APES UNIT 2 EXAM
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
genetic diversity
variability in genetic makeup among individuals in a pop. if too few DNA differations, there will be a chance for genetic bottleneck and extinction
genetic bottleneck
when a population is greatly reduced in size, limiting the genetic diversity of the species.
causes of bottleneck
mass hunting, natural disaster, loss of food, intro of non-native species
species diversity
number of species in area
high biodiversity area
rainforest
low biodiversity area
desert
anthropogenic
originates from human activity
Ecological Services
Natural things.
Provisioning: Ecosystem provides things “stuff” (matter) Ex: water, lumber
Regulating: BIG PICTURE, greenhouse gas regulation, water quality, air quality
Supporting: Without these, others could not exist. EX: Photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, soil formation
Cultural: Aesthetic beauty, religious purposes
Ecotone
A transitional zone where 2+ communities meet high biodiversity (ex: Intertidal zones)
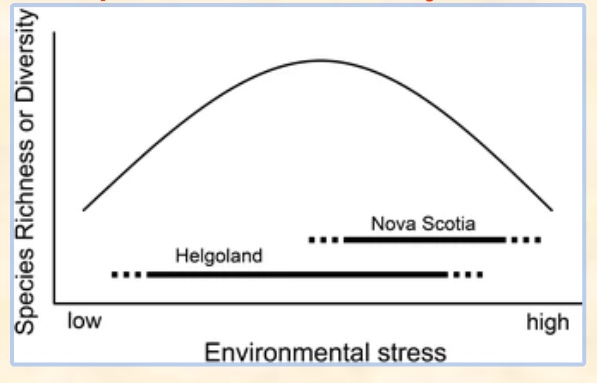
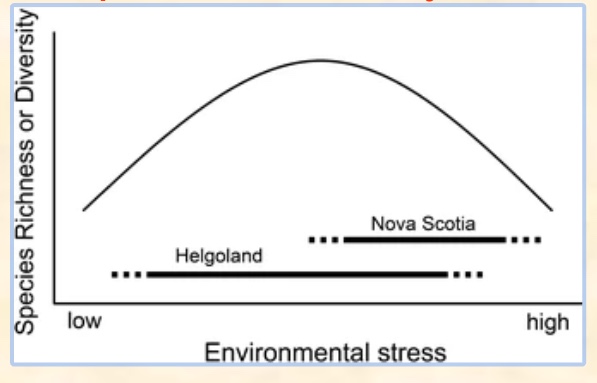
what do you notice from this graph
there is more diversity with medium stress
factors that determine species diversity
-Habitat stress
-Available niches
-Dominance of species
-Geological history
true or false: does genetic diversity make populations more resiliant to env. disturbances
true
high species richness means
high resiliance
how do lichen and mosses intiate primary succession
secrete acids onto rocks, leading to chem weathering
hardiness
species can survive in harsh conditions
climax species / climax community
when this ecosystem stops experiencing sporadic change and instead reaches stability. This means that, under the current climate conditions, little to no changes are occurring. Most diagrams depict this as a forest, though the Sahara Desert has remained unchanged for almost five thousand years.
If conditions change, the ——- ——- will change and succession will begin again.
species
Considered separate if they cannot interbreed
Same ——————- create viable offspring
succession
communities change over time
primary succession
Starts w/ new land.
Species land on new material and colonize (pioneer community). Bare rock→ Mosses and lichen form soil → Soil → soil thickens shrubs grow
examples of lichen getting to new land
Can be N fixers - Put Nitrate into soil for other plants to grow! Can also measure air poll.
secondary succession
Starts w/ already formed land.
