Lecture 23 - Viruses and Prokaryotes
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
infectious particle w/gene packed in protein coat - not living … “borrowed life”
Must infect host cell to reproduce and carry out metabolic activities
Viruses
double stranded dna
Single stranded dna
Double strand RNA
Single stranded rna
Single linear or circular molecule
Genome of viruses
Capsid
Protein shell enclosing viral genome… made up of capsomeres. # of different kinds of proteins is small, but duplicate number may be high
Membranous envelope - viral envelopes
Surrounds flu virus… derived from membrane of host cell… made up of phospholipids and glycoproteins from host and from viral origin
Bacteriophages / phage
Virus that infect bacteria… most complex capsids, may have protein tailpiece to attach to host and injects viral dna
Obligate intracellular parasites
Can only replicate within host… lack enzymes, ribosomes, etc.
Host range
The number of host cells a virus can infect
Recognition system determines what cells a virus can infect… proteins match up on outside of virus and receptor molecule on hosts surface
Specific host recognized by “lock and key”
West Nile can effect multiple types organisms, birds horses humans and mosquitos.
Measles can only effect humans
Human cold virus infects all cells in upper respiratory track
AIDS only binds to certain white blood cells
Viruses have a range to infect several species,while others only infect a single species
"T - even “ use tail to inject DNA
Others taken up by endocytosis ov fusion of viral envelope w/ plasma membrane of hosts
Ways viruses share DNA with host cell
Once inside… reprogram cell to produce viral dna and proteins
Host provides materials and atp
Dna viruses use dna polymerase
RNA virus use rna polymerase
nuclei acid and capsomeres self-assemble into viral particles
Exits cell, resulting in Cellular damage which results in symptoms of infection
Lytic cycle or lysogenic cycle
double stranded dna viruses replicate by two alternative mechanisms
The phage replicative cycle culminates in death of host… bacterium lyses and releases phases
Virulent phages - replicate only by this cycle
Lytic cycle is…
Natural selection favors mutations where receptor site can no longer be recognized by phages
Restriction enzymes will cut up foreign dna
Methylation of its own dna prevents destruction
Bacteria have defenses against phages… (3)
Instead of losing cell, places can coexist w/ host - this state is ____
What is lysogeny?
During a lysogenic cycle, Viral dna is added into the bacteria’s chromosome, this segment within the bacteria dna is called ________
Viral proteins can break circular dna and join together
Single infected cell can result in population of bacteria with the virus in the dna
Prophage?
Can resist high salt concentration, found in great salt lake
Halobacteria
increased radiation
acidic pH
salt concentration
Under ground
Prokaryotes adapt to harsh conditions like…
Prokaryotes
Most abundant and diverse group of organisms on the planet
no membrane bound nucleus… nucleoid region. looped chromosome
Cell wall
No membrane bound organelles
Have fimbriae and pili for attaching and anchoring
Flagella for motility (analogous to eukaryotic flagellum)
Characteristics of Prokaryotes (5)
Prokaryotes
First organisms to live on Earth and are typically unicellular
