MicroTheory- Cost Curves
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What is a cost curve?
A cost curve is a graph relating a firm’s costs to output choice. The image lists some examples

What is a fixed cost?
These are costs that do not vary with the firm’s output level. (Only in the short run)
What is a variable cost?
Costs which vary with the firm’s output level.
What is a sunk cost?
These are costs that have already been paid and cannot be recovered.
What is true about some fixed costs but not all fixed costs?
Some fixed costs are also sunk costs if they cannot be recovered (but not all fixed costs are sunk costs).
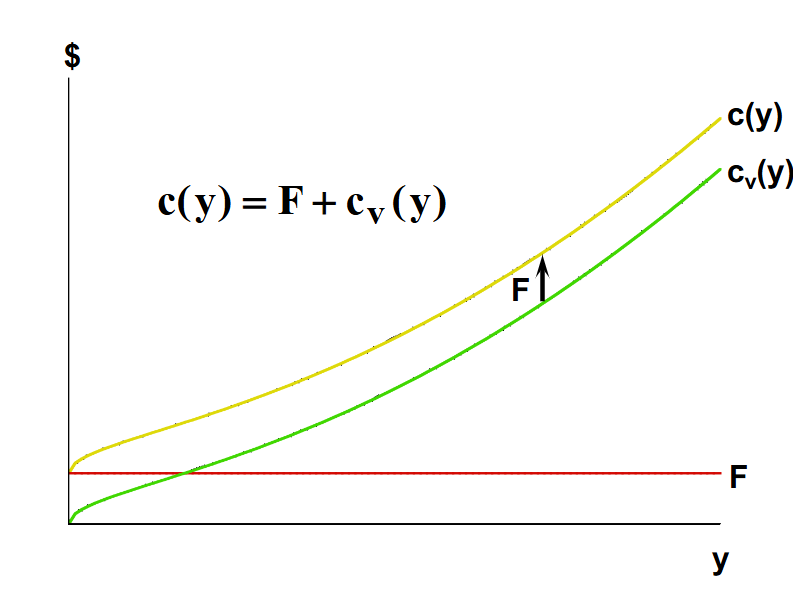
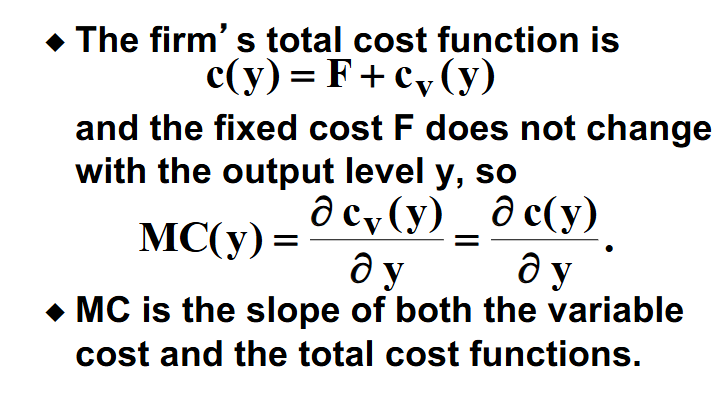
What is the equation for a firm’s total cost function (in the short run)?
c(y) = F + cv (y)
What does the firm’s fixed cost curve look like, graphically? (Keep in mind the fact that this is only for the short-run supply)

What does the firm’s variable cost curve look like, graphically?
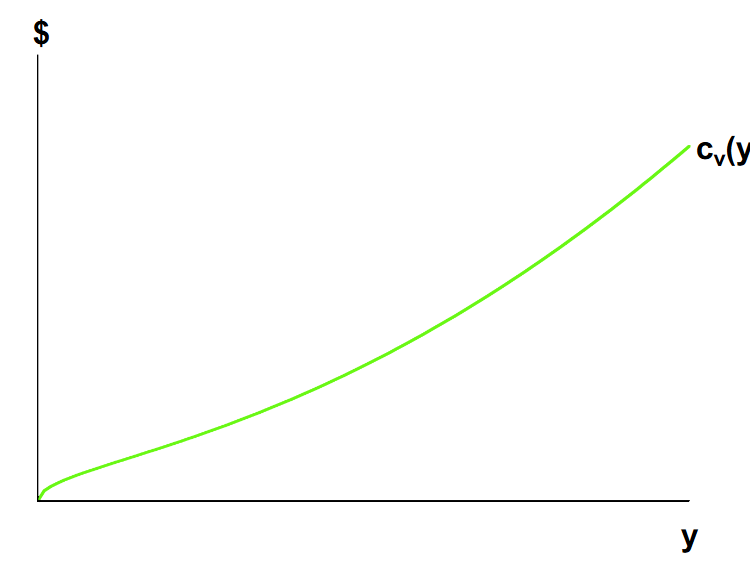
How is the total cost curve expressed, graphically?
