Male reproductive system
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
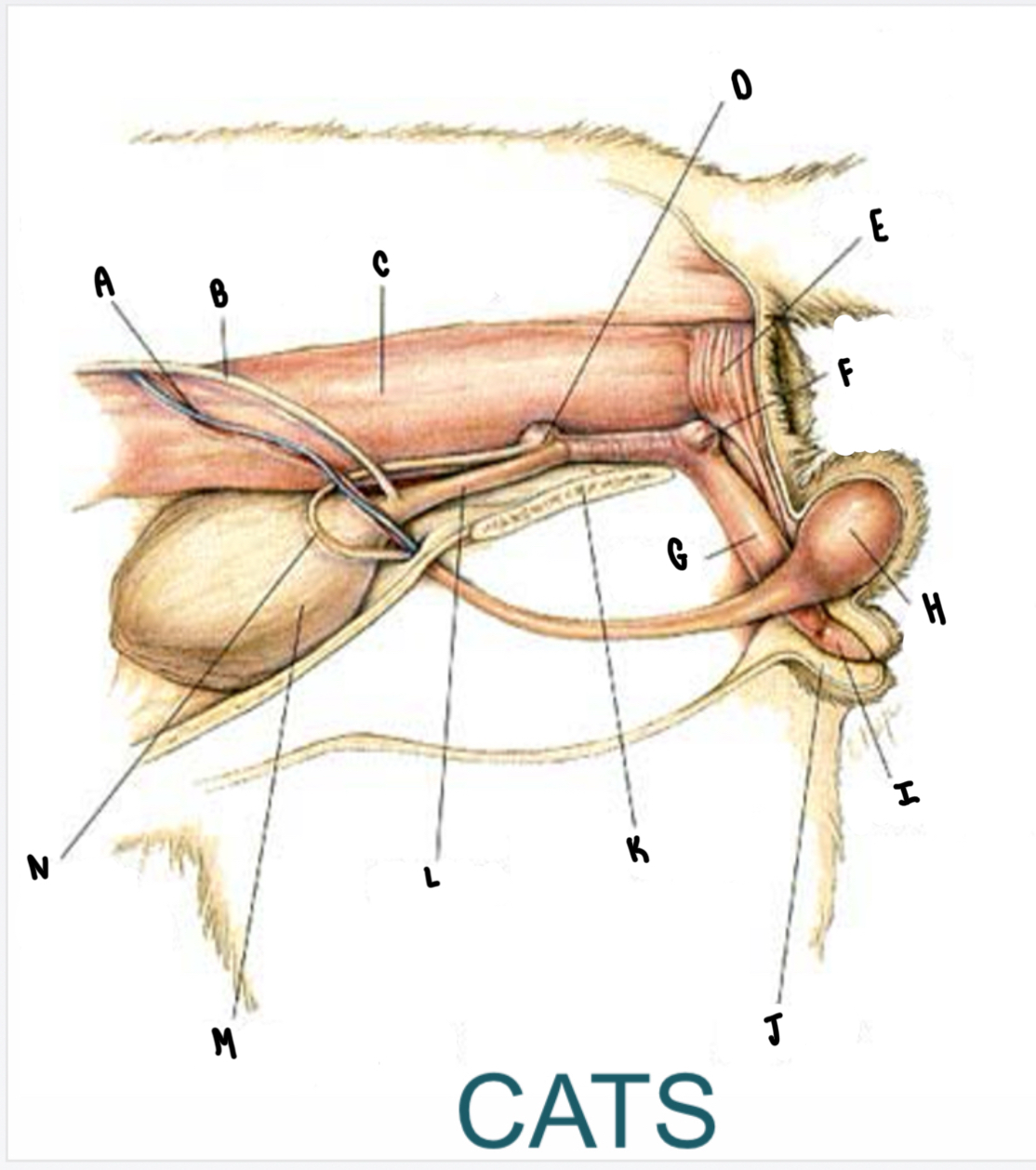
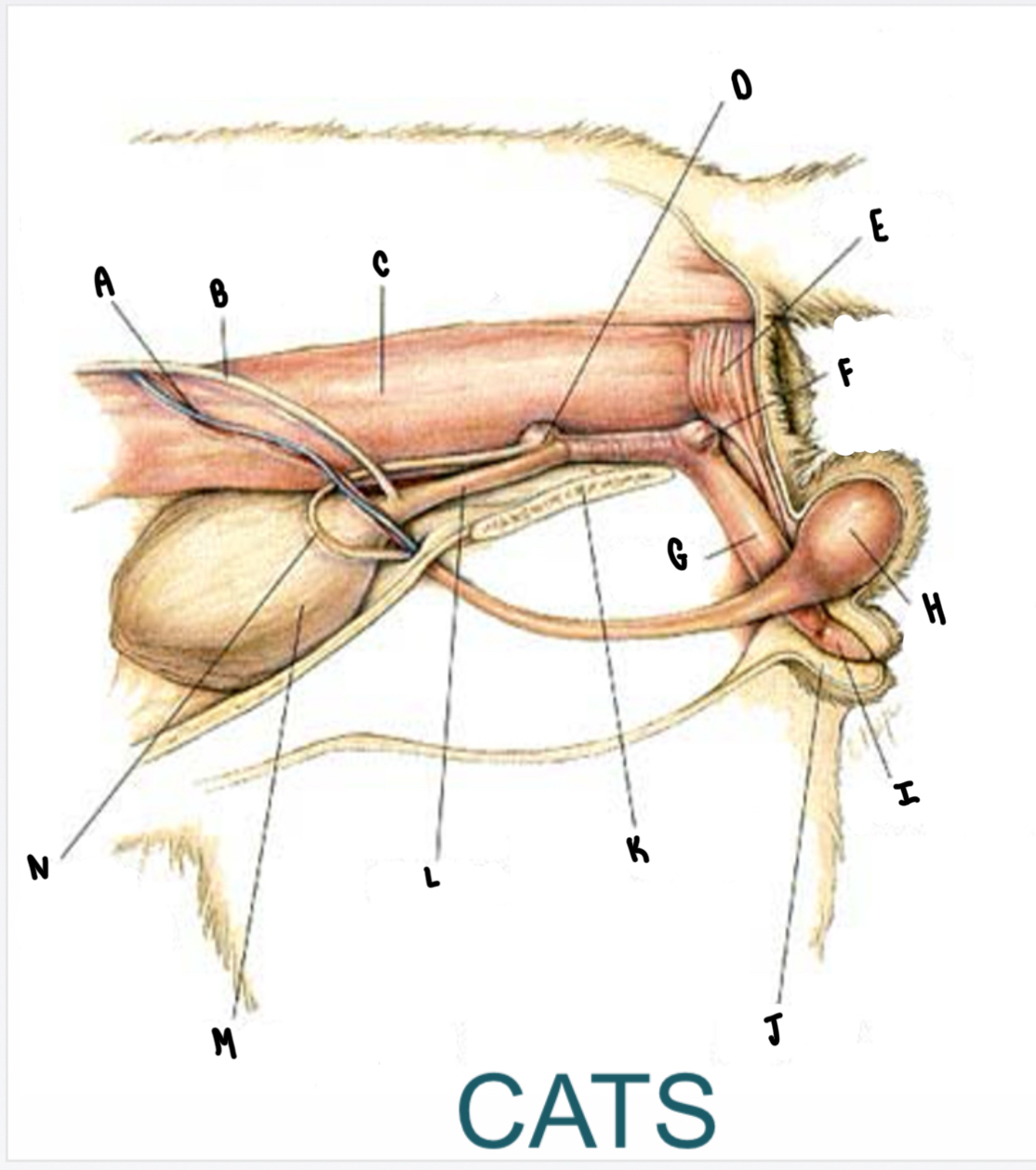
What is the structure labeled A?
Testicular vessels
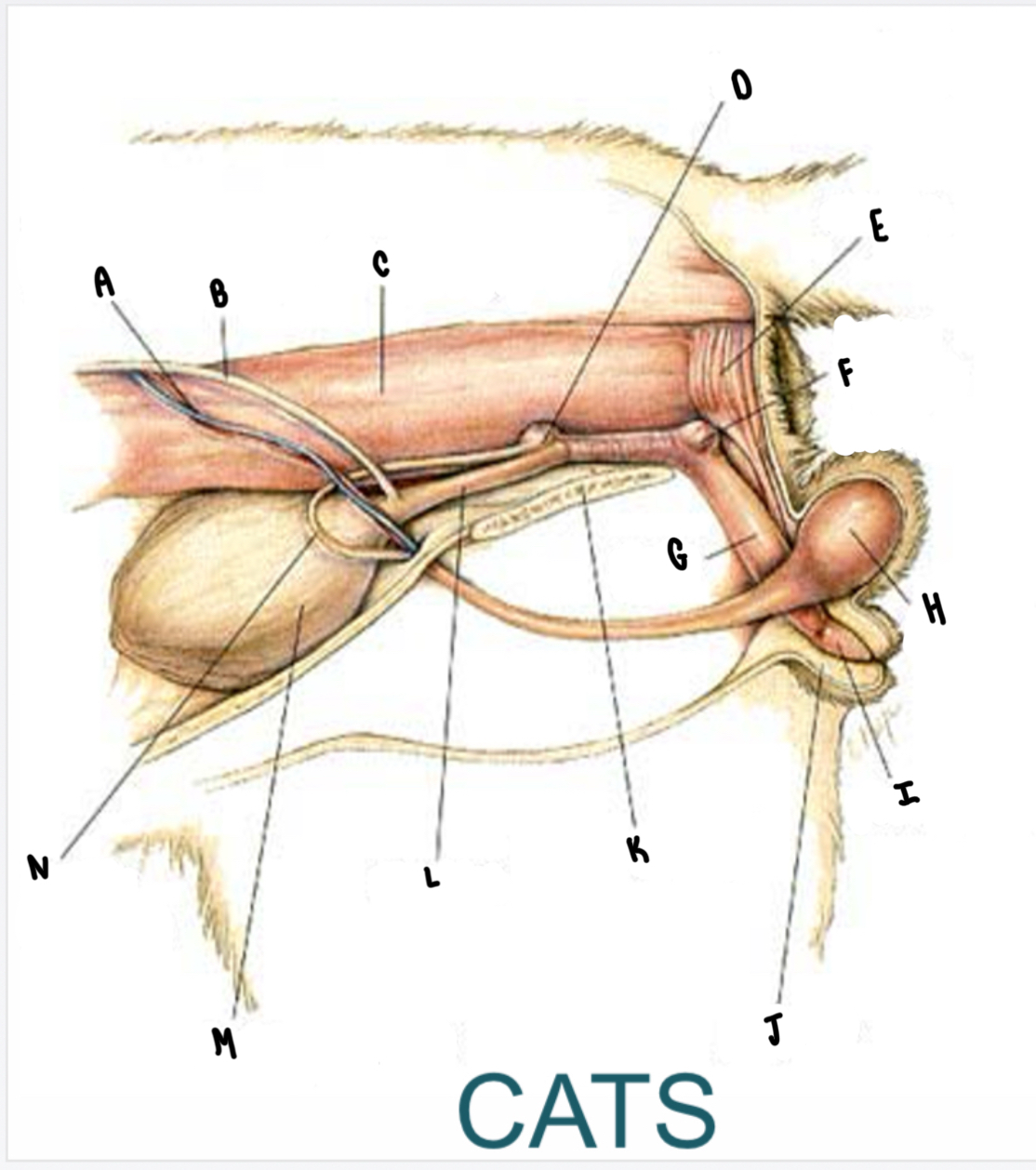
What is the structure labeled B?
Ureter
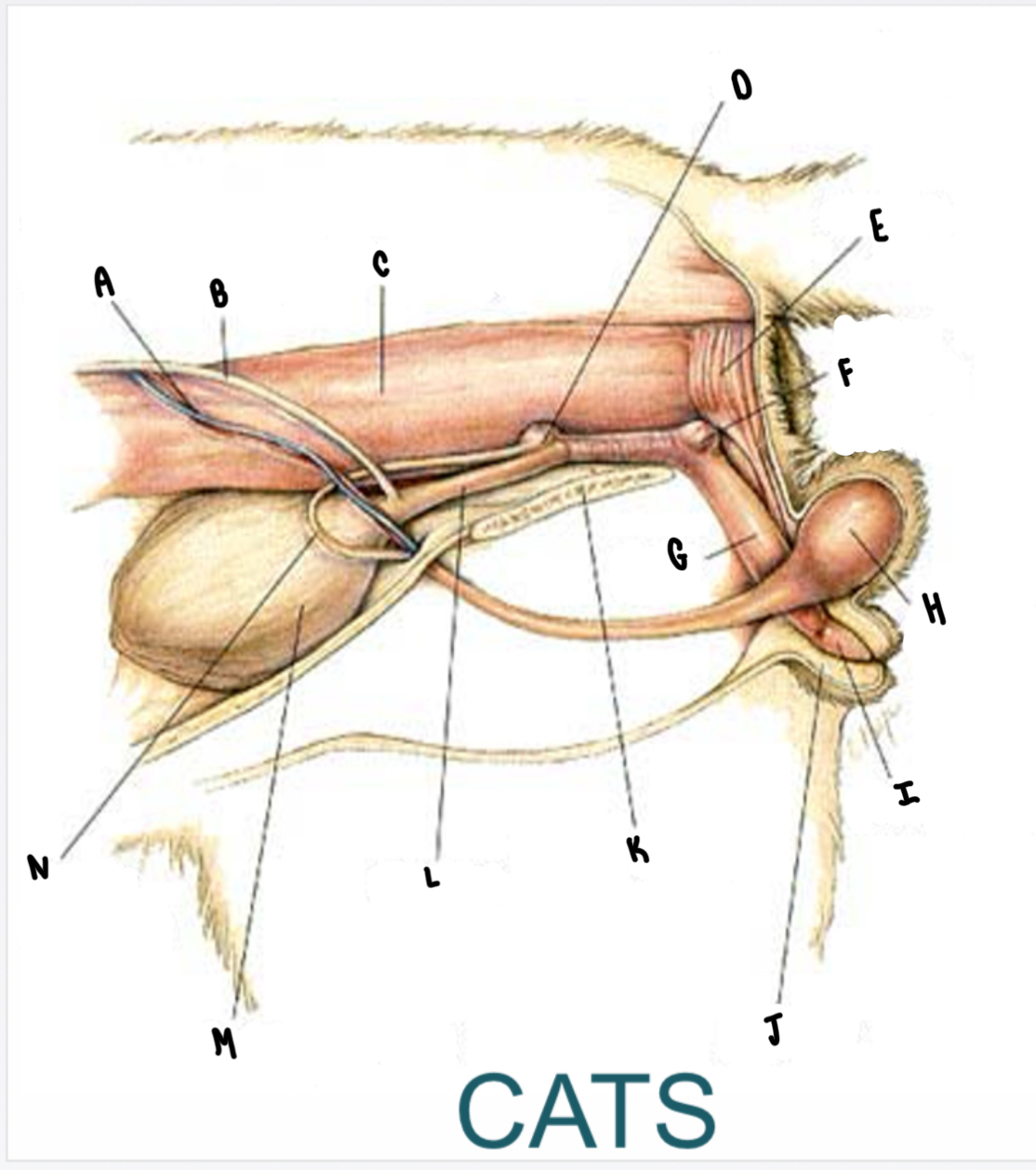
What is the structure labeled C?
