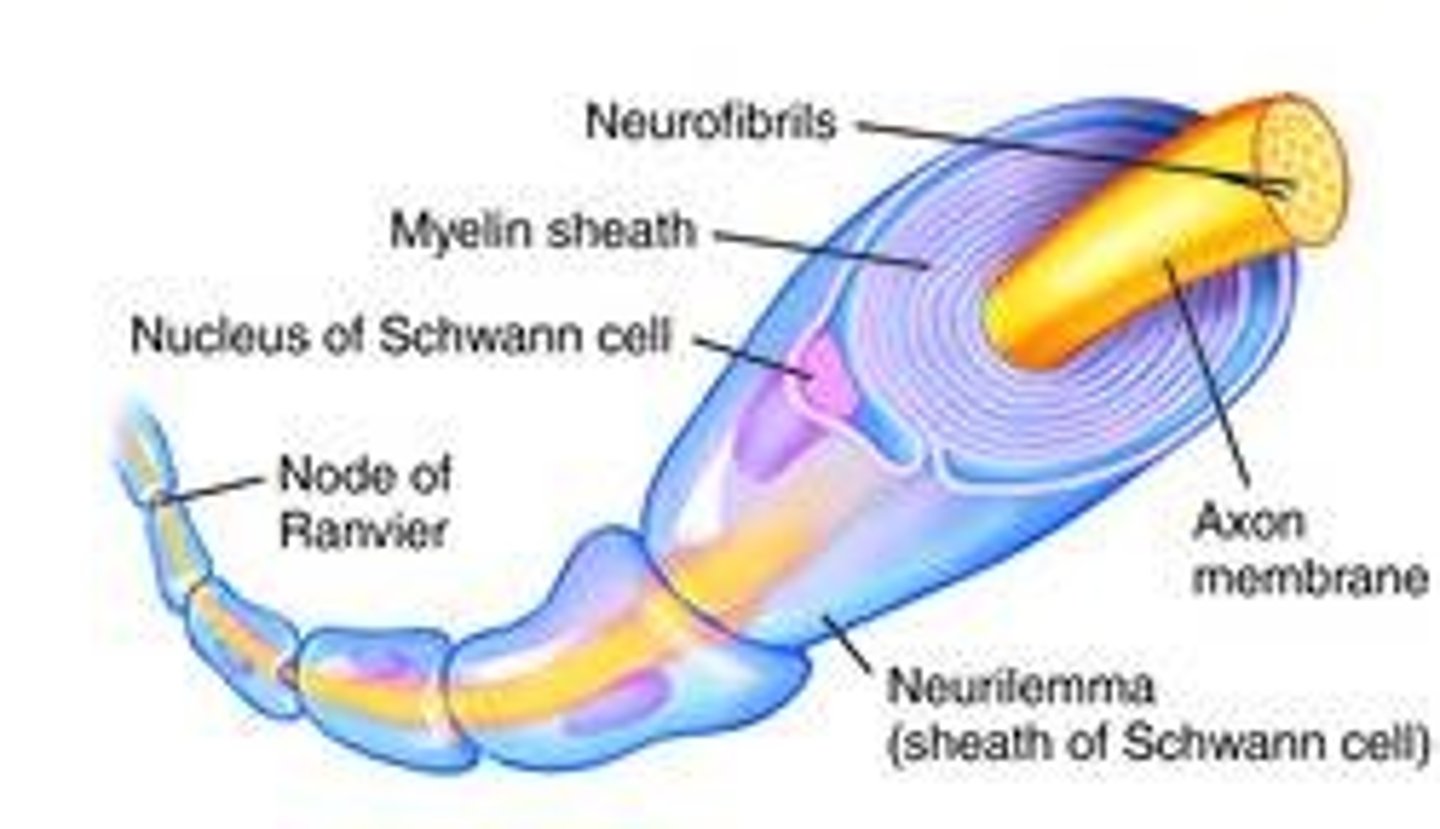
myelin sheath function
insulates axon and speeds up conduction
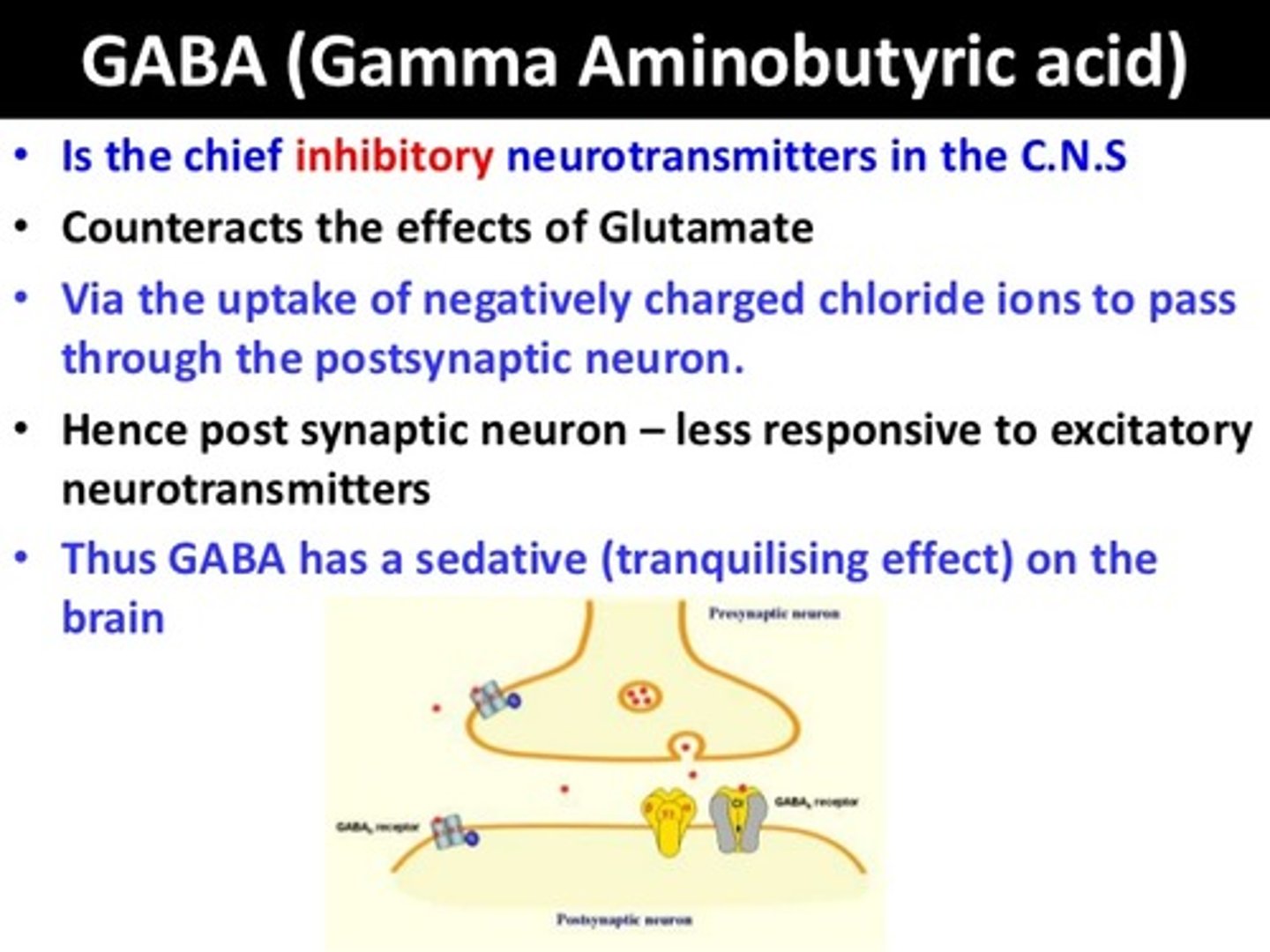
GABA --inhibitory or excitatory? How does it affect anxiety?