Species land on disturbed material.
as community complexity increases..
more species are able to live in community
genetic diversity
the range of different inherited traits within a species. The more ——- a species has, the more resilient it is; it has more “options” for response/adaptation to occur if the environment changes
species diversity
–the number of different species present in an ecosystem and relative abundance of each of those species (takes into account species richness and species evenness)
The more —— there is; the more resilient that ecosystem is to changes
habitat diversity
–the range of habitats where different species live (habitat→the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism)
When ——- are lost, specialist species are lost followed by generalist species and then species that require a lot of territory (space) are lost
Habitat loss
the number one cause of organism extinction!!!
species richness
# of different species
species evenness
describes distribution of abundance (total number) across the species; it is high when all species have a similar number
generalists categories
broad niche, adaptable to many environments. diet, not picky, variety. location, can be found around world. range of tolerance, high “go with flow” tolerant to changes.
specialist categories
narrow niche, not adaptable to change in environment. limited diet. location, found in specific habitats. range of tolerance is low, “thats NOT how we do it.” highly sensitive to change, the pop declines to change
examples of generalists
Raccoons, rats, mice, cockroaches, coyotes, whitetail deer, brown rats, horseshoe crab
specialists
Panda, river otter, owls, koala, sword-billed hummingbird, venus flytrap
alleles
alternative forms of a gene found at the same place on a chromosome; arise due to mutations
-Different ——-⇒variation of traits
Example: petal color in plants
bottleneck effect
-Occurs when a population is sharply reduced in size by a natural disaster (ex: earthquakes, floods, fires)
founder effect
A small group splits off from the main population to found a colony (ex: islands, habitats cut off due to urbanization)
natural selection
there is a struggle for existence among organisms, there is physical and behavorial variation in living organisms (even within species level), common descent/descent with modication as every living species has descended with changes from other species over time.
why can'‘t humans evolve to cope with our new enviornmental conditions
genes for new traits have to already be present in a population’s gene pool through a random mutation. human gen times are too long to keep up with rapid conditions.
islands that are larger and closer to the mainland have…
higher species richness
edge effect
The phenomenon where selective logging will cause caps in the canopy, and the —- slowly degrade bc of wind, invasion, and sunlight, leading to habitat fragmentation, and species being more susceptible to viable populations
Why is habitat fragmentation bad
it cuts species off from larger populations thus causing inability to support viable populations.
provisioning ecosystem service
products that are directly provided
regulating ecosystem service
maintaining processes
cultural ecosystem service
nonmaterial benefits, habits, or traditions
supporting ecosystem services
allows for other services to exist
Simpson’s Diversity Index
D= D = Σni(ni-1) / N(N-1)
where:
ni: The number of organisms that belong to species i
N: The total number of organisms
Measurements range from 0 to 1, with 1 being highest richnessas
as extinction increases …
immigration of species decreases
larger islands closer to land have what rate of immigration
higher rate of immigration bc of their proximity to other larger ecosystem
what is ideal point btwn immigration and extinction for an island
point of equlibrium
maximum species diversity is reached when
an ecosystem experiences an intermediate level of disturbance. It is because both early and late succession species are able to survive at the same time.
reproductive isolation
when two populations are no longer able to reproduce with each other.
allopatric speciation
If there is a physical barrier between them (a road cutting through a forest. 2 populations are forced to avoid reproduction.
sympatric seciation
if the populations are in the same area but do not reproduce. the populations coexist and do not reproduce.
fauna
vegetation being replaced over time, becoming larger as long as succession progresses. shown in many diagrams
keystone species
depended upon by other species in the ecosystem such that if it were removed, the ecosystem would undergo dramatic changes. disproportionate in size, meaning that they have relatively low population density for how extremely important their effect on their ecosystem is
indicator species
one that reflects the health of its ecosystem- if it dies or has low population density, the ecosystem’s health is poor
where do specialist species thrive
in habitats that remain constant
where do generalist species thrive
in habitats that are changing
pioneer member
pioneer members relating to ecological succession
s
members moving into bare, uninhabited areas, then colonizing them as they are a hardy, fast-growing species. prepare the environment for more complex species to thrive.