Descending colon
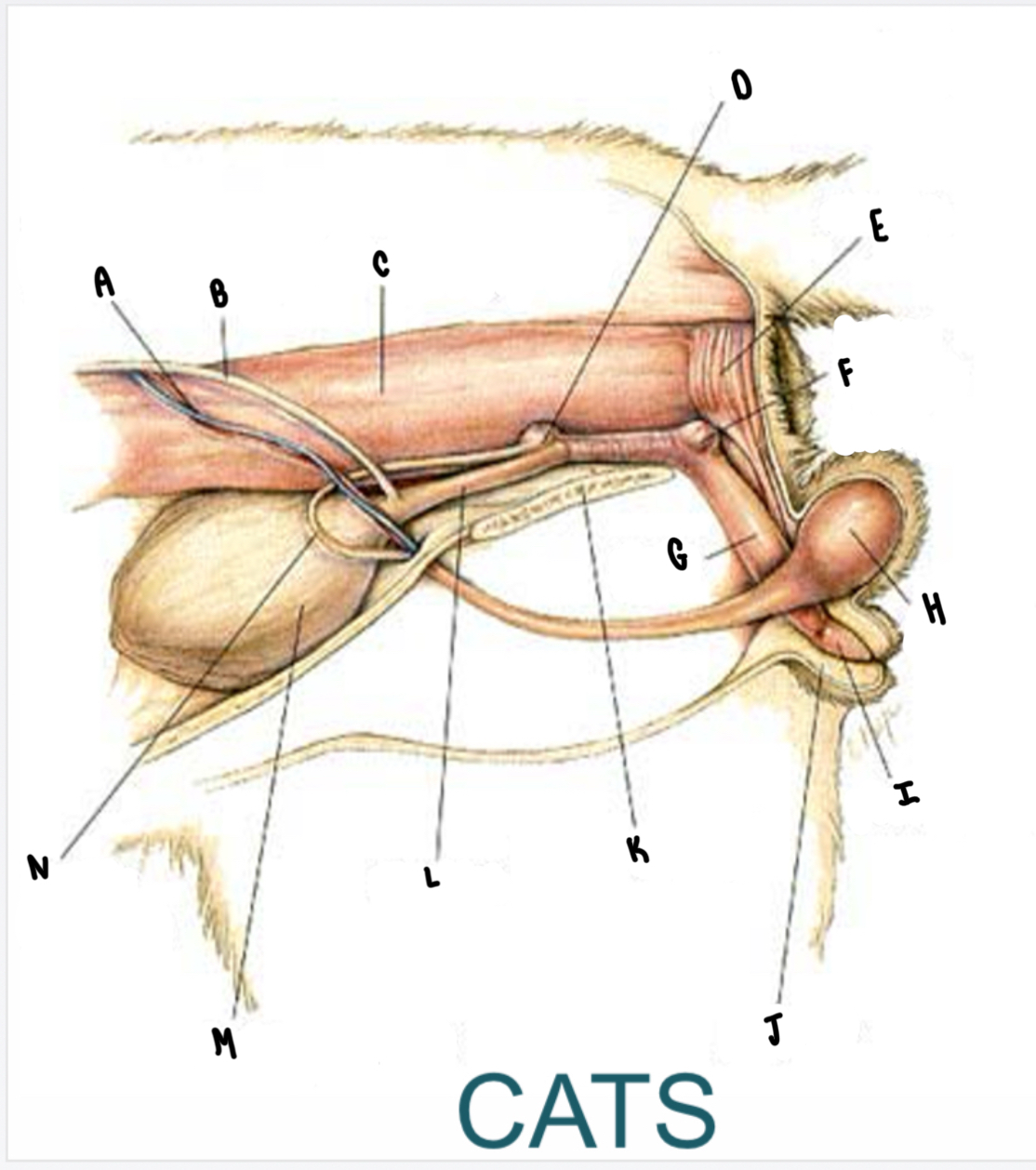
What is the structure labeled D?
Prostate gland
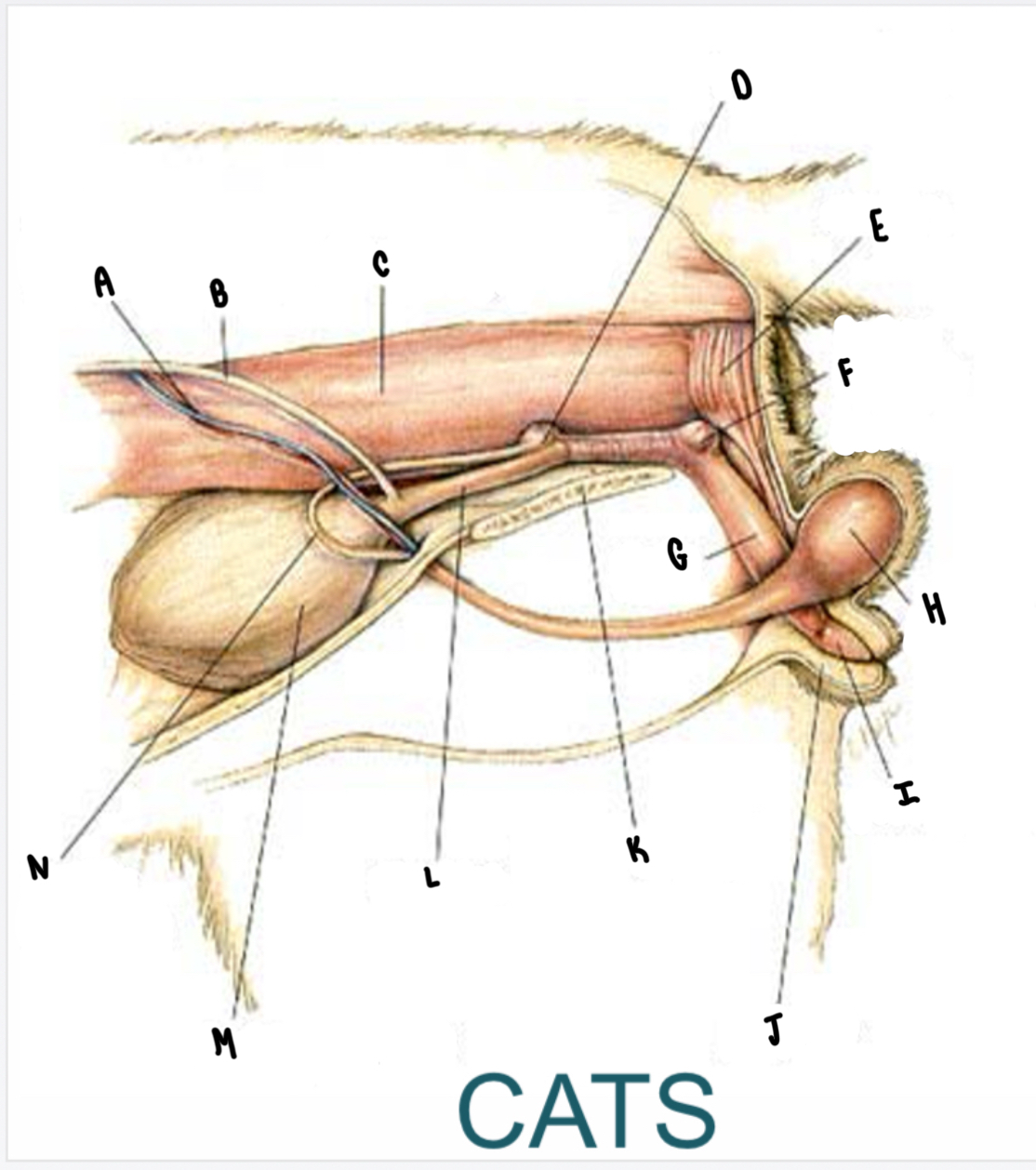
What is the structure labeled E?
Rectum
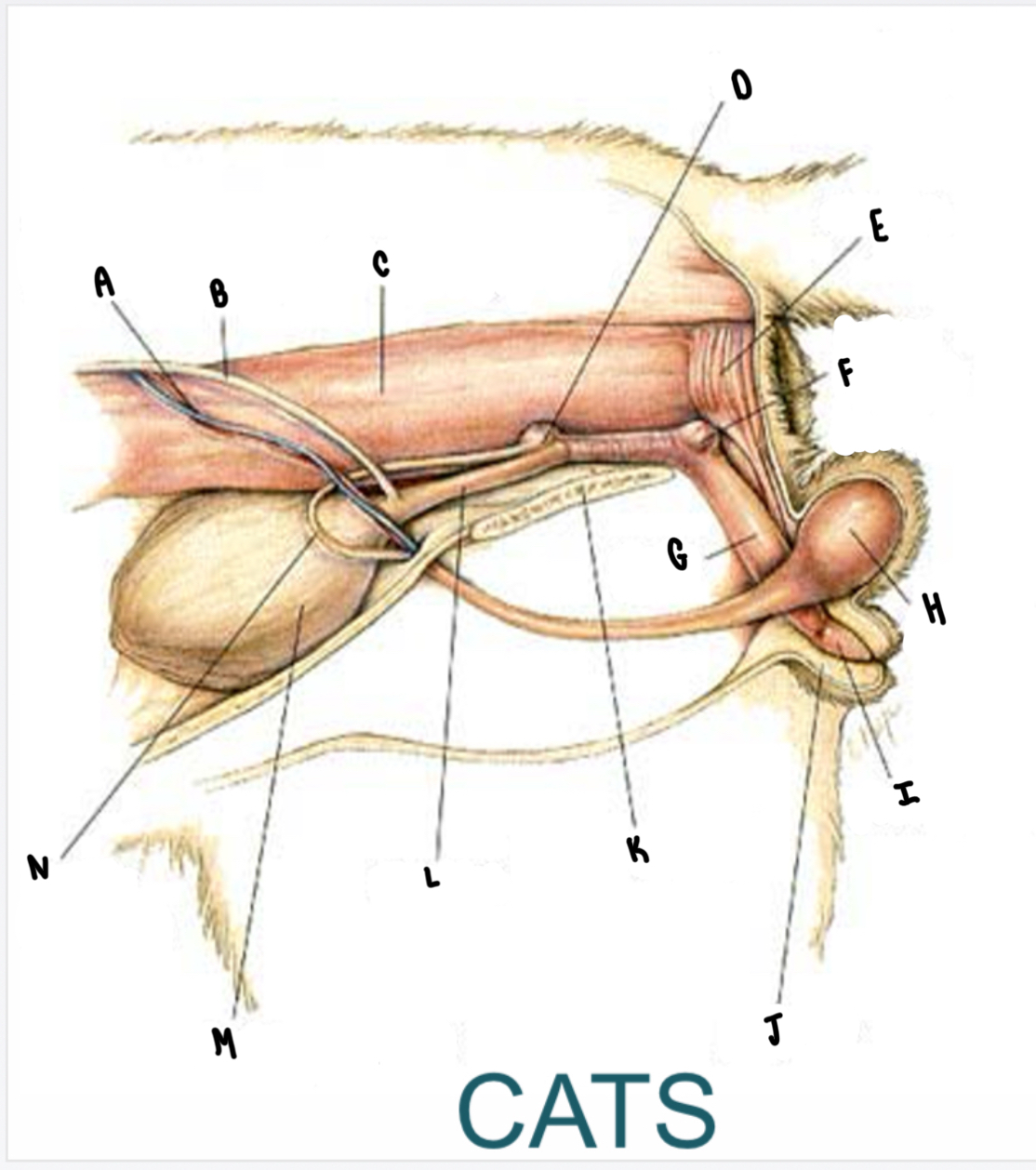
What is the structure labeled F?
Bulbourethral gland
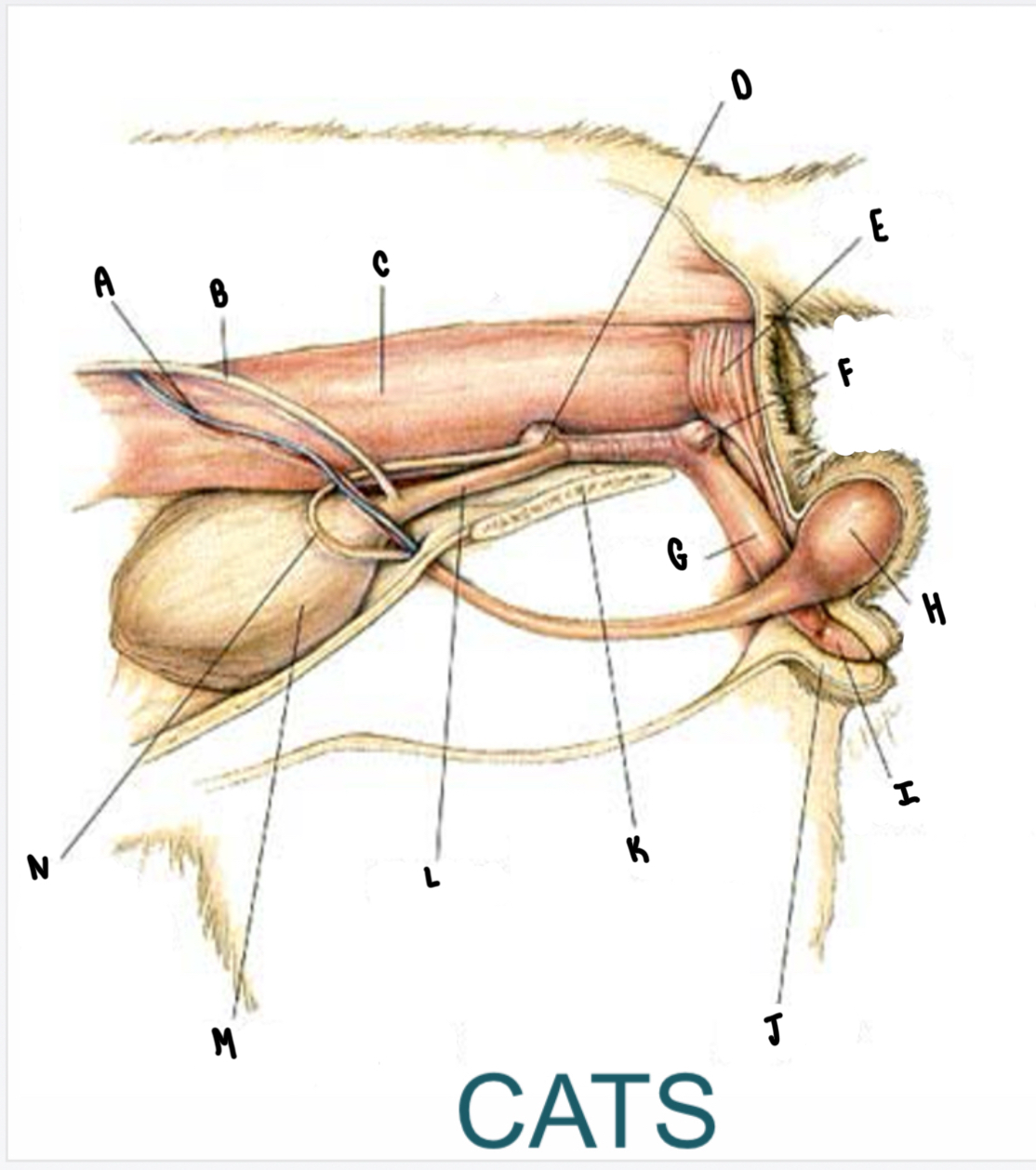
What is the structure labeled G?
