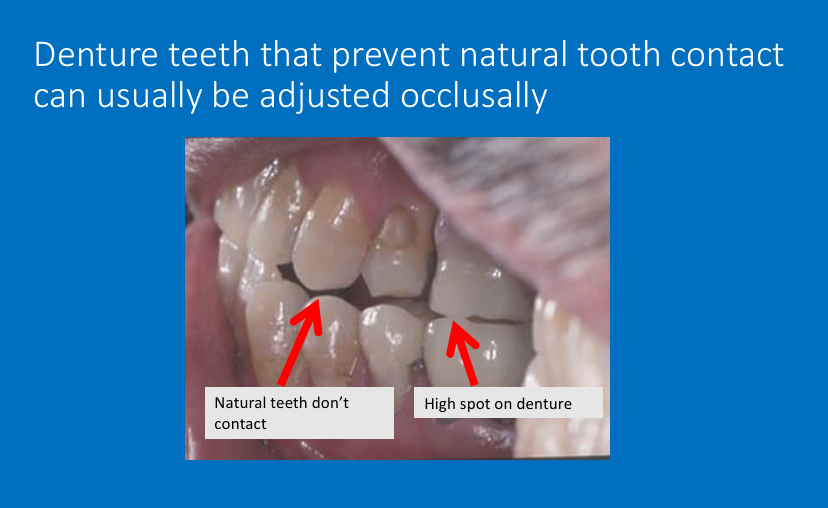
Jaw registration and occlusion in partially dentate patients
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is meant by jaw relationship? what are the 2 components?
3D spatial relationship between the upper and lower jaws or teeth
Both a vertical and a horizontal component
What is important when choosing an occlusal relationship?
Choose an occlusal relationship that is reproducible in the patient so that it is kept the same throughout all stages of making a denture
What joint allows the mandible to move?
TMJ - temporomandibular joint
mandibular movements can be vertical and horizontal explain more?
Vertical - liek a door opening and closing around a hinge
Horizontal - moving forwards and backwards and also side to side
what is the name given to these mandibular movements?
dynamic movements
What is the difference between dynamic movements and dynamic occlusion?
if the teeth are in contact during movements - dynamic occlusion
What 4 things work together to limit how much the mandible can move?
Teeth
Ligaments
TMJ
Facial muscles
What are border movements?
The outer limits of mandibular movements
What is a hinge axis?
A straight line through the heads of both condyles
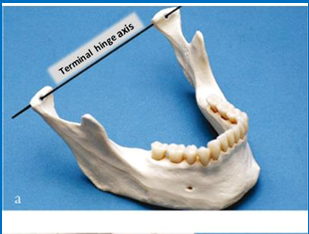
When does the mandible open and close around this ‘hinge’?
When the mandible is retruded - centric relation/retruded contact position
What does Posselt’s envelope or Posselt’s diagram represent?
mandibular border movements as it moves in the sagittal plane
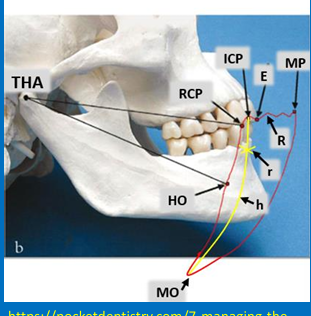
What is ICP?
The tooth position where there is most tooth-tooth contact (mainly referring to the posterior teeth)
centric occlusion vs centric relation
Centric relation - Retruded contact position RCP
Centric occlusion - ICP - intercuspal position

Changes in ICP during treatment?
Patients an adapt to small changes in their ICP
Large changes in restorative treatment - test changes first to make sure patient can cope
What is the complete definition of RCP

What is the relationship between ICP ad RCP?
A slide from the initial tooth contact in RCP to the maximum contacts in ICP
1.24 ± 1mm
forwards slide but may have a lateral component
ICP and RCP are in the horizontal position

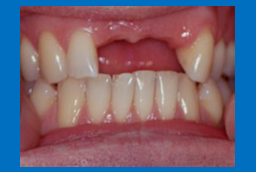
What occlusion will you use for this patient?
for partial dentures, in this case you can use the natural teeth as a guide to denture tooth position
there is a reproducible ICP
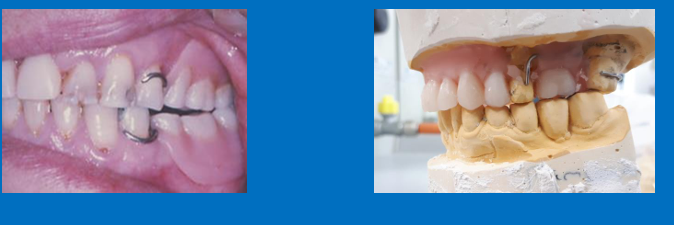
What occlusion is used here and why?