inhibitory, decreases anxiety
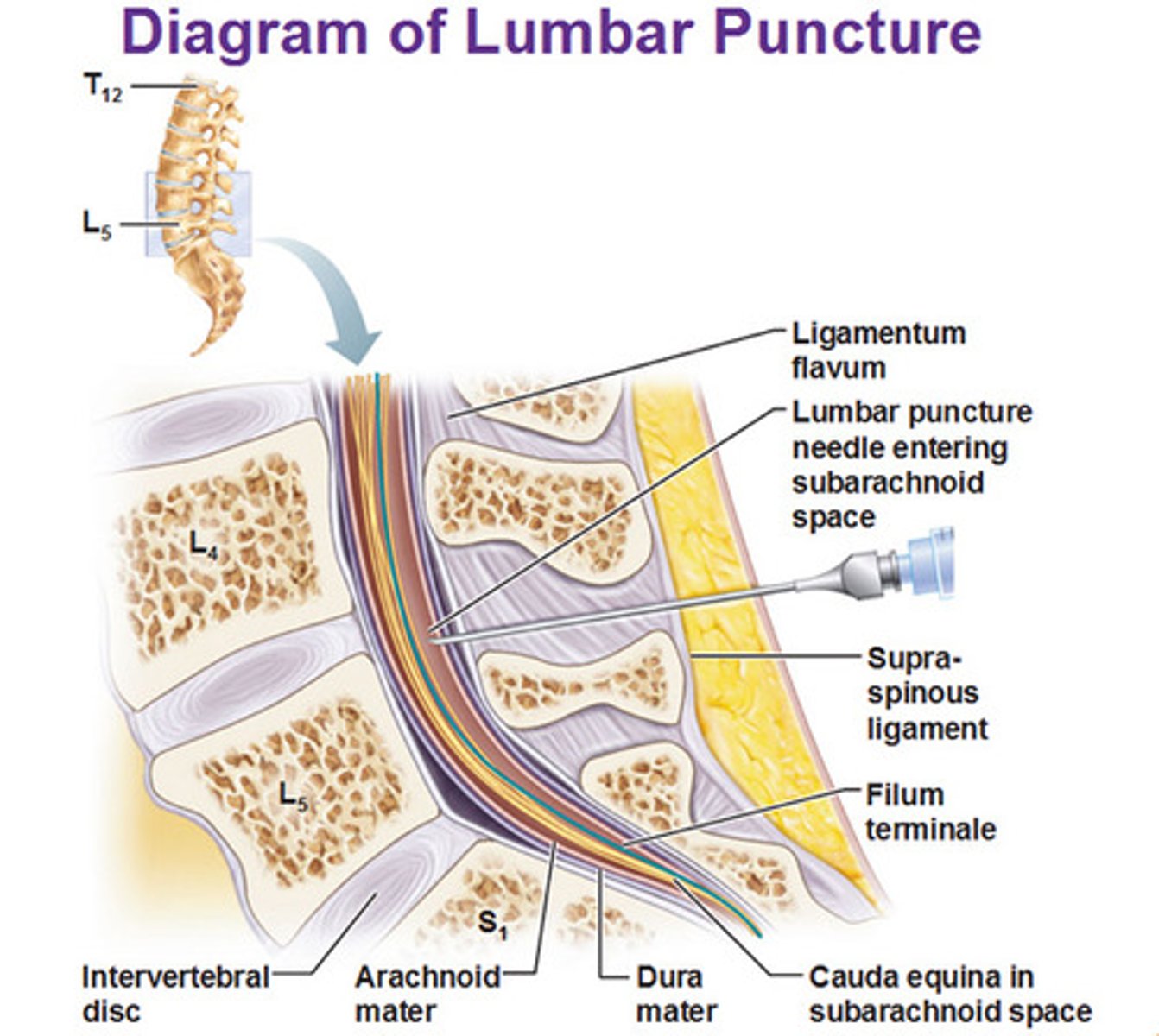
spinal tap (lumbar puncture)
Procedure performed by using a needle to withdraw CSF --fluid drawn from subarachnoid space
