Lecture 14 Genetics BIOL 302: Posttranslational Modifications and Chromosome Structure
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Signal Sequence
First 15-20 Amino Acids of a protein that is labeled to directed to the correct cellular destinations
Cleavage
Removal or Splitting of protein to form different functions, is a posttranslational modification
Plasmids
Nonessential, Extrachromosomal DNA that can help guide DNA expression. Only found in Bacteria
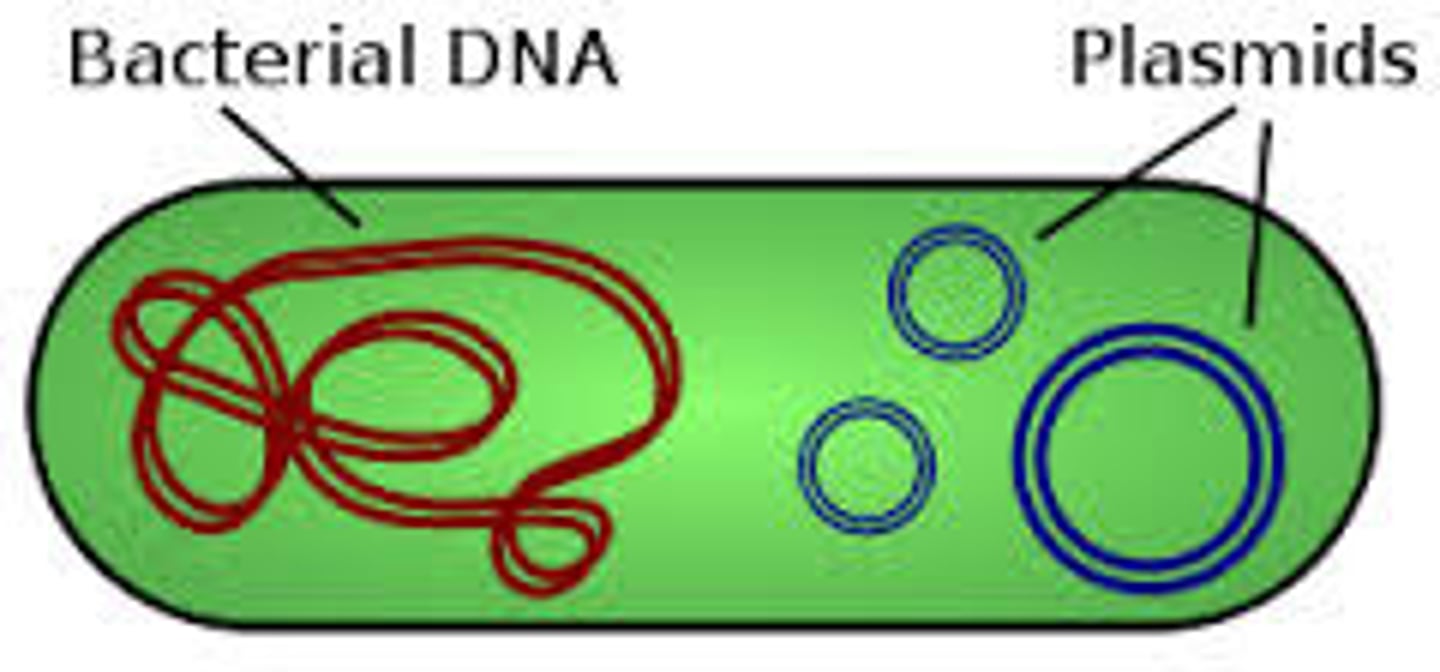
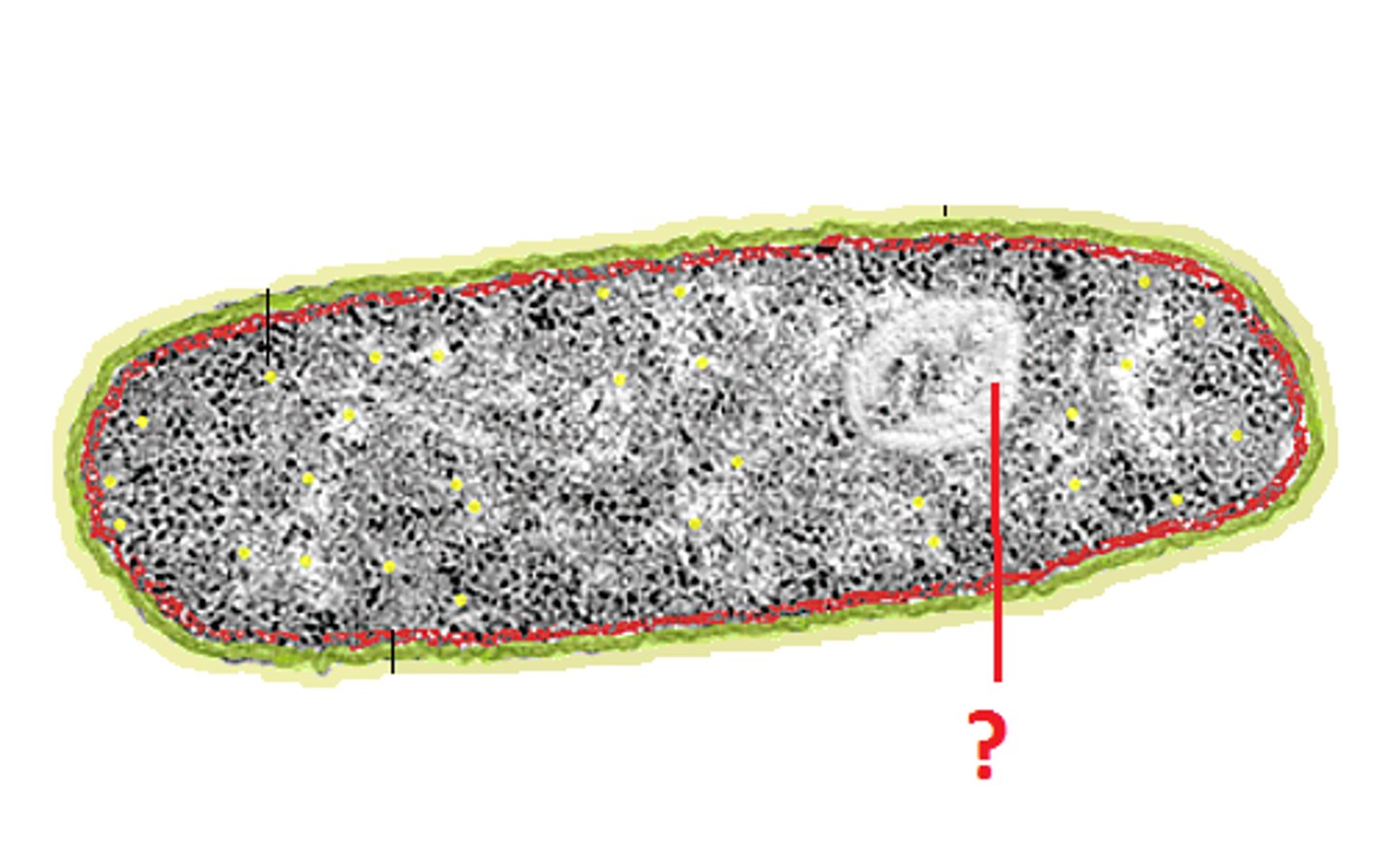
Nucleoid
Region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell that consists of tightly packed chromosomes
Supercoiling
