Biology SL - Topic 2, Molecular Biology (2.1-2.5)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:48 PM on 1/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
what does molecular bio explain
living processes in terms of the chemical substances involved
2
New cards
why are carbon atoms the unit of life?
carbon atoms can form covalent bonds with 4 other atoms, practical, allowing a diversity of stable compounds to exist
3
New cards
what exist as carbon compounds?
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids (life)
4
New cards
what is metabolism?
the web of all the enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a cell or organism
5
New cards
what is anabolism?
the synthesis of complex molecules from simple molecules including the formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions (CONDENSATION = - H2O)
6
New cards
what is catabolism?
the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers (HYDROLYSIS = + H2O)
7
New cards
what is an example of a compound that is produced by living organisms and can be artificially synthesized?
urea
8
New cards
how did the artificial synthesis of urea falsify vitalism?
vitalism: the theory that the origin of life is dependent on a force or principle distinct/different to chemical or physical forces.
\
The synthesis of urea proved that organic matter from living organisms could be produced simply from the basic building blocks of non-living things (chemical compounds)
\
The synthesis of urea proved that organic matter from living organisms could be produced simply from the basic building blocks of non-living things (chemical compounds)
9
New cards
molecular diagram of glucose
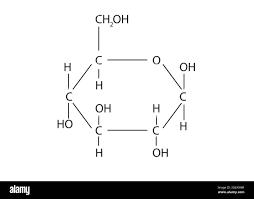
10
New cards
molecular diagram of ribose
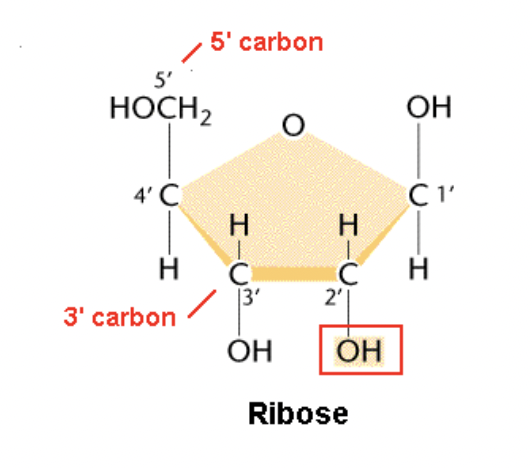
11
New cards
molecular diagram of a saturated fatty acid
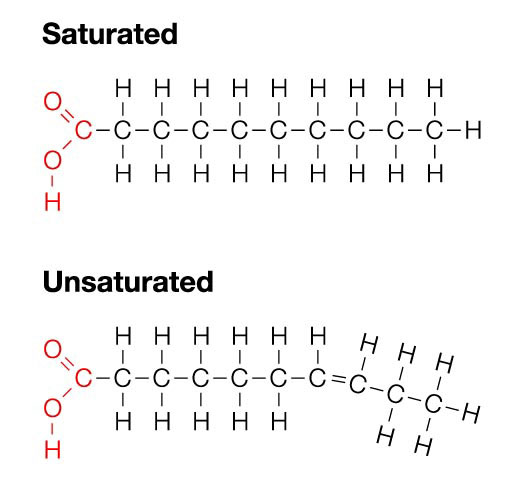
12
New cards
molecular diagram of a generalized amino acid
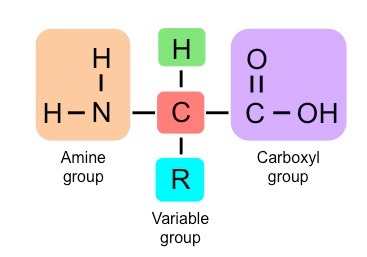
13
New cards
how to identify sugars in a molecular drawing
C H O, ring shape (lots of OH, C, H)
14
New cards
how to identify lipids in a molecular drawing
linear shape, C H O, carboxyl group, (no N or amine group)
15
New cards
how to identify amino acids from molecular drawings
star shape, amine group, R variable group, carboxyl group, C H O N
16
New cards
describe water molecules
they are polar and hydrogen bonds form between them
17
New cards
what are the properties of water?
cohesive, adhesive, thermal, and solvent
18
New cards
how can the properties of water be explained
due to water’s hydrogen bonds and its polarity (can repel or attract other molecules because of charge. between the 2 atoms, one of them is attracting electrons more than the other)
19
New cards
why are water molecules polar?