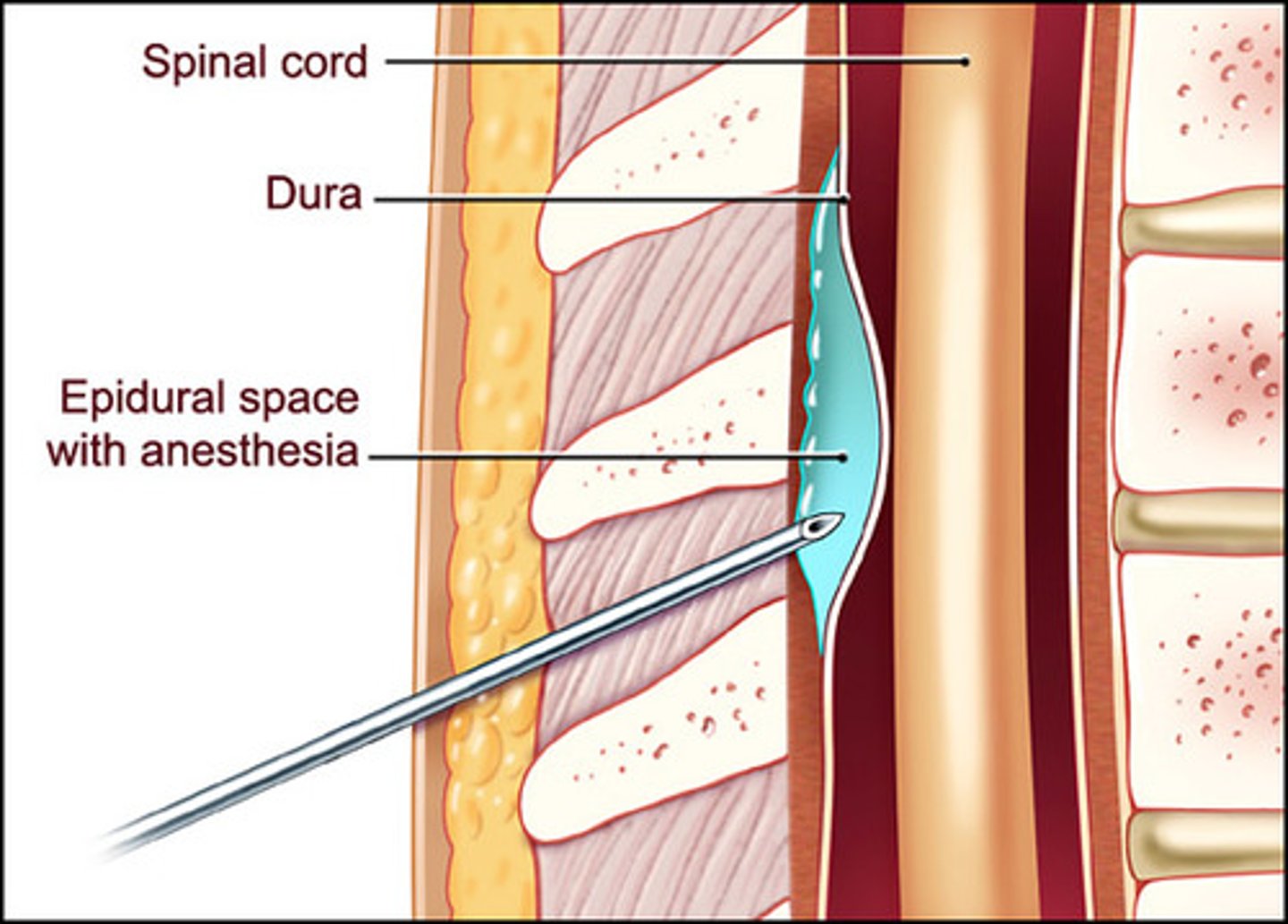
epidural anesthesia
used in vaginal live child birth because it blocks much of the pain from sensory nerves in pelvic region (only blocks sensory)
how many pairs of spinal nerves?