The vertical dimension can be determined by the natural teeth
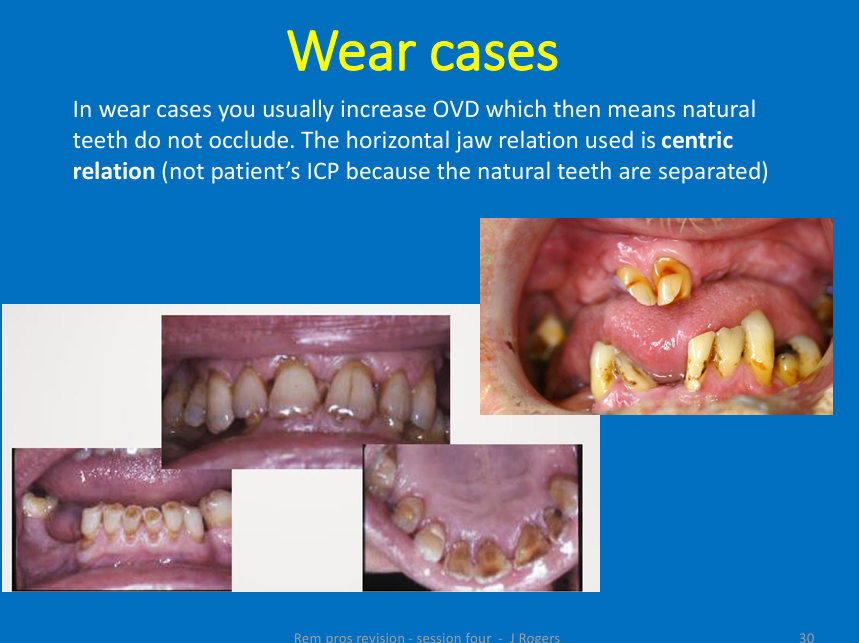
there are not enough inter-cuspating posteriors to determine the mandibular horizontal position so you use RCP - centric relation
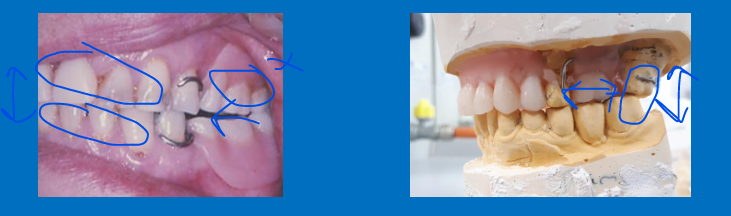
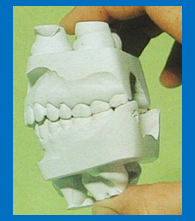
How can these casts be articulated? (2)
Can be hand articulated
to mount these casts on an articulator all you need is a face bow
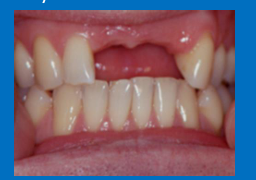
How would you articulate this cast?
Can be hand articulated as well
so all you need is a facebow
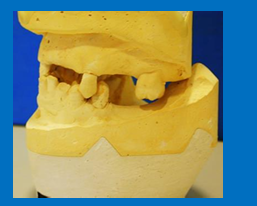
How would you articulate these?
These casts cannot be hand articulated because insufficient opposing pair of posterior teeth
To mount these casts on an articulator - need occlusal rims, and interocclusal record and a facebow
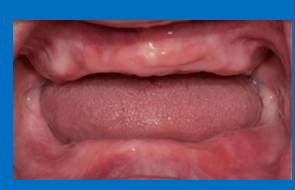
How would you articulate this?
to mount casts for this patient you need rims and interocclusal record and a facebow
How do you the OVD of the patient?
what articulating paper do you use?
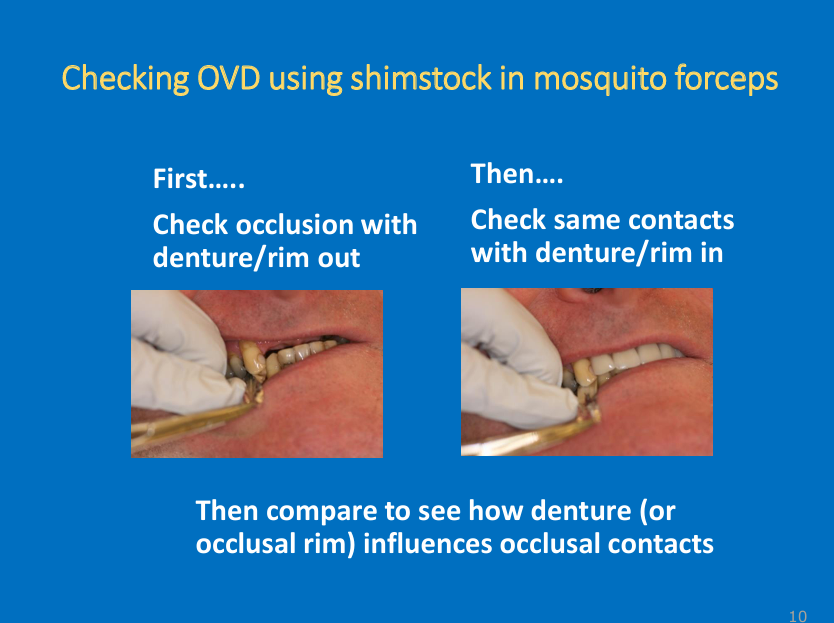
use Shimstock with mosquito forceps
First check the occlusion/ if the natural opposing teeth are occluding or not with denture/rim out of the mouth - pull on the Shimstock to assess the contacts
Then check the same contacts with denture/rim in the patient
“The aim is that this is the same - so the natural contacts are still there when you make the denture, if you make a denture that separates these contacts they will be aware it is too high and stops them from chewing properly - might cause them to close jaw tighter causing denture to push into the tissues so don’t want dentures to be too high so you want the correct OVD” (so we’ve done getting the correct horizontal relationship now its about getting the right vertical relationship for the patient)
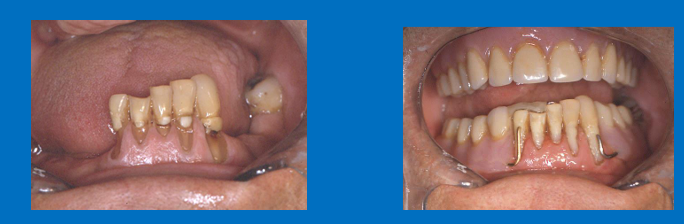
In an edentulous arch opposing a partially dentate arch
what horizontal relationship/occlusion will be used?
