Unit 3 genetics questions
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
The genotypic ratio of the F2 progeny of a monohybrid cross is typicallyA. 9:3:3:1B. 3:1C. 9:7D. 1:2:1E. 4:3
D. 1:2:1
Why are antibiotic resistance markers important components of plasmid cloning vectors
A. They allow identification of bacteria that have taken up a plasmid.
B. They ensure the presence of the ori site.
C. They ensure that the plasmid can be cut by a restriction enzyme.
D. The plasmid must have resistance to accept DNA insert.
A. They allow identification of bacteria that have taken up a plasmid.
When a PCR reaction is performed using genomic DNA as a template a 4.6-kb product is amplified. When the same reaction is set up using cDNA as a template, a 2.6 kb product Is amplified. The explanation for the different sized products can be
A. The cDNA is degraded
B. There is an intron in the gene
C. Primers always bind to different sequences in different templates
D. there is a mutation in the genomic DNA
B. There is an intron int he gene
Why is it advantageous to screen a genomic library constructed in a BAC vector instead of a plasmid vector
A. BAC libraries can be screened by an antibody.
B. More inserts can be screened.
C. Plasmid libraries contain only cDNA not genomic DNA
D. fewer inserts can be screened
D. Fewer inserts can be screened.
DNA and RNA are polymers ofA. nucleosidesB. ribonucleotidesC. nucleotidesD. nucleaseE. pentose sugars connected by phosphodiester bonds
C. nucleotides
During transcription mRNA synthesis is in which direction
First 5’ to 3’
Which of the following is not a DNA marker
A. AFLP
B. MD
C. RFLP
D. SNP
E. STS
B. MD
A StrS strain:A. Can grow in the presence of streptomycin.B. Can make its own streptomycin.C. Cannot grow without streptomycin.D. Cannot grow in the presence of streptomycin.E. Cannot make its own streptomycin.
D. Cannot grow in the presence of streptomycin
In a Chi-square test a P value equal to 0.10 indicates that
A. The null hypothesis is likely true.
B. The null hypothesis is false and must be rejected.’
C. The null hypothesis must be true.
D. The null hypothesis is unlikely to be true.
D
Bacterial operons contain protein-coding genes for metabolism. The ara operon is inducedA. When arabinose is absent.B. When arabinose is present.C. When lactose is present.D. When lactose is absent.E. None of the above
B. When arabinose is present
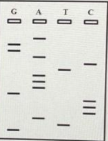
If you obtain a result as below in Sanger Sequencing what should the sample template sequence be(
A. 5’- AGGACTAAAGCCCATG -3’
B. 5’- GTACCCGAAATCAGGA -3’
C. 5’- CATGGGCTTTAGTCCT -3’
D. 5’- TCCTGATTTCGGGTAC -3’
D
Polypeptide hormonesA. Bind to the cell membrane and regulate gene expression through second messengers.B. Are in the cytoplasm and then transported into the nucleus.C. Are in the cytoplasm.D. Are in the cytoplasm and act via second messengers.
A. Bind to the cell membrane and regulate gene expression through second messengers.
Genes encoded by the chloroplast genome showA. Paternal inheritance.B. Dominance.C. Recessive.D. Mendelian inheritance.E. Maternal inheritance.
E. Maternal inheritance
In eukaryotes cell- and tissue-specific gene expression is achieved via
A. RNA polymerase activity.
B. The use of operons.
C. A cell- and tissue-specific set of activators and repressors.
D. Selective deletion of genes not active in differentiated cells.
C
To study the maternal relationship, which of the following is a good material to start withA. Chromosome 21B. Chromosome 22C. Y chromosomeD. X chromosomeE. The mitochondrion genome.
E. The mitochondrion genome.
Which of the following is not an assumption about a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibriumA. Random mating occurs in the population.B. The population is free of migration.C. The population is free of natural selection.D. The population is free of human habitats.E. The population is free of mutation.
D. The population is free of human habitats
Changes in the DNA-histone complex that increase transcriptional activity are termed asA. Nucleosome formation.B. Gene regulation.C. Chromatin remodeling.D. Induction.E. None of the above.
C. Chromatin remodeling
Who first proposed the concept of genetic linkageA. Gregor MendelB. Barbara McClintockC. Thomas MorganD. Francis CollinsE. Watson and Crick.