31 pairs
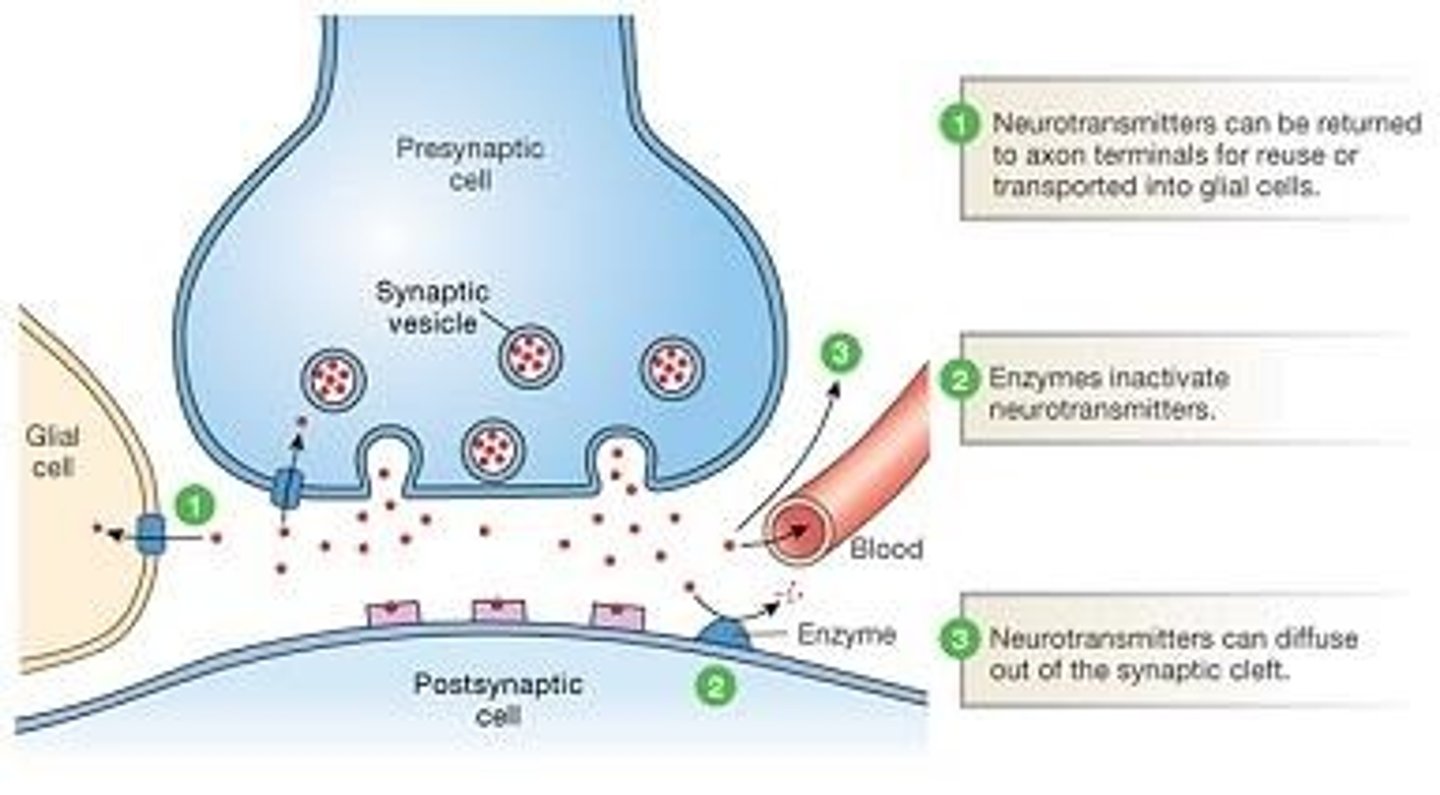
3 ways that neurotransmitters are removed from the synaptic cleft are _______.