What is the problem with the vertical/OVD determination for this patient?
Natural teeth do not occlude, jaw relation used is always centric relation - not ICP as there isn’t one (remember it’s dependent on posterior teeth)
As there are no opposing natural teeth contacts - you cant determine a suitable OVD for this patient (no natural stops between teeth)
If there are no opposing natural tooth contacts to provide a suitable OVD, what do you use instead?
Use the freeway space FWS as a guide instead
Mandible relaxed with lips together , teeth are usually apart at rest - vertical measurements between maxilla and mandible - rest vertical dimension- OVD is when teeth are in contact
the gap between is the free way space
If no FWS then in rest there is no gap
with any patient at rest regardless of what’s in mouth you can measure the RVD instead - OVD can be calculated from the free way space avg
use FWS to determine the OVD
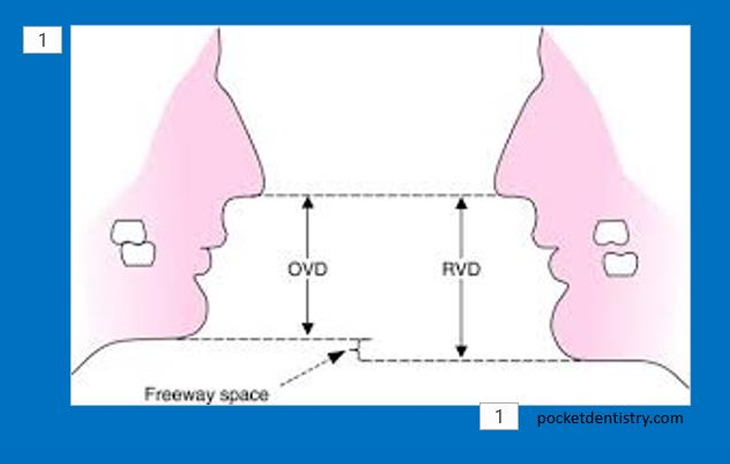
Free way space should ideally be what?
2-4mm
What is used as a measuring tool?
Willis gauge or dividers and ruler
How do you calculate the FWS?
Measure the OVD when patient has either the occlusal rims/denture try-ins in their mouth
Measure rest vertical dimension RVD with at least one occlusal rim/denture try-in out (complete dentures take one out/)
RVD-OVD = FWS
based on the average FWS then the OVD you are aiming for you get to know using the RVD (as RVD can be measured in anyone)
Not always reliable as Willis gauge can eb difficult/measuring between 2 points/ can be difficult to put patient in relaxed position
do it in edentulous cases
and if you cant determine OVD

What could happen if there is not enough freeway space? (4) (so increased OVD)
Might get soreness under one/both dentures - (trauma may be visible on soft tissues) (great extent as small area might be dentures not fitting well - get Willis gauge and dividers to measure if you have provided sufficient FWS)
Aching jaw muscles (OVD too excessive or not enough freeway space and no room to move) (muscles and jaw joints work harder)
Patients wants to leave dentures out because uncomfortable to wear . Patient may say “dentures feel too big or they feel like a mouth full” (again use Willis gauge and dividers to check the FWS)
Appearance may be unacceptable - showing too much tooth (as teeth are taller for the increased OVD)/or patients lip becomes incompetent because the mandible and maxilla are too far apart
Not enough FWS means there is a larger OVD
What happens if there is too much FWS? (shorter OVD) (6)
Might notice deep creases at the corners of the patients mouth (both sides usually) (patient is over closed)
Deep creases sometimes predispose patients to infection/redness/soreness a corners of the mouth - angular cheilitis
May also have denture stomatitis on palate - possible same time as angular cheilitis, because both can be candida related
Patient may complain of poor appearance - poor lip supports or reduced denture tooth height (teeth are short)
Patient may have jaw/muscle ache before they are over-closed (OVD is too short)
Patient may show very worn denture teeth/have difficulty chewing food if occlusal surface flat or misshappen (over years pt dentures will naturally decease due to alveolar ridge resorption)
What is the problem for occlusal rims that are made entirely out of wax?