Twisting of bacterial DNA that allows it to condense. Occurs negatively in bacteria (against its helical twist)
Topoisomerase II
An enzyme that induces supercoiling in bacterial DNA
Histone
Molecule around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin
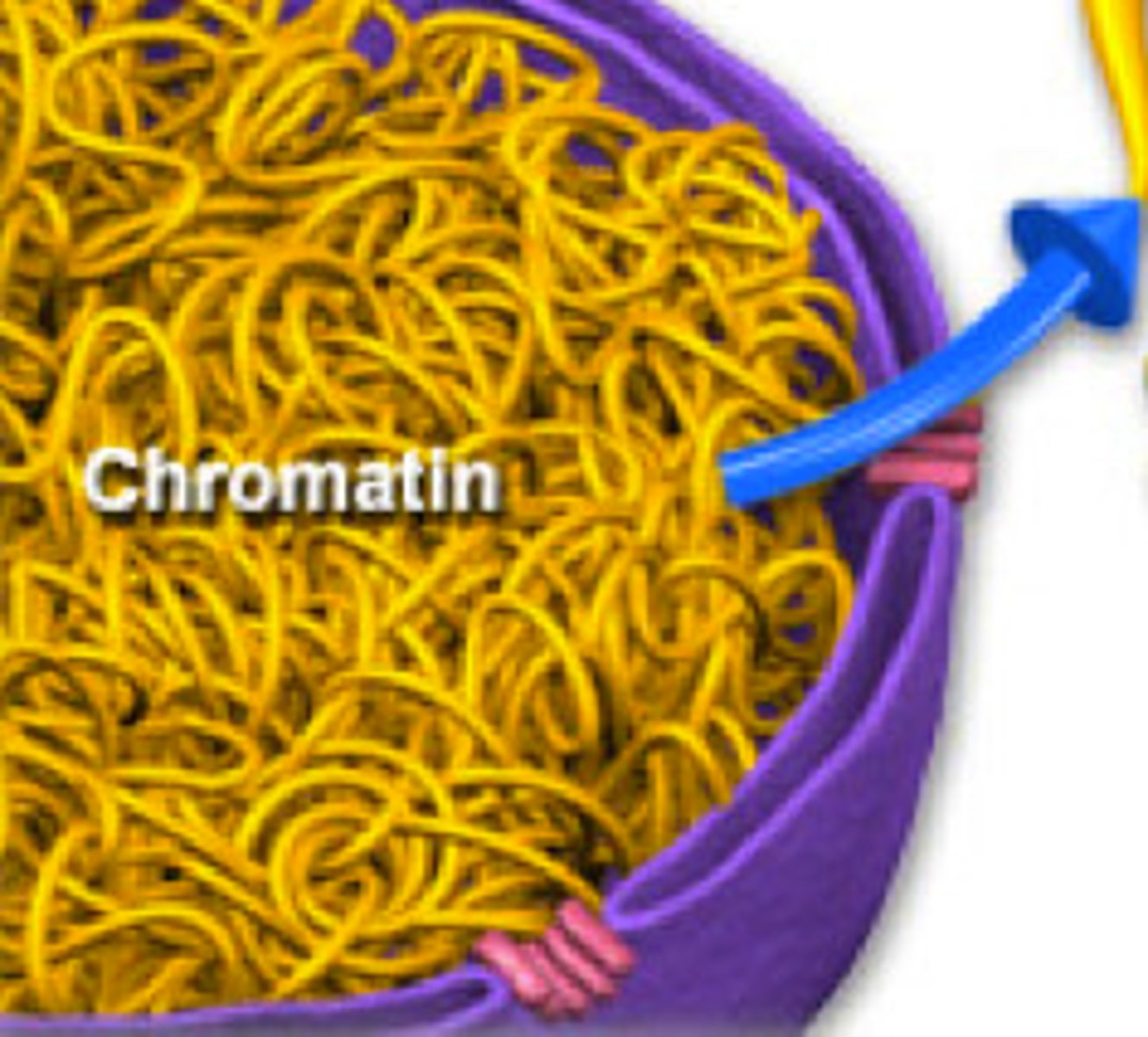
Chromatin
Strand of DNA associated with histones and functional proteins, roughly