1. degradation by an enzyme
2. simple diffusion away from cleft
3. re-uptake via active transport
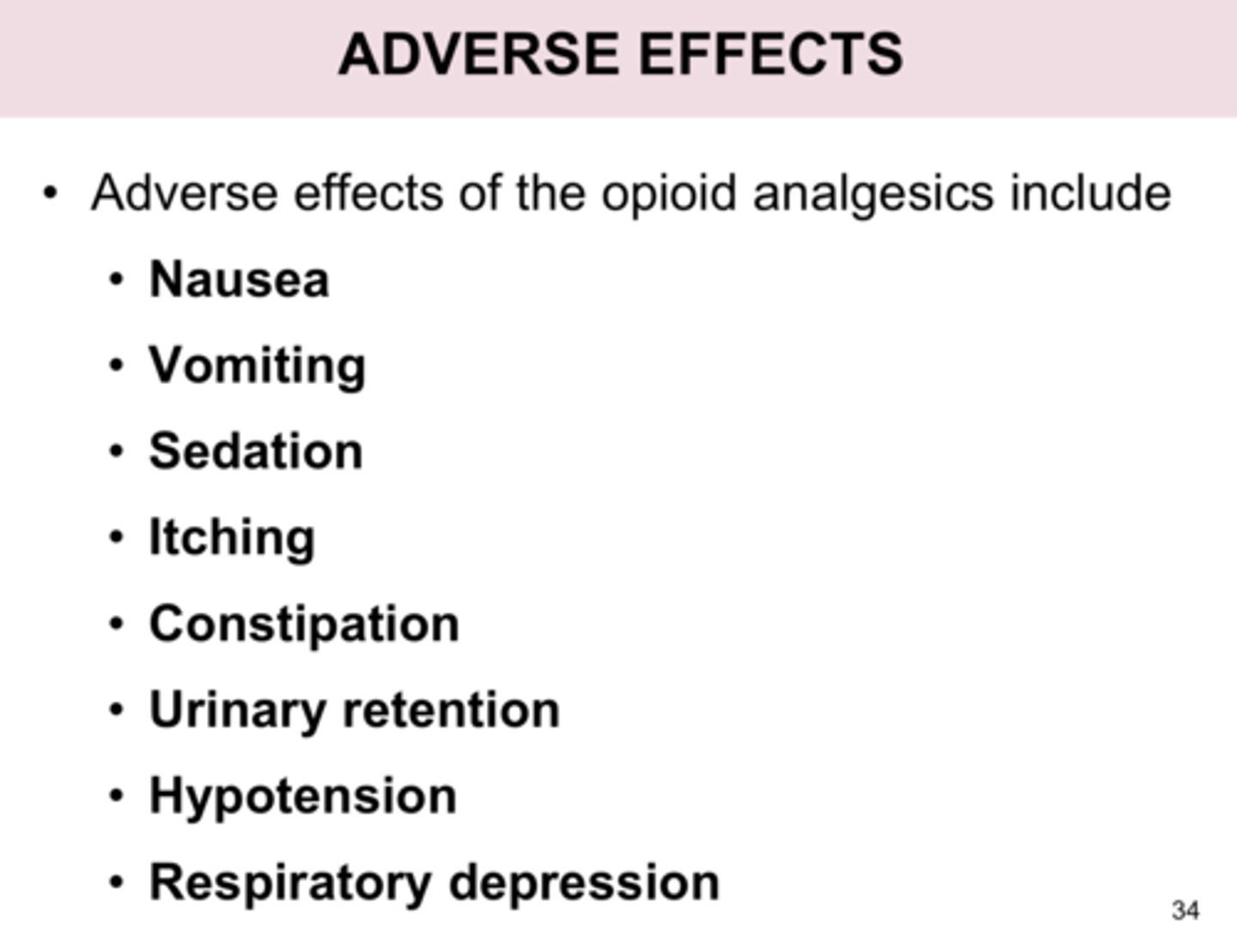
Opioids
Any drug or agent derived from opium. Effective at blocking pain, but highly addictive.