Penis
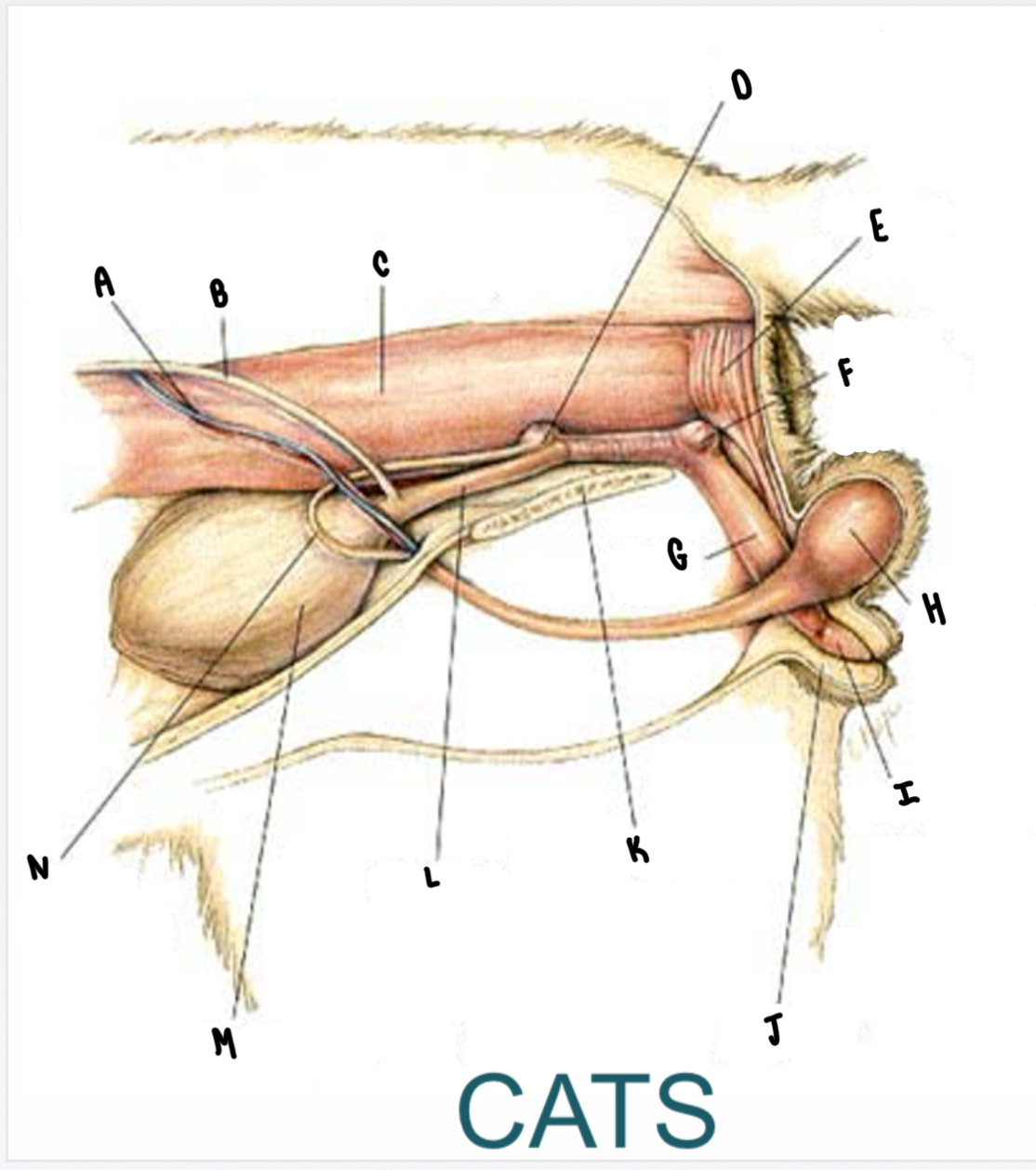
What is the structure labeled H?
Testicle
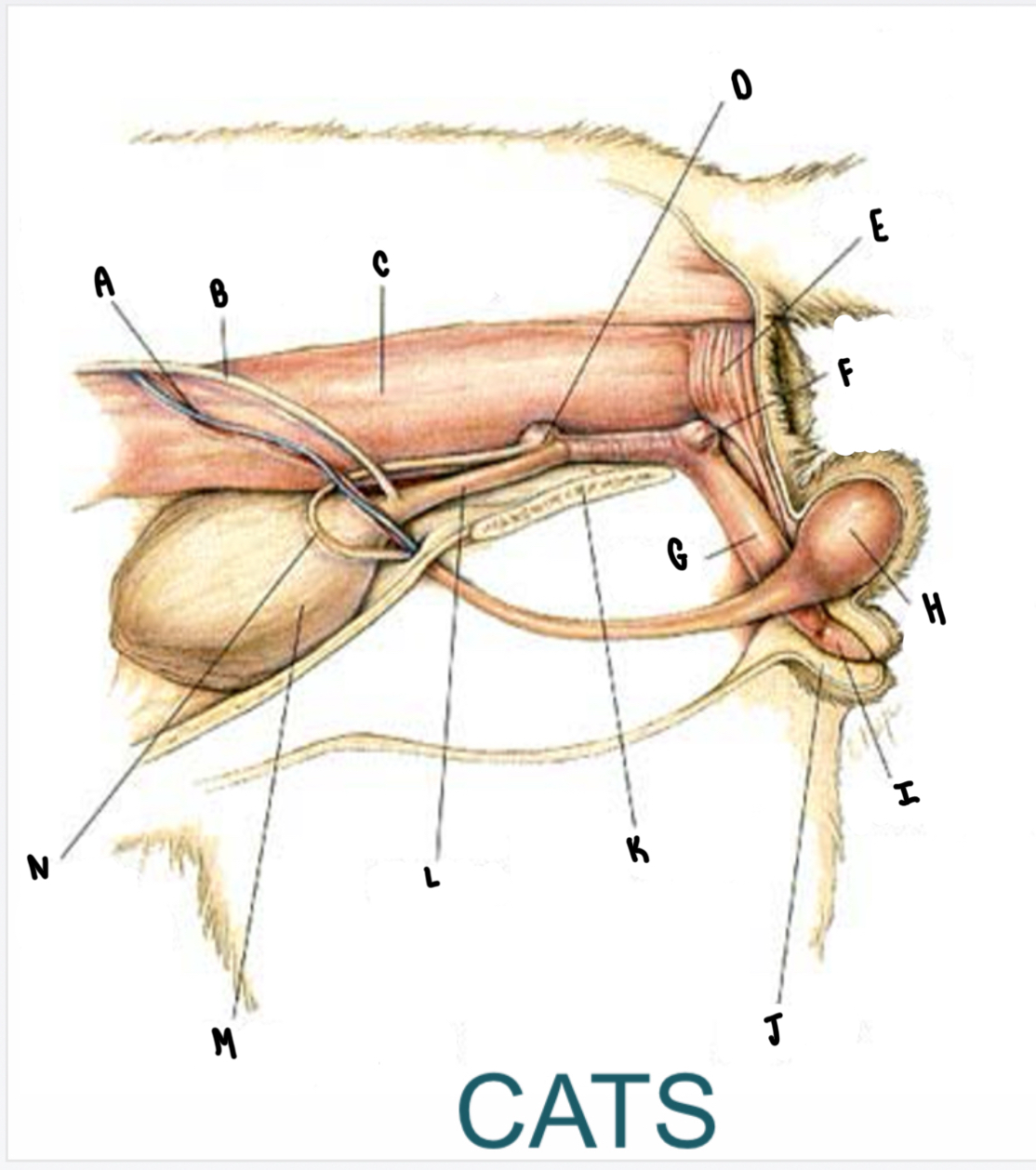
What is the structure labeled I?
Glans penis
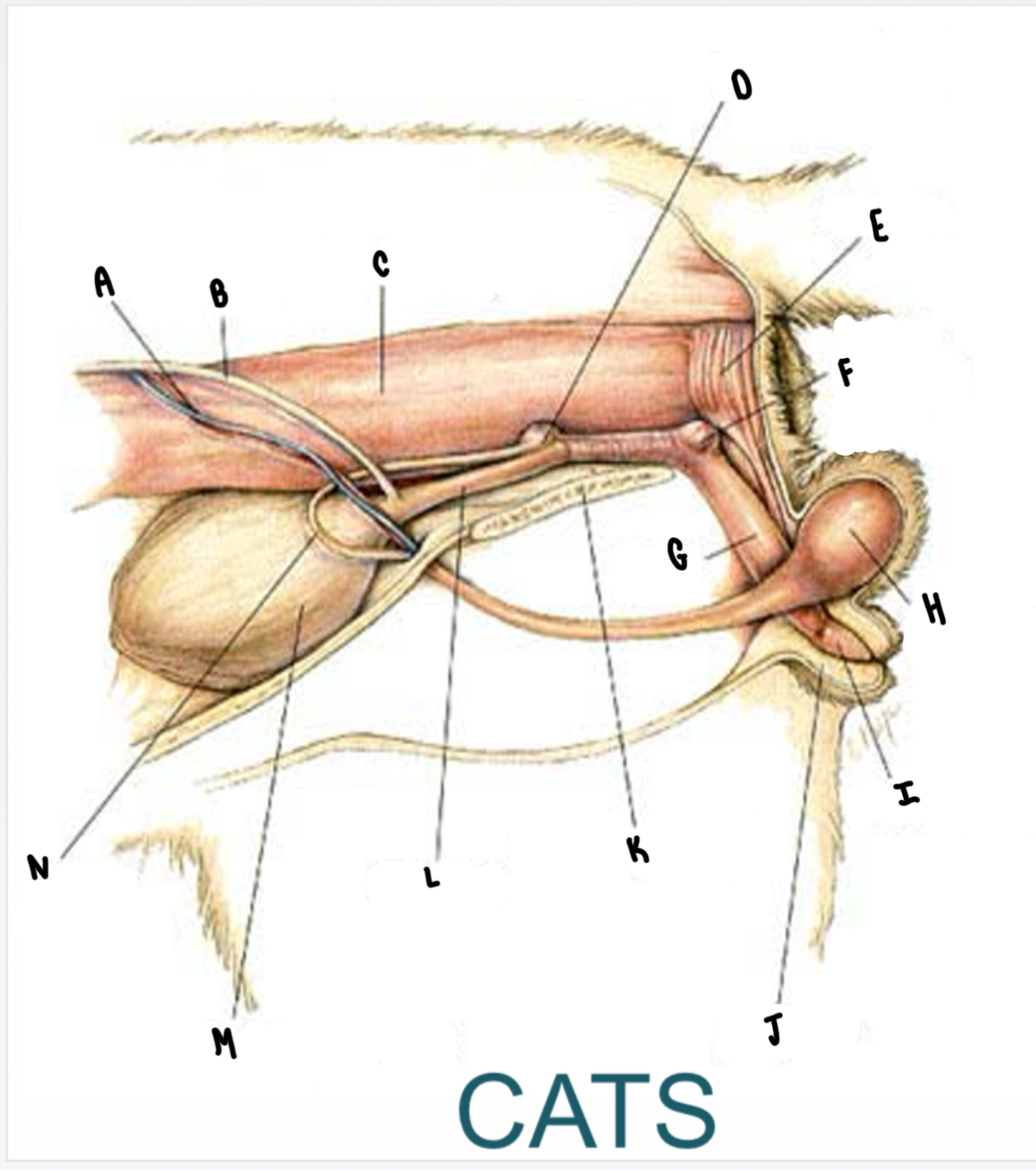
What is the structure labeled J?
Prepuce
What is the structure labeled K?
Pubic symphysis
What is the structure labeled L?
Urethra
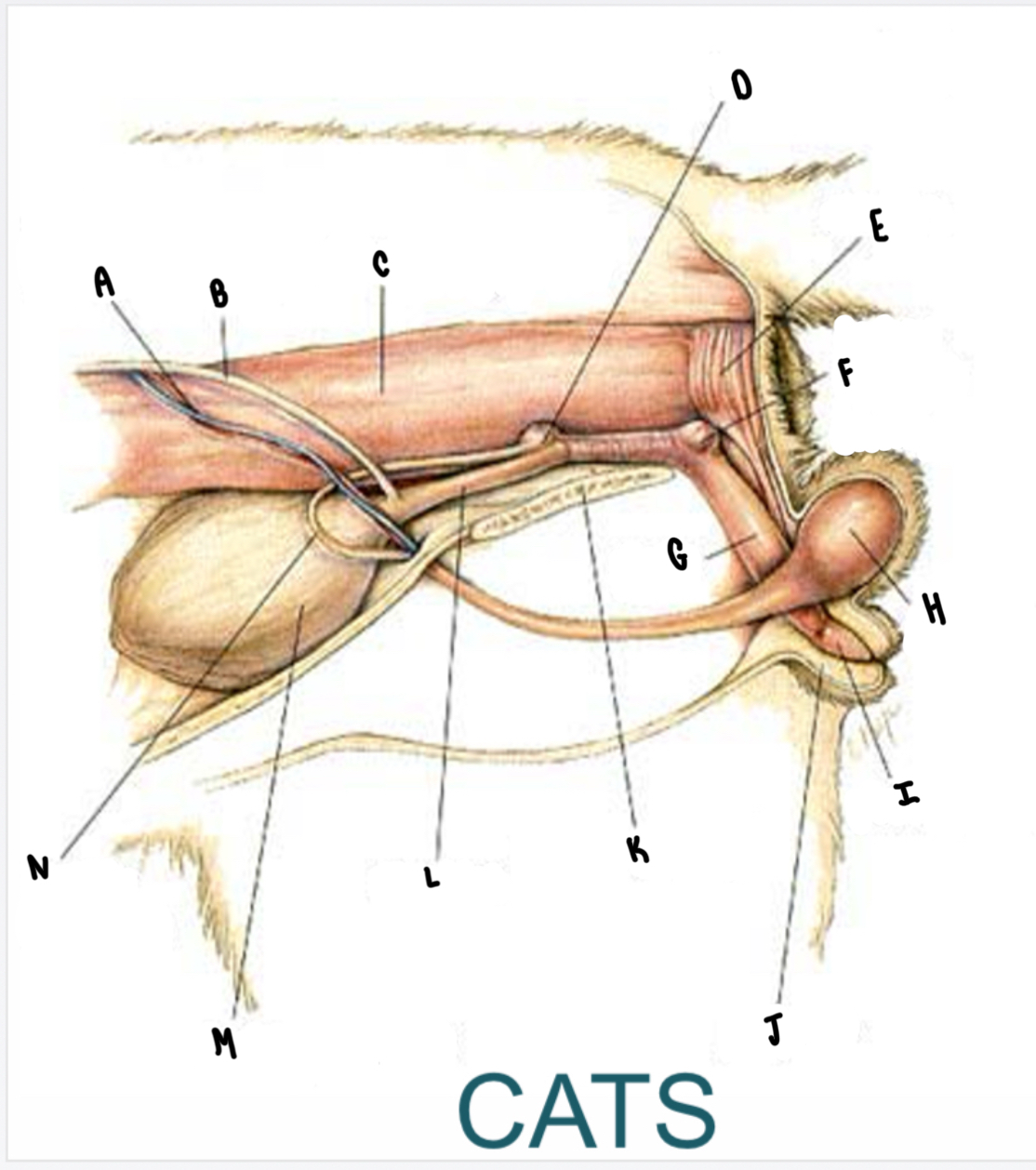
What is the structure labeled M?
