lecture 20: drug solubility and dissolution rate 3.1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
our main interest is how to increase the solubility of class 2 drugs with low solubility in water but high permeability
class 2 can be used oraly or topically
what are the easiest ways to change solubility?
to use a drugs salt form
what are inclusion compounds?
also known as cyclodextrins
a way to bring a molecule into solution by inglobing it into its structure
results from the incorporation of the non-polar portion of one molecule into the non-polar cavity of another molecule that is water soluble
similar to micelles
reduce non-polar water interfacial area by inserting the solute(guest) into the complex agent(H2O)
what are the structures of cyclodextrins?
enzymatically modified starches
less toxicity therefore large range of use in the pharmaceuticals and delivery
composed of alpha beta or gamma rings (alpha-CD)
the outershell of all cyclodextrins is hydrophilic so can easily be dissolved in aqueous solution
inner circle in ring is non-polar/lipophilic, can accomodate non-polar molecules
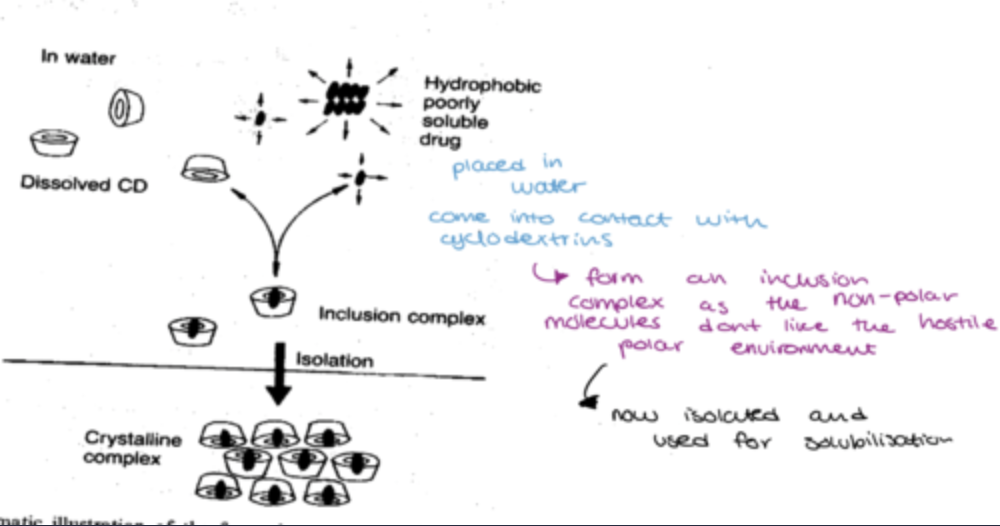
cyclodextrins in practice:
placed in water and come into contact with cyclodextrins
form an inclusion complex as the non-polar molecules dont like the hostile environment
now isolated and used for solubilisation
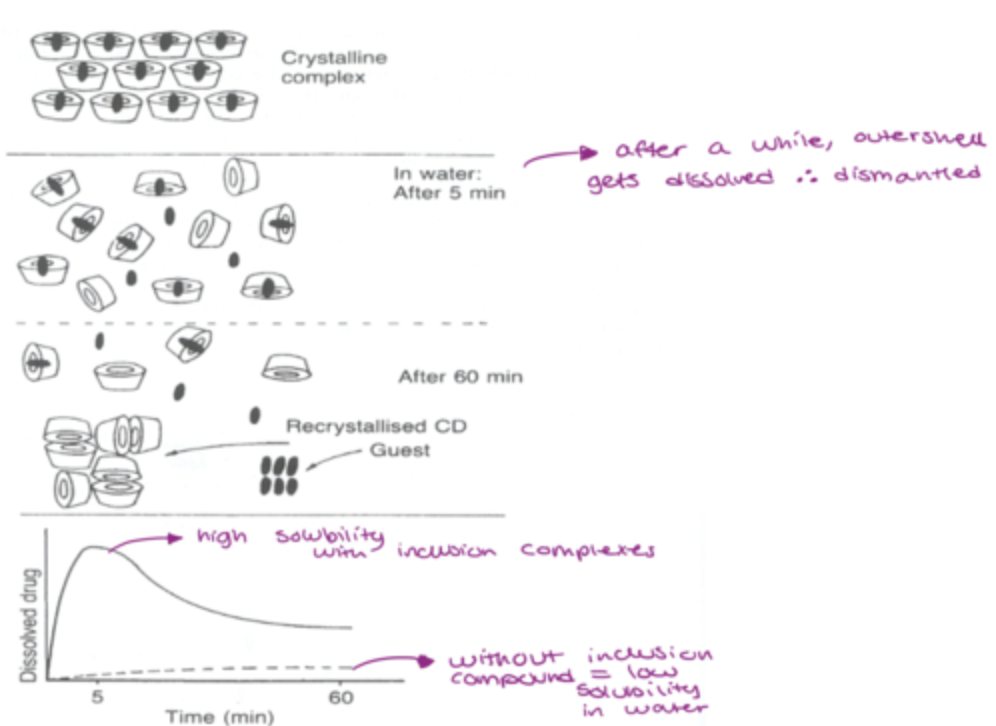
how is the crystaline complex solubilised in water?