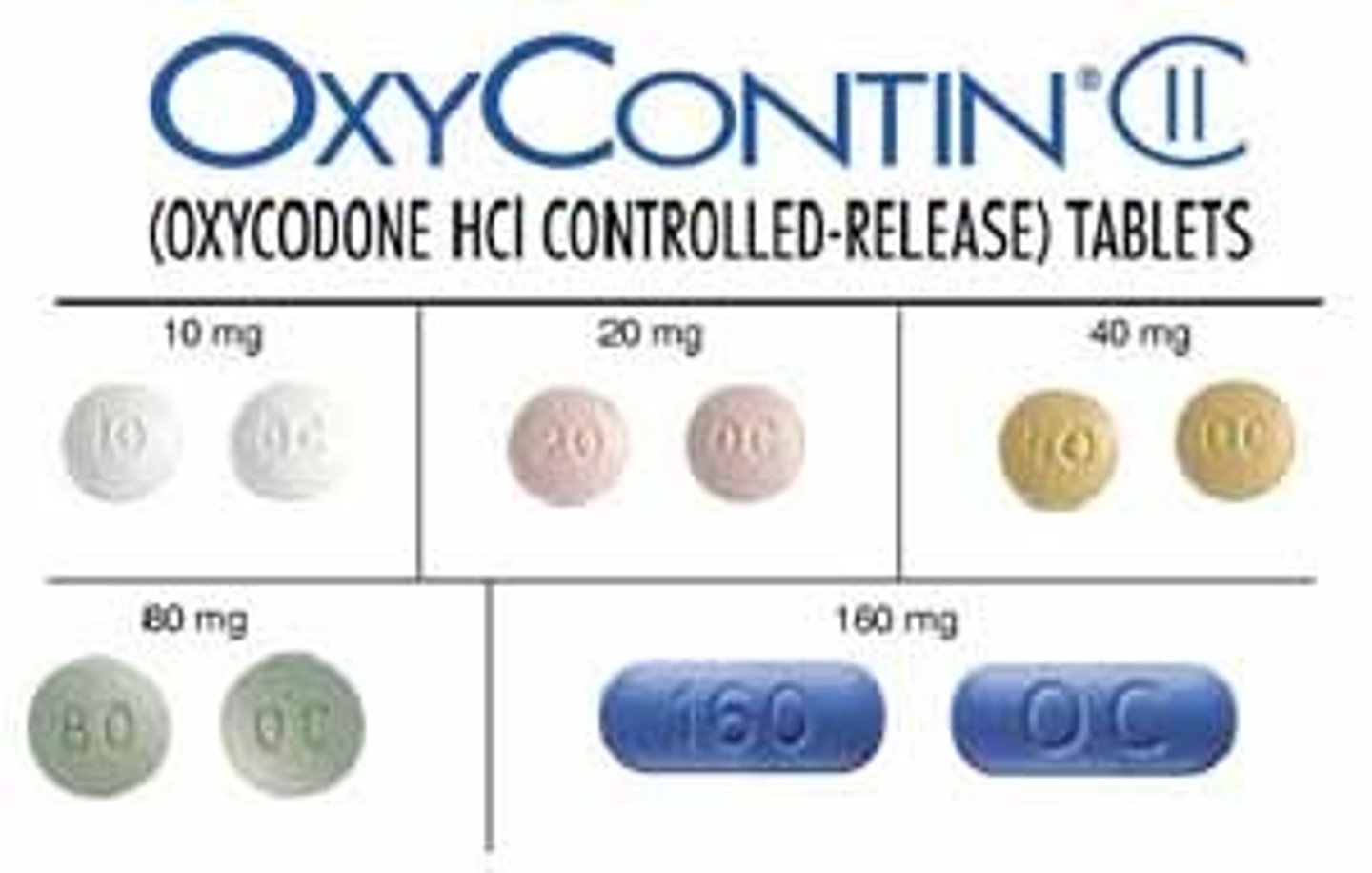
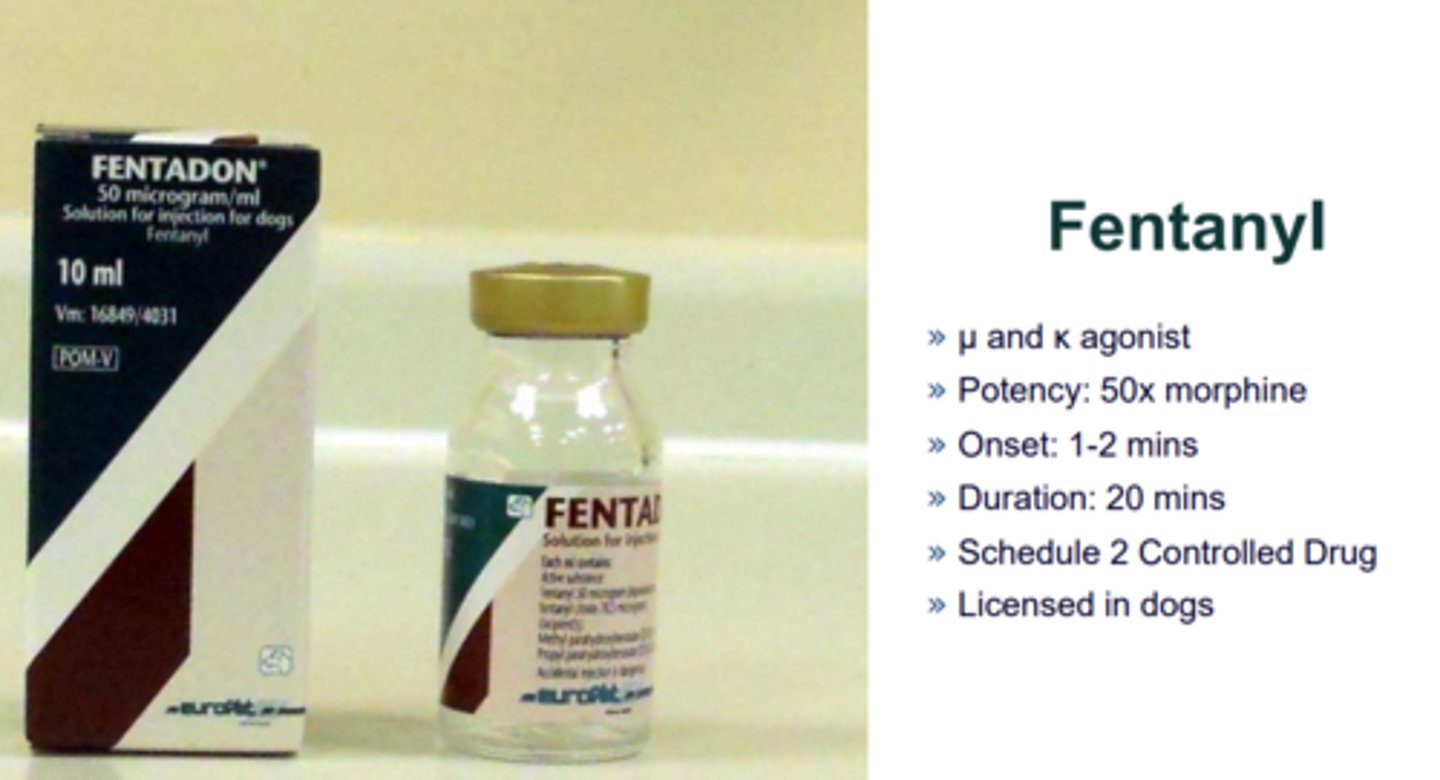
fentanyl
Extremely powerful opioid
Synapses that release acetylcholine are called _________ synapses.