Urinary bladder
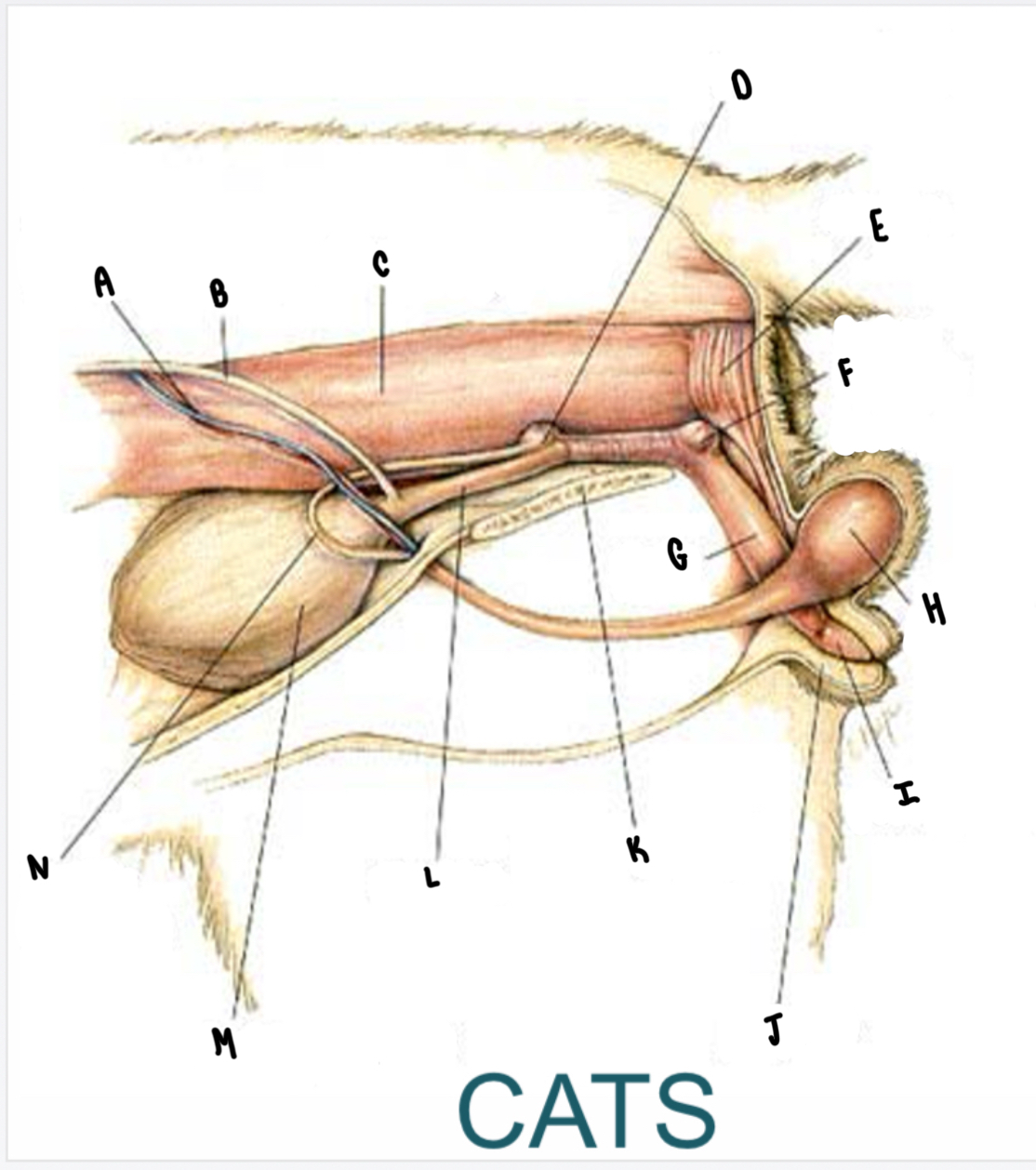
What is the structure labeled N?
Ductus deferens
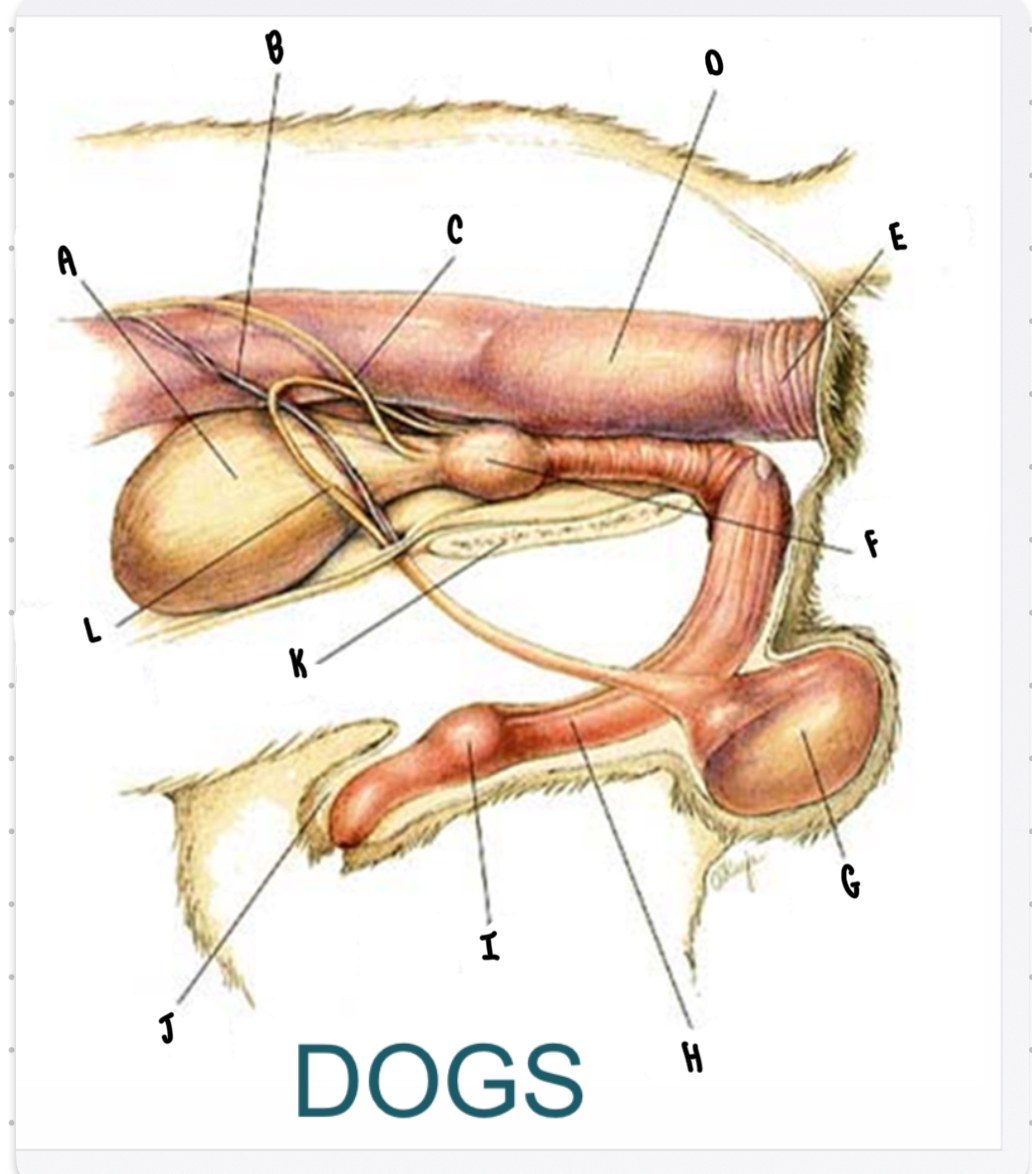
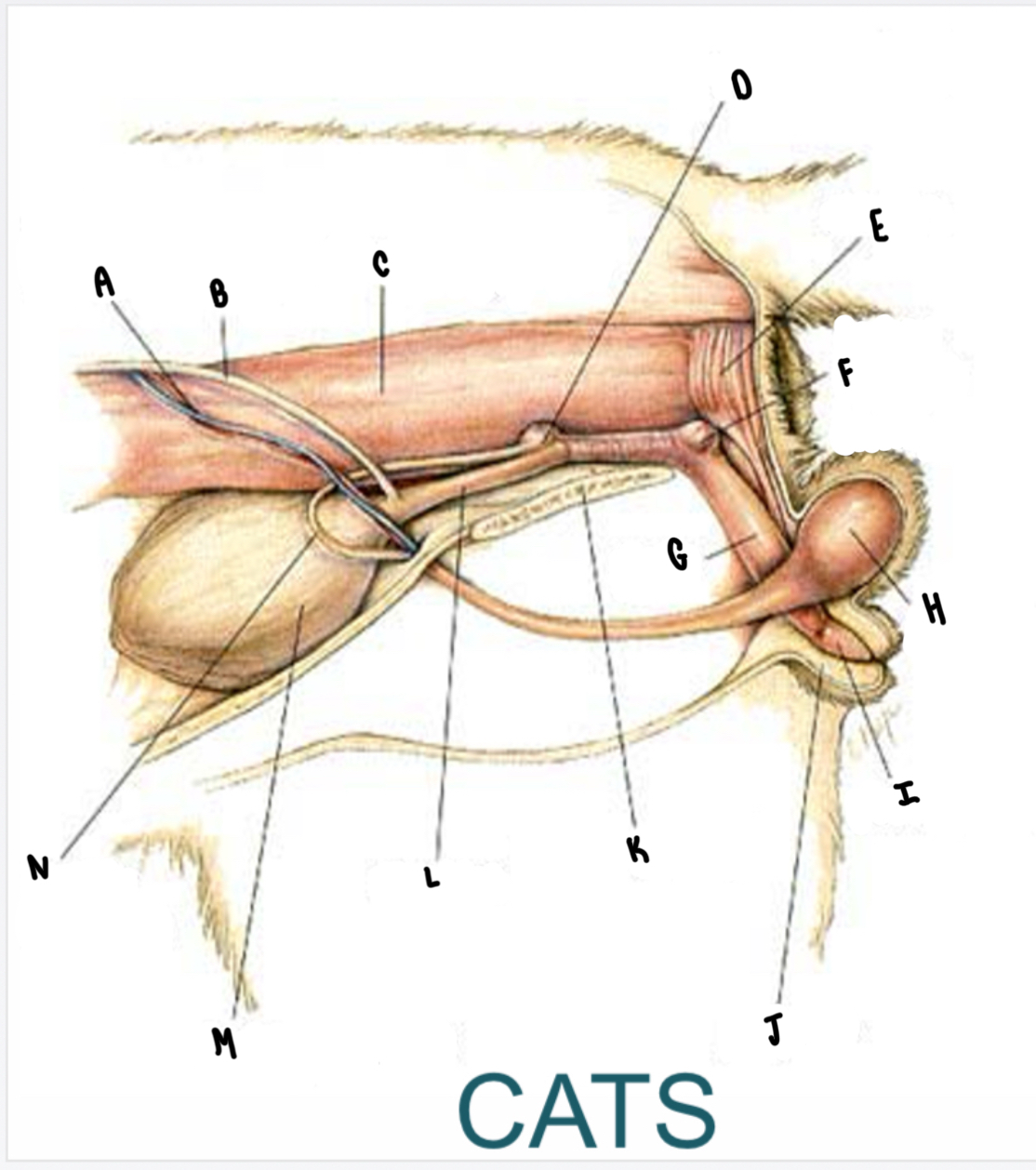
What is the structure labeled A?
Urinary bladder
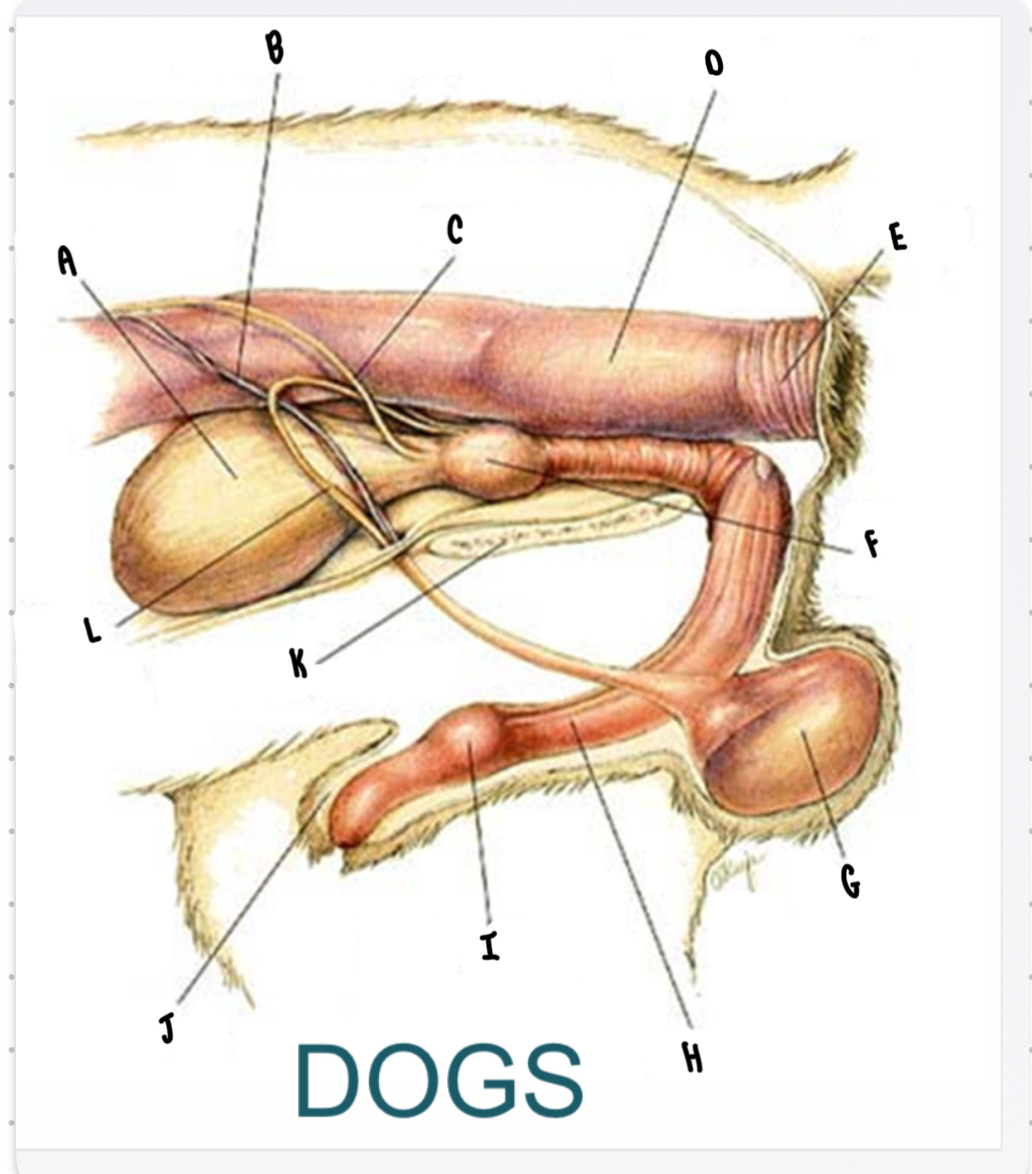
What is the structure labeled B?