What is added for strength?
2 things that may happen
What is better to support the wax rims?
What can be used in edentulous arches?
has wire strengthener
can easily distort
the rims don’t seat properly in mouth or cast
Cold-cure bases (these are temp)
In edentulous arches - heat-cured bases - heat cured are permanent and are incorporated in the final denture
bases are better as this means no distortion and helps with accuracy when recording jaw relationship
after its been in patients mouth - warm - distorts

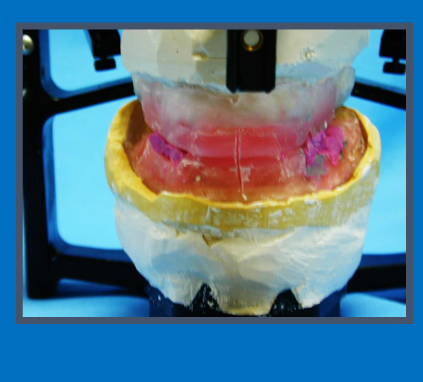
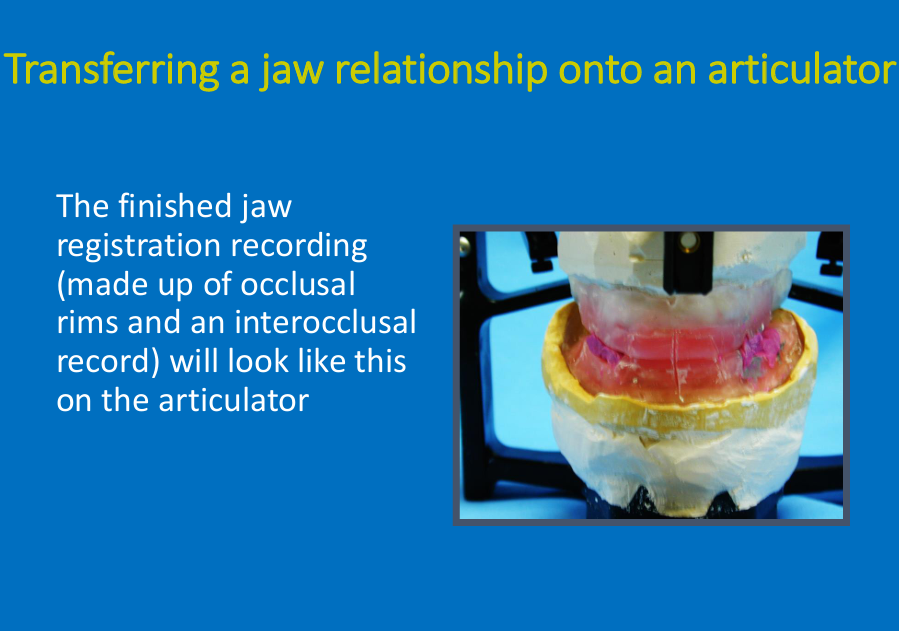
What is this?
Finished jaw registration recording made up of occlusal rims and interocclusal record
“when you’ve done jaw reg, once trimmed rims to shape and restored natural tooth contacts, right amount of free way space you need to take final record which involves grooves in surface of rims and putting bite reg in lower arch to get patient to bite together - remind yourself which ICP or RCP
Grooves in the surfaces of the rims - get patient to bite together”
How do you find RCP in your patient using hands only?
some can be guided
relaxe, pt upright
mandible guided backwards into position then teeth closed and stop at first contact

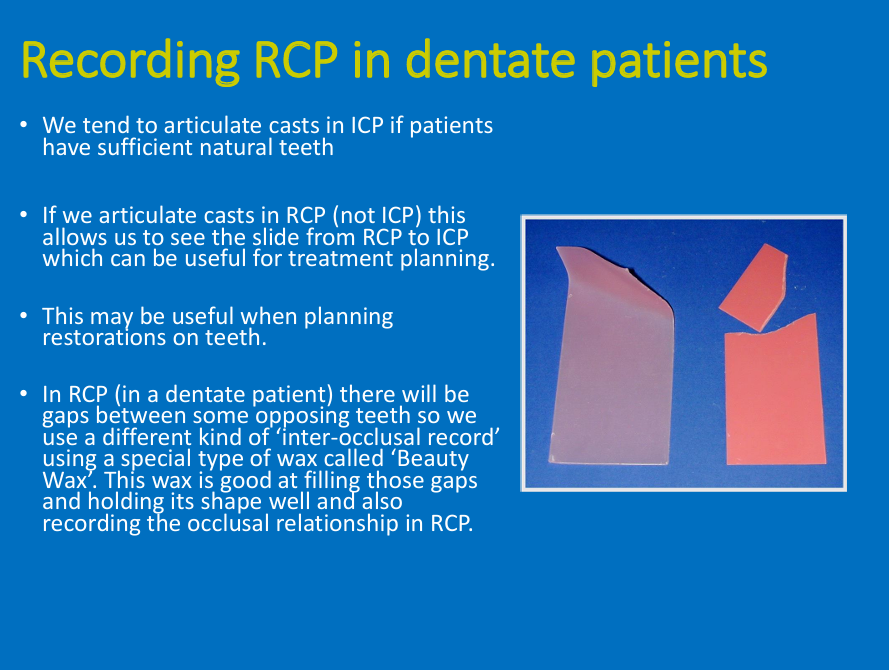
Recording RCP in dentate patients?
what may you use and why is it more difficult
what do we usually use and why might you use RCP?