C. Thomas Morgan
Which of the following gene mutations is less likely to result in cancer
A. Tumor suppressor genes
B. CFTR
C. Transcription factors
D. Mutator genes
E. Proto-oncogenes.
B. CFTR
Which of the following methods was used by the Celera Genomics Corporation to sequence the human genomeA. Marker-based cloning FISHB. The FISH hybridization techniqueC. Whole genome shotgunD. Radiation hybridE. Pedigree analysis.
C. Whole genome shotgun
An operon that is inducible may be underA. Constitutive control onlyB. Negative control onlyC. Both positive and negative controlD. Positive control only
C. Both positive and negative control
The condition resulting from a trisomy of chromosome 21 is
A. Down syndrome
B. Turner syndrome
C. Reye syndrome
D. Klinefelter syndrome
E. Cri du chat syndrome
A. Down syndrome
Systems Biology is an interdisciplinary study field that focuses on the systematic study of complex interactions in biological systems usingA. An integration approachB. A reverse genetics approachC. A Mendelian genetics approachD. A forward genetics approachE. A reduction approach
A. An integration approach
Two pairs of independently segregating genes with two alleles each, A/a and B/b determine plant height additively in the population. The homozygote AABB is 50 cm tall and the homozygote aa bb is 30 cm tall. What is your prediction of the height of AABb plant in the F2?
A. 35
B. 40
C. 45
D. 60
E. 80
C. 45
Which stages of the cell cycle are not very tightly regulated
A. The checkpoint between G1 and M
B. During M before the separation of chromatids
C. The checkpoint between G2 and M
D. The checkpoint between G1 and S
E. The checkpoint between M and G1
E. The checkpoint between M and G1
Transcription in eukaryotes is activated if activators are bound to
A. Enhancer elements
B. Promoter elements
C. The operator
D. Both A and B
E. Both A and C
D. Both A and B
Compared to euchromatin heterochromatin is usually
A. Poor in genes and comprised of densely packed nucleosomes
B. Poor in genes and comprised of loosely packed nucleosomes
C. Rich in genes and comprised of densely packed nucleosomes
D. Rich in genes and completely lacking nucleosomes
E. Rich in genes and comprised of loosely packed nucleosomes
E
What can be generally said about quantitative traits such as crop yield, human height and Blood Pressure
A.They are continuous
B.They are controlled by one important gene
C. They are inactable to molecular genetics
D.They Are not heritable
E.They are discontinous
A
Four clones (A, B, C, and D) of human genomic DNA are tested for sequence-tagged sites 1 through 5. A
shows 2 and 3; B shows 2 and 5; C shows 1 and 5; D shows 3 and 4. What is the order of the clones in their
contig?
A) CDAB
B) CDBA
C) BDAC
D) CBAD
E) DCAB
C. BDAC
Positional cloning
A. Is when a cDNA has been cloned into a specific orientation in an expression vector
B. Requires knowledge of the gene product before the gene can be cloned
C. Is to clone a gene based on its relative chromosomal location by markers
D. Generates a transgenic organism that expresses a gene only in certain tissues
C. Is to clone a gene based on its relative chromosomal location by markers
In the trp Operon, which stem-loop formations will result in a full-length transcript of the five structural genes
A. 1-2
B. 1-3
C. 2-3
D. 1-4
E. 3-4
C. 2-3;
Which chromosome is involved in Robertsonian translocation, which can lead to familial Down syndrome
A. 11
B. 12
C. 13
D. 14
E. 15
D. 14;
Which of the following statements is true
A. Oncogenes found in cancer cells are usually recessive and loss-of-function mutations.
B. Mutations of tumor suppressor genes found in cancer cells are usually recessive and loss-of-function mutations.
C. Mutations of mutator genes found in cancer cells are usually recessive and gain-of-function mutations.
D. Oncogenes found in cancer cells are usually dominant and loss-of-function mutations.
E. Oncogenes found in cancer cells are usually recessive and gain-of-function mutations.
B. Mutations of tumor suppressor genes found in cancer cells are usually recessive and loss-of-function mutations;
What kind of specific mutations does a nuclear war usually cause in the human genome
A. Unequal cross over
B. Inversion
C. Double-stranded DNA break
D. Translocation
E. T:A to G:C mutation
C. Double-stranded DNA break;
To cover the human genome with 9-fold confidence using an average BAC insert of 300 kb, roughly how many BAC colonies are needed