Testicular vessels
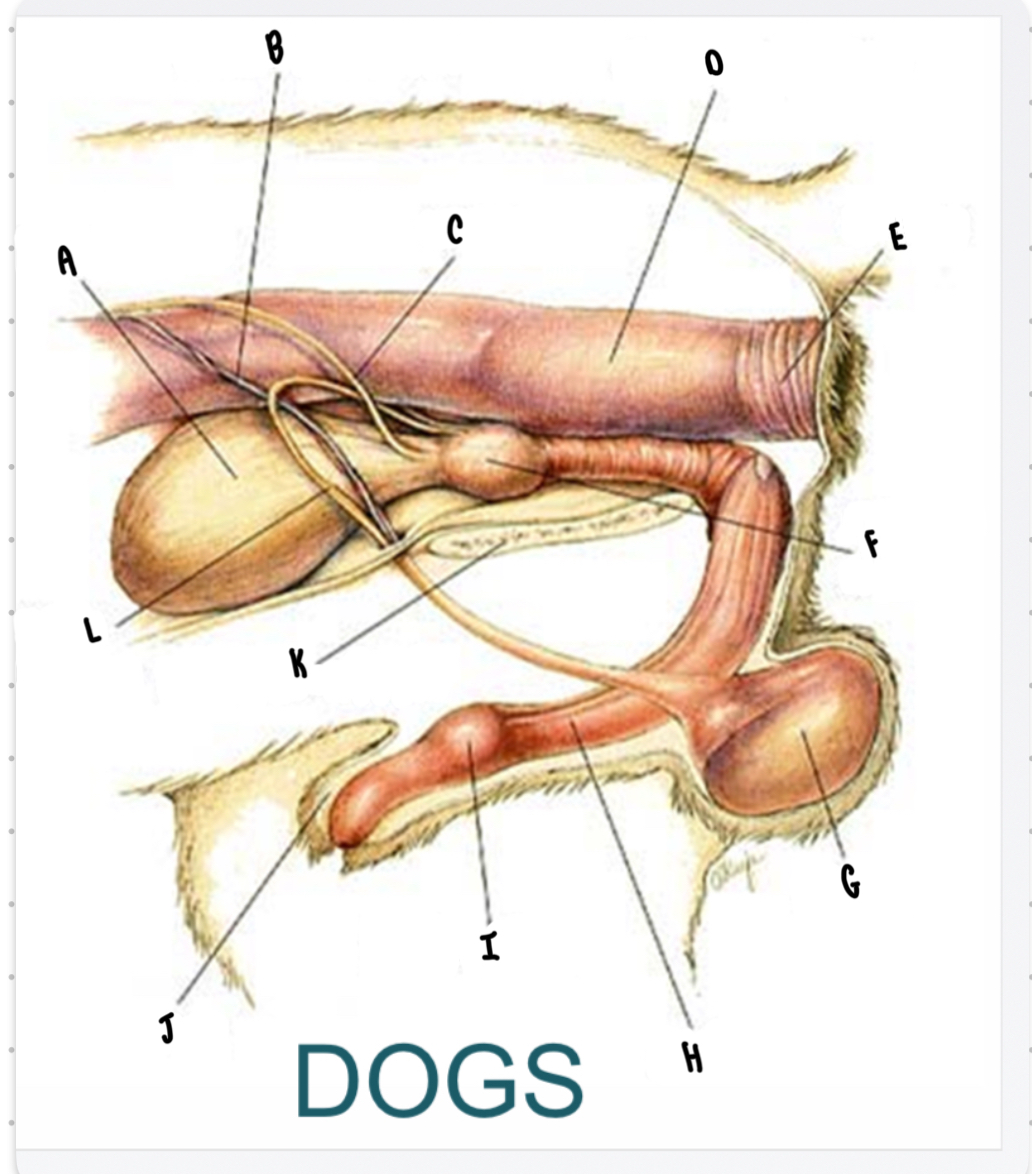
What is the structure labeled C?
Ureter
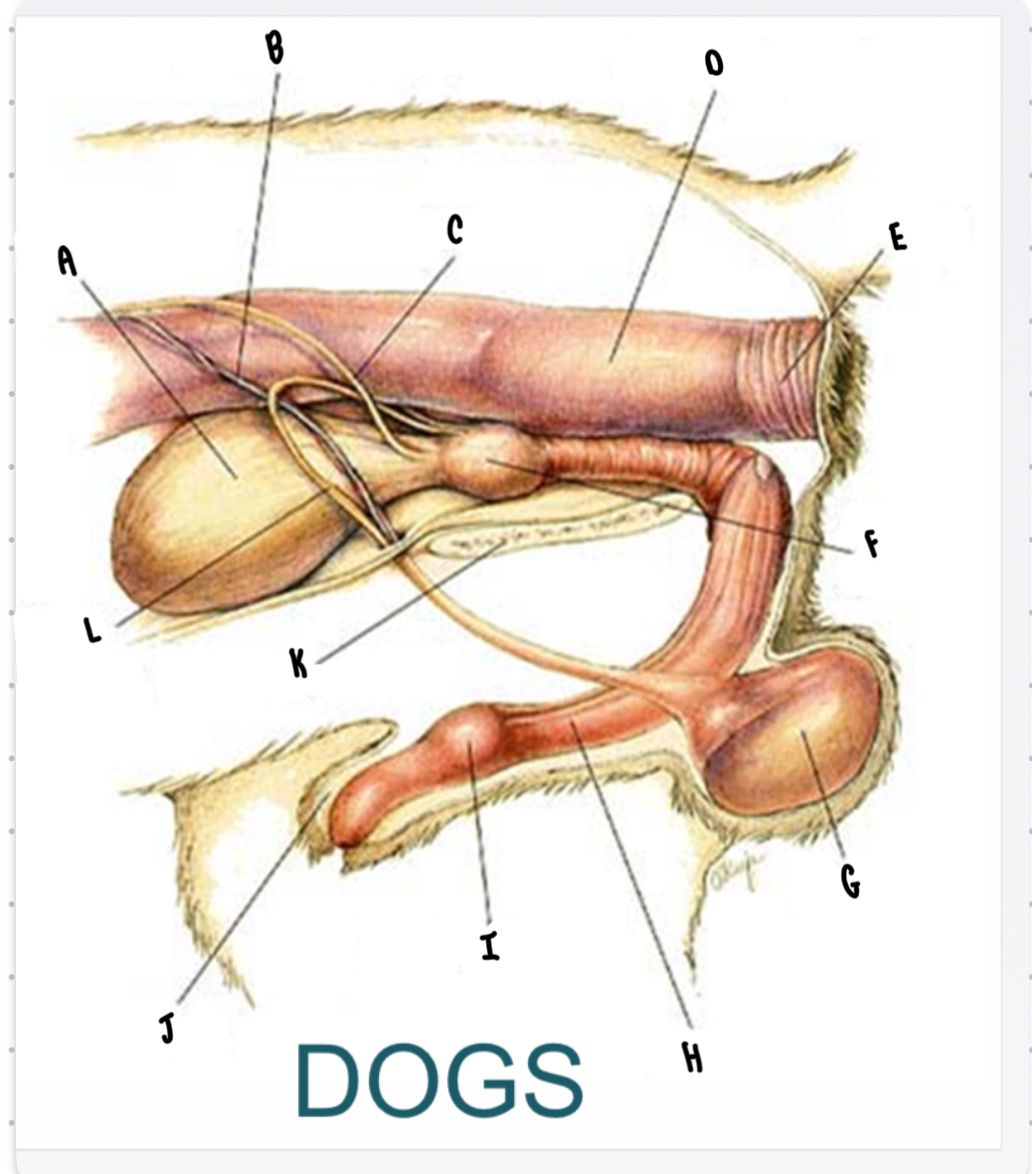
What is the structure labeled D?
Descending colon
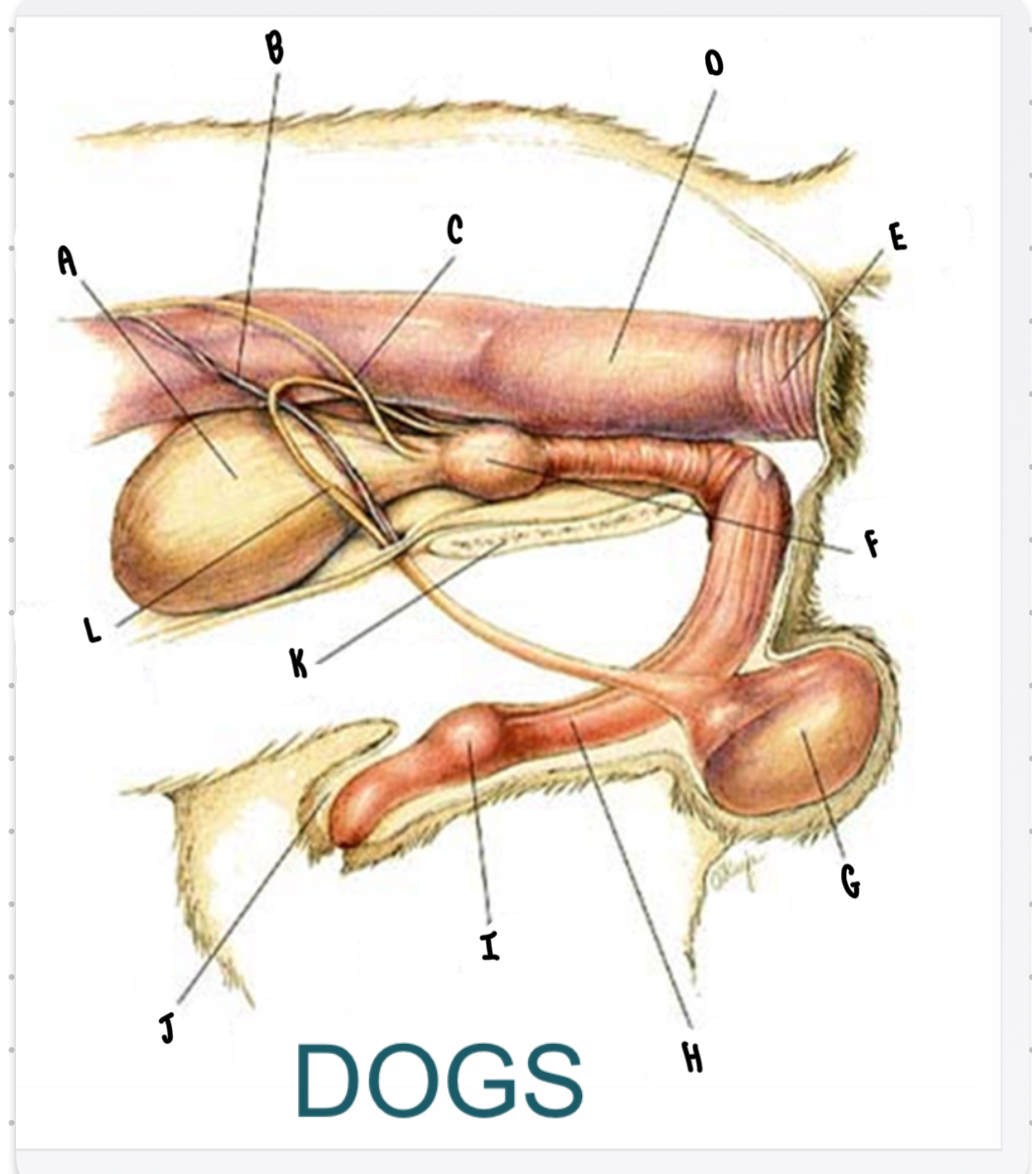
What is the structure labeled E?
Rectum
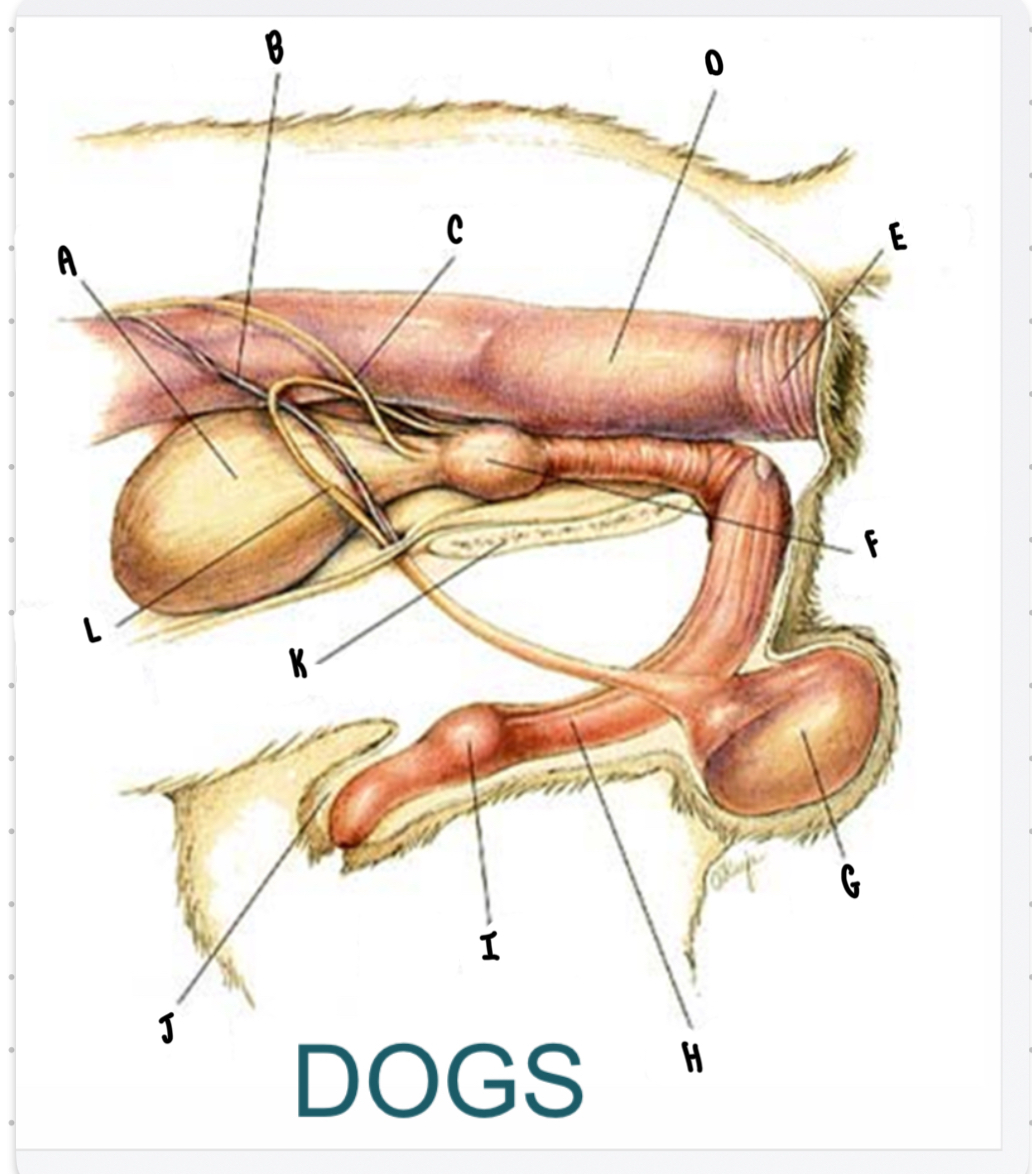
What is the structure labeled F?