Tend to use ICP in dentate (ask pt to bite naturally and use ICP as the horizontal relationship)
Might be useful when planning restoration (e.g wear cases) to see the slide from RCP to ICP
Sometimes may need wax between upper and lower teeth
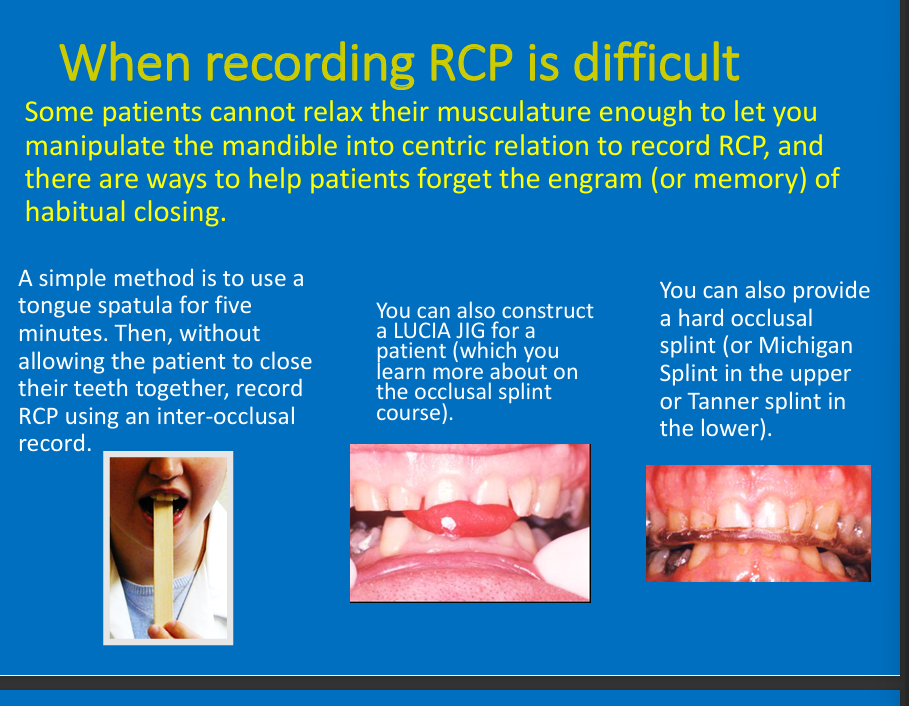
Why may recording RCP be difficult? what are 3 methods that may be used?
Unable to relax musculature to manipulate the mandible
Bite on spatula at angle, Lucia jig, hard occlusal splint
What are the 4 types of articulators from simple to more complex?
which type is better and why?
simple hinge articulators
free plane articulators
semi adjustable
fully adjustable

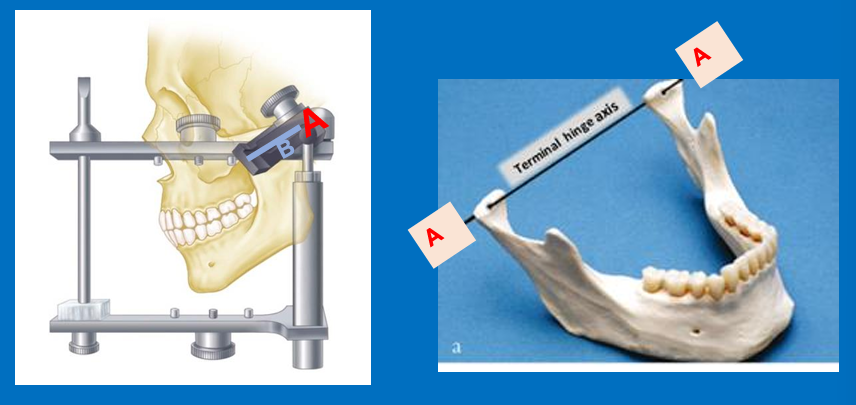
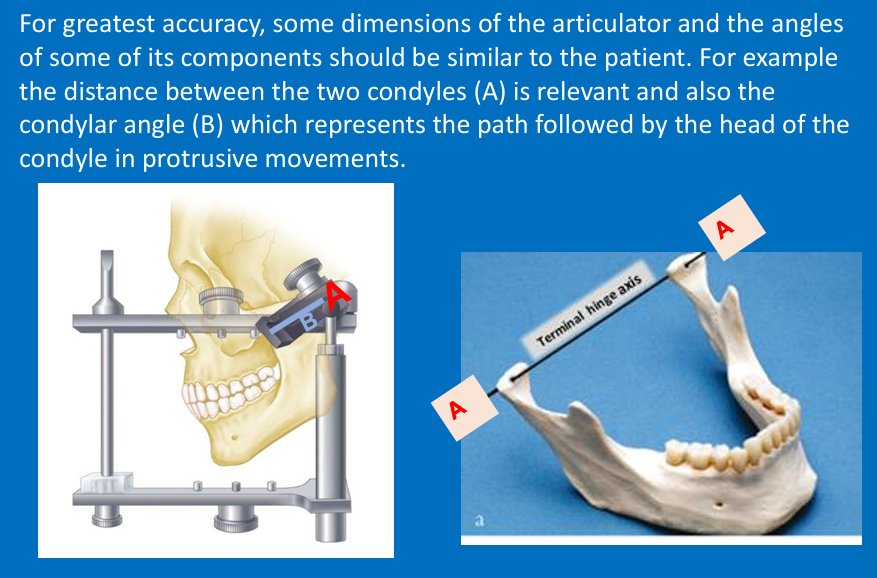
What does A and B represent?
