physics electric currents
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/85
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
1
New cards
what are the the fundamental laws of electrostatics
positive and negative charges like charges repel dissimilar charges attract
2
New cards
what is coulumbs law
the electrostatic attraction or repulsion force between two charges is proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportionate to the square of their distances
\
\
\
\
3
New cards
what does K stand for
constant of proportionality 9\*10^9 Mc^2/c^2
4
New cards
what is charges concentration
in a system electrons are only treanfered from one medium to another. the systems net charge is always the same
5
New cards
what are insulators
they are poor conductors of electricity and can be charged through firction
6
New cards
what conductors
they are good conductors of electricity and electrons flow freely
7
New cards
what is current
current is the rate of flow charge
8
New cards
what is the symbol for current
I
9
New cards
what does I stand for
current
10
New cards
what is Q stand for
coulumb
11
New cards
what is the letter for
charge
12
New cards
what is the formula to find current
I=q/t
\
current=charge/time
\
current=charge/time
13
New cards

what is the symbol for
symbol for connecting wire
14
New cards
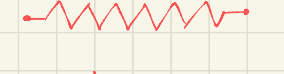
what is the symbol for
symbol for resistor
15
New cards

what is this the symbol for
symbol for cell
16
New cards
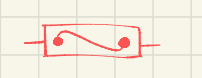
what is this the symbol for
symbol for fuse
17
New cards

