Week 4 (pt. 1): Musculoskeletal Dysfunction
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Effects of Immobilization in Children
Physiologic: muscle atrophy, bone demineralization, decreased joint mobility, venous stasis (risk of DVT), and skin breakdown
Psychological: regression, anxiety, and depression
Nurs Care: focuses on maintaining circulation, nutrition, respiratory function, skin integrity, providing diversional activities for coping, repositioning, passive ROM exercises
Nursing Care for the Immobilized Child
Maintaining circulation → repositioning, passive ROM exercises
Maintain skin integrity → assessing for pressure injuries, repositioning
Ensure proper nutrition → protein, calcium intake
Address family anxiety by explaining treatment and involving them in care.
Provide diversional activities for coping
Soft Tissue Injury
Injury to muscles, ligaments, or tendons
types: contusions (bruises), dislocations, sprains, and strains
management: RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation)
Dislocation
Displacement of bone ends from their normal articulation. Often causes severe pain, joint deformity, and limited movement
Sprain
Partial or complete tear of a ligament, usually from twisting. Presents with swelling, instability, and pain.
Strain
Microscopic tear to a muscle or tendon
Fractures
resistant of bone against stress exerted yields to stress force
types: compound (open), complicated, comminuted, greenstick
Types of Fractures → Compound (open)
Bone breaks through skin (aka open wound); risk of infection
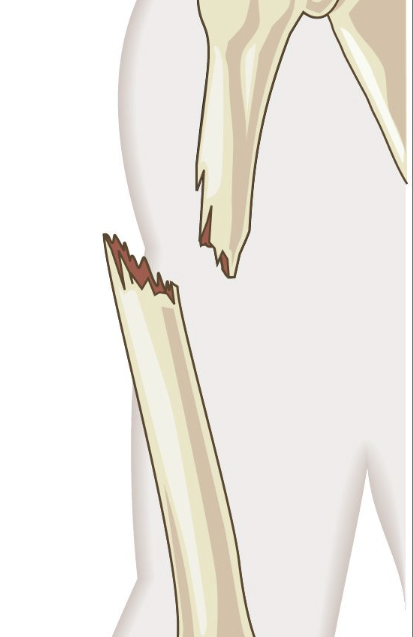
Types of Fractures → Complicated
Bone fragments damage other organs or tissues
Types of Fractures → Comminuted
Bone shatters into several pieces and lie in the surrounding tissue
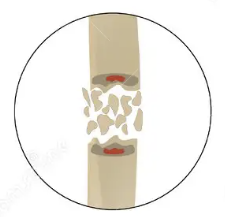
Types of Fractures → Greenstick
Incomplete fracture common in children; bone bends and partially breaks on one side

Pediatric Bone Healing
Children’s bones heal faster than adults due to rich blood supply and thick periosteum. Immobilization and alignment are crucial to prevent deformity.
Compartment Syndrome + 5 P’s
limb-threatening condition where swelling increases pressure within muscle compartments, impairing circulation and nerve function
5 P’s: Pain, Pallor, Pulselessness, Paresthesia, Paralysis.
Management: immediate involving remove cast/splint, surgical fasciotomy
How is a cast constructed?
using gauze strips and bandages impregnated with plaster of Paris or synthetic; molded to body part
Cast Care
Keep the cast dry
Check for skin irritation
Monitor circulation and sensation (compartment syndrome) → instruct families to report pain, swelling, or color changes
Elevate the limb
Avoid inserting objects inside
Pediatric Cast Types
long leg cast, short leg cast, bilateral leg cast, full spica cast, single spica cast, short arm cast, long arm cast
Traction
application of a pulling force to a body part (usually a limb or the spine) to achieve therapeutic goals such as:
bone alignment → position distal and proximal bone ends
reduction of muscle spasms
immobilization of a fracture before casting or splinting
help prevent or improve contracture deformity
Traction → Types
Skin Traction: force applied to the skin surface using adhesive materials, foam boots, or wraps; used for short-term treatment
Skeletal Traction: pins, wires, or tongs are surgically inserted into bone; used for long-term treatment & stronger
Traction → Nursing Care
Check ropes and pulleys for function, assess neurovascular status, prevent pressure injuries, and encourage movement of unaffected limbs. Provide emotional support and maintain hygiene.