The F with the upwards arrow is referencing that the total cost curve comes from variable cost curve plus the fixed cost.
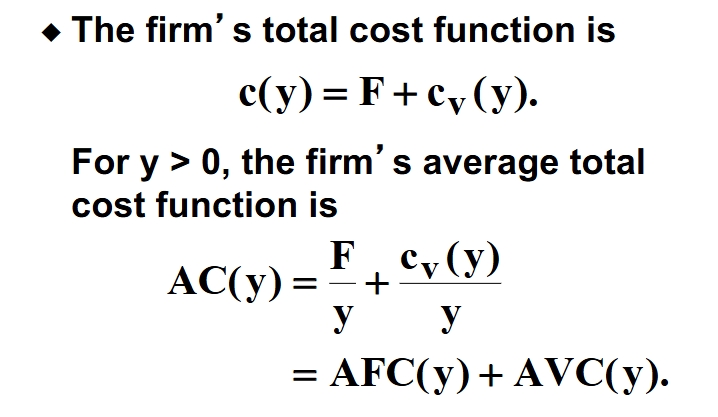
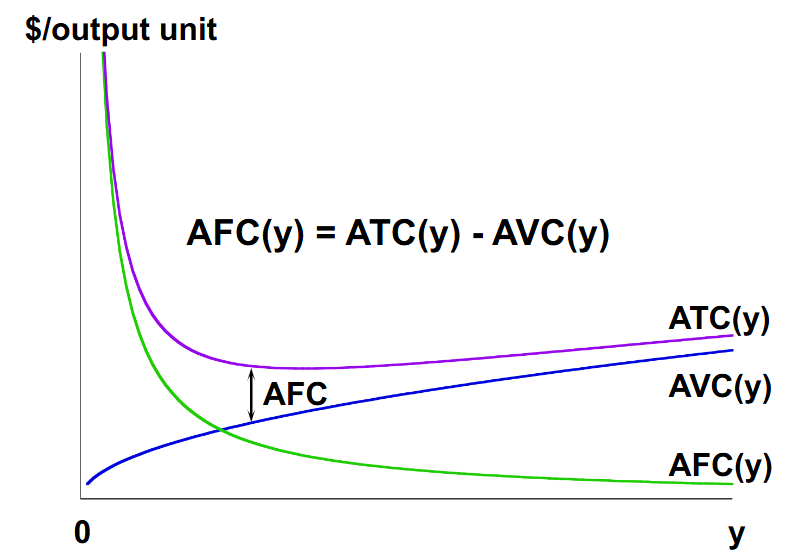
What is the equation that connects Average fixed cost and Average variable cost to average total cost?
Fixed cost divided by output is average fixed cost. Variable cost divided by output is average variable cost.
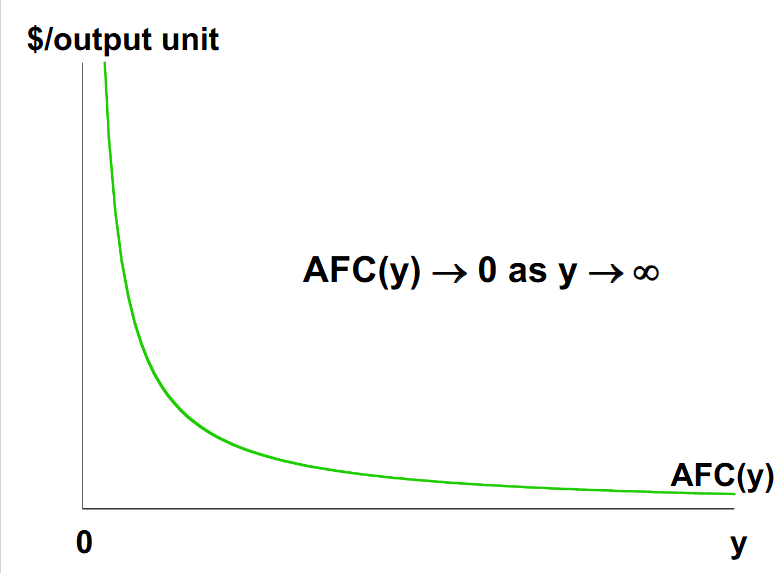
How does average fixed cost change in response to output increasing?
