Nematodes + Tissue Nematodes + Filarial Worms
1/218
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
219 Terms
What are nematodes?
They are roundworms, are nonsegmented, cylindrical worms with a well-developed digestive and reproductive system.
How can nematodes be identified in clinical diagnosis?
By observing their characteristic eggs in the stool.
How are nematode infections typically transmitted?
By ingesting eggs, or
Through skin penetration by larvae.
What is the common name for Strongyloides stercoralis?
Threadworm.
Where is the parasitic form of S. stercoralis found?
Parasitic form inhabits the intestine.
Where is the free-living form of S. stercoralis found?
Free-living form is found in the soil.
What are the three phases in the life cycle of S. stercoralis?
Direct
Indirect (free-living)
Autoinfective
What is the infective larval stage of S. stercoralis called?
The filariform larva.
How do filariform larvae of S. stercoralis infect the host?
By penetrating the skin, then migrating via the bloodstream to the heart and lungs, entering the bronchi, and being swallowed to reach the intestines.
What is autoinfection in S. stercoralis?
When filariform larvae penetrate the intestinal mucosa, allowing the parasite to reinfect the same host without leaving the body.
How does the female S. stercoralis reproduce?
Through parthenogenesis, a form of asexual reproduction that occurs without fertilization.
What is the diagnostic stage of S. stercoralis?
The rhabditiform larva, not the egg.
What are the key identifying features of the rhabditiform larva of S. stercoralis?
250–300 μm long
Short buccal cavity
Large esophageal bulb
Prominent genital primordium
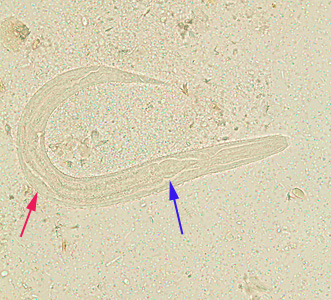
How does the filariform larva differ from the rhabditiform of S. stercoralis?
It is longer (up to 500 μm).
How can S. stercoralis larvae be distinguished from hookworm larvae?
S. stercoralis has a short buccal cavity and prominent genital primordium
Hookworm larvae have a long buccal cavity and an indistinct or absent genital primordium
If larvae (not eggs) are found in stool, what parasite is most likely present?
Strongyloides stercoralis, not hookworm.
What environmental conditions help sustain the life cycle of S. stercoralis?
The presence of organic material in moist soil, which supports free-living adult parasite forms.
How can person-to-person transmission of threadworm occur?
In institutional settings, daycare centers, and among homosexual men.
What are the three symptomatic phases of threadworm infection?
Cutaneous phase
Pulmonary phase
Intestinal phase
What symptoms may occur in the cutaneous phase of threadworm infection?
Urticarial or maculopapular rashes
Serpiginous rash on the thighs and buttocks
Rashes often occur along the waist
What symptoms may occur in the intestinal phase of threadworm infection?
Asymptomatic in mild cases
Abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, constipation
Blood loss in more severe cases
What causes pulmonary symptoms in threadworm infection?
The migration of filariform larvae to the lungs.
What is hyperinfection in the context of S. stercoralis?
A condition where filariform larvae penetrate the intestinal wall, increasing worm burden in the lungs or intestines.
What hematologic finding is associated with acute S. stercoralis infection?
An increase in eosinophils in the peripheral blood.
What is the treatment for S. stercoralis infection?
Ivermectin
What are the two species responsible for human hookworm infections?
Necator americanus (New World hookworm)
Ancylostoma duodenale (Old World hookworm)
How do the life cycles of N. americanus and A. duodenale compare?
Their life cycles are similar, and their eggs and rhabditiform larvae are indistinguishable.
What is the diagnostic stage of hookworm infection?
The egg, which is passed in feces and hatches into rhabditiform larvae in the environment.
Are hookworm larvae usually found in feces?
No, larvae are generally not seen in the feces.
What environmental conditions support hookworm transmission?
Warm, moist soil is needed for the parasitic life cycle to be maintained.
What sanitation issue is commonly linked to hookworm transmission?
Inadequate sewage disposal, which allows hookworm eggs to hatch and develop in the soil.
What happens to hookworm eggs after they are passed in stool?
They hatch into rhabditiform larvae within 1 to 2 days and develop into filariform larvae in the soil or feces.
How long can hookworm filariform larvae survive in favorable conditions?
For about one month.
What is the infective stage of hookworm?
The filariform larva.
How do hookworm larvae enter the human body?
By penetrating the skin, then migrating through the bloodstream to the lungs, ascending the bronchial tree to the pharynx, and being swallowed into the digestive tract.