A - Distance between the 2 condyles
B - Represents the path followed by the head of the condyle in protrusive movements
Simple hinge articulators
allow which movements and no?
what is the problem with the hinge? (2)
when is it used?
Up and down/ no lateral excursion
Hinge is close to teeth and only one when patients have 2
simple dentures

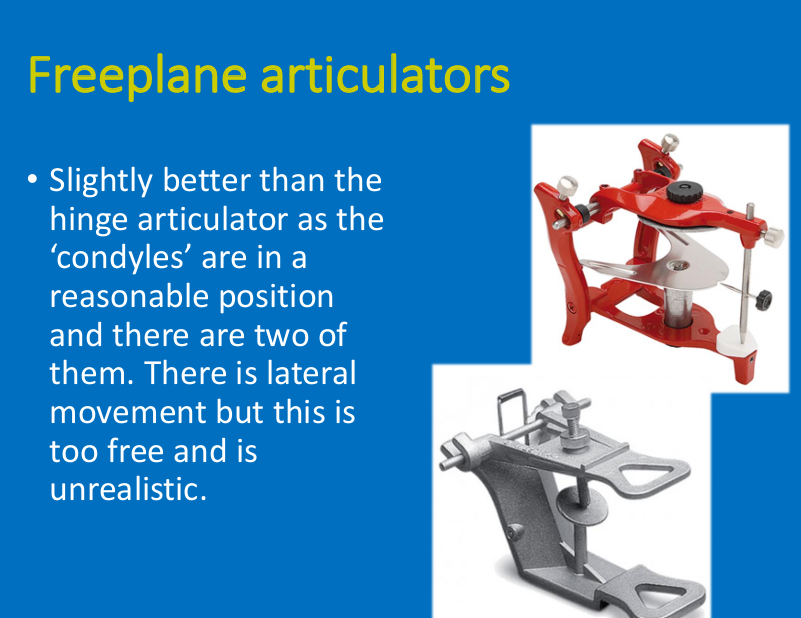
Free plane articulators:
why is it better than the simple hinge articulators?
2 hinges in reasonable position
lateral movements - but too free and unrealistic
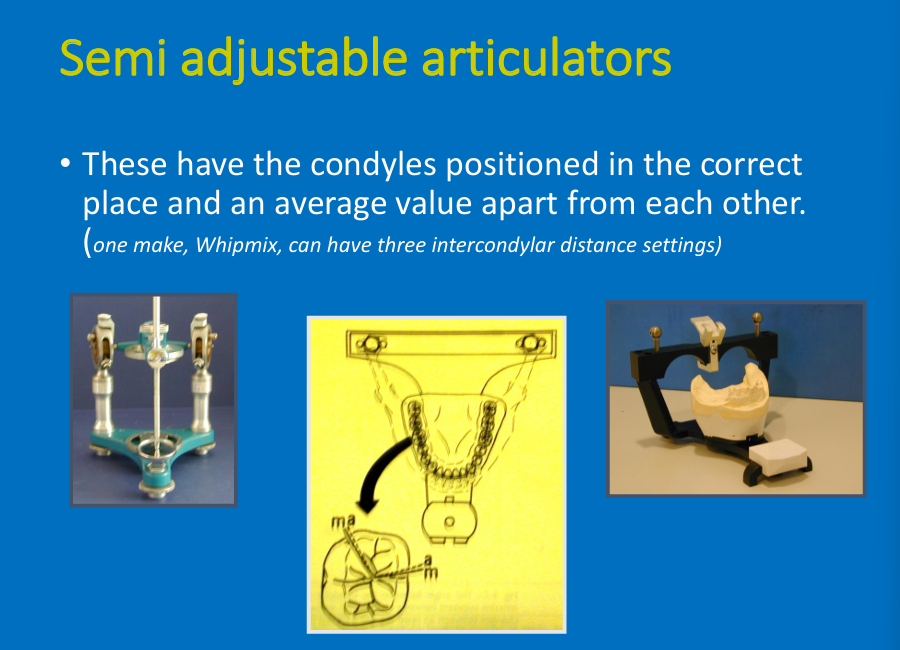
Semi-adjustable: adv?