Average fixed cost will fall as output increases because it’s a cost that will get smaller in comparison to the cost of other inputs as output increases.
How does average variable cost change in response to output increasing?
Average variable cost will rise with output because the law of diminishing returns (you will see diminishing returns on the variable input, so you end up spending more on the variable input to see output rise).
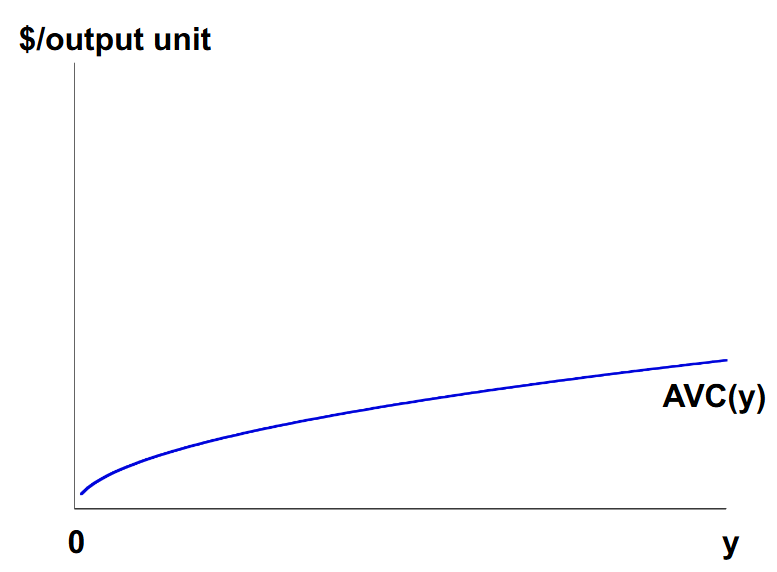
What does the average total cost curve look like, graphically?
The AFC in between ATC and AVC is in reference to how AVC + AFC = ATC
What does the new meaning of marginal cost refer to?
This now is referring to the rate of change of variable production as output level changes as opposed to input level like before. It is the partial derivative of variable cost over the partial derivative of output.
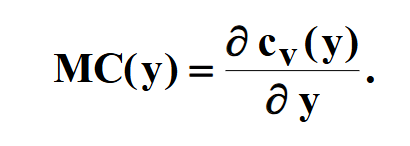
What is the slope of the variable cost function and total cost function?
Marginal cost is the slope of the variable and cost function because fixed cost doesn’t change with output level.
What happens to average variable cost (and average total cost) as marginal cost rises above them?
Average cost and average variable cost are both increasing if marginal cost is greater than AC or AVC.
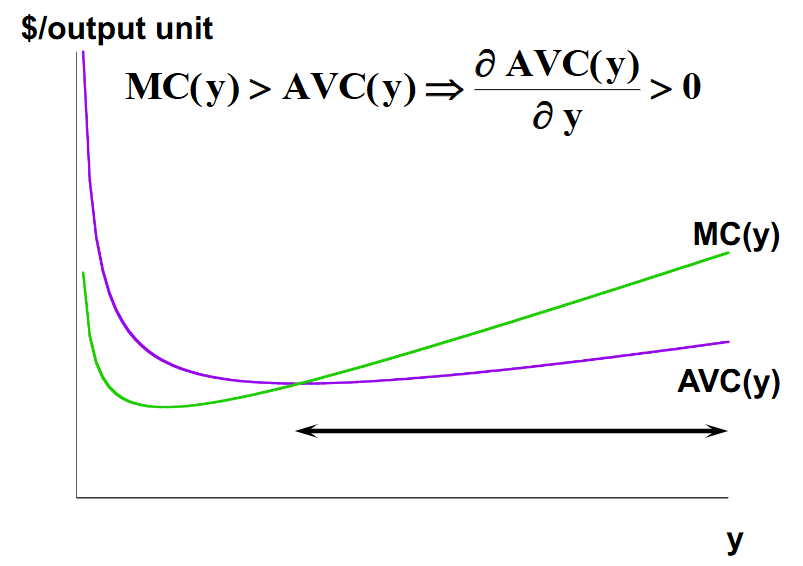
What happens to average variable cost (and average total cost) as marginal cost falls below them?