2 hydrogen bonds are bonded covalently with an oxygen atom. the o atom is larger (contains more (+) protons) the protons attract more electrons than those in h atoms. The o “end” of the molecule is negatively charged, while the h “end” is SLIGHTLY positively charged. = water is polar
20
New cards
what does hydrophobic mean
REPELS water (doesn’t like it) - insoluble (NON-POLAR)
21
New cards
what does hydrophillic mean
ATTRACTS water (likes it) - soluble (POLAR)
22
New cards
how does water’s thermal property compare to that of methane?
water is polar and can form hydrogen bonds between its atoms. methane is non-polar and can only form weak dispersion forces between its atoms.
* Water has a significantly higher melting and boiling point
* Water has a higher specific heat capacity (energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of substance by 1ºC)
* Water has a higher heat of vaporization (energy absorbed per gram as it changes from a liquid to a gas / vapor)
* Water as a higher heat of fusion (energy required to be lost to change 1 g of liquid to 1 g of solid at 0ºC)
* Water has a significantly higher melting and boiling point
* Water has a higher specific heat capacity (energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of substance by 1ºC)
* Water has a higher heat of vaporization (energy absorbed per gram as it changes from a liquid to a gas / vapor)
* Water as a higher heat of fusion (energy required to be lost to change 1 g of liquid to 1 g of solid at 0ºC)
23
New cards
how is water used as a coolant? (automobile radiators)
due to its high specific heat, water can absorb heat from other bodies very easily.
* it has a HIGH SPECIFIC HEAT TOLERANCE/CAPACITY
* it’s cheap
* it can be mixed with anticorrosion inhibitors and antifreeze = perfect !
* it has a HIGH SPECIFIC HEAT TOLERANCE/CAPACITY
* it’s cheap
* it can be mixed with anticorrosion inhibitors and antifreeze = perfect !
24
New cards
substances insoluble in water are … and therefore…
1. hydrophobic 2. non-polar
25
New cards
substances soluble in water are… and therefore…
1. Hydrophilic 2. polar
26
New cards
carbohydrates
CHO, make up cellulose, important for storage of energy (cells) important in all biological functions.
\
monosaccharide subunits (eg glucose) can make up disaccharide/polysaccharide links by condensation reactions (removing h2o so the O can bond the 2 molecules can bond)
\
monosaccharide subunits (eg glucose) can make up disaccharide/polysaccharide links by condensation reactions (removing h2o so the O can bond the 2 molecules can bond)
27
New cards
unsaturated fatty acids
(can fit more hydrogen) - have an unlinear molecular shape. they can be trans(bad. hydrogens on different sides) or cis (good. hydrogens on the same side)
28
New cards
how are triglycerides formed?
condensation reactions. (3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol)
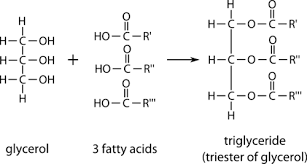
29
New cards
structure and function of cellulose and starch in plants + glycogen in humans
starch is the main storage carbohydrate source in plants whereas cellulose is the main structural component of the cell wall of plants and glycogen is the main storage carbohydrate energy source of fungi and animals.
30
New cards
heatlth risks of trans and saturated fats
* Saturated fats increase LDL levels within the body, raising blood cholesterol levels
* *Trans* fats increase LDL levels **and** decrease HDL levels within the body, significantly raising blood cholesterol levels
* Unsaturated (*cis*) fats increase HDL levels within the body, lowering blood cholesterol levels
* *Trans* fats increase LDL levels **and** decrease HDL levels within the body, significantly raising blood cholesterol levels
* Unsaturated (*cis*) fats increase HDL levels within the body, lowering blood cholesterol levels
31
New cards
lipids are more suitable for long-term energy storage than carbohydrates, true or false?
true
32
New cards
BMI
can be calculated or measured using a nonogram
33
New cards
2 main health claims:
* Diets rich in saturated fats and *trans* fats increase the risk of CHD
* Diets rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated (*cis*) fats decrease the risk of CHD
how have they been tested?
