Animal Behavior Quiz 12
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Polygyny
male with multiple mates
Polygynandry
female with multiple mates
What shapes mating systems? (evolutionary forces that mold mating systems)
1) Differential Parental Investment
2) Needs of young and potential help by mate
3) Certainty of paternity
4) Environmental potential for polygamy
Differential parent investment (arising from anisogamy)
sexual differences parental investment
male RS limited by matings
female RS limited by resources
Basic sexual difference leads to a higher potential for males to mate multiply
Needs of young & potential help by male
altricial - highly dependent
precocial - not as dependent
determines the degree to which males and females can maximize RS
either spend a lot on care or on mating
Certainty of paternity
males certain of paternity are more likely to stay to help
External vs internal fertilization
external : synchronization of egg laying and mating
internal : separation in time of egg laying and mating
Environmental potential for polygamy
degree to which one sex can monopolize access to the other
Extent of monopolization dependent on social and ecological factors that affect distribution of females
1) Spatial distribution (uniform/clumped) - where located
2) Temporal distribution (asynchronous/synchronous) - when fertile
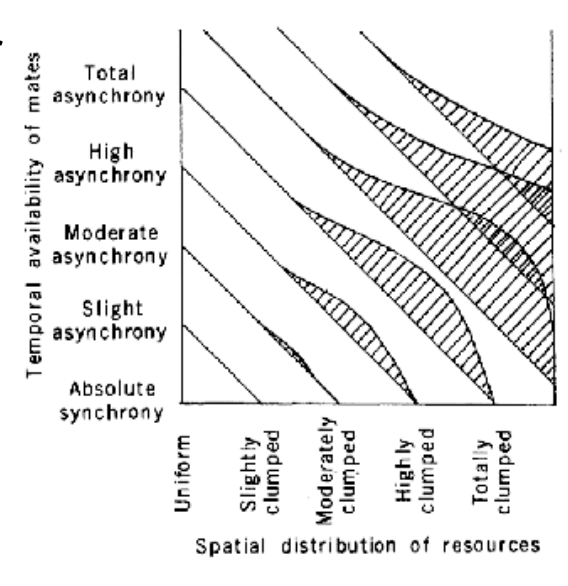
Height of bars = potential for polygany
x axis : spatial distribution of males
uniform (evenly spread out)
totally clumped (all together)
when all clumped, can monopolize more females
y axis: temporal availability of mates
Absolute synchrony : all females receptive at once
Total asynchrony : females become receptive at diff times
if all females synchronous, single male cannot mate with many at once
if females asynchronous, one male can mate with multiple females → increase polygany potential
What is the ideal for polygany
moderate asynchronous and clumped
clumped : multiple females in on area
moderate asynchrony : staggers female receptivity just enough for a single male to mate with several females
efficiently monopolize access to multiple mates in both space and time
Why monogamy?
1) Female Dispersion
2) Mate assistance monogamy
3) Mate guarding monogamy
Female Dispersion
one of best predictors of monogamy
when females live separately and widely dispersed, males cannot dominate or defend more than one
Mate assistance monogamy
if involvement of both parents needed to raise baby → expect monogamy
parental care sometimes essential for offspring survival
Emperor Penguins
parents take turns going to sea for fish
Hamsters
males pull offspring out of birth canal
Example of mate assistance monogamy (Starlings)
parental care sometimes significantly increases offspring survival
incubating by males keep temp high and stable
males treated with anti-androgen → provided more food, males treated with T → less food
Males can increase fitness if stay home to take care of babies
Mate guarding monogamy
prevent female from mating with others
if females are
receptive after mating
hard to encounter
males can stick around and mate guard → monogamy
Why is monogamy rare in mammals (<10%)?
Delayed Fertilization
males have low confidence of paternity
Female biased parental care
internal gestations
only females can care for young during early egg stage
Female only feeding
care for newborns in a way that males cannot
Some exceptions : males bring food
Why is (social) monogamy common in birds (>90%)
Delayed Fertilization
males have low confidence of paternity but…
Both sex parental care
external gestation
one egg laid, male can care for them as well as female
Both sexes feed
Why do females engage in multiple matings? (costs)
STDs/ infection
primates (41 species)
# of males typical of species and correlated w/ white blood cells (measure of immune system readiness)
What benefits counter costs of mating multiply?
1) fertility insurance
2) good genes
3) genetic compatibility
4) infanticide reduction
Fertility insurance
increasing the chance of having all eggs fertilized
EX
increase hatching of eggs in multiply mated - red wing blackbirds
Good genes
Trading up mating w/ genetically superior males
assortative parenting - mating w/ similar rank
EX
blue tit females solicit EPCS only from higher quality males
yellow toothed cavy females increase offspring survival when mating multiply
What are male options? why stick around and care for youn that might not be yours
good for males if they are the one to get EPCS
can be best of bad situations
Genetic compatibility
Genotype matching
females prefer males w/ dissimilar immune system
in blue throat - nest environment was held constant → extra pair youn stronger immune system than within pair young
Infanticide reduction
confuse males abt paternity, so infanticide less likely
Four types of polygyny
Scramble competition
Female Defense
Resource Defense
Leks
Scramble competition
distributed widely - scramble for access to females
what do females get out of this?
males of highest quality most likely to mate
NO CHOICE
Female defense
males gain access to females directly by keeping rivals away
huge variation in mating success among males
ex) southern elephant seals
Why do females stick together?