Have the condyles positioned in the correct place and average evaluate apart from other
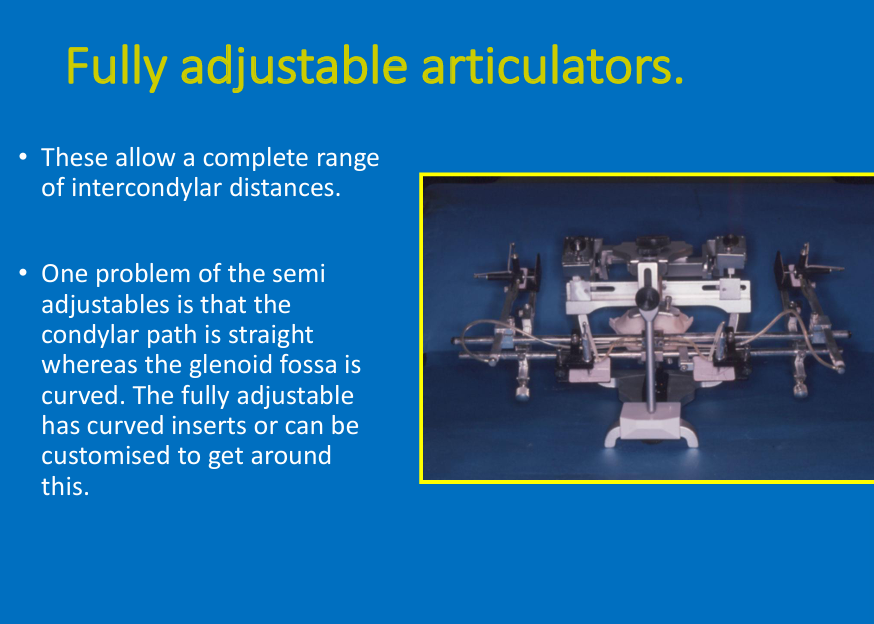
Fully adjustable articulators: adv (1)? how is it better than the semi-adjustable?
Allow range of intercondylar distances
Curved inserts
when using a facebow what is sent to the lab?
Only the jig is sent
Don’t always have to use but the more detail the better
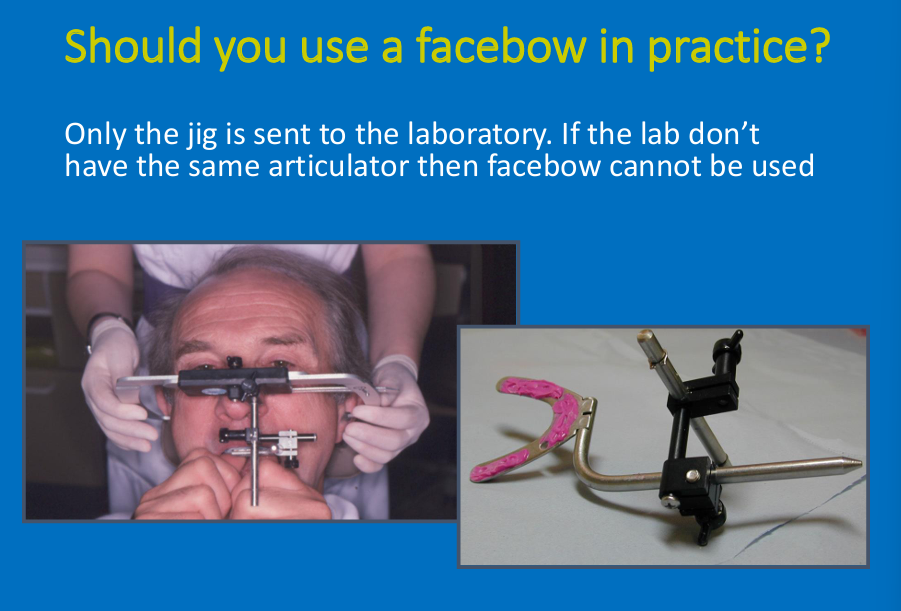
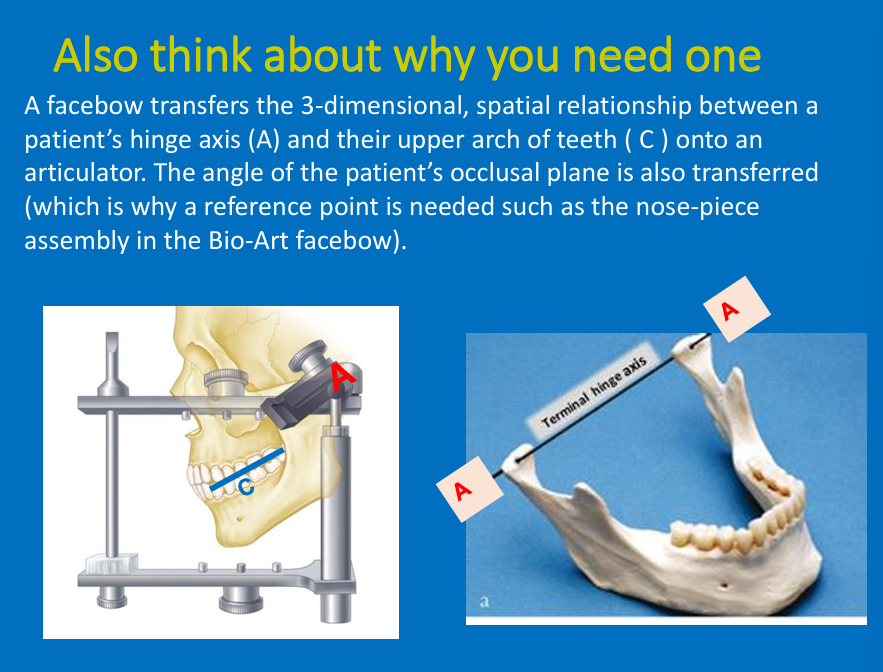
Why is using a facebow good?
