[RMT0 12] PRELIM: Lesson 3
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Anatomical Position
Initial point of reference to accurately describe location and direction
Body is erect and facing forward, feet slightly apart and arms at the side with palms directed forward.
Anatomic Directions
Anterior (Ventral)
Posterior (Dorsal)
Medial
Lateral
Proximal
Distal
Superior
Inferior
Cephalad
Caudad
Superficial
Deep
External
Internal
Parietal
Visceral
Ipsilateral
Contralateral
Palmar
Plantar
Dorsum / Dorsal
Anterior (Ventral)
Refers to forward or front part of the body or forward part of an organ
Posterior (Dorsal)
Refers to back part of a body or organ
Medial
Refers to parts toward the median plane of the body
Lateral
Refers to parts towards the side or away from the median plane of the body
Proximal
Refers to parts nearer to the point of attachment or to a given reference point
Distal
Refers to parts farther from the point of attachment or from a given reference point
Superior
Refers to nearer the head or situated above
Above, in a higher position
Inferior
Refers to nearer the feet or situated below
Below, in a lower position
Cephalad
Refers to parts toward the head of the body
Caudad
Refers to parts away from the head of the body or toward the lower end of the spine
Superficial
Refers to parts near the skin or surface of the body
Deep
Refers to parts far from the surface
External
Refer to parts outside an organ or on the outside of the body
Internal
Refer to parts within or on the inside of an organ.
Parietal
Refers to the wall or lining of a body cavity
Visceral
Refers to the covering of an organ
Ipsilateral
Refers to a part or parts on the same side of the body
Contralateral
Refers to a part or parts on the opposite side of the body
Palmar
Refers to the palm of the hand
Plantar
Refers to the sole of the foot
Dorsum / Dorsal
Refer to the top or anterior surface of the foot, or to the back or posterior surface of the hand.
Body Planes
anatomical planes that divide the body into sections
three main ___ are the sagittal, coronal, and transverse planes
Sagittal Plane
longitudinal line that divides the body into right and left portion
Coronal / Frontal Plane
longitudinal line that divides the body into anterior and posterior portion
Horizontal / Axial Plane
horizontal line that divides the body into superior and inferior portion
Body Cavities
A space created in an organism which houses organs
Functions:
Protect delicate organs
Allow organs to change shape and size
Two Main Cavity of the Body:
Dorsal Cavity
Ventral Cavity
Dorsal Cavity
Cranial Cavity
Vertebral Cavity
Cranial Cavity
Area within the skull and encloses the brain
Vertebral Cavity
Encases the vertebral column and spinal cord
Ventral Cavity
Thoracic Cavity
Abdominopelvic Cavity
Thoracic Cavity
Left and right pleural cavity (lungs)
Contains the pericardial cavity (heart)
Mediastinum separates the three cavities
Abdominopelvic Cavity
Subdivided into superior and inferior ___ cavity
Superior ___ Cavity
Inferior ___ Cavity
Superior Abdominopelvic Cavity
Contains stomach, liver, spleen, kidneys, small and large intestine
Inferior Abdominopelvic Cavity
Contains the bladder and internal reproductive organs
Quadrants of Abdomen
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
Right lobe of liver, gallbladder, right kidney, portions of small and large intestines
Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
Cecum, appendix, portions of small and large intestines, reproductive organs (right ovary in female and right spermatic cord in male), right ureter
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)
Left lobe of liver, stomach, pancreas, left kidney, spleen portions of small and large intestines
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
Most of small intestine, portion of large intestine, left ureter, reproductive organs (left ovary in female and left spermatic cord in male)
Regions of Abdomen
Right Hypochondriac
Epigastric Region
Left Hypochondriac
Right Lumbar
Umbilical Region
Left Lumbar
Right Iliac
Hypogastric Region
Left Iliac
Right Hypochondriac
Liver, Gallbladder, Right Kidney, Small Intestine
Epigastric Region
Stomach, Liver, Pancreas, Duodenum, Spleen, Adrenal Glands
Left Hypochondriac
Spleen, Colon, Left Kidney, Pancreas
Right Lumbar
Gallbladder, Liver, Right Colon
Umbilical Region
Umbilicus (navel), parts of the small intestine, Duodenum
Left Lumbar
Descending Colon, Left Kidney
Right Iliac
Appendix, Cecum
Hypogastric Region
Urinary Bladder, Sigmoid Colon, Female Reproductive Organs
Left Iliac
Descending Colon, Sigmoid Colon
Body Positions
Prone
Supine
Erect
Recumbent
Dorsal Recumbent
Ventral Recumbent
Lateral Recumbent
Seated
Trendelenburg
Fowlers
Lithotomy
Sim’s Position
Knee-chest Position
Jackknife Position

Prone
Lying on abdomen facing downward (head may be turned to one side)

Supine
Lying on back
Erect
Upright position to stand or sit
Recumbent
Lying down in any position (prone, supine, lateral)