overall faster and more complete release of drug when compared to mixtures without CD
have major advantages
what are some disadvantages of cyclodextrins?
di-o-methyl beta CD has strong affinity for cholesterol and is haemolytic(destuction of rbc) but is one of the best solubilisers for non-polar molecules
beta CD also find a way to be used as controlled-release of drugs
what is a surface active solute(surfactant)?
need to reduce surface tension without using large concentrations
in interface( when 2 different faces are touching eachother) there is a lot of surface tension
they increase miscibility between 2 faces therefore they can mix and get solubilized
reduces ST
what identifies as a surfactant?
highly polar head: important as it pulls aliphatic chain into the water
highly non-polar tail: aliphatic chains
hydrophilic/polar head: ionic or nonionic
lipophilic/ nonpolar chain
why is the polarity of the head important?
the bigger the difference in the polarity between the polar head and non-polar tail, the better the surfactant
if polarity isnt high, it will have to be improved
how can the hydrophilic lipophilic balance be observed in different regions and what does it determine?
surfactant solubility in water and oil
its applications
its place on the scale of hydrophile-lipophile balance also known as the HLB
hydrophilic and lipophilic moieties:
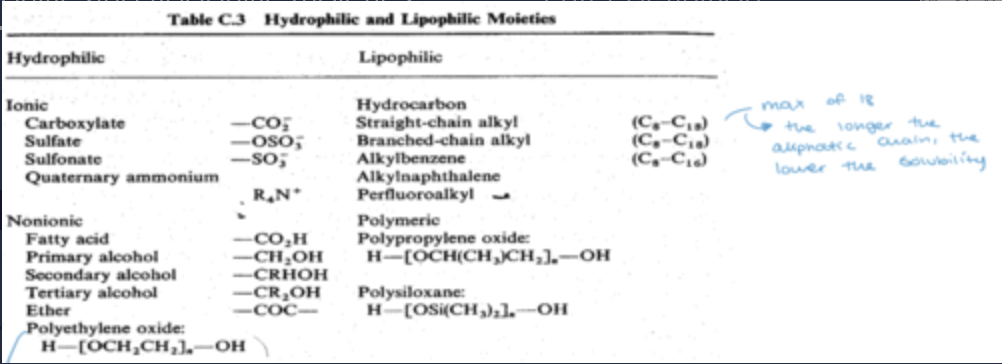
what is polyethylene oxide used for?
used to increase polarity of non-ionic surfactants by preparing a chain
its hydrophilic
what are features of the polar region?
affinity for water
capable of pulling long hydrocarbon chains into water
polar group must be sufficiently polar to hold the nonpolar region of the surfactant in solution
what are the classifications of surfactants: the charges carried by polar heads
anionic
cationic
non-ionic
zwitterion
different characteristics in terms of polarity
what are the properties of surfactants: micellisation?
surfactants at very dilute concentrations in water, act as normal solutes and disperse as a sub-colloidal solution(no reaction)
surfactants at concentrated solutions will self-aggregate and form micelles which contain 50+ monomers
their typical size is about 50 angstroms
depending on the size range theyre usually defines as colloidal
what is CMC?
critical micelle concentration- the concentration at which cells self aggregate(micelles form)
what is the aggregation number?
the number of monomers/surfactants that aggregate to form a micelle
what is the process of micellisation?