Where do adult hookworms mature and live in the human body?
In the small intestine, where they attach to the mucosal walls.
What do adult hookworms feed on, and what do they secrete?
They ingest blood and secrete anticoagulant compounds.
How long can adult hookworms remain in the intestines?
Indefinitely, but many are eliminated within 1–2 years.
What is “ground itch” in hookworm and what causes it?
a local skin reaction (urticaria, redness, swelling) at the site where larvae penetrate the skin.
What are the symptoms during the pulmonary phase of hookworm infection?
Pharyngitis
Cough
Bloody sputum
What are the gastrointestinal symptoms during the intestinal phase of hookworm?
Abdominal pain
Diarrhea
Nausea and vomiting
Anorexia
What complications can arise from heavy hookworm infections?
Blood loss
Iron deficiency anemia
Fatigue and weakness
Edema
Eosinophilia
Occult blood in stool
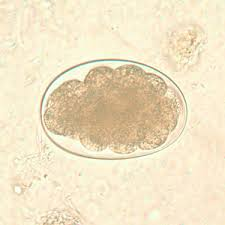
What are the features of a hookworm egg?
Oval, thin-shelled, and colorless
Measures 60–70 μm by 35–40 μm
Contains a clear space and yolk cells or developing larvae
How are hookworm infections treated?
With albendazole or mebendazole.
Are light hookworm infections always treated?
No, in endemic regions, light infections may not be treated due to high reinfection rates.
What is the common name for Enterobius vermicularis?
Pinworm.
What disease is caused by E. vermicularis?
Enterobiasis.
Who is most often affected by E. vermicularis (pinworm)?
School-age and preschool children, especially in crowded living conditions.
How is E. vermicularis transmitted?
Direct person-to-person contact
Ingestion or inhalation of infective eggs
Self-infection via contaminated hands after scratching the perianal area
What is the infective stage of E. vermicularis?
The embryonated egg containing third-stage larvae.
Where does the gravid female E. vermicularis deposit her eggs?
In the perianal region, typically at night.
How long does it take for the gravid female E. vermicularis eggs to become infective after being laid?
Within just a few hours.
What happens after the gravid female E. vermicularis infective eggs are ingested?
Larvae hatch in the small intestine
Adult worms develop in about 1 month
Gravid females lay eggs, continuing the cycle
How long do adult pinworms typically live?
About 2 months.
What is retroinfection in the context of enterobiasis?
When hatched larvae crawl back through the anus into the rectum, re-enter the intestines, and mature into adults.
Do adult E. vermicularis worms migrate through the bloodstream?
No, unlike threadworms and hookworms, pinworms do not migrate through the circulatory system.
How large are mature adult pinworms?
5 mm to 10 mm in length.
What are distinguishing physical features of adult pinworms?
A wing-like bulge at the anterior end
A long, pointed “pin-shaped” tail

Where are pinworm eggs typically found?
On the perianal folds, not usually in the feces.
When is the best time to collect samples for diagnosing pinworm infection?
In the morning, before bathing or using the toilet, because eggs are deposited at night.
How are pinworm eggs collected for diagnosis?
Using clear cellophane tape or a sticky paddle pressed against the perianal area.
What is the diagnostic stage of pinworm infection?
The egg.
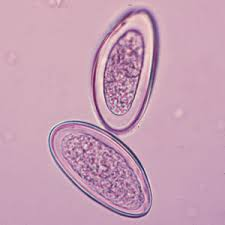
What are the characteristics of a pinworm egg?
Measures 60 μm by 20–30 μm
Has a slightly flattened side
Are adult worms commonly recovered in pinworm diagnosis?
No, adult worms are generally not recovered.
How is pinworm infection transmitted?
By ingesting contaminated food or hands
Through person-to-person contact
From contaminated clothing, bedding, or objects
How can children self-infect with pinworms?
By scratching the perianal area at night, allowing eggs or larvae to collect under their fingernails, which are then ingested.
What are common symptoms of pinworm infection?
Perianal, nocturnal itching
In heavy infestations: bleeding, nausea, abdominal pain, irritability, and nervousness
What is the treatment for pinworm infection?
Pyrantel pamoate
How can pinworm reinfection be prevented?
Good personal hygiene
Laundering bedding, clothing, and other contaminated articles
What is the common name for Ascaris lumbricoides?
The large intestinal roundworm.
How is A. lumbricoides transmitted?
By ingestion of embryonated eggs that contain second-stage larvae.
What is significant about Ascaris lumbricoides?
It is the most common and largest roundworm infecting humans.