Average cost and average variable cost are both decreasing is marginal cost is less than AC or AVC.
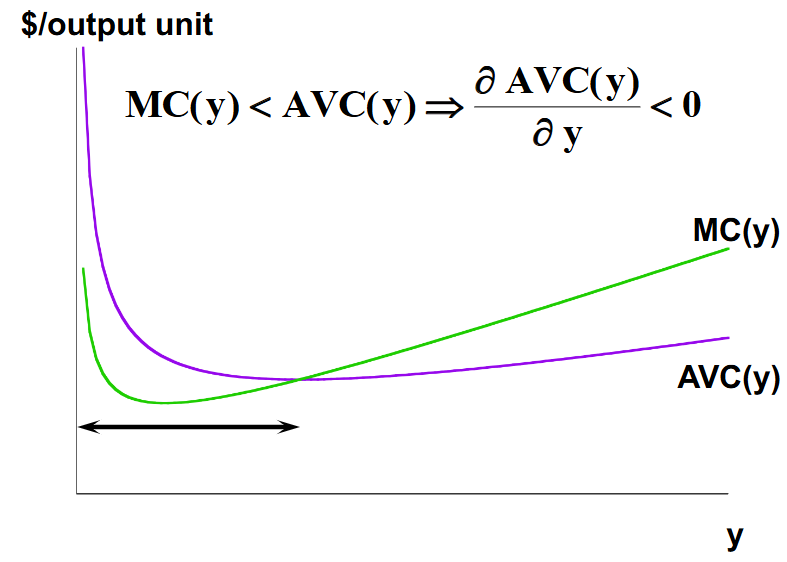
What happens to average cost and average total cost as marginal cost remains constant?
Average cost and average variable cost remain constant as marginal cost remains constant.
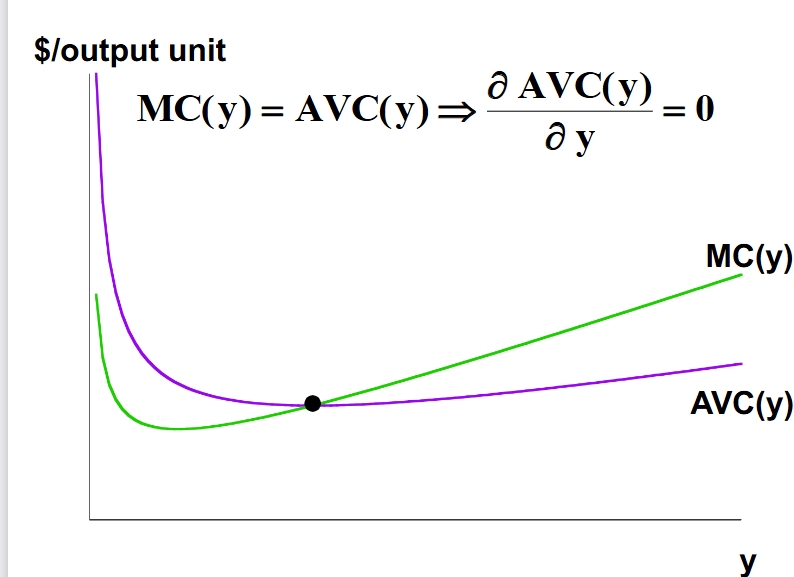
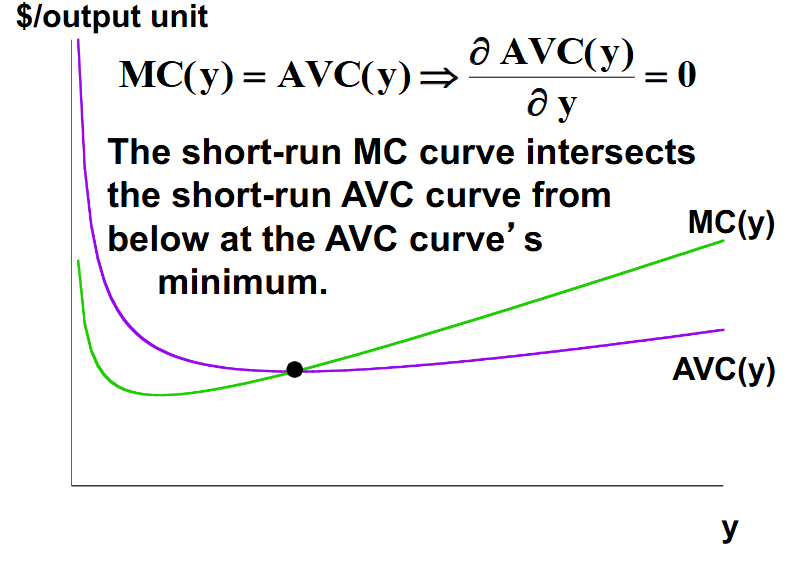
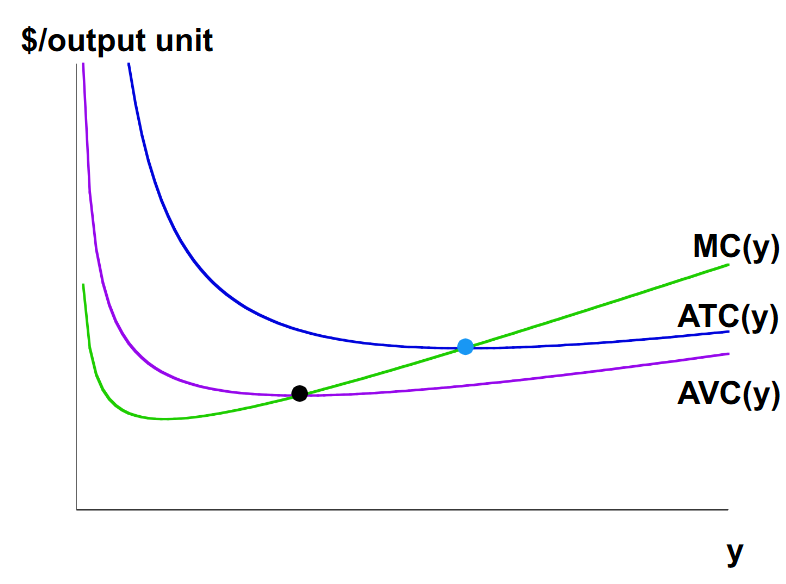
In the short run, where does the MC curve intersect the AVC curve?
The marginal cost curve will intersect the average variable cost curve from the average cost curve’s minimum.
In the short run, where does the MC curve intersect the ATC curve?