what is this the symbol for
plug key
18
New cards

what is this the symbol for
battery
19
New cards

what is this the symbol for
symbol for electric bulb
20
New cards

what is this the symbol for
symbol for linked connecting wires
21
New cards
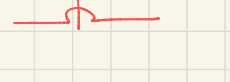
what is this the symbol for
symbol for crossing wires
22
New cards
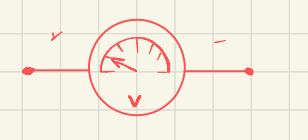
what is this the symbol for
symbol for volt meter
23
New cards
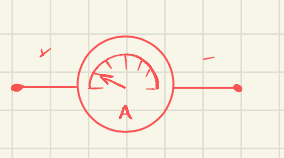
what is this the symbol for
symbol for ammeter
24
New cards
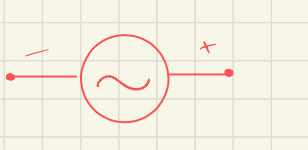
what is this the symbol for
symbol for alternating current
25
New cards
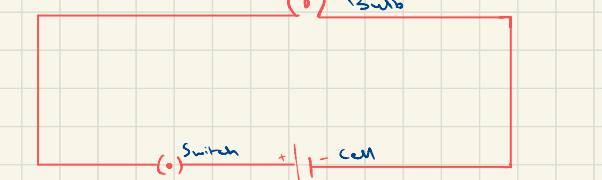
what is this
circuit diagram
26
New cards
what is electric potential
work done in carrying a unit positive charge from infinity to a point
27
New cards
what does W stand for
work
28
New cards
what is the symbol for work
W
29
New cards
what is the symbol for electric potential
v
30
New cards
what is v the symbol of
electric potential
31
New cards
formula to find electric potential
v=w/q
32
New cards
what is the SI unit for electric potential
volts(v)
33
New cards
what is the SI unit of current
ampere(a)
34
New cards
is current scaler or vecotr
scaler
35
New cards
what is electric potential difference
work done to move a unit energy from one location to another in a electric circuit carrying some current
36
New cards
what is the symbol for electric potential energy
VAB= electric potential difference between a and b
37
New cards
formula to find electric potential difference between a and b
VAB= work done to carry charge form A and B/charge
38
New cards
what is electric potential energy
work done to transport charges against the electric field using a source of energy. the potential energy of the charges stores the work done.
39
New cards
what is ohms law
under similar physical conditions, the current flowing through a wire is directly proportional to the difference in potential applied across its ends
40
New cards
what does R stand for
resistance
41
New cards
how to find resisitance formula
r=v/i. resistance=electric potential/current
42
New cards
what is resistance
opposition to the flow of current
43
New cards
SI unit of resistance
ohm(omega symbol)
44
New cards
what is variable resistance
regulates current without changing the voltage source
45
New cards
what is rheostat
device uses to commonly adjust the resistance in a electric circuit
46
New cards
factors affecting resistance
nature of the material of the wire, length of the wire, and cross-sectional area of the wire.
47
New cards
what is the relation between resistance and length
directly proportional
48
New cards
what is the relationship between resistance and cross section area
inversely proportional
49
New cards
what does P stand for
rho
50
New cards
what is rho
proportionality constant referring to the electrical resistivity of the conductors substance
51
New cards
what is resistivity
resistance offered by a wire of unit length and unit cross-sectional area
52
New cards
what is a factor affecting resistivity
temperature
53
New cards
what is the reciprocal of resistivity