Where do adult Ascaris worms live in the human body?
In the small intestine.
How many eggs can a gravid female Ascaris worm produce daily?
Up to 200,000 eggs per day.
Are unfertilized Ascaris eggs infectious?
No, unfertilized eggs do not develop and are not infectious.
What conditions are needed for Ascaris eggs to become infective?
Warm, moist soil where the eggs embryonate over 2–3 weeks.
What happens after ingestion of infective Ascaris eggs?
Larvae hatch in the small intestine
Penetrate the intestinal wall
Migrate through the hepatic portal circulation to the lungs
Reach the bronchi, then pharynx, and are swallowed again
Return to the small intestine to mature into adult worms
How long do adult Ascaris worms typically live?
About 1 to 2 years.
What is the size of adult Ascaris lumbricoides worms?
200–300 mm in length
3–5 mm in diameter
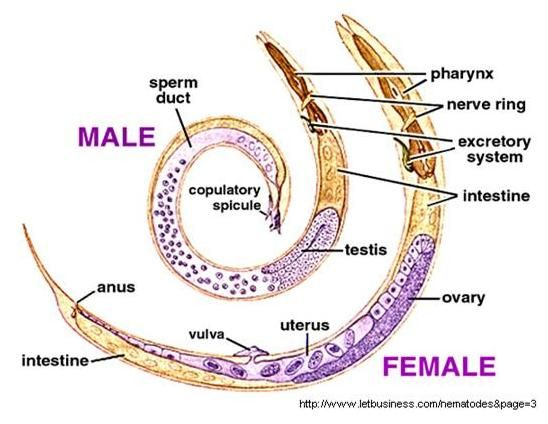
How do male and female Ascaris worms differ?
Male worms are shorter and have a curved tail.
What is the diagnostic form of Ascaris lumbricoides?
The egg.
What are the features of a fertilized Ascaris egg?
Large and oval
Brown-stained from bile
Often mammillated with a thick albuminous (cortical) coat
May show cleavage or a developing embryo
Measures 60 μm × 45 μm
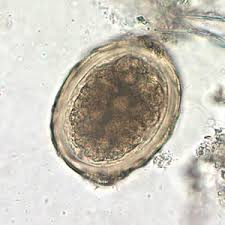
What does a decorticated Ascaris egg lack?
It lacks the outer albuminous coat.
How do unfertilized Ascaris eggs differ from fertilized ones?
Longer and irregularly shaped
Have a thin shell
May have a distorted coat
Often contain undifferentiated protoplasm
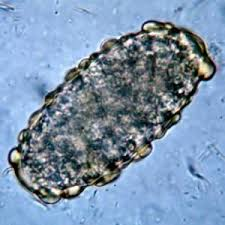
How are Ascaris eggs best recovered in the lab?
Using sedimentation concentration methods, because the eggs are too heavy to float in zinc sulfate solution.
Who is most commonly infected by Ascaris?
Young children, often due to eating dirt or putting contaminated fingers in their mouths.
How can Ascaris infection be acquired through food?
By eating raw food contaminated with soil containing human feces with Ascaris eggs.
What are pulmonary symptoms of Ascaris infection during larval migration?
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
Cough
Hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
What intestinal symptoms may occur with Ascaris infection?
Abdominal pain
Diarrhea
Intestinal obstruction (in heavy infections)
What complications can arise from large infestations of Ascaris?
Malnutrition and weight loss
Liver damage, including hepatic abscesses
Obstructive cholangitis
How is ascariasis treated?
With albendazole or mebendazole.
What is the common name for Trichuris trichiura?
Whipworm
How is whipworm infection acquired?
Through ingestion of food or water contaminated with embryonated eggs containing first-stage larvae.
What happens to Trichuris eggs after they are passed in stool?
They are unembryonated at first
Develop into a two-cell stage in the soil
Embryonate in 2–4 weeks in warm, moist conditions, becoming infective
After ingestion, where do Trichuris trichiura larvae go?
Hatch in the small intestine
Migrate to the cecum, where they mature into adult worms
How long after infection do Trichuris females begin producing eggs?
About 2 months
Does Trichuris trichiura have a tissue migration phase?
No
What is the diagnostic form of T. trichiura?
The egg
What are the identifying features of Trichuris eggs?
Brown, elongated, lemon-shaped or football/barrel-shaped
Measure 50–55 μm by 22–25 μm
Have thick walls and hyaline polar plugs at both ends
Often few eggs are present in stool samples

What do adult Trichuris worms look like?
30–50 mm long
Resemble a whip with a thin anterior esophagus and thicker posterior end (the “handle”)