a 50/25/25 split respectively. Smallest unit of chromosomes, only 2nd to the actual DNA strand itself
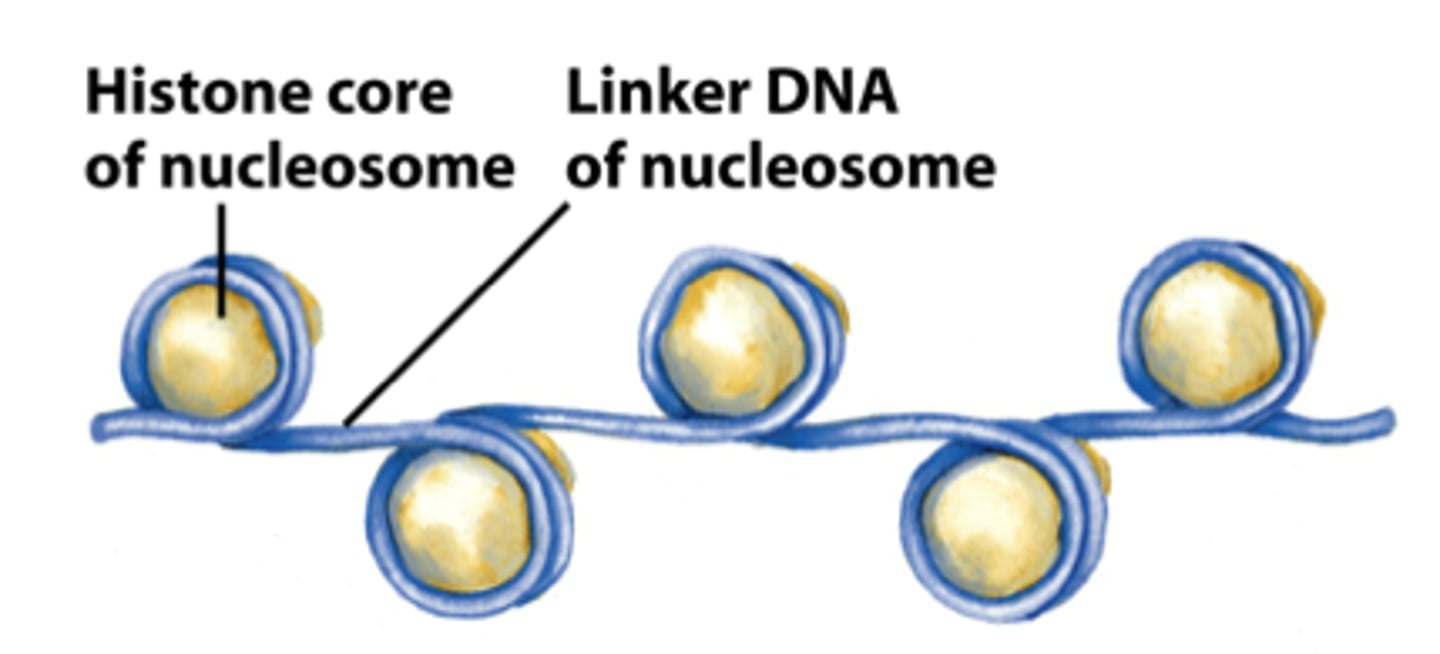
Nucleosome
Repeating subunit of chromatin fibers, consisting of DNA coiled around histones. Only found in Eukaryotes
H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4 Histones