Dorsal Recumbent
Lying on back (supine)
Ventral Recumbent
Lying face down (prone)
Lateral Recumbent
Lying on side (right or left)
Seated
Upright position in which the patient is sitting on a chair or stool.
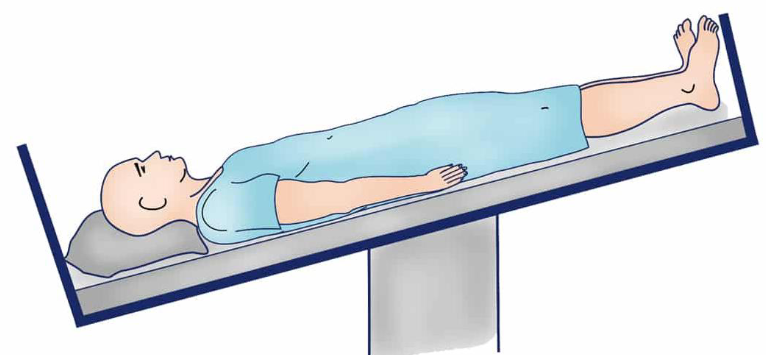
Trendelenburg
Supine position with the head tilted downward
Head lower than the feet
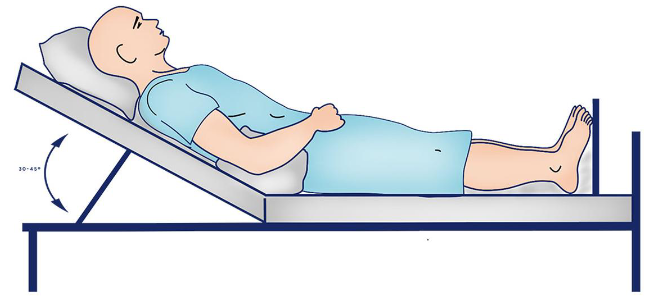
Fowlers
Supine position with the head higher than the feet.
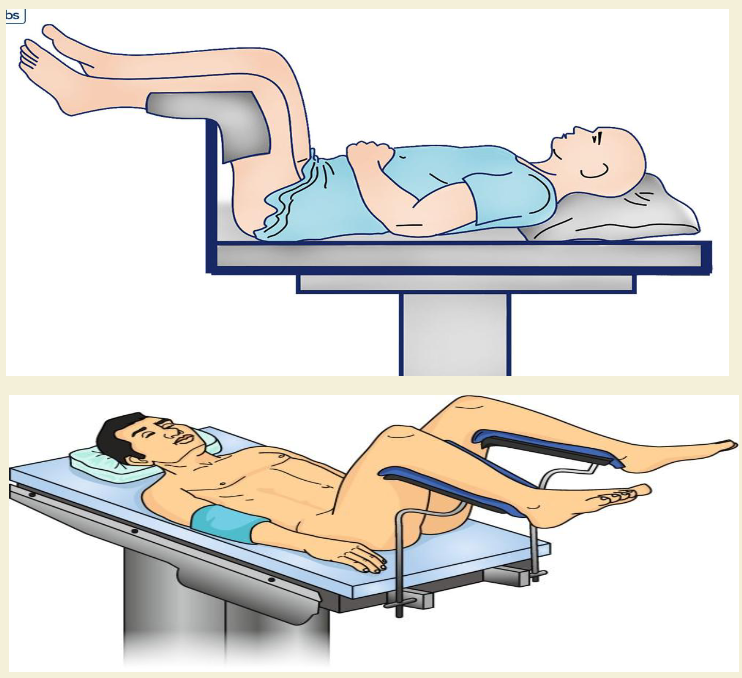
Lithotomy
A supine position with the knees and hip flexed and thighs abducted and rotated externally, supported by ankle supports.
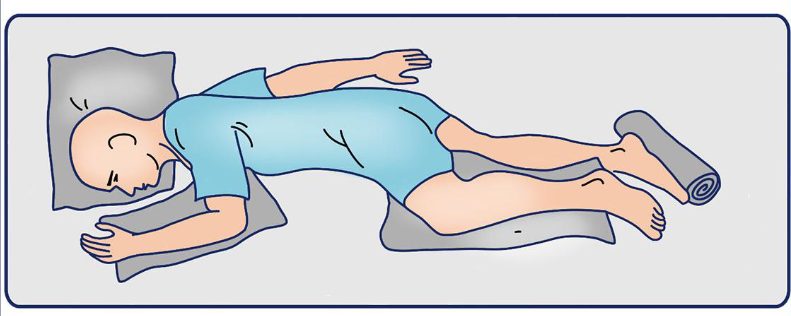
Sim’s Position
A recumbent position with the patient lying on the left anterior side (semiprone) with the left leg extended and the right knee and thigh partially flexed.
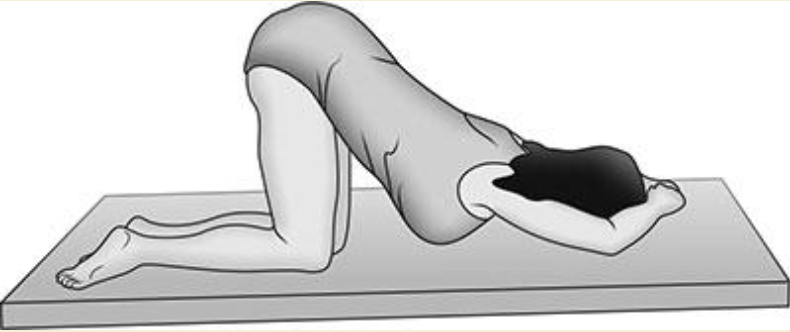
Knee-chest Position
Position where the knees are as closes as possible to the chest
Jackknife Position
On back with shoulder elevated, legs flexed and thighs at right angles to the abdomen
cephal/o
head
cervic/o
neck
thorac/o
chest, thorax
-tomy
incision
abdomin/o
abdomen
celi/o
abdomen
centesis
puncture
lapar/o
abdominal wall
lumb/o
Lumbar region, lower back
periton, peritone/o
peritoneum
acro
extremity, end
brachi/o
arm
dactyl/o
finger, toe
ped/o
foot
pod/o
foot
circum-
Around
peri-
around
orbit
eye socket
intra-
in, within
vascul/o
vessel
epi-
on, over
extra-
outside
infra-
below
scapula
shoulder blade
sub-
below, under
lingu/o
tongue
inter-
between
cost/o
ribs
juxta-
near, beside
para-
near, beside
retro-
behind, backward
supra-
above
patella
kneecap