Prostate gland
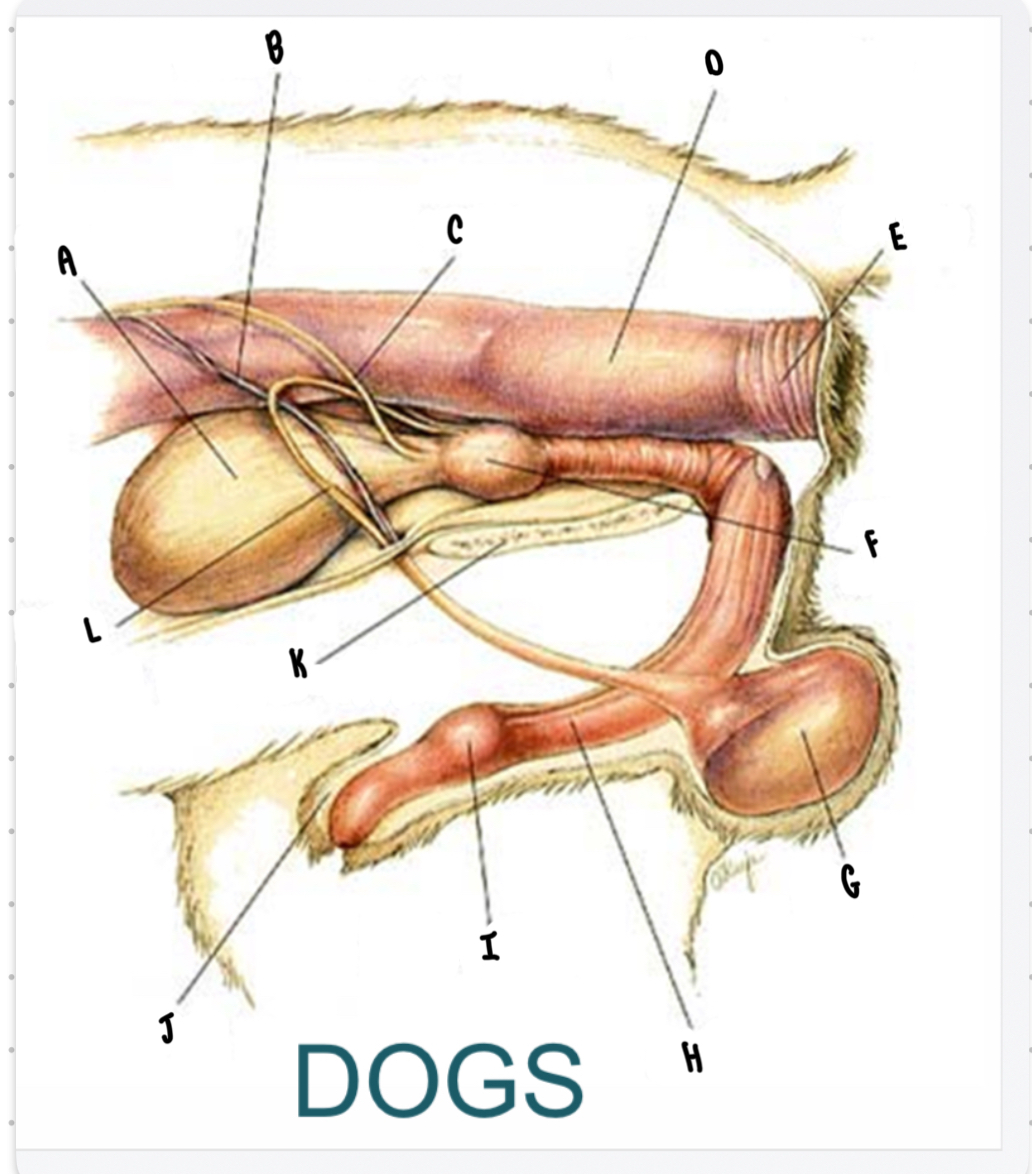
What is the structure labeled G?
Testicle
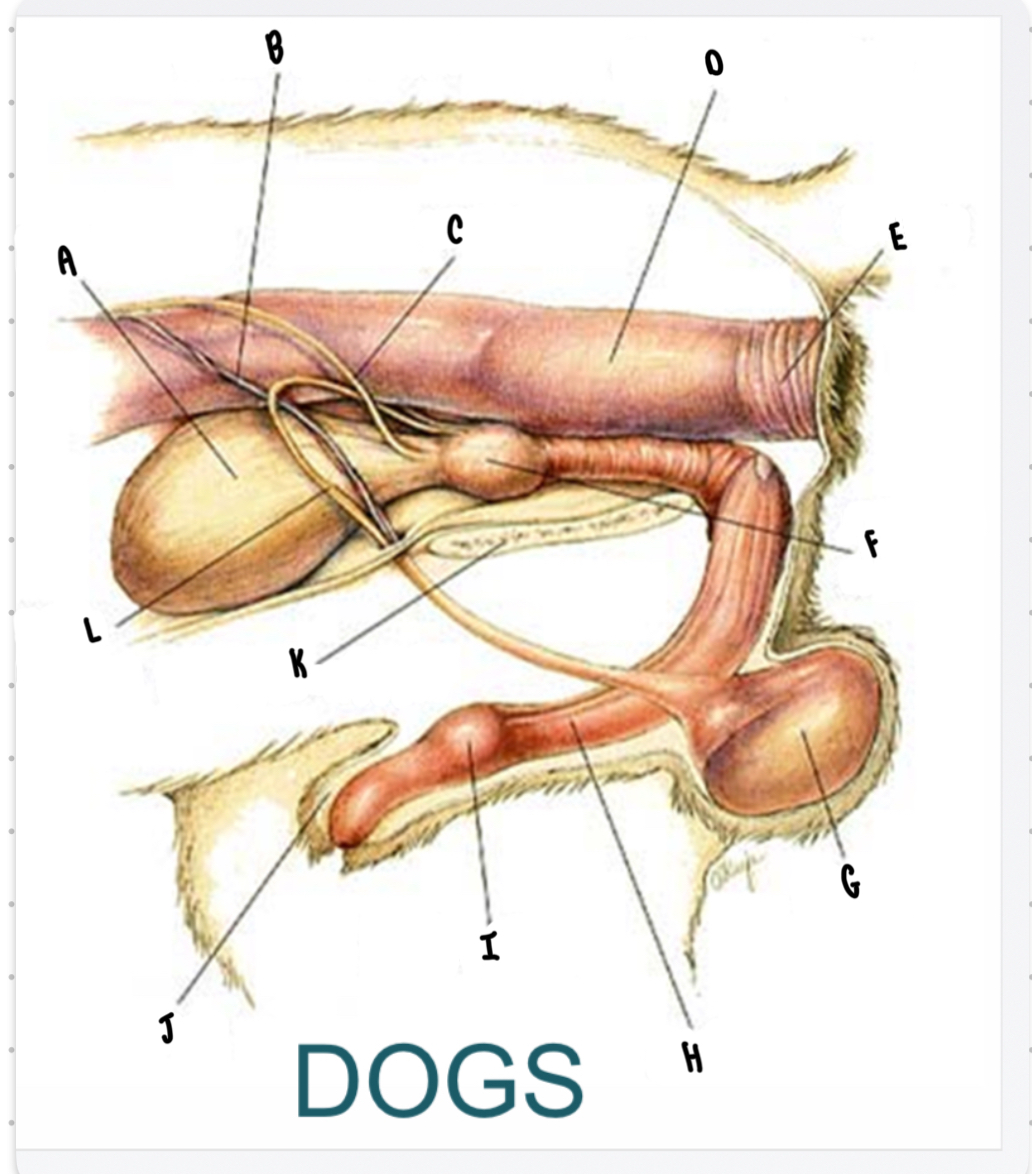
What is the structure labeled F?
Penis
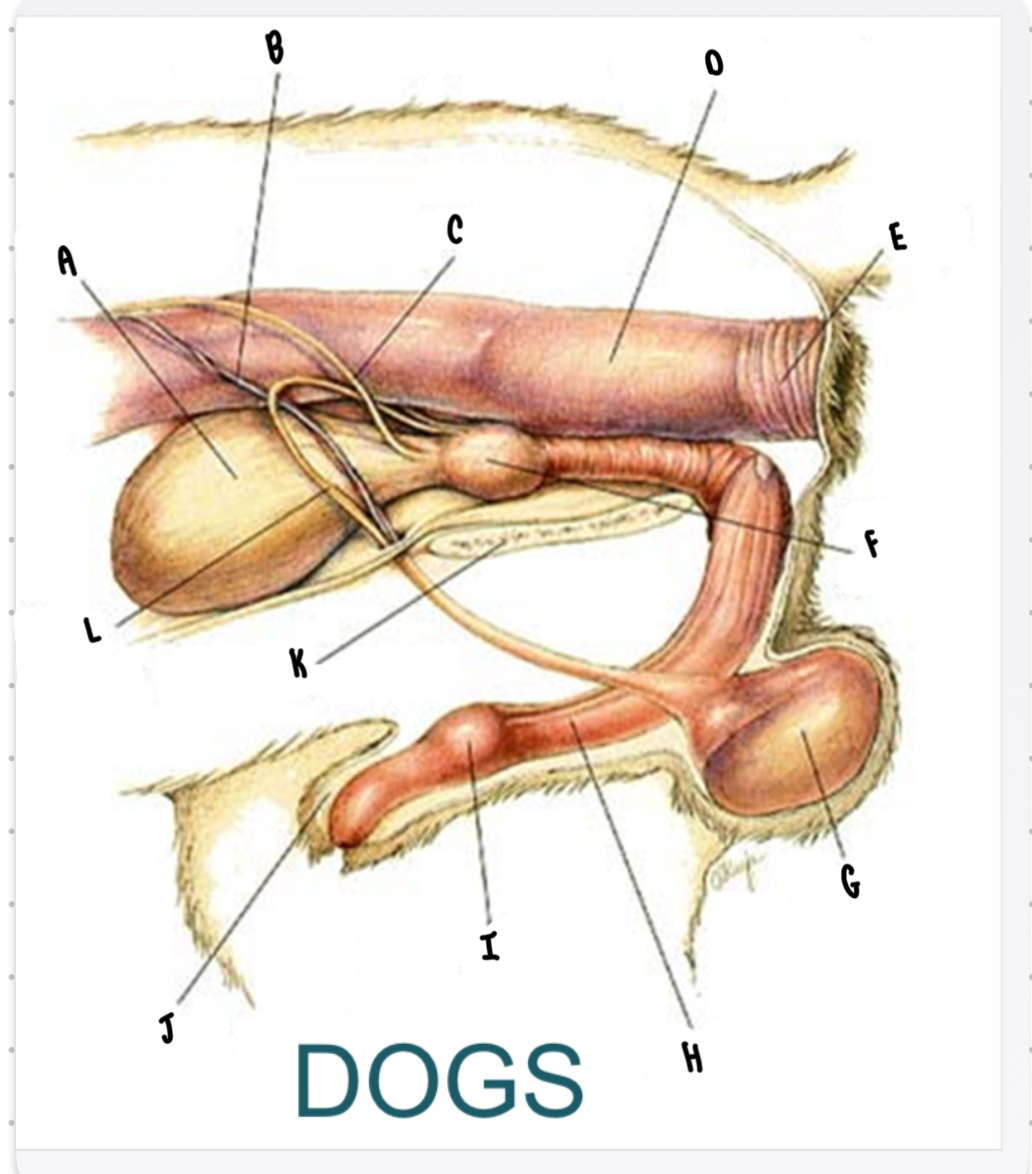
What is the structure labeled I?
Bulbus glandis
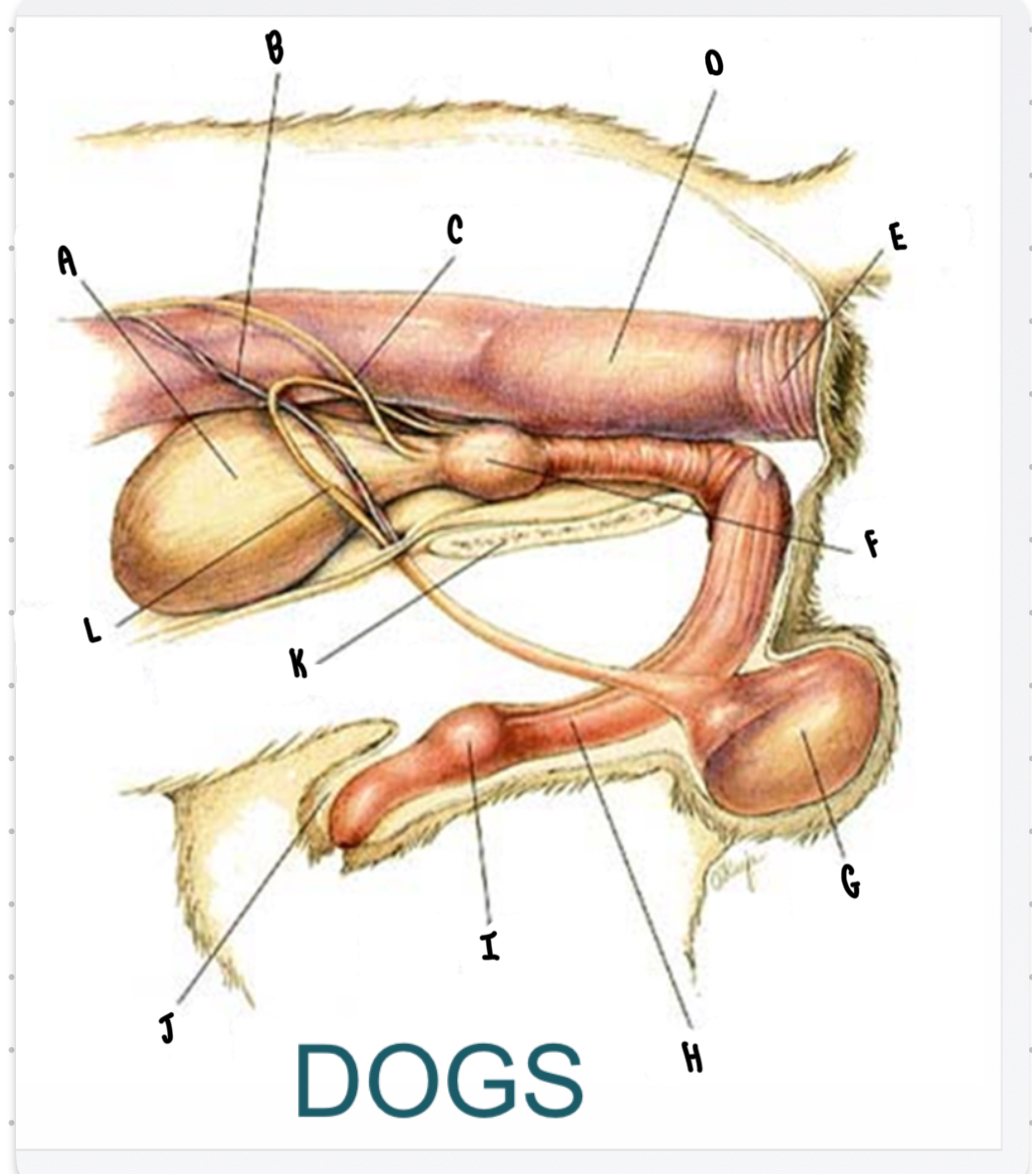
What is the structure labeled J?