Form polymer in which chromatin wraps around, creating the nucleosome. H2A-H2B and H3-H4 associate with each other, creating the polymer disc
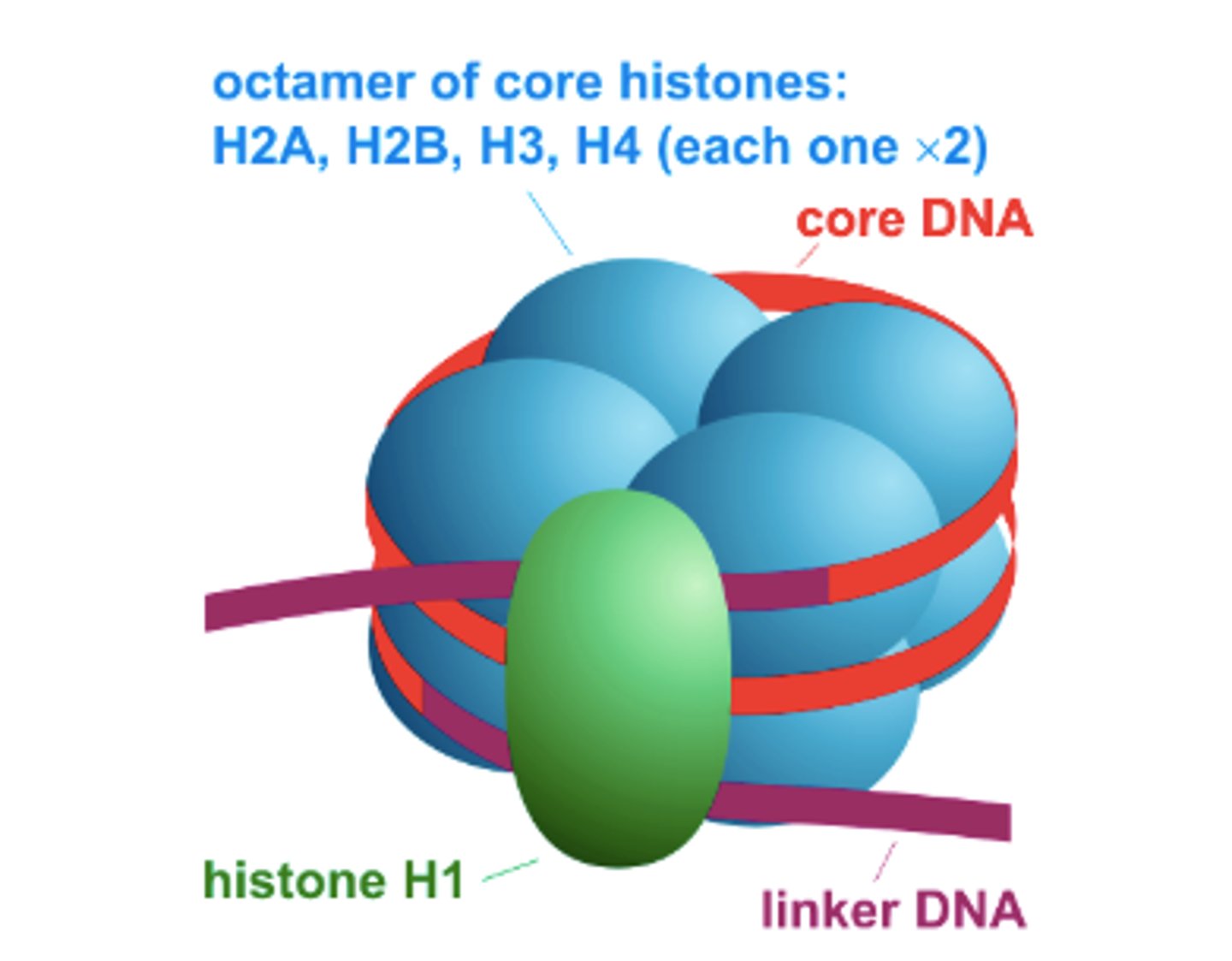
Linker DNA
Region of DNA linking the nucleosomes together
Chromatid
Each half of the chromosome, composed of solenoids which are composed of nucleosomes. Are shaped by chromosome scaffolding.