cholinergic
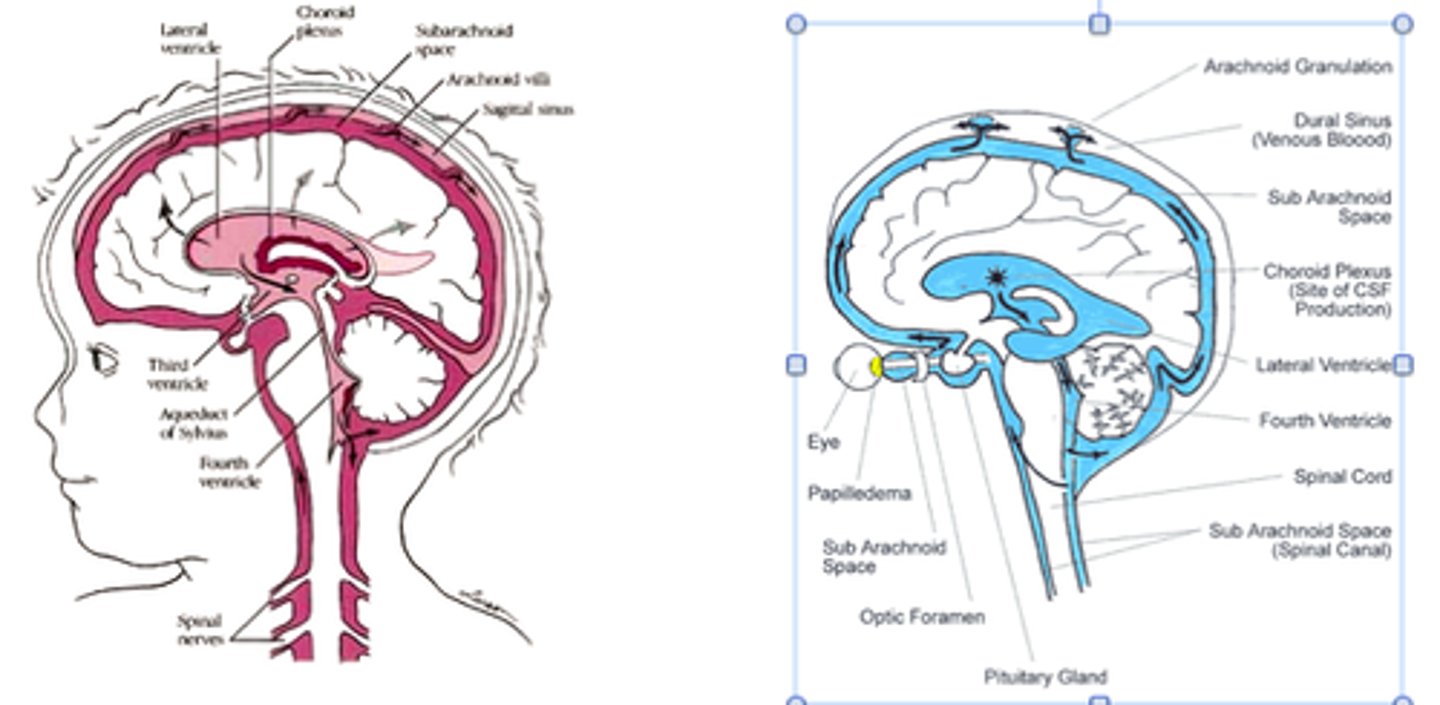
Cerebral-spinal fluid (CSF) circulates in which 3 areas of the CNS?
1) brain ventricles, 2) central canal of spinal cord, 3) subarachnoid space
Which nerve controls movement of the diaphragm, affects respiration, and results in hiccups when it spasms?
phrenic nerve
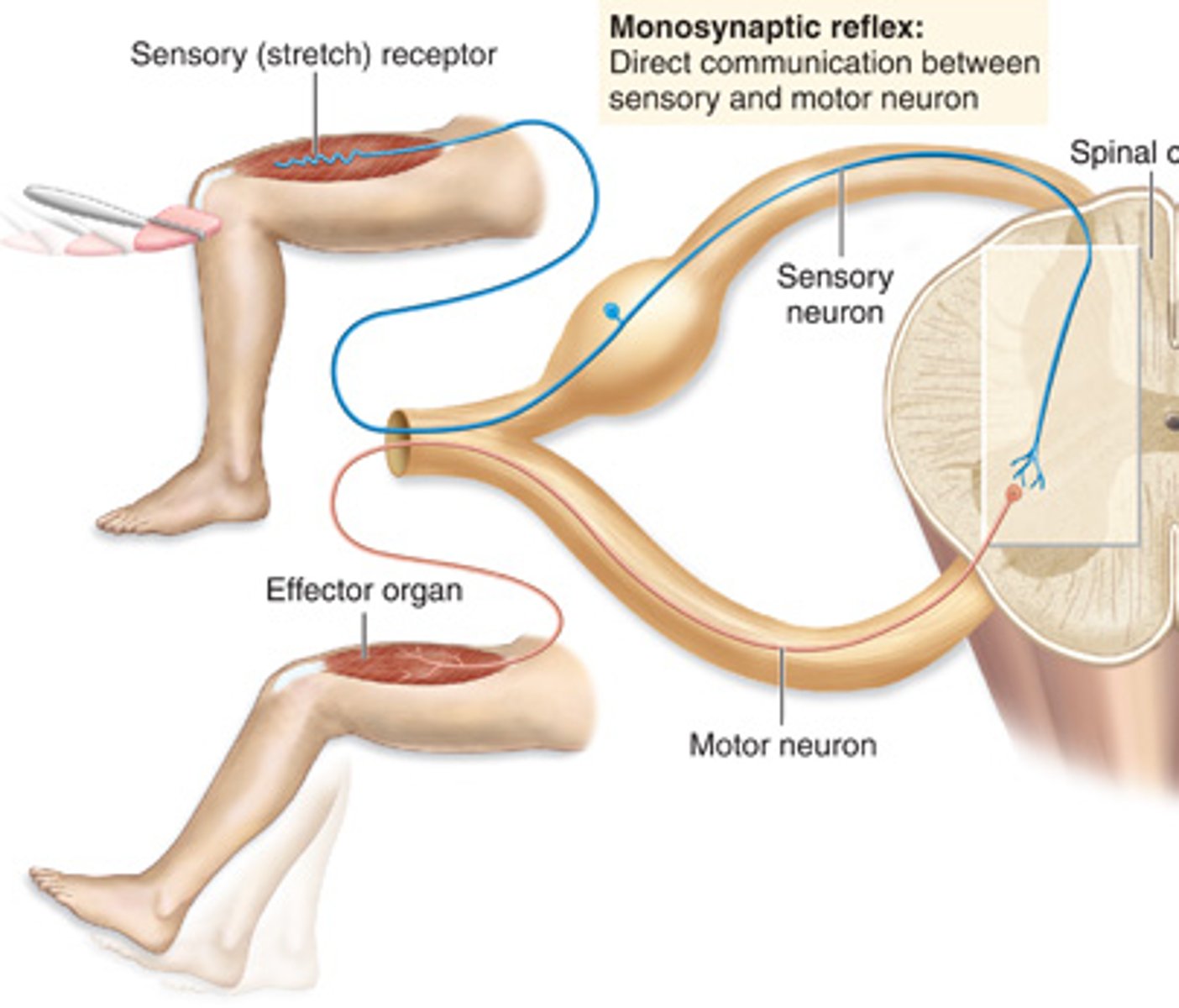
monosynaptic reflexes
-The simplest of all reflexes
-No interneurons
-The stretch reflex is an example (patellar or knee jerk reflex)