* Diets rich in saturated fats and *trans* fats increase the risk of CHD
* Diets rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated (*cis*) fats decrease the risk of CHD
how have they been tested?
* Epidemiological studies comparing different population groups
* Intervention studies that monitor cohorts following dietary modifications
* Experimental designs utilising animal models or data based on autopsies
* Intervention studies that monitor cohorts following dietary modifications
* Experimental designs utilising animal models or data based on autopsies
34
New cards
evidence supporting health claims
* A positive correlation has been found between the intake of saturated fats and the incidence of CHD in human populations
* Intervention studies have shown that lowering dietary intakes of saturated fats reduces factors associated with the development of CHD (e.g. blood cholesterol levels, blood pressure, etc.)
* n patients who died from CHD, fatty deposits in diseased arteries were found to contain high concentrations of *trans* fats
* Intervention studies have shown that lowering dietary intakes of saturated fats reduces factors associated with the development of CHD (e.g. blood cholesterol levels, blood pressure, etc.)
* n patients who died from CHD, fatty deposits in diseased arteries were found to contain high concentrations of *trans* fats
35
New cards
evidence against health claims
* *Counter:* Certain populations do not fit this trend (e.g. the Maasai tribe in Africa have a fat-rich diet but very low rates of CHD)
* *Counter:* Validity of intervention studies is dependent on size and composition of cohort, as well as the duration of the study
* *Counter:* Genetic factors may play a role (e.g. blood cholesterol levels only show a weak association to dietary levels)
Proportion of saturated and *trans* fats in Western diets has decreased over the last 50 years, but incidence of CHD has risen
* *Counter:* Increased carbohydrate intake may cause detrimental health effects associated with CHD (e.g. diabetes, obesity)
* *Counter:* Incidence of CHD dependent on a myriad of factors besides dietary intake (e.g. exercise, access to health care, etc.)
* *Counter:* Validity of intervention studies is dependent on size and composition of cohort, as well as the duration of the study
* *Counter:* Genetic factors may play a role (e.g. blood cholesterol levels only show a weak association to dietary levels)
Proportion of saturated and *trans* fats in Western diets has decreased over the last 50 years, but incidence of CHD has risen
* *Counter:* Increased carbohydrate intake may cause detrimental health effects associated with CHD (e.g. diabetes, obesity)
* *Counter:* Incidence of CHD dependent on a myriad of factors besides dietary intake (e.g. exercise, access to health care, etc.)
36
New cards
use of molecular visualization software to compare cellulose starch and glycogen
starch (amylopectin) - plants
* is branched every 30 glucose, helical shape
* polymer of beta glucose
* branches allow quick unloading of glucose
glycogen - animals
* branched every 8-12 glucoe,
* polymer of alpha glucose
mammals use it to store glucose in liver
cellulose - plant cells, cell walls
* straight unbranched (linear)
* polymer of beta glucose
* forms cross-links with hydrogen bonds
* very strong (makes cell wall)
* is branched every 30 glucose, helical shape
* polymer of beta glucose
* branches allow quick unloading of glucose
glycogen - animals
* branched every 8-12 glucoe,
* polymer of alpha glucose
mammals use it to store glucose in liver
cellulose - plant cells, cell walls
* straight unbranched (linear)
* polymer of beta glucose
* forms cross-links with hydrogen bonds
* very strong (makes cell wall)
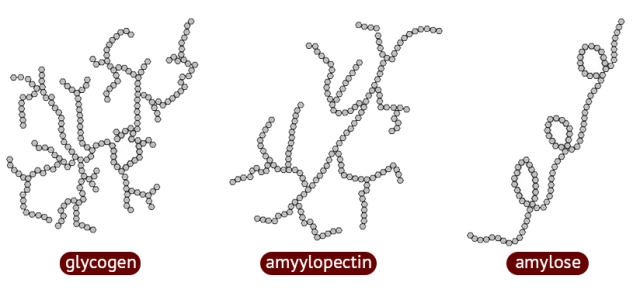
37
New cards
generalized amino acid structure
38
New cards
the formation of polypeptides (including peptide bond and condensation reaction)
39
New cards
amino acids are held linked by.. to form…
1. condensation reactions 2. polypeptides
40
New cards
what is the amount of different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ribosomes?