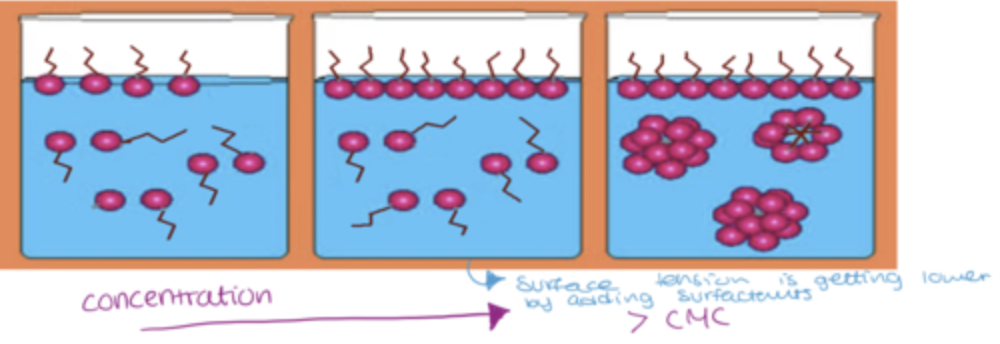
surfactants can adsorb at interface of water and air. bcs if you add surfactants to water there is no hindrance with the molecules of water due to similar properties
lipophilic non-polar tail(hydrophobic) will experience hindrance from water molecules. so waters around aliphatic chains pull out and create a void around aliphatic chain making the system very unstable
to stabilise the system, surfactants start adsorbing to the surface to excape aliphatic chain into the air to escape hostile environment
therefore are low conc theres no instability, but if you increase they will adsorb at the surface
if you add more surfactants, the phenomena of adsorption will not be enough to stabilise the system, so molecules try to self aggregate( this conc is called CMC)
place polar heads outside in contact with water and hide aliphatic chains inside, stabilising system
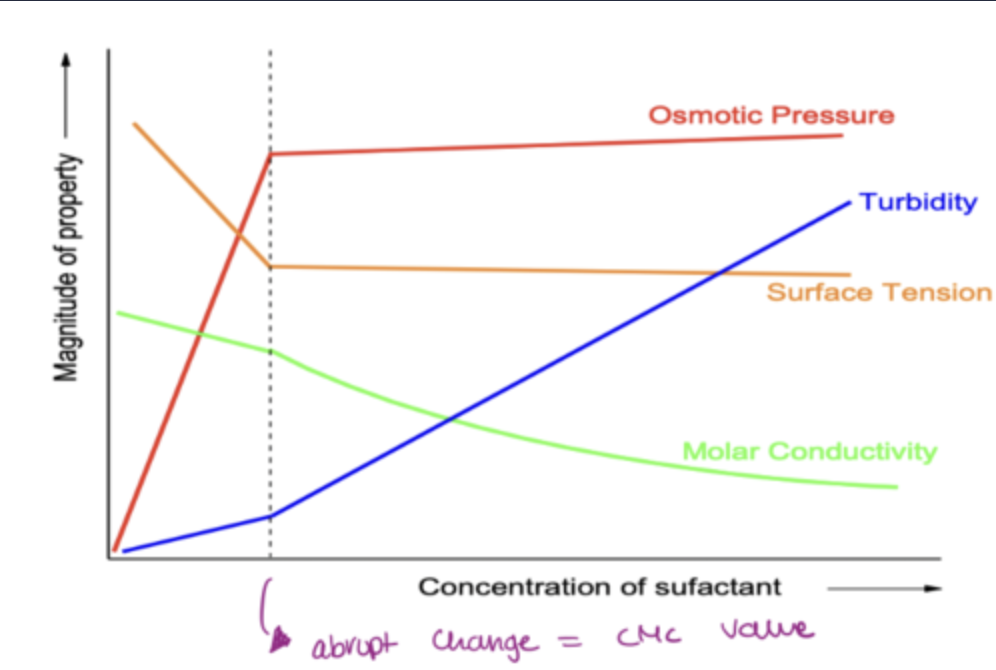
what are the several changes of the properties of the surfactants at CMC?
osmotic pressure
turbidity
electrical conductance
surface tension: once micelles form, surface tension wont change anymore as they have thermodynamically the most stable structure
CMC graph:
what are the factors that increase the CMC?
increases with increase in polarity of head group
what are the factors that decrease the CMC?