A. 30,000
B. 60,000
C. 90,000
D. 300,000
E. 3,000,000
C. 90,000;
From E. coli, yeast to humans, the gene density (i.e., the number) decreases
A. From E. coli, yeast to humans, the gene density increases.
B. From E. coli, yeast to humans, the gene density decreases.
C. It depends on the genotypes of E. coli, yeast, and humans.
D. All of the above.
E. None of the above.
B. From E. coli, yeast to humans, the gene density decreases;
Which of the following is not true about genomic or cDNA libraries
A. cDNA libraries can tell provide tissue-specific gene expression.
B. In genomic libraries, the genomic clones represent all regions of DNA relatively equally.
C. In cDNA libraries, cDNA clones reveal which parts of the genome contain the information used in making proteins in specific tissues.
D. cDNA libraries can provide information on which parts of the genome have more DNA repeats.
E. All of the above.
D. cDNA libraries can provide information on which parts of the genome have more DNA repeats;
What is the narrow-sense heritability
A. 16%
B. 19%
C. 27%
D. 48%
E. 69%
D. 48%;
Which of the following is unlikely to be a goal of Synthetic Biology
A. To redesign of a biological system.
B. To increase production of an enzyme.
C. To clone a tumor suppressor gene in humans.
D. To produce biofuels.
E. To produce anti-tumor drugs.
C. To clone a tumor suppressor gene in humans
What is approximately the frequency of the M2 allele in the following population
A. 0.80
B. 0.60
C. 0.40
D. 0.30
E. 0.20
C. 0.40
In yeast, lactose utilization genes are expressed at a low level when there is
A. Galactose and lactose.
B. Glucose and lactose.
C. Lactose and arabinose.
D. Lactose.
E. All of the above.
B. Glucose and lactose
Which of the following statements is not true concerning the comparisons between genetic, physical, and cytogenetic maps
A. The distance between two linked markers is not the same in genetic and physical maps.
B. In physical maps, the distances between markers are given in megabases (Mb), where 1 Mb is approximately equal to 1 cM in Drosophila.
C. Restriction maps, contig maps, and STS maps are examples of physical maps.
D. The banding patterns of chromosomes created by different staining techniques are used in constructing cytogenetic maps.
E. All of the above.
B. In physical maps, the distances between markers are given in megabases (Mb), where 1 Mb is approximately equal to 1 cM in Drosophila;
Which of the following markers involve mRNA during its identification
A. AFLP
B. EST
C. RFLP
D. STR
E. VNTR
B. EST
F2 plants segregate 9/16 colored: 7/16 colorless. If one plant among the colorless plants in the F2 generation is chosen at random and self-pollinated, what is the probability that there will be no segregation into different genotypes among its progeny
A. 1/16
B. 1/9
C. 1/7
D. 9/16
E. 16/16
C. 1/7;
The genotype frequencies at one locus are 0.5 AA, 0.4 Aa, and 0.1 aa. The frequency of the a allele is approximately
A. 0.20
B. 0.32
C. 0.50
D. 0.70
E. 0.90
B. 0.32
Which of the following proteins binds DNA
A. GAL1
B. GAL4
C. GAL7
D. GAL10
E. GAL80
B. GAL4
The genome size of Sars-CoV-2 is approximately what percentage of the human genome
A. 0.1%
B. 0.01%
C. 0.001%
D. 0.0001%
E. 0.00001%
C. 0.001%
Approximately what percentage of the human genome encodes mRNA
A. 20%
B. 10%
C. 5%
D. 3%
E. 1%
E. 1%
A population in equilibrium has eight times as many heterozygotes (Aa) as homozygous recessives (aa). What is the frequency of the dominant allele (A) approximately
A. 0.10
B. 0.20
C. 0.40
D. 0.60
E. 0.80
E. 0.80
Since Gregor Mendel discovered Mendel’s laws in the 1860s, many great geneticists have discovered more genetic principles. Who first found an epigenetic phenomenon
A. Thomas Morgan
B. Paul Berg
C. Barbara McClintock
D. James Watson
E. Jennifer Doudna
C. Barbara McClintock
Synthesis of the BRCA1 protein in humans is sensitive to
A. Cycloheximide
B. Streptomycin
C. Neomycin
D. Gentamicin
E. Chloramphenicol
A. Cycloheximide
Which of the following is the largest fraction of repeats in the human genome
A. Retrovirus-like elements
B. LINEs
C. SINEs
D. DNA transposons
E. RFLP
B. LINE
The development of chronic myelogenous leukemia is due to mutations in which of the following chromosomes