20
41
New cards
why are polypeptides diverse?
amino acids chains can be linked together in any sequence; therefore there is a huge variety in possibility
42
New cards
how is the amino acid sequence of a specific polypeptide decided?
genetic code (on the genes)
43
New cards
what can a protein consist of?
a single polypeptide or more than 1 polypeptide linked together
44
New cards
what does the amino acid sequence determine for a protein?
its three-dimensional conformation (configuration) eg primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
45
New cards
living organisms synthesize…
many different proteins with a wide range of functions
46
New cards
everyone has an individual proteome, true or false?
true
47
New cards
rubisco
globular, used in photosynthesis by catalyzing oxygen
48
New cards
spider silk
fibrous, used for making webs, ligament, surgical sutures because it holds things together with strength
49
New cards
Insulin
globular, used to regulate blood sugar levels in the pancreas
50
New cards
immunoglobin
globular, defense against infectious disease, antibodies attack antigens on pathogens
51
New cards
rhodoposin
globular, used in light-sensitive pigments in rod cells of the eye
52
New cards
collagen
fibrous, structural helps prevents cracks in teeth and bones, builds up the framework of cells/tissues
53
New cards
fibrous vs globular proteins
fibrous = IS SOMETHING
globular = DOES SOMETHING
globular = DOES SOMETHING
54
New cards
What causes the denaturation of proteins
deviation from the optimum pH and temp for a certain protein (which is dependent on where it’s meant to function)
55
New cards
what do enzymes control?
the metabolism
56
New cards
enzyme definition
a globular protein that acts as a catalyst for reactions (increases the rate of reaction) by lowering the activation energy threshold
57
New cards
metabolism definition
a web of all the enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a cell or organism
58
New cards
enzyme structure
active site to which specific substrates bind
59
New cards
what does enzyme catalysis involve?
molecular motion and the collision of substrates with the active site.
60
New cards
what 3 things affect the rate of enzyme activity?
temperature, pH, and substrate concentration
61
New cards
if temp/substrate conc/pH diverge from the optimum, what happens?
the enzyme is denatured
62
New cards
what are immobilized enzymes?
enzymes that are fixed to a static surface so they don’t move, in order to increase the efficiency of the reaction (used in industry)
63
New cards
advantages of immobilized enzymes?
* continuous flow of products formed
* enzymes can constantly be reused (cheaper)
* to not get the enzyme in the product (could have adverse negative effects)
* enzymes can constantly be reused (cheaper)
* to not get the enzyme in the product (could have adverse negative effects)
64
New cards
examples of enzymes used in industry
* detergents (lipase, fat stain removal)
* textiles (amylase, digest starch. cellulase, metabolize cellulose)
* food processing (amylase, making more glucose from starch, xtra sweetness)
* pulp and paper (cellulase, breaks down cellulose, catalase, bleaching)
* textiles (amylase, digest starch. cellulase, metabolize cellulose)
* food processing (amylase, making more glucose from starch, xtra sweetness)
* pulp and paper (cellulase, breaks down cellulose, catalase, bleaching)
65
New cards
how is lactose free milk produced?
by reacting it with lactase enzyme.
66
New cards
advantages of lactose free milk?
* for lactose intolerant people
* increase sweetness without the need for added sweeteners
* reducing the crystallization of ice creams
* reduce production time for cheese + yogurts
* increase sweetness without the need for added sweeteners
* reducing the crystallization of ice creams
* reduce production time for cheese + yogurts