temperature - cloud point
pH(surfactants are weak electrolytes)
a second surfactant
addition of electrolytes and organic matter
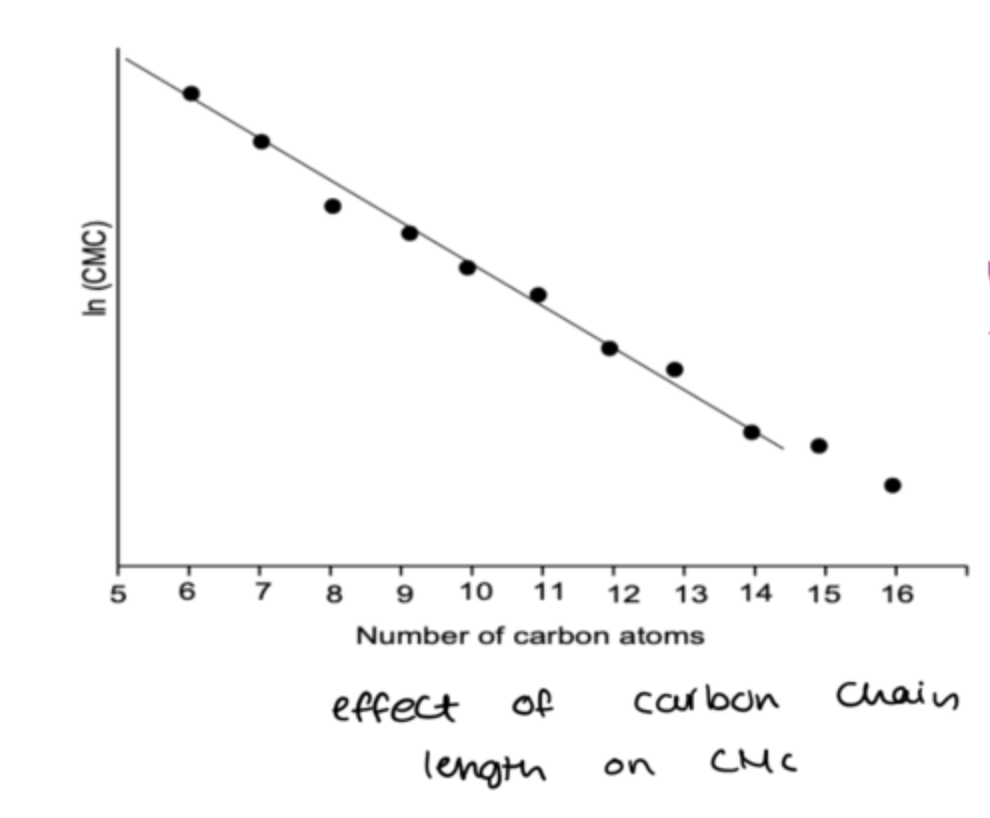
how does the length of carbon chain affect the CMC?
longer chain= stick together easier =system is thermodynamically unstable much faster= micellisation concentration occuring is smaller
what are the critical values for micelles?
CMC
kraft point( critical micelle temperature)
cloud point
critical micelle pH
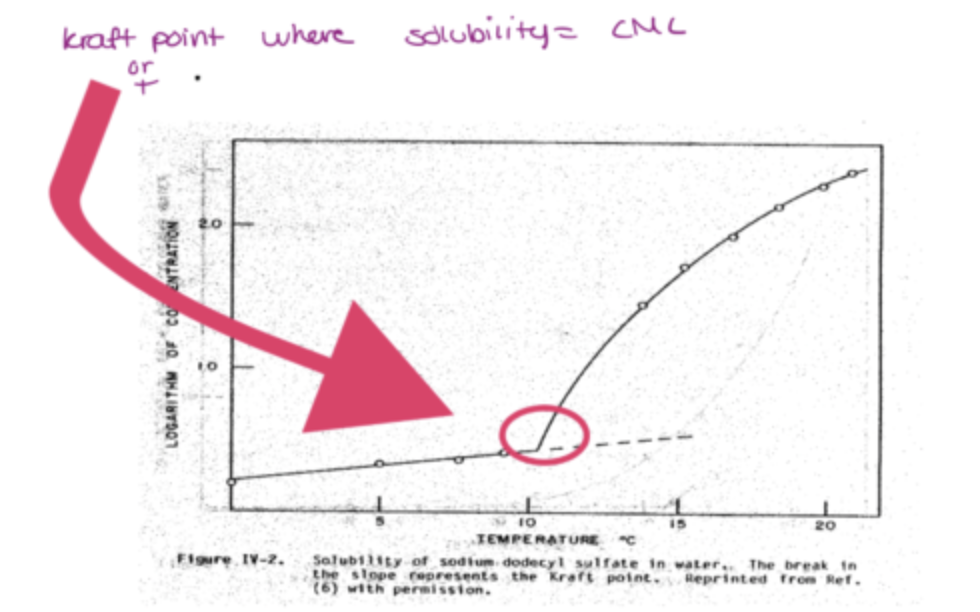
what is the kraft point?
