ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY IN DENTISTRY
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
define environmental sustainability
environmental sustainability: meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
list some environmental threats
climate change
pollution
biodiversity loss
what has the IPCC said about the temperature of the earth
IPCC = The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
warned that the earth is at a tipping point
currently we are 1.1°C warmer than pre-industrial levels and reaching 2°C will significantly impact health and livelihoods
what was the 2015 Paris Agreement
legally binding agreement amongst 196 parties
overarching goal is to hold “the increase in the global average temperature to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels”
“limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels”
how will the Paris Agreement of 2015 be achieved
through reducing emissions and eventually reaching ‘net zero’
image of UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)

sustainability venn diagram

state the health effects of climate change
increase in cardiovascular and pulmonary disease
rise in infectious diseases
loss of life due to extreme weather events
increase in mental illness
reduction in oral health
how does climate change increase inequality
lower socioeconomic groups typically live in places more susceptible to extreme climate events
therefore lower socioeconomic populations will feel the greatest impact
what percentage of global net emissions does global healthcare make up
global healthcare = approx. 4.4% of global net emissions
equivalent to the emissions produced by the 5th largest country in the world
pie chart showing environmental impact of dentistry
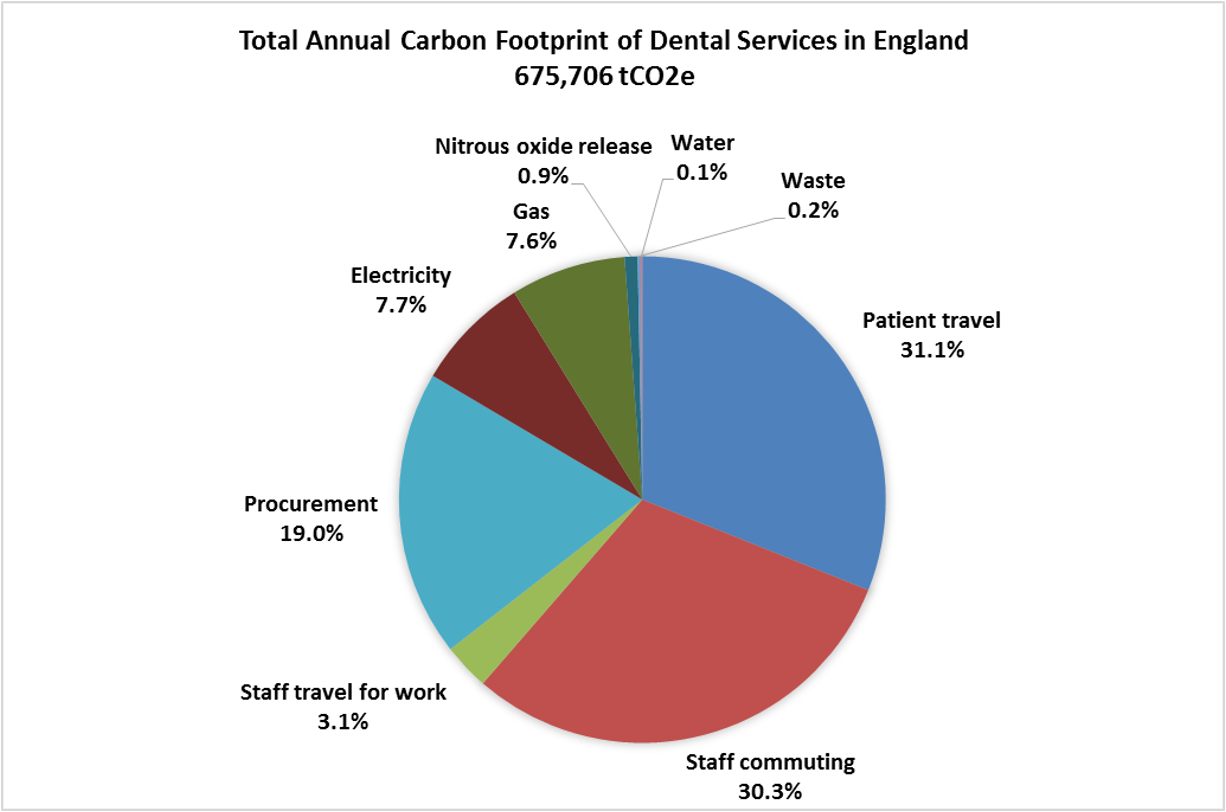
what are the 3 most significant contributors of dentistry to the environment and why
travel - patient, staff (∵ oral healthcare is typically provided in small, geographically dispersed practices)
procurement - instruments, materials, clinical items (∵ uses a lot of instruments, materials and energy)
energy use (∵ produces significant amounts of waste)
what dental clinical material is one of the most wasteful
single use plastics (SUPs)
what is the average number of SUP items used per procedure
35 SUP items per procedure - more if the additional PPE requirements during COVID-19 is accounted for
2 billion items of SUP waste per yr = 14.4 tonnes
1st, 2nd and 3rd dental materials with the greatest environmental impact and why
amalgam: metals that go into amalgam esp. mercury are harmful to the environment
resin based composite: uses a lot of energy in processing material and lots of packaging (also concerned about microplastic pollution associated with composite)
glass-ionomer cement: least environmental impact, much less energy and packaging used compared to composite
—
NEED TO CONSIDER MATERIAL LONGEVITY THOUGH (GIC does not last as long as composite/ amalgam)
what kind of dental procedures have the lowest environmental impact
simple, short procedures
assessments, preventive items of care
what kind of dental procedures have a moderate environmental impact
direct restorations
simple endodontic procedures
what kind of dental procedures have the highest environmental impact
treatments that require multiple visits thereby increasing travel, material and energy use
fixed and removable prosthodontics
complex endodontic treatment
orthodontics
those involving nitrous oxide
outline the Joint Stakeholder Statement made in 2022
wide range of stakeholders from academia, healthcare providers, industry and NGOs agreed to a consensus on environmentally sustainable oral healthcare
Colgate
Dentsply Sirona
HALEON
Tepe
strategy to achieve meaningful and measurable environmental outcomes across the oral healthcare supply chain
list characteristics of patients that would have a low environmental impact
good oral health
no active disease
no restorative interventions
low disease risk
—
low dental treatment needs
list characteristics of patients that would have a high environmental impact
poor oral health
failing dentition
active disease
extensive restorative history
high disease risk factors
—
high dental treatment needs therefore imperative to promote and maintain good oral health + preventive regime
outline the pillars/ types of care in the FDI sustainability toolkit
preventive care
operative care
integrated care
ownership of care
FDI sustainability toolkit: preventive care