Prepuce
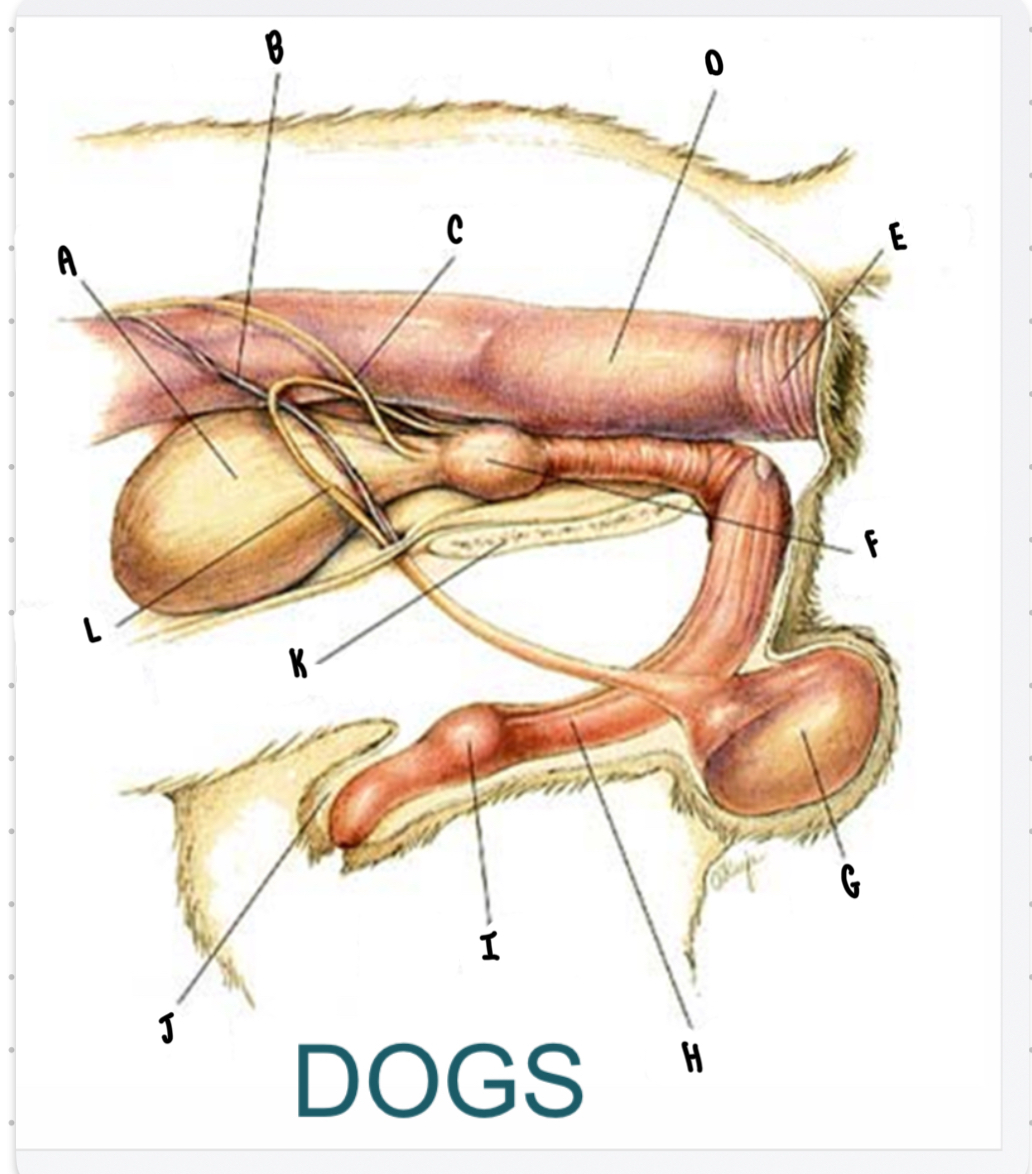
What is the structure labeled K?
Pelvic sympysis
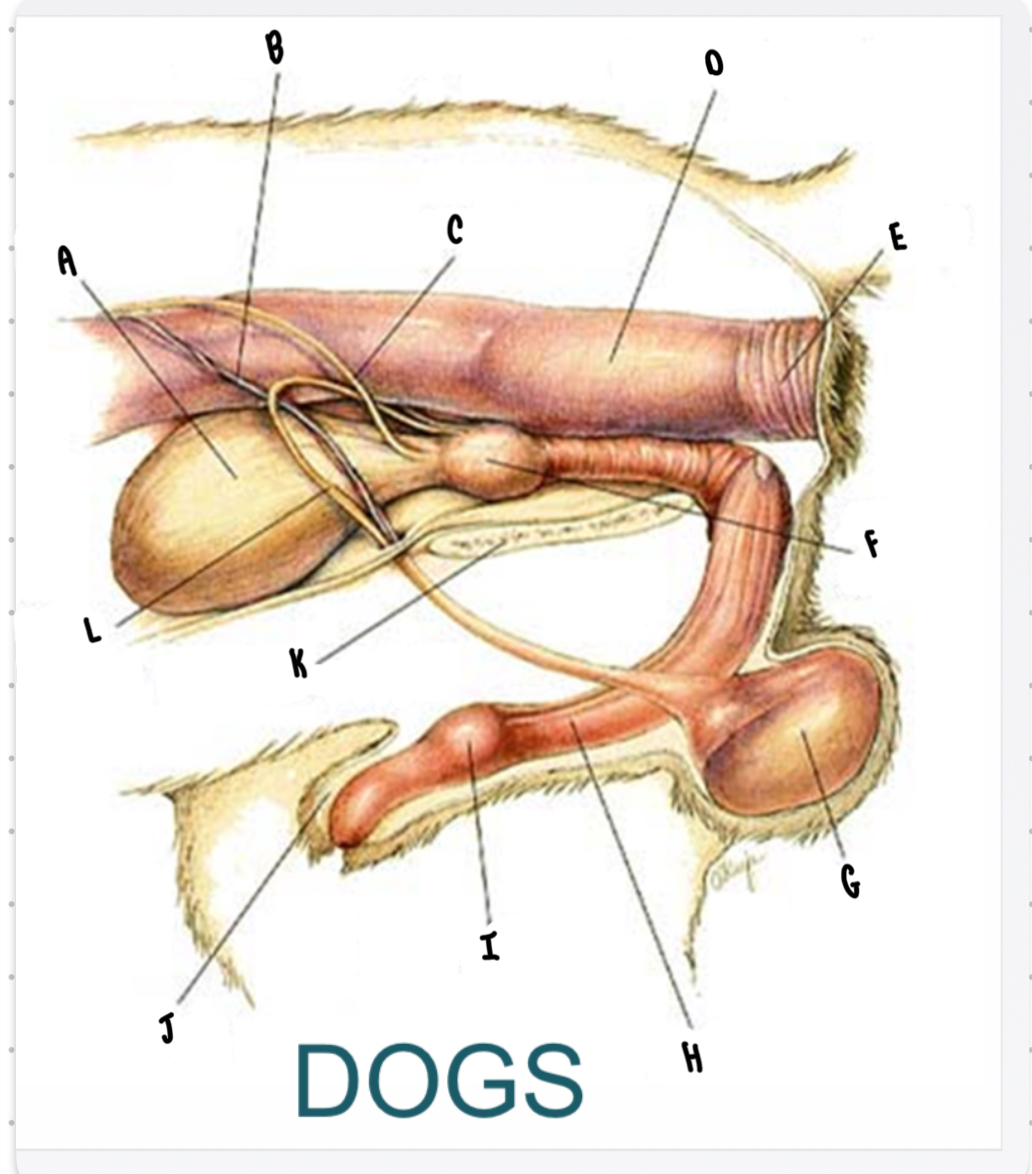
What is the structure labeled L?
Ductus deferens
Where does the scrotum lie in dogs?
Between the hind legs
Where does the scrotum lie in cats?
On the perineum below the anus
What is the scrotum?
A membranous pouch containing testicles divided into two halves by a septum
Why is the scrotum located outside of the body?
For temperature control to promote spermatogenesis
What muscle is responsible for controlling the position of the scrotum?
Cremaster muscle
What does cryptorchid mean?
One or both testicles retained
What does monorchid mean?
Only one testicle was developed/descended at birth
What is the function of the testicle?
To produce sperm and secrete testosterone
Briefly describe the histological structure of the testes:
Contains many open ended seminiferous tubules which drain into the efferent ducts which lead to the epididymis. This then drains into the vas deferens via the spermatic cord or urethra.
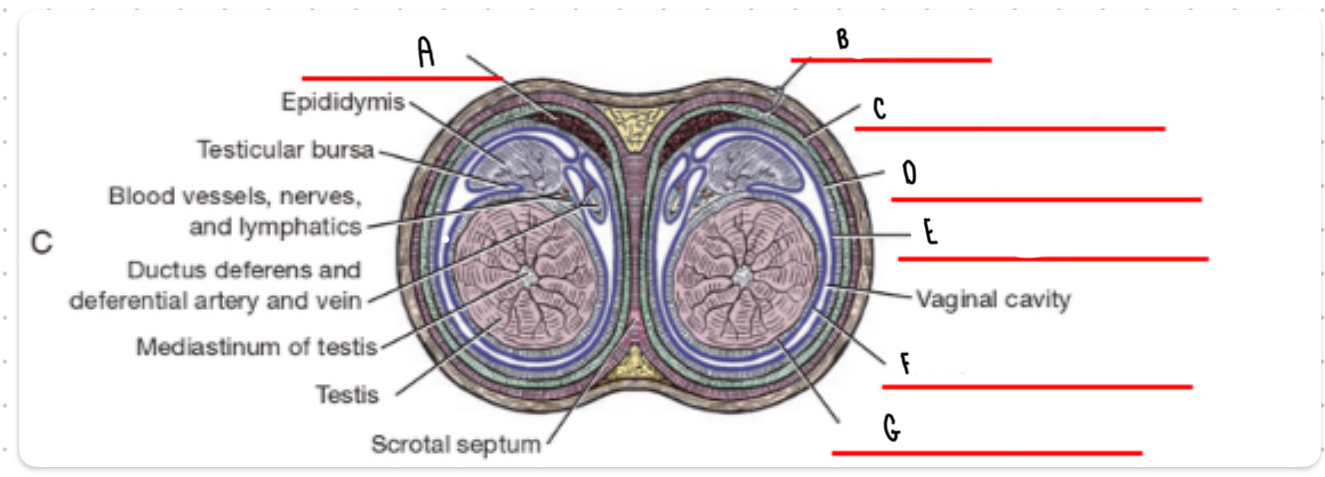
What is the layer labeled A?
Cremaster
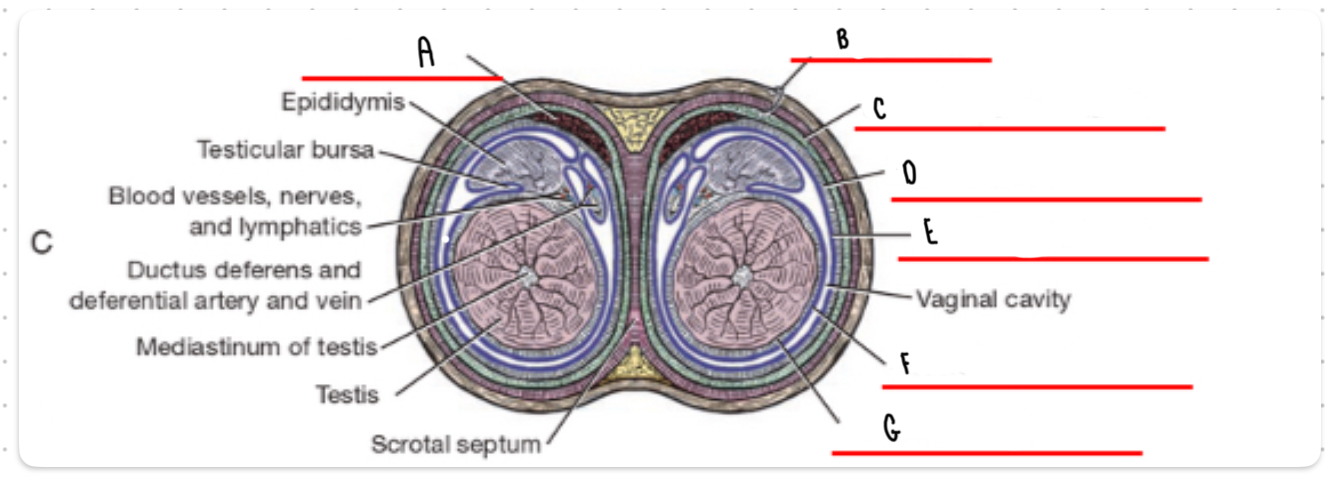
What is the layer labeled B?
Skin and dartos
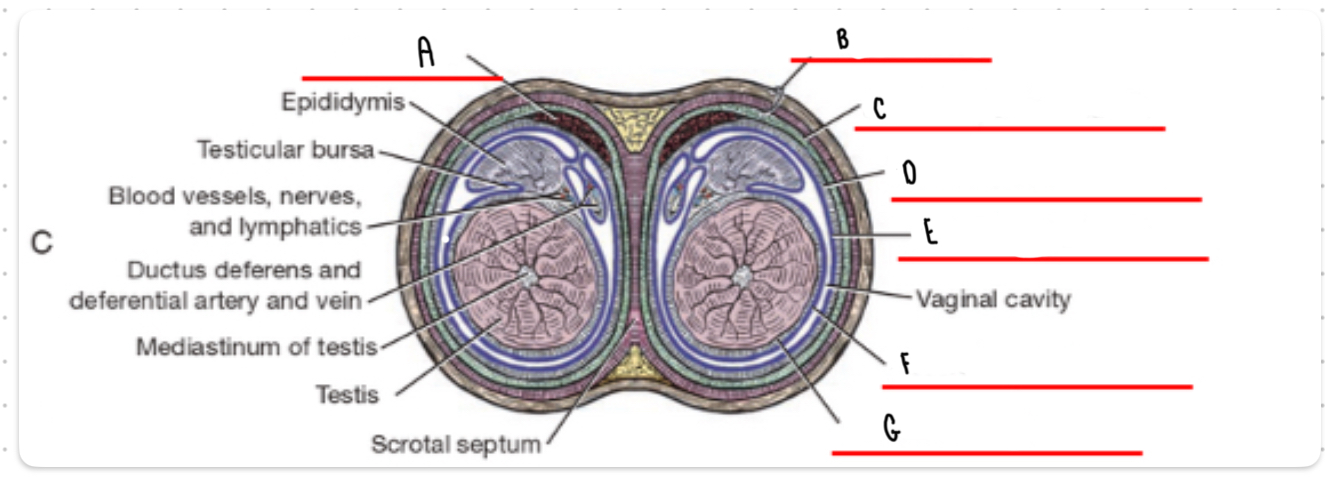
What is the layer labeled C?