benefits of grouping outweigh breeding solitarily
various group benefits (reduce predation, increase foraging success)
Resource Defense
Males gain access to females indirectly by monopolizing access to resources that are valuable to females
ex)
water striders
floating leaves (oviposition)
African cichlids
guard shells (oviposition)
What do females get out of this
good territory, food, oviposition, protection
Polygyny threshold model
Is polygyny best for females
ex) pied flycatchers
females in polygynous relationship often have reduced fitness as result of sharing the male
Why be secondary female when OSR typically male biased?
benefit depend on variation in territory and male quality
Process of polygyny threshold model
males arrive first and settle
females arrive sequentially
1st female goes to best territory
2nd goes to next - best territory
when does it benefit females to join as seconday females
weigh btwn : male’s undivided care
versus male/territory quality
the point where it pays to go to an already occupied territory = polygyny threshold
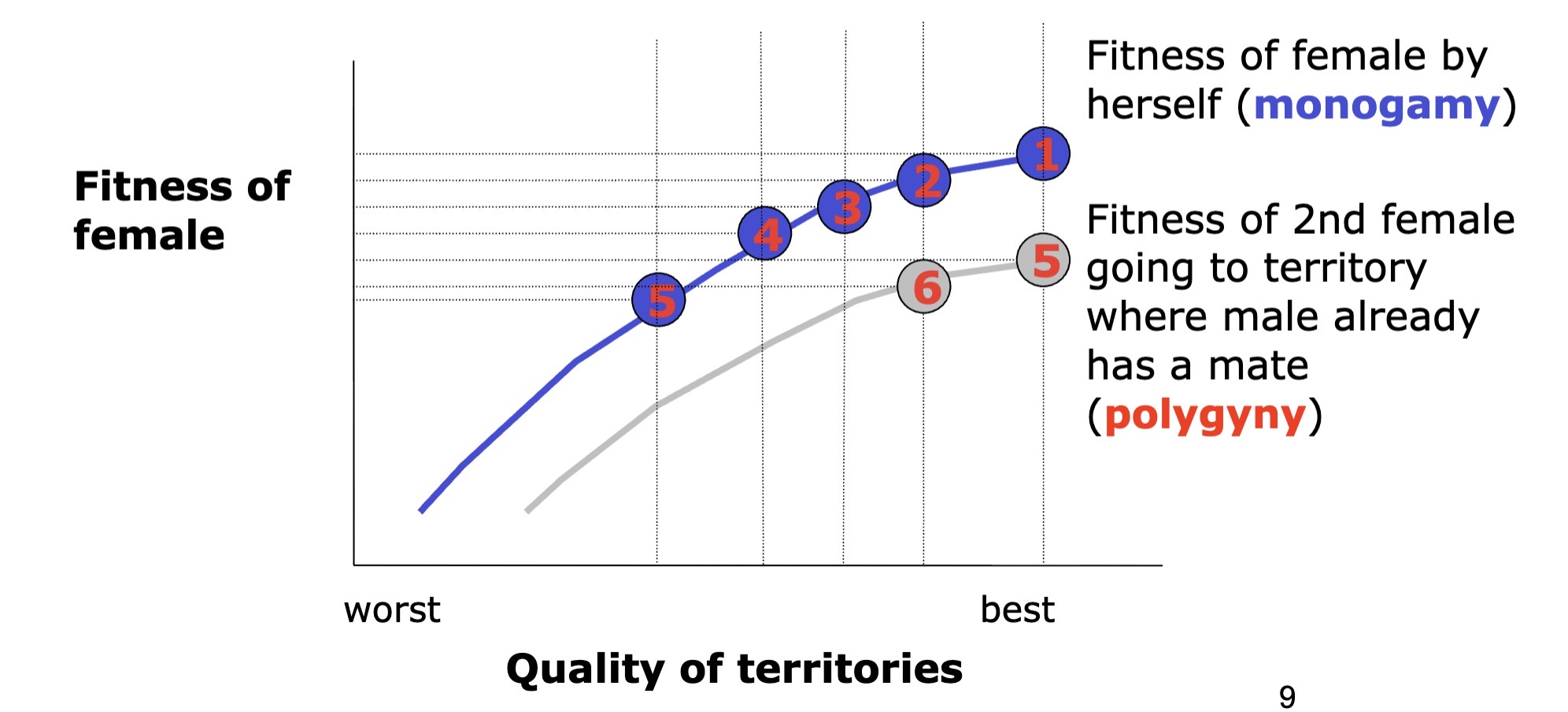
its all abt individual decision
each female decides what is best for her
variation in habitat quality leads to polygyny
Lek polygyny
an area where males that provide no parental care, strut their stuff and attract males but don’t defend any resources (other than display site)
Why are leks rare
lack of parental care is rare in birds
resources are usually monopolizable
Question remains: in a system with no direct benefits and widely dispersed females, you usually have scramble competition. Why do leks evolve sometimes?
NO CLEAR ANSWER
Where leks from
1) hotspots - males congregate around areas that females pass through
2) hot shots - males congregate around superior individuals
Lek paradox: how genetic variation maintained
when selction is very strong only a few individuals will contribute genes to next gen
when most everyone in next gen have same dad, will be genetically similar - so there won’t be much genotypic variation after few gens
what benefit is there to females in exhibiting choice
two ways genetic variation maintained HYP 1
Hypothesis 1: genic capture (polygenic effects -many genes effect a trait)
sexually selected traits often have differential costs (handicaps) and ability to pay costs depends on overall physiological conditions
bc overall condition is influenced by many genes, huge target where genetic variation can arise
wo ways genetic variation maintained HYP 2
Hypothesis 2: Red Queen
long term environmental (biotic) shifts may favor diff traits over time
what is best now may be difference in future - due to red queen cycling
leading to constant benefits to rare genotypes