conductivity
54
New cards
effect of temperature to resistance in conductors and insulators
temperature rise and resistance also rises
55
New cards
effect of temperature to resistance in semi conductors
is temperature rises then resistivity decreases
56
New cards
effect of temperature to resistance in alloys
temperature rise and resistance also rises
57
New cards
what are semiconductors
resistivity between insulators and conductors
58
New cards
what are superconductors
they lose their resistivity at low temperature
\
\
59
New cards
what is equivalent resisitance
the resistors of individual resistance of multiple resistors in series
60
New cards
what happens if resistance are connected in a series resisitance
r5=r1+r2+r3………RN. current is the same. potential difference varies.
61
New cards
what happen if the series is parallel resistance
1/rp=1/r1+1/r2+1/r3………1/rn. potential is the same. current varies
62
New cards
what happens if one component fails in a series circuit
the entire circuit breaks
63
New cards
when is parallel resistance used
when each device needs different current and resistance
64
New cards
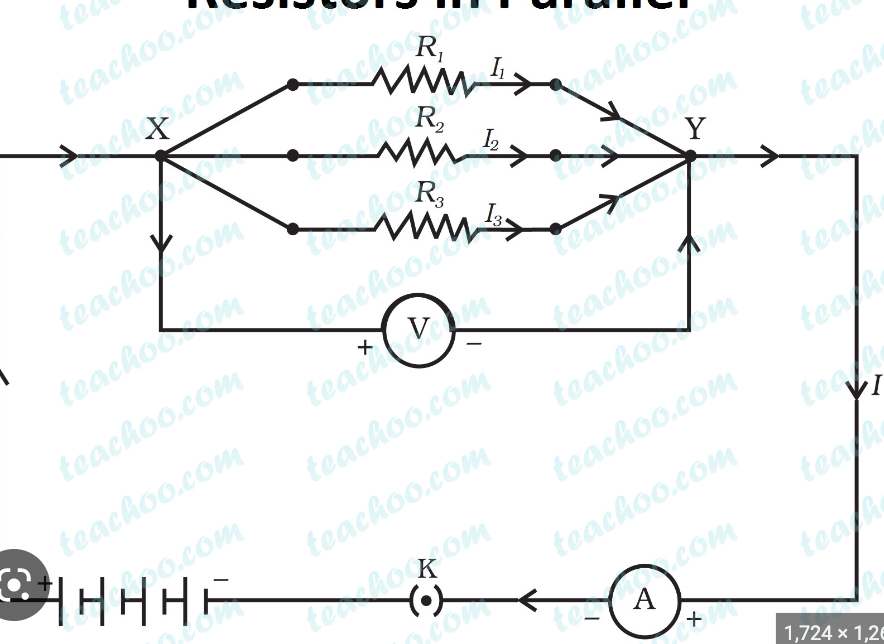
what resitance is this
parallel resistance
65
New cards
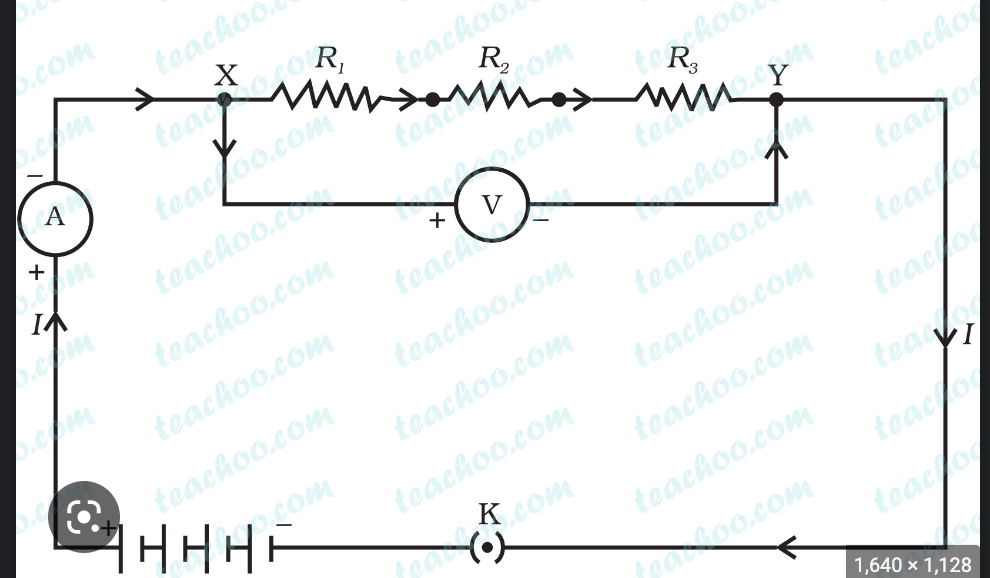
what resistance is this
series resisitance
66
New cards
what is joules law of heating
when current flows through resistivity, heat is produced
67
New cards
what are apllicators
they turn useful electrical energy into heat like toaster, oven, electric bulb, electric circuit fuse
68
New cards
what is a fuse wire
it melts to break the circuit, prevent high current flow,
69
New cards
what is electrical energy
work done to carry charge
70
New cards
what does W stand for
electric energy
71
New cards
how to find electric energy
v^2 t/r.
72
New cards
what is work done stored as
energy
73
New cards
SI unit or electrical energy
joules
74
New cards
what is electrical power
rate at which electrical energy is consumes
75
New cards
what is the formula to find electric power
p=v *i electric power= current ** potential
76
New cards
what is the SI unit for electric power
watt
77
New cards
what are the types of resistors
ohmic and nonohmic
78
New cards
what are ohmic conductors
obey ohms law, they are silver, copper aluminium
79
New cards
what are non ohmic conductors
do not obey ohms law. semi conductors-LED, solar cell, diode
80
New cards
what is a diode
it is a semi conductors
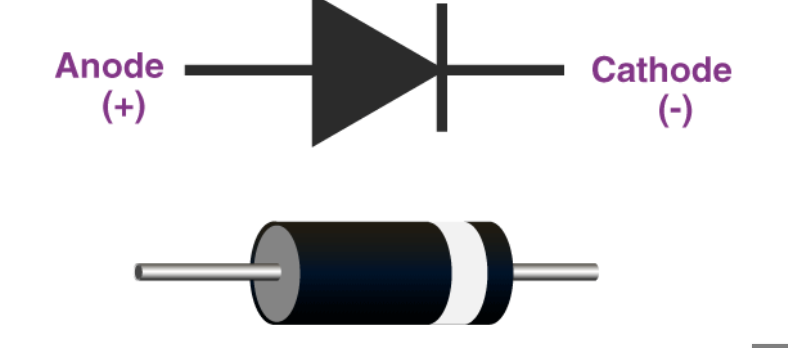
81
New cards
what is a thermistor
it is a resistor. used in digital thermometer
82
New cards
what is a voltage dividers
allows voltage to be divided between 2 resistors. allows voltage to the desired value
83
New cards
what are capictators
they store electric charge, can charge and discharge quickly, and collects energy in a circuit
84
New cards
what are maglev trains
superconductors, superconducting magnets, superconductors repel aproaching magnets, magnetic levitaiton
85
New cards
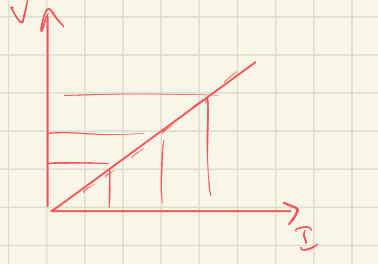
what conductor is this
ohmic conductor
86
New cards
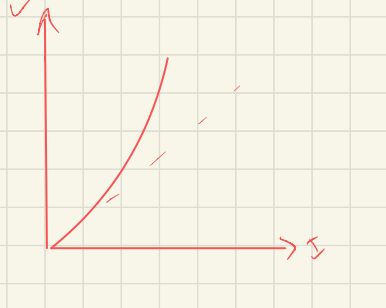
what conductor is this
non ohmic ocnductor