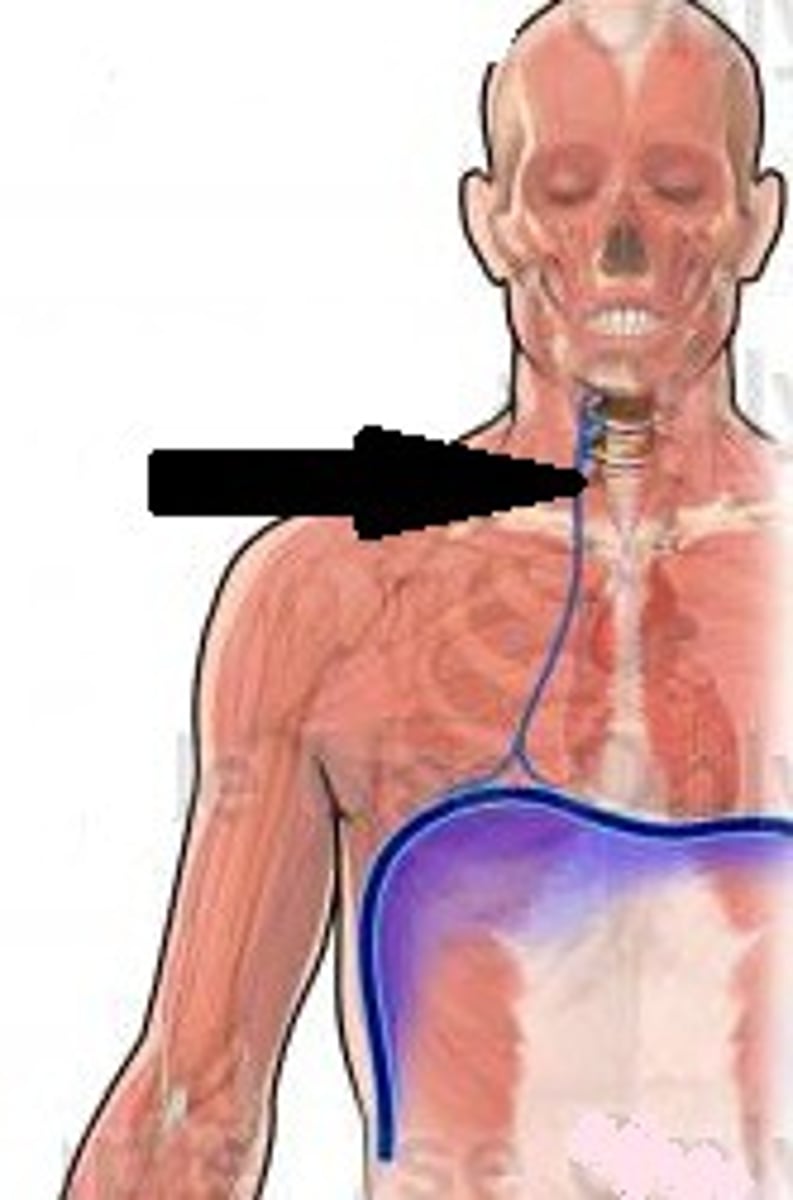
endorphins
released during exercise and blocks or inhibits pain

polysynaptic reflex
at least one interneuron between sensory neuron and motor neuron
Why are there so many opioid related deaths?
Because opioids affect the brainstem, which can result in depressed or slowed breathing
autonomic reflexes
regulate the activity of smooth muscles, the heart, and glands
action potential
Be able to label and discuss the steps of an action potential in a graph similar to this