Amputation in Children + Nursing Care
surgical removal or repair of a limb
nurs care: pain control (phantom limb pain), stump shaping for prosthetic fit, infection prevention, and emotional support to aid body image adjustment
Overuse Syndromes + Management
Repetitive microtrauma from sports or improper biomechanics leading to stress fractures or tendonitis
risks: training errors, muscle/tendon imbalance, anatomic malalignment, incorrect footwear, associated disease state, growth
management: includes rest, physical therapy, and correcting technique or footwear
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)
formerly known as congenital hip dysplasia; abnormal development of the hip joint where the femoral head dislocates from the joint; commonly seen in newborns
type: idiopathic, teratologic, dysplasia, subluxation, dislocation
symptoms: hip click, uneven thigh folds, or limb shortening
diagnosis: Barlow, Ortolani test
management: depends on age
Barlow Test
exam used to test for developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns by trying to dislocate the hip by bringing them together toward the midline
positive sign indicates hip instability
Ortolani Test
exam used to test for developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns by trying to put hip back into place by moving them apart, away from midline
positive sign indicates hip dislocation
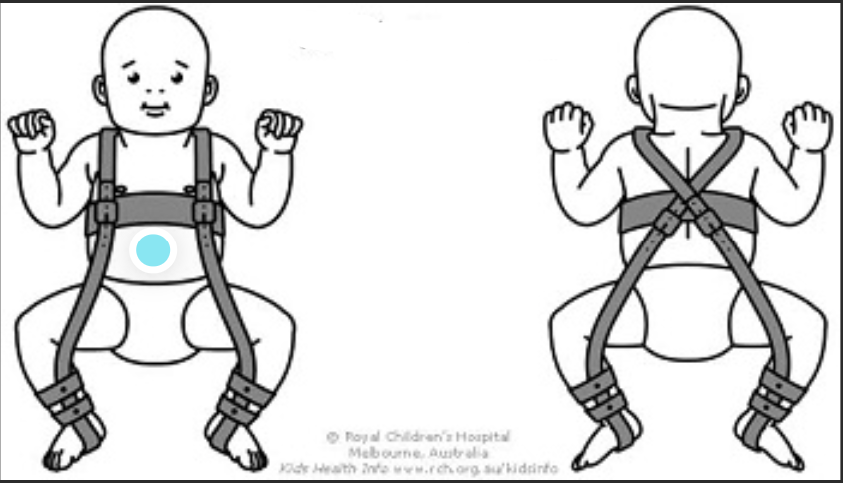
Pavlik Harness
soft, dynamic splint commonly used to treat DDH in infants under 6 months; worn 23 hours/day; holds the hips in a stable, flexed, and abducted position, to allow for proper hip joint development
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) → Dysplasia
mildest form of DDH; femoral head remains in place, but the socket is too shallow or oblique
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) → Subluxation
partial or incomplete dislocation of the hip joint; most common; femoral head is partially displaced remaining in contact with the acetabulum but not fully seated within it; causes joint capsule and ligaments to be stretched
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) → Dislocation
most severe form of DDH; femoral head is completely displaced; no contact between the femoral head and the socket
Congenital Clubfoot
Foot deformity with ankle inversion and foot pointing inward
types: positional, congenital, and syndromic
diagnosis: physical exam or fetal ultrasound
management: serial casting, bracing, or surgery
nurs care: skin care and support family through treatment
Congenital Clubfoot → Positional
flexible deformity caused by intrauterine crowding or positioning; bones are normal; can be manually corrected to a neutral position
Congenital Clubfoot → Congenital
true structural deformity present at birth
Congenital Clubfoot → Syndromic (teratologic)
rigid, resistant form of clubfoot that occurs as part of a neuromuscular or genetic syndrome (spina bifida or cerebral palsy); requires surgical correction after initial casting
Metatarsus Adductus
also known as metatarsus varus; inward curvature or medial adduction of toes and forefoot; no change to the ankle
types: type 1, type 2, type 3
management: gentle stretching or casting if rigid
Metatarsus Adductus → Type 1
forefoot flexible, corrects with easy manipulation
Metatarsus Adductus → Type 2
forefoot partial flexibility, corrects passively
Metatarsus Adductus → Type 3
forefoot rigid, will not stretch to neutral with manipulation
Skeletal Limb Deficiency
Congenital underdevelopment or absence of limb parts resulting from genetic, vascular, or environmental causes.