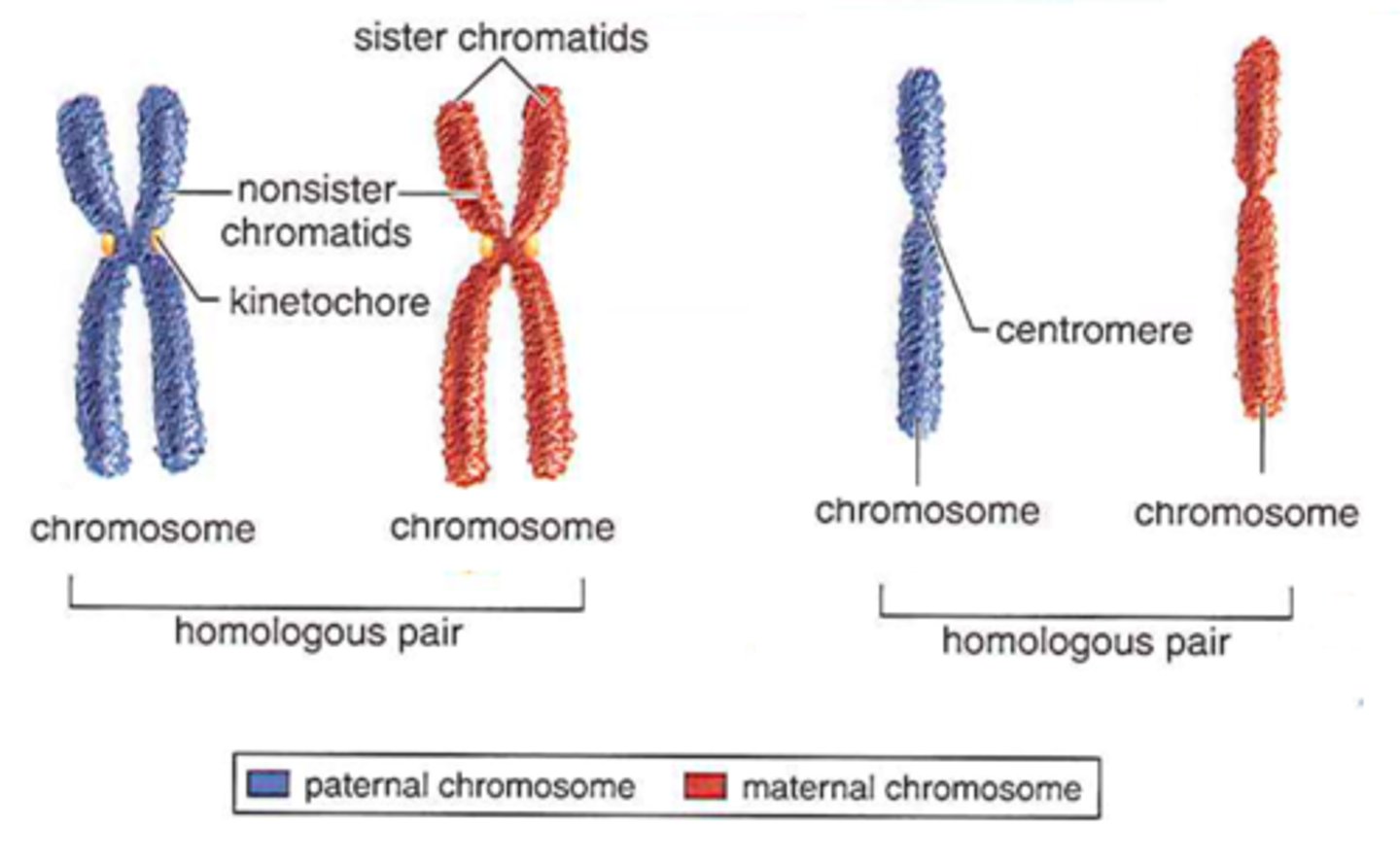
Chromosome scaffolding
Non-Histone proteins that give the shape of chromatids