Similar to AVC curve, the Marginal cost curve will intersect the average total cost curve from below, at the ATC curve’s minimum.
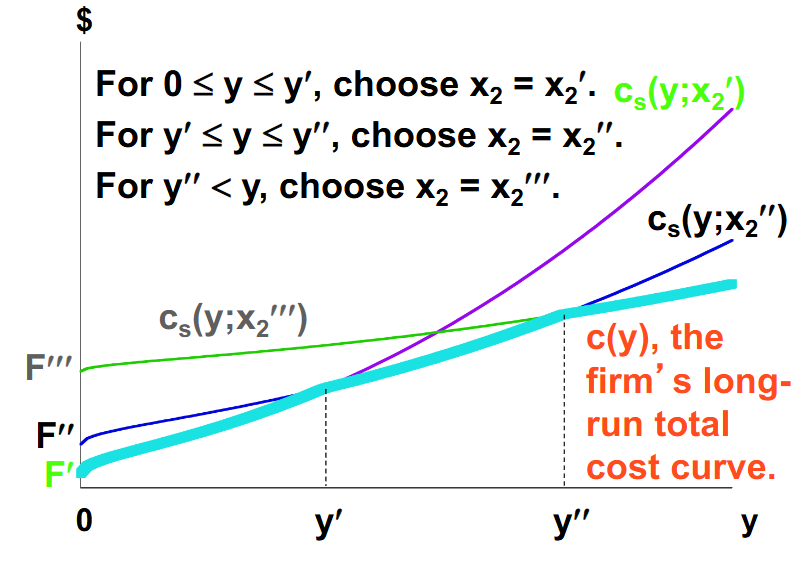
What is the firm’s long run total cost curve?
A firm’s long run total cost curve will be the cheapest methods of production from different short-run circumstances. This is because these short run circumstances all have various levels of output and in the long run firms have a choice between these three short runs and are able to choose whichever short run is the cheapest in that moment. In this case, purple short run is the cheapest, then the blue short run is the cheapest, and finally the green short is the cheapest.