FDI sustainability toolkit: operative care
high quality operative care reduces repair, replacement and waste

FDI sustainability toolkit: integrated care
integrated healthcare services with patients as co-managers of their care mitigates environmental impacts
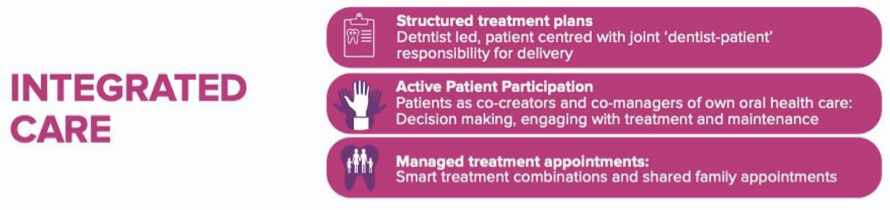
FDI sustainability toolkit: ownership of care

outline strategies to reduce the environmental impact of travel
promote and encourage active travel or public transport/ car sharing
reduce appointments by performing multiple procedures in one visit
engage with remote clinical consultations and digital dentistry
centralised care delivery where possible
optimise practice logistics - family appointments, effective scheduling and transport between laboratories
what parts of the supply chain contribute to the environmental impact of procured goods
sourcing of raw materials
manufacturing
packaging
distribution
procurement
waste management
» linear economy, need to move to a circular one
outline strategies to reduce the environmental impact of procurement
purchase durable equipment that will last and are easy to maintain
effective stock management - only order what is necessary, avoid waste
engage with suppliers to assess their sustainability practices
select fit for purpose dental materials, clinical items and equipments
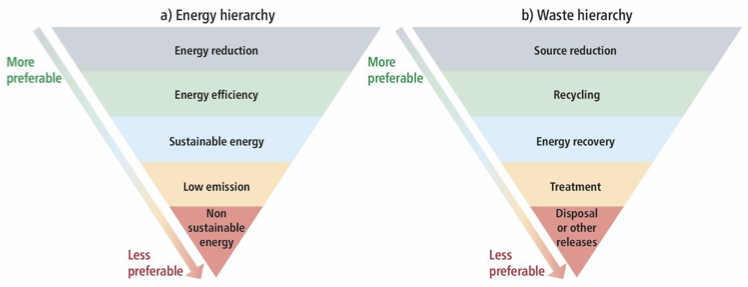
outline strategies to reduce the environmental impact of energy and water consumption
use energy efficient appliance e.g. LED lights, washer disinfectors
turn off tap when brushing
use appliances when fully loaded
consider renewable energy sources
outline strategies to reduce the environmental impact of waste management
4R’s: reduce, reuse, recycle, RETHINK
segregate waste accordingly
follow waste disposal regulations for hazardous materials
reduce medicinal waste through evidence-based prescribing
reduce plastic waste where possible
energy and waste hierarchy diagrams
outline strategies to reduce the environmental impact from dental materials
minimise amalgam use in line with the Minamata Convention
reduce nitrous oxide use for relative analgesia/ inhalation sedation
reduce gypsum use for dental casts (gypsum can be recycled)
recover and recycle dental materials where possible
use digital radiography
mindset and arithmetic

environmental sustainability should form a part of…
your clinical thinking alongside:
delivering high-quality care
patient safety
ethics
finances
what should environmental sustainability be considered alongside
clinical effectiveness (of a therapy)
what methods of caries prevention are (not) environmentally sustainable
water fluoridation
supervised toothbrushing
fluoride varnish
what renowned document should be taken into account from an environmentally sustainable perspective
HTM 01-05