below kraft point, cant form micelles
above kraft point, forms micelles
what happens when temperature is less than kraft point and when temperature is more than kraft point?
at t< kraft point, CMC is less than solubility therefore micelle cannot form
at T> kraft point, CMC is higher than solubility therefore micelles can form, self solubilization
unassociated surfactant has limited solubility
micelles= highly soluble= accomodate large amount of surfactant
what are key points about the kraft point graph?
increasing temperature increases solubility of surfactants
if you have micelle form, its a way of increasing solubilization
if you have surfactaants, they make a solution clear
when they become micelles, the solution becomes turbid
what is cloud point and what are its features?
RS between temperature and non-ionic surfactants
for nonionic, at the beginning if you increase temperature:
lower than cloud point = clear, cant form micelles
forms large micelles so the solution becomes cloudy, also known as cloud point
reversible:
if cooled down, small micelles form, the solution becomes clear
what is critical micelle pH?
some surfactants act as weak electrolytes therefor can be ionised as a function of pH
ionised form= surface active
unionised form=surface inactive(lower CMC)
change in pH induces micellisation
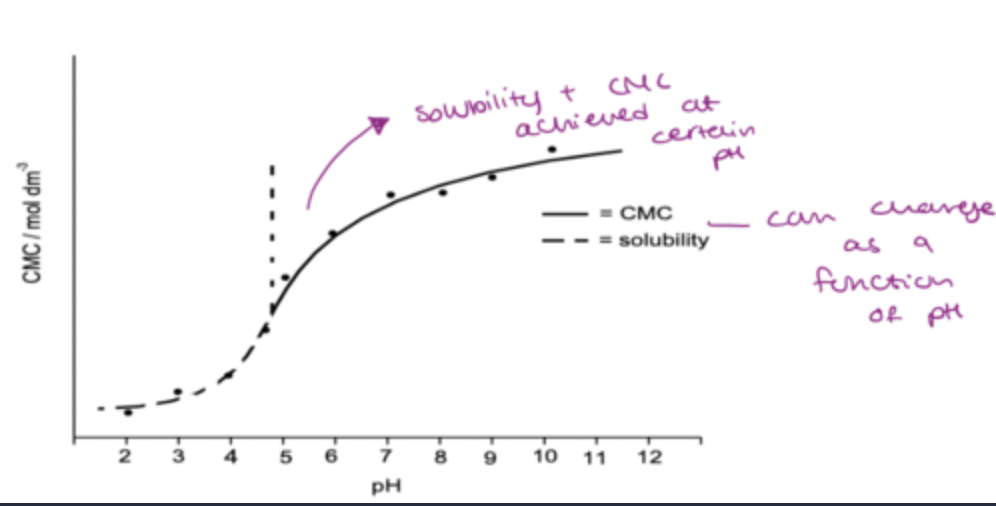
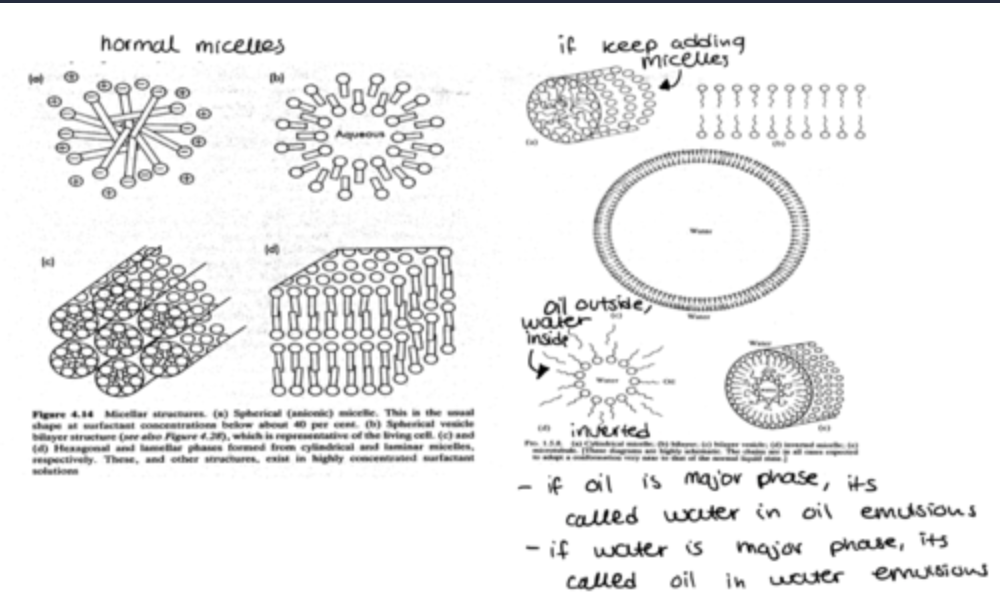
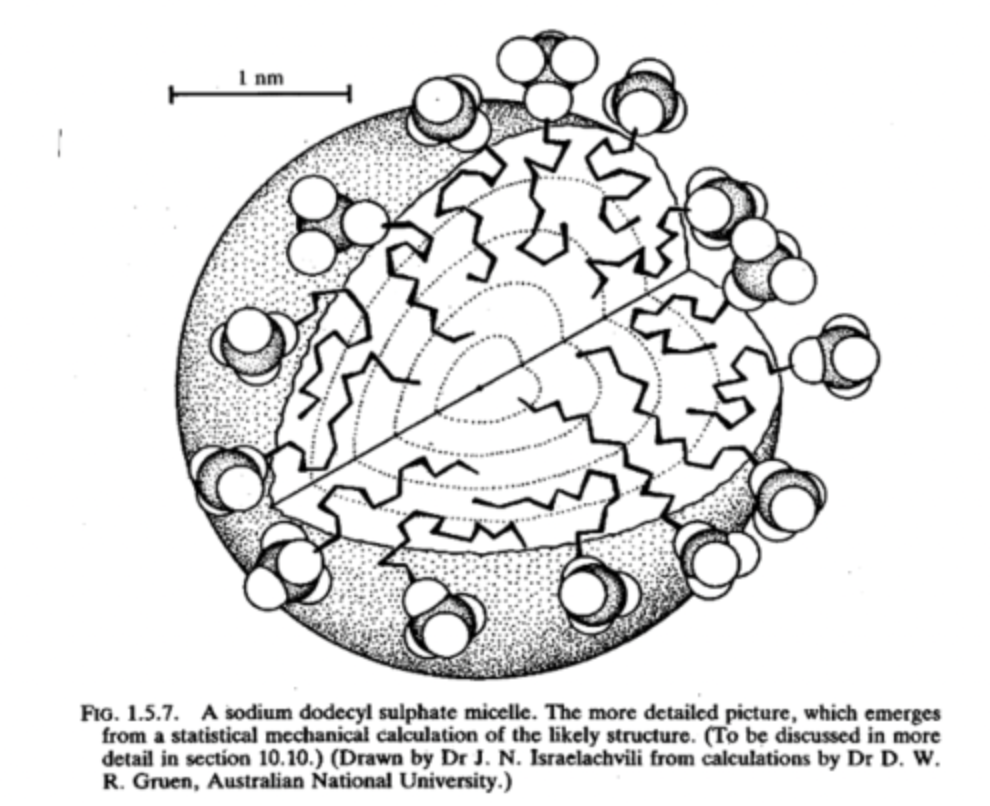
diagram of a micelle in polar environment:
n. of surfactants that make a micelle is aggregation number approx 50-100 monomers
what are the geometric properties of micelles?
At a high conc of surfactants:
Cylindrical rods, flattened disks
Liquid crystals (hexagonal phase, middle phase)
Lamellar phase (neat phase)
Bilayers
Vesicles
what are the different shapes of micelles?