A. 12
B. 13
C. 14
D. 15
E. 22
E. 22
What do scientists mainly learn from the experiment
A. Lac operon is inducible.
B. Lac operon is repressible.
C. Protein acts in trans.
D. DNA acts in cis.
E. Both B and C
C. Protein acts in trans
For a randomly selected 90-kb autosomal gene, the expected number of intronic nucleotides at which a person’s paternally and maternally inherited alleles differ is
A. 90 nucleotides
B. 100 nucleotides
C. 168 nucleotides
D. 188 nucleotides
E. 210 nucleotides
E. 210 nucleotides
If you want to develop an STR marker to screen potential patients among a population for the following diseases (A-E), in which diseases are you more likely successful in finding the mutation
A. Sickle-cell anemia
B. Fragile X syndrome
C. Huntington's disease
D. Both A and B
E. Both B and C
E. Both B and C.
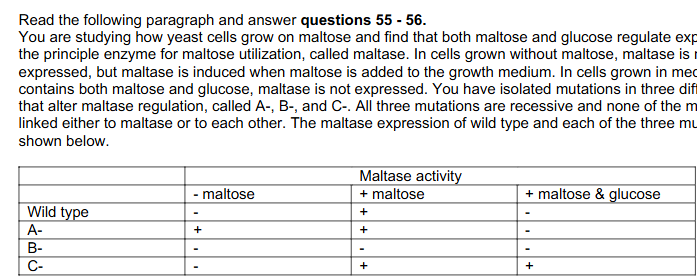
55. For gene B,
A. It affects regulation by maltose and it is a positive regulator
B. it affects regulation by maltose and it is a negative regulator
C. It affects regulation by glucose and it is a positive regulator
D. it affects regulation by glucose and it is a negative regulator
Answer: A
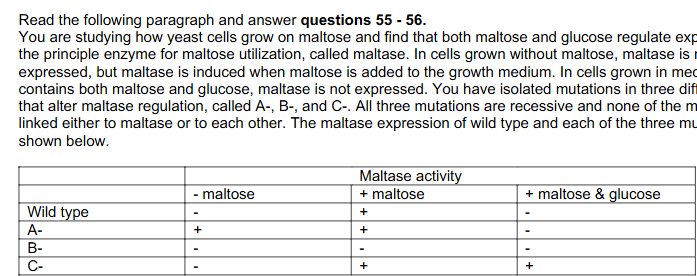
56. For gene C
A. It affects regulation by maltose and it is a positive regulator
B. it affects regulation by maltose and it is a negative regulator
C. it affects regulation by glucose and it is a positive regulator
D. it affects regulation by glucose and it is a negative regulator
Answer: D
We learned that p53 is an important tumor suppressor. Which of the following is not true?
a. p53 is a 393-AA protein encoded by P53 gene on chromosome 17 in humans.
b. p53 is a transcription factor.
c. In the cells with DNA mutations, p53 activates Cdk4.
d. p53 can bind the promoter of the WAF1 gene.
e. In the cells with DNA mutation, E2F is not activated.
c
58. We learned that scientists designed specific experiments to show gene regulation works in bacteria. For the
experiment shown in the following figure, what do scientists mainly learn from the experiment?
A Lac operon is inducible
B Lac operon is repressible
C Protein acts in trans.
D DNA acts in cis
E Both B and C
Answer: C
In the human genome, Hnuc, the average heterozygosity per nucleotide site, is approximately 0.0025 in human
populations. We assume that an average gene size is 100 kb (excluding the promoter) and an average mRNA size
is 6 kb in humans. For a randomly selected 90-kb autosomal gene, the expected number of intronic nucleotides at
which a person’s paternally and maternally inherited alleles differ is.
A. 90 nucleotides
B. 100 nucleotides
C. 168 nucleotides
D. 188 nucleotides
E. 210 nucleotides
E
We have learned many DNA markers and human genetic diseases in the class. If you want to develop a STR
marker to screen potential patients among a population for the following diseases (A-E), in which diseases are you
more likely successful in finding the mutation?
A Sickle-cell anemia
B Fragile X syndrome
C Huntington's disease
D Both A and B
E Both B and C
E