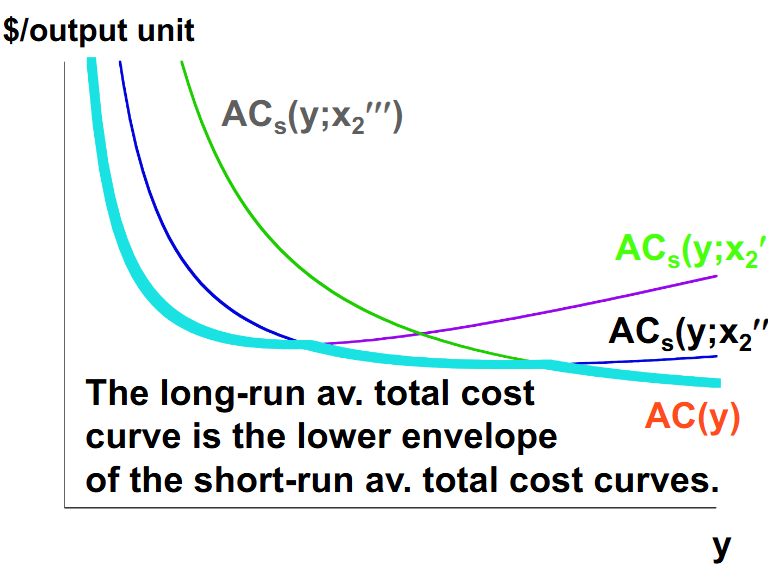
What is the firm’s long run average total cost curve?
The reason it is the lower envelope is because the short-run total cost curves have various levels being in the short run, but in the long run firms can choose whichever total cost curve is the lowest (the cheapest).
What is the firm’s long run marginal cost curve?
The long run marginal cost curve is Mutiple short run marginal cost curves that don’t intersect because marginal costs will be different in every short run.
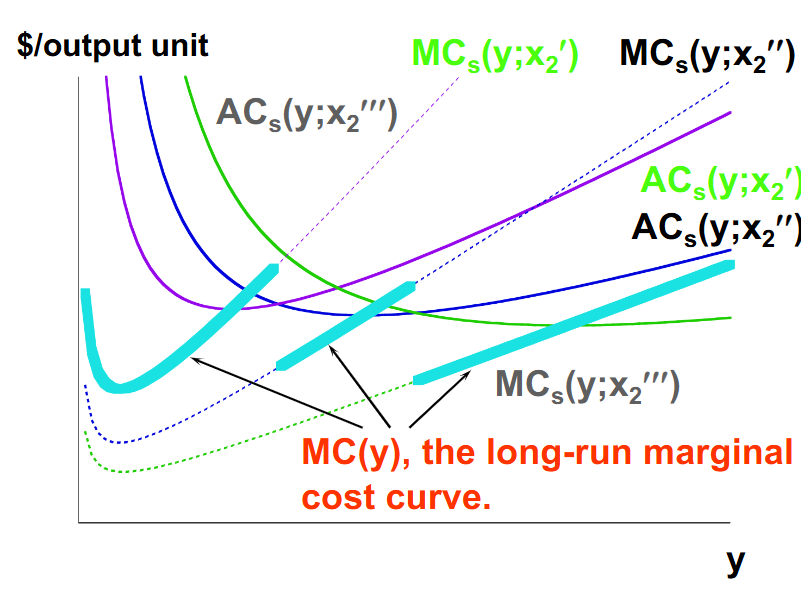
What is true of marginal costs in the long run and short run?
The long run marginal cost will equal the marginal cost that the firm chose in the short run.
What is the equation of the total cost curve in the short run?
TC = F + cv (y)
What is the equation of the total cost curve in the long run?
TC (y) = cv (y) *No fixed costs
What is the adjustability of the firm in the short run?
In the short run, firms are constrained by one input.
What is the adjustability of the firm in the long run?
In the long run, firms are fully flexible and aren’t constrained by any inputs.
What is the main cost minimization problem for firms in the short run?
The main CMP is trying to optimize while dealing with a fixed input.
What is the main cost minimization problem for firms in the long run?
The CMP for firms in the long run is working while unconstrained (they can fully optimize to cost minimize).
What is the shape of a cost curve in the short run?
Short run cost curves are higher due to fixed inputs.
What is the shape of a long run cost curve?
The shape of a long run cost curve is the lower envelope of the short run total cost curves