Common shapes: bacilli, cocci, and spirals
cell wall protects cell from hypotonic environment
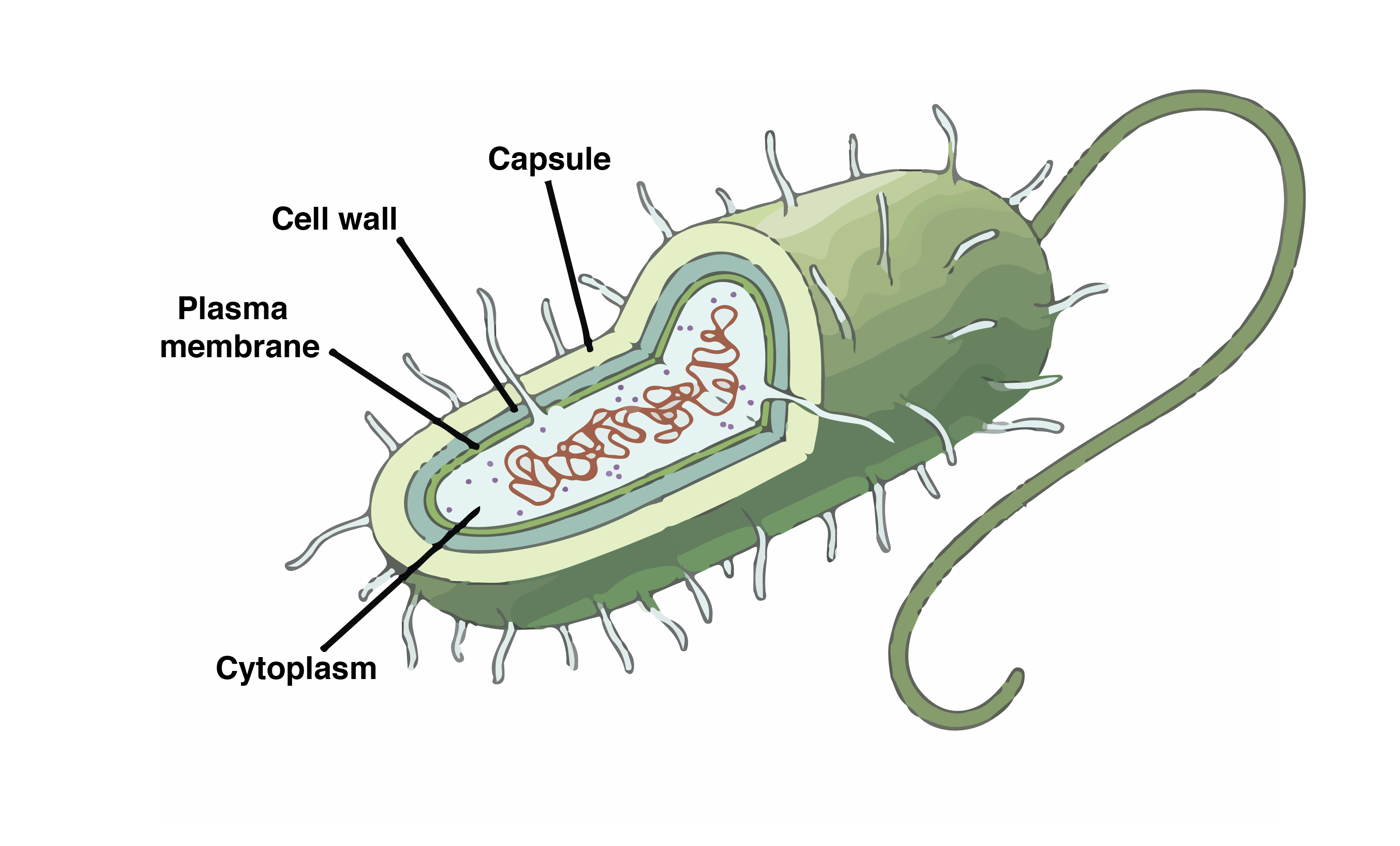
Capsule if dense or slime layer if poorly organized
protects against dehydration
increases resistance to host defenses
Secrete sticky protective layer of polysaccharide or protein… allow cells to adhere to substrate or other individuals. Name 2 benefits.
are small
reproduce by binary fission (asexual)
short generation times
3 key features in prokaryotes for reproduction
Increased chances for mutations… they adapt rapidly to environmental changes as natural selection favors those that are of greater fitness
Benefit of having a short generation time and large population…
Photoautotrophs
Examples: cyanobacteria, plants and algae
Photosynthetic organisms that use light to drive synthesis of organic compounds from CO2.
Chemoautotrophs - unique to prokaryotes
Need inorganic molecules like CO2 for carbon source, but get energy from oxidizing inorganic substances (like H2S, NH3, Fe2+)
Photoheterotrophs
Ex: few marine and halophilic prokaryotes
Use light to generate ATP but get carbon from organic form
Chemoheterotrophs
Ex: prokaryotes, protists, fungi, and animals
Humans
Consume organic molecules for both energy and carbon
Obligate aerobes
Require O2 for cellular respiration
Facultative anaerobes
Use O2 if it is present, but can also grow by fermentation in anaerobic environment
Obligate anaerobe
Die by O2, use either fermentation or anaerobic respiration (inorganic molecules other than O2 accepts electrons from ETC)
Nitrogen-fixing Prokaryotes
*Most self-sufficient
Convert N2 to NH3, can incorporate it into organic molecules
Result is large portions of the genome in many prokaryotes are actually a mosaic of genes and imported from other species.
Horizontal gene transfer in the evolution of prokaryotes
Extremophiles
Live in extreme environments - archaea species
Extreme halophiles
Live Salty places
extreme thermophiles
Live in hot environments
Methanogens — strict anaerobes
Obtain energy by using CO2 to oxidize H2, producing methane as waste
Gram -
Subgroups:
Proteobacteria
Chamydias
Spirochetes
Cyanobacteria
Pathogenic species deadlier than gram +… 4 subgroups
Decomposers
Chemoheterotrophic prokaryotes act like ____, by breaking down dead organisms and waste products = C, N, and other elements
Symbiosis
Ecological relationship between organisms that are in direct contact.
Host
Larger organism in a symbiotic relationship
Symbiont
Smaller organisms in a symbiotic relationship
Parasitism
A symbiotic organism that benefits at expense of host - parasite
Parasite
Eats cell contents, tissues, or body fluids of hostPa
Pathogens
Parasite diseases, _____ are prokaryotic M
Mutualism
Both symbiotic organisms benefit
Bioremediation
Use of organisms to remove pollutants from air, water, and soil
anaerobic bacteria decompose organic matter in sewage for landfill or fertilizer
Vitamins, antibiotics, hormones, and many other products
Through genetic engineering, humans have developed prokaryotes that can produce…
1/2
Prokaryotes cause what percentage of human diseases?
Exotoxins
Proteins released by certain bacteria that can produce disease
Endotoxins
Lipopolysaccharide components of outer membrane of some gram - bacteria
released when bacteria dies and cell wall breaks