management: prosthetics & therapy, promote mobility and self-esteem
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI)
Genetic disorder of collagen production leading to fragile bones, multiple fractures and bone defects; parents have been accused of abuse
symptoms: hearing loss, blue sclera, multiple fractures
types: I-IV
management: supportive
nurs care: handle gently, prevent fractures, educate parents, encourage safe mobility
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI) → Type I
most common and mildest
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI) → Type II
most severe, lethal in infancy
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI) → Type III
multiple fractures present at birth, short stature, severe bone deformity, disability
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI) → Type IV
similar to Type I but more severe, short stature
Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease
Insidious onset of avascular necrosis of the femoral head causing hip pain and limp in children (ages 4–8)
management: rest, traction, or surgery
nurs care: family-centered care, supports adherence, provide education on limited weight-bearing
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)
Spontaneous displacement of the proximal femoral head from the neck at the growth plate; common in obese or adolescent males; similar to hip displacement for newborns
symptoms: hip or knee pain, limp, decreased ROM
diagnosis: physical exam, x-ray
management: surgery
nurs care: assess for pain and limit weight-bearing pre-surgery
Kyphosis vs Lordosis
kyphosis: excessive thoracic curvature (hunchback) resulting from posture or disease; treatment → exercises, bracing, or surgery
lordosis: excessive inward lumbar curvature (“swayback”); linked to obesity or hip flexion contractures; treatment → weight management, posture correction
Idiopathic Scoliosis
most common spinal deformity characterized by lateral curvature, spinal rotation causing rib asymmetry and thoracic hypokyphosis; often seen in preadolescent girls
types: thoracic scoliosis, lumbar scoliosis, thoraco-lumbar scoliosis, combined scoliosis (defined according to location)
diagnosis: clinical evaluation, radiographs (x-ray)
management: bracing or spinal fusion if severe
nurs care: pre/post op care, monitor for respiratory compromise, provide emotional support
Osteomyelitis
Infection of the bone usually caused by bacteria (Staph aureus)
symptoms: localized pain, fever, and limited mobility
treatment: IV antibiotics, maybe surgery
nurs care: monitor IV therapy, pain control, maintain mobility
Septic Arthritis
Bacterial infection of the joint space, often the hip, knee or shoulder
symptoms: acute pain, fever, limited motion
treatment: IV antibiotics, pain meds, ROM exercises post-treatment, mobility
Skeletal Tuberculosis
Bone or joint infection due to hematogenous spread of pulmonary TB
diagnosis: clinical eval, tb test, imaging tests (x-ray)
symptoms: spinal deformity, swelling, pain, decreased movement, can progress to Pott’s disease (late)
treatment: long-term TB therapy, isolation, sometimes surgery
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)
chronic childhood arthritis causing inflammation in joint synovium and surrounding tissues
types: systemic, oligoarticular, and polyarticular
symptoms: joint swelling, pain, stiffness, and loss of motion
management: NSAIDs, corticosteroids, DMARDs, physical therapy
nurs role: relieve pain, promote comfort, prevent deformity, encourage activity/adherence, support child/family
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Severe multisystem progressive autoimmune disease of connective tissue and blood vessels causing inflammation in connective tissues and multiorgan damage; cause unknown
symptoms: cutaneous lesions, generalized weakness, CNS symptoms, proteinuria, pericarditis, nausea, diaherra
treatment: corticosteroids, immunosuppressants
nurs care: monitor for infection, support coping, and prevent triggers (sun exposure, stress)
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) → Oligoarthritis
1-4 joints for the first 6 months
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) → Polyarthritis rheumatoid factor negative
5+ joints in the first 6 months w/ negative rheumatoid factor
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) → polyarthritis rheumatoid factor positive
5+ joints in the first 6 months with positive rheumatoid factor