angle to the horizontal
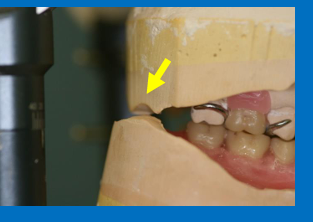
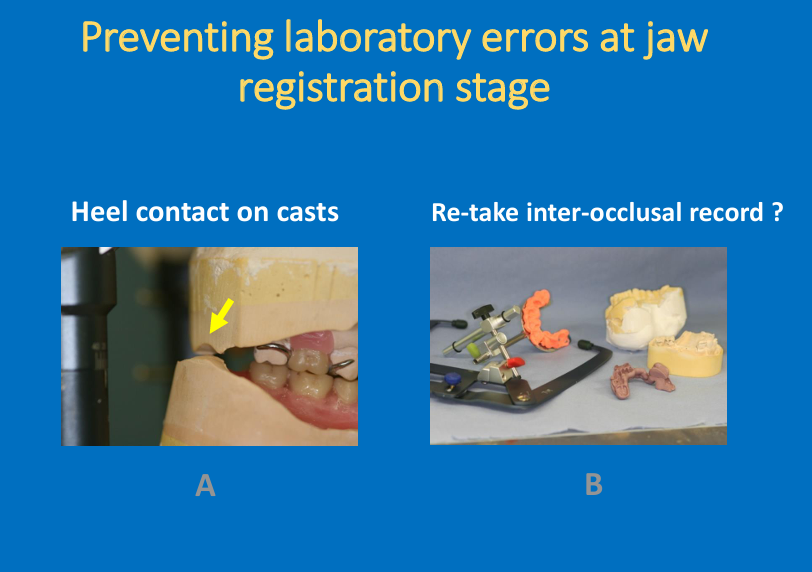
What is the problem here?
Check for a gap between upper and lower at the back when you articulate the lower - a gap is required to avoid error
What horizontal jaw relation is used wear cases and why?
Centric relation
copy dentures?
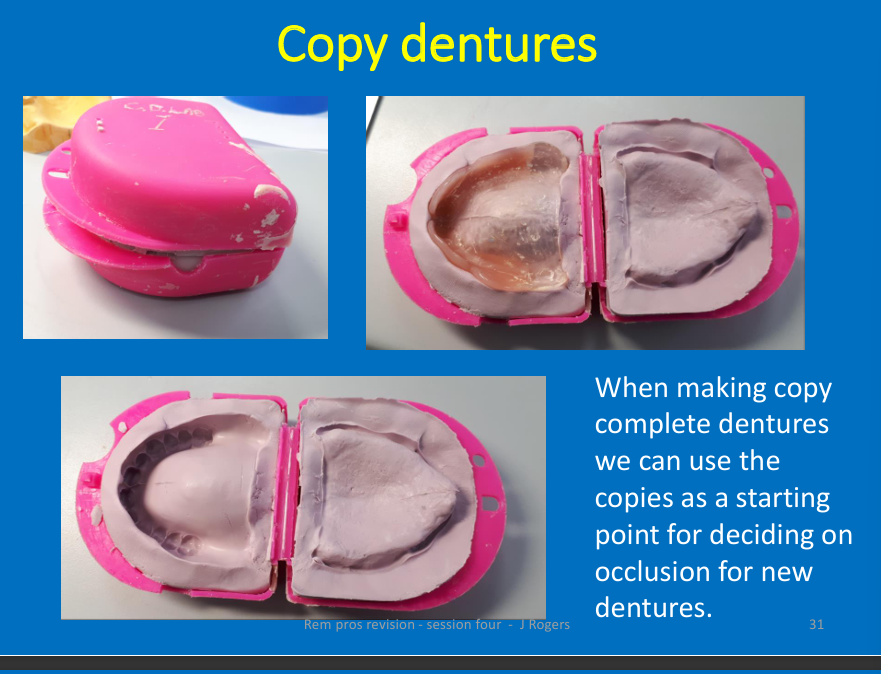
can you change occlusion if it is not right?
metal framework and crowns - careful when recording jaw relationship as there is more room for adjustment in acrylic dentures