External spermatic fascia
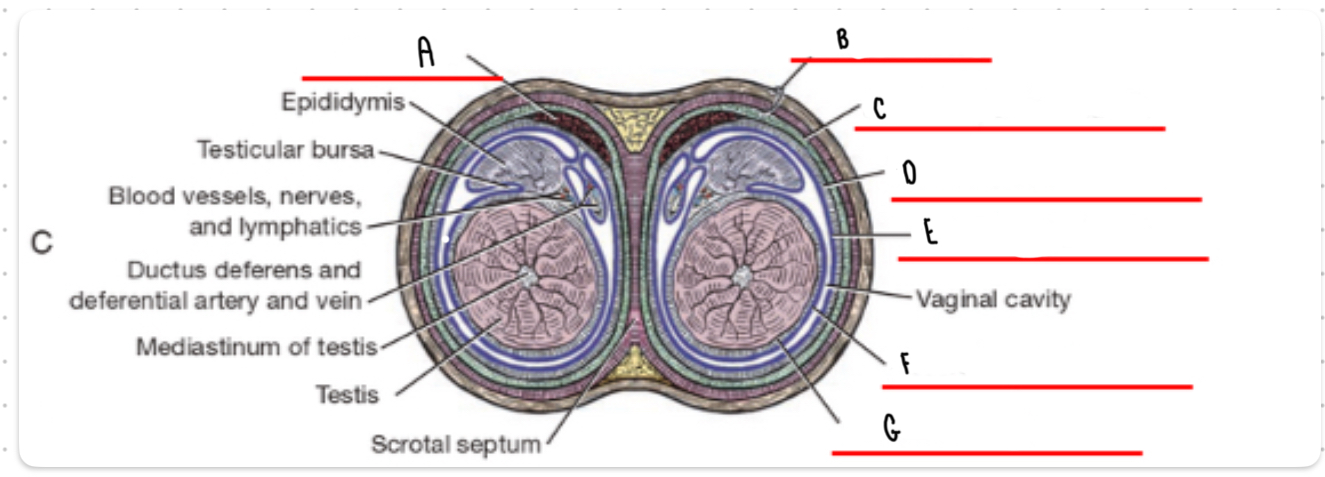
What is the layer labeled D?
Internal spermatic fascia
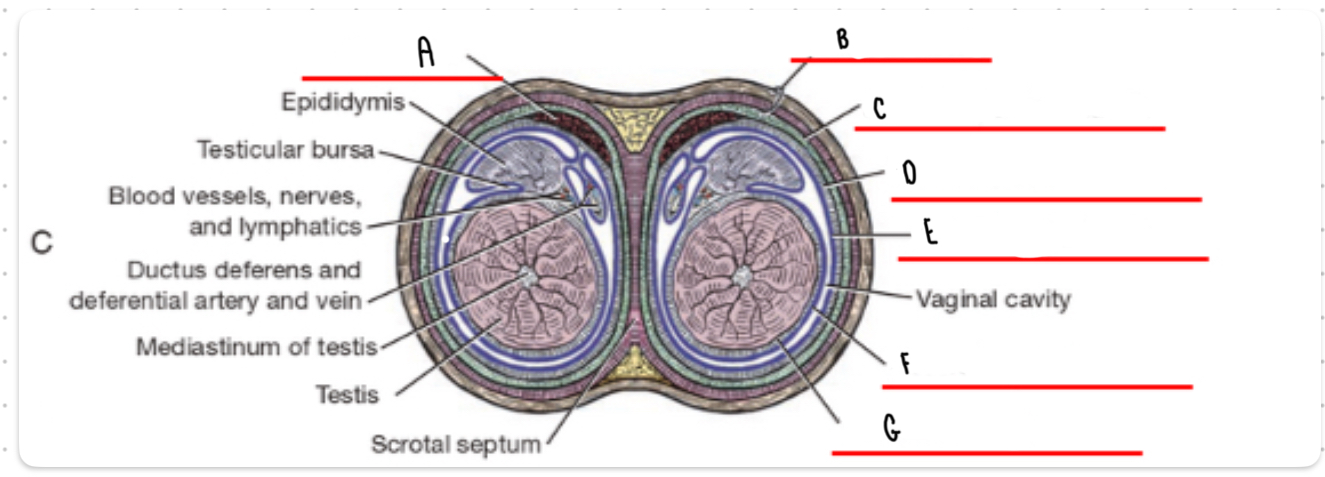
What is the layer labeled E?
Parietal vaginal tunic
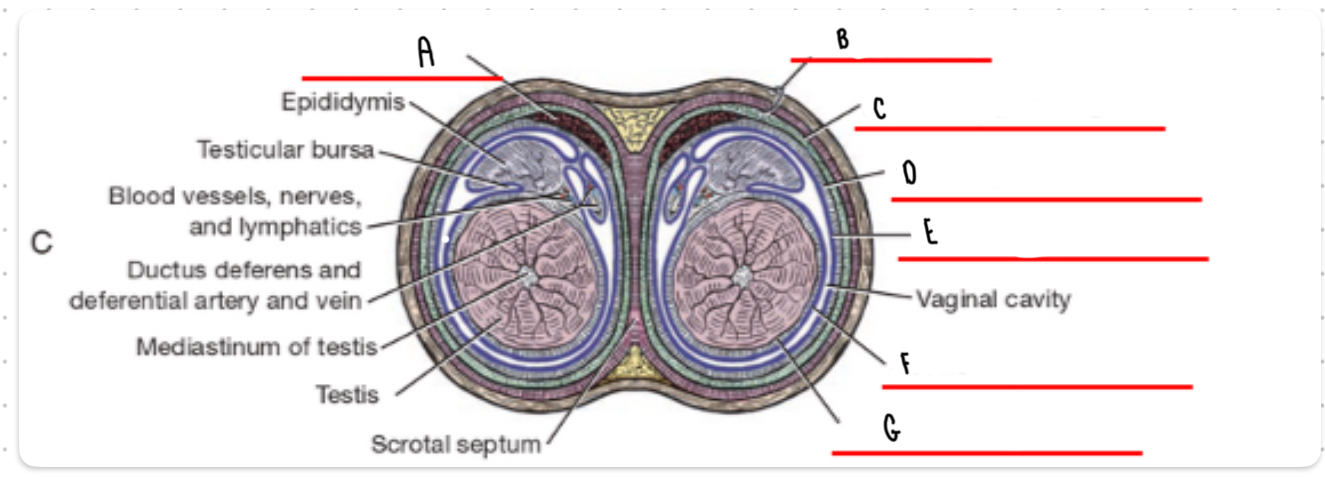
What is the layer labeled F?
Visceral vaginal tunic
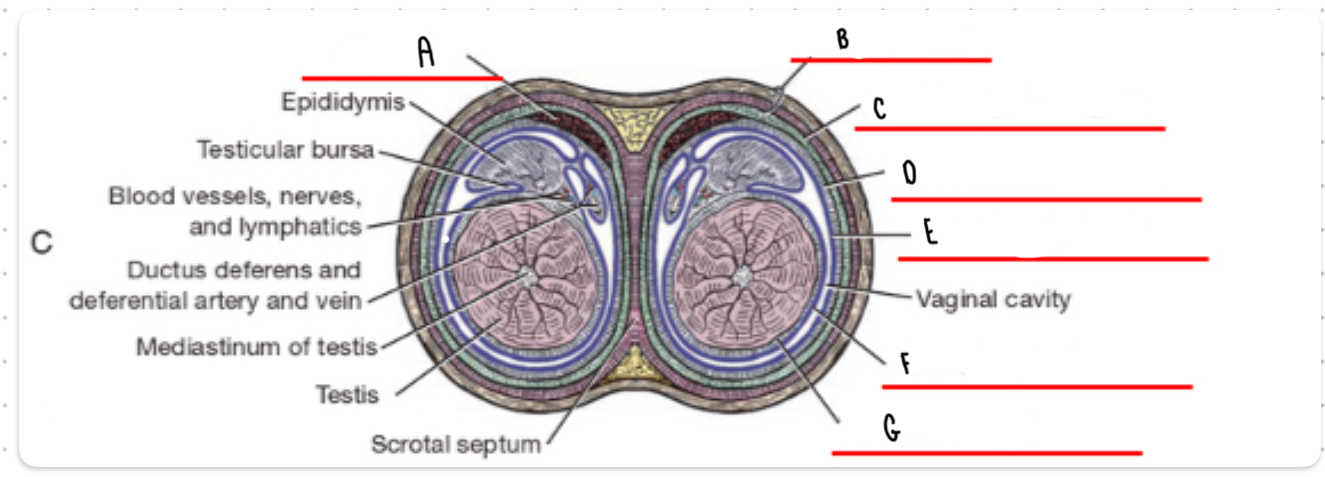
What is the layer labeled G?
Tunica albuginea
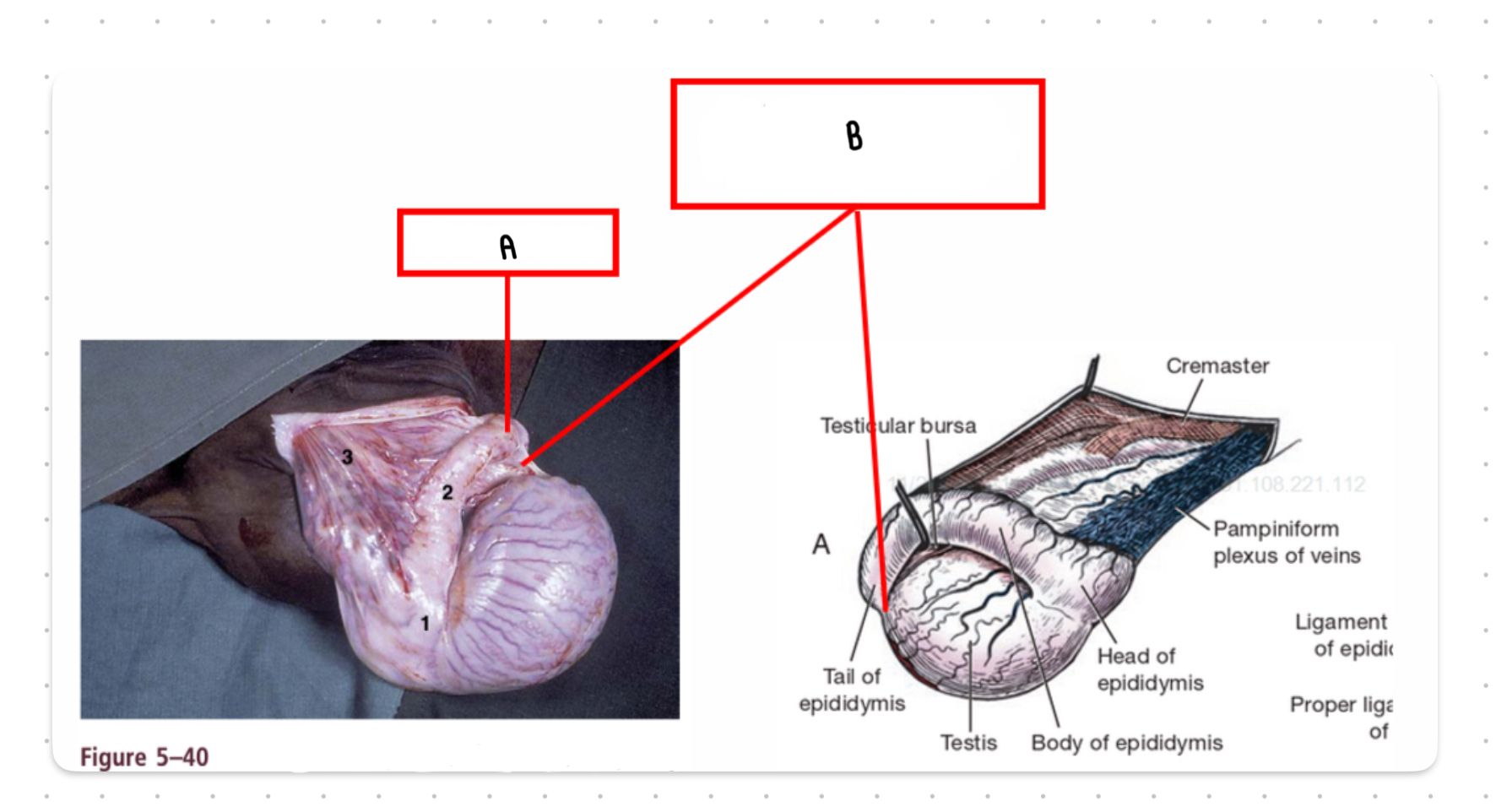
What is the structure labeled A?
Tail epididymis
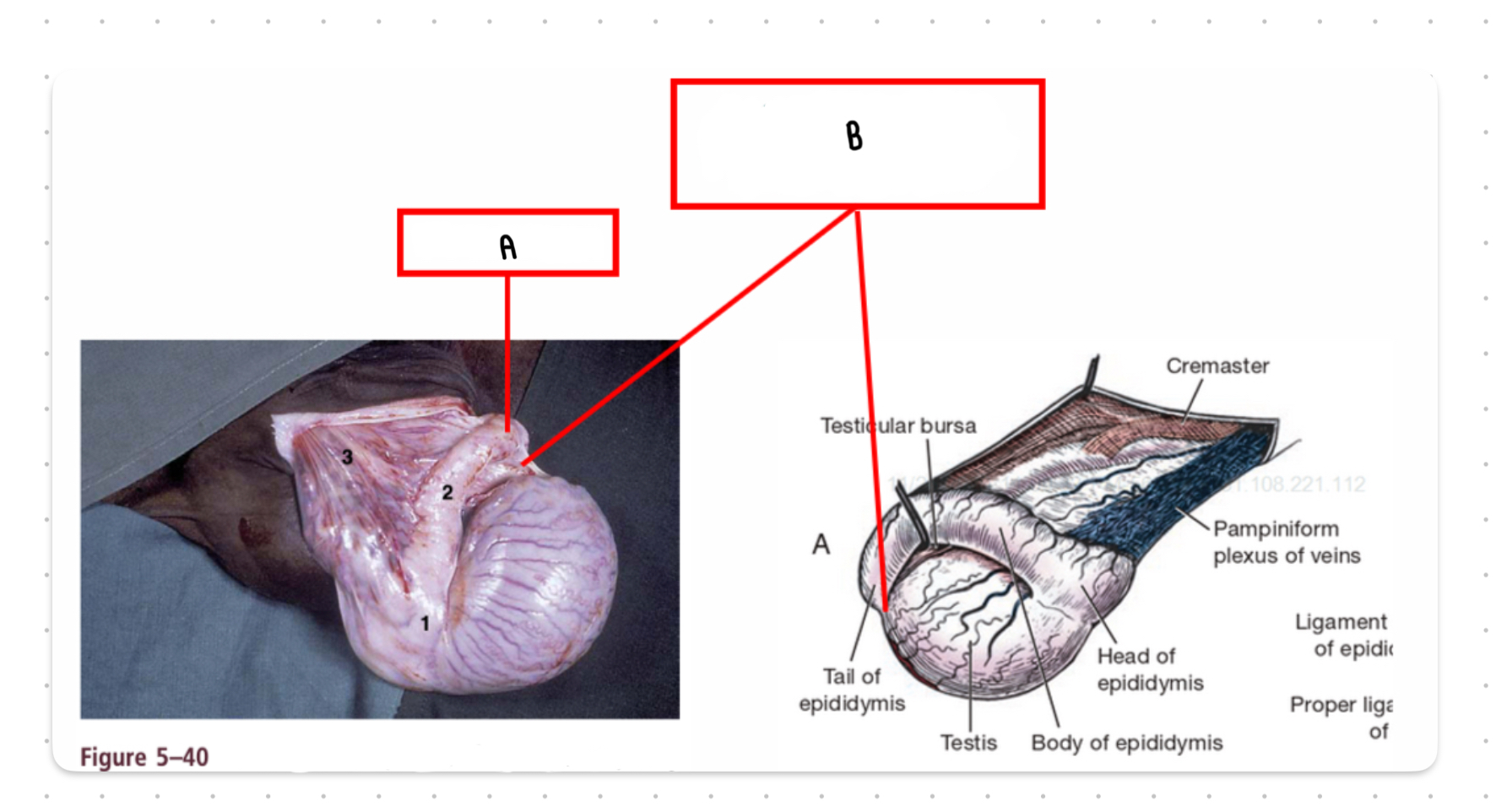
What is the structure labeled B?
Proper ligament of the testis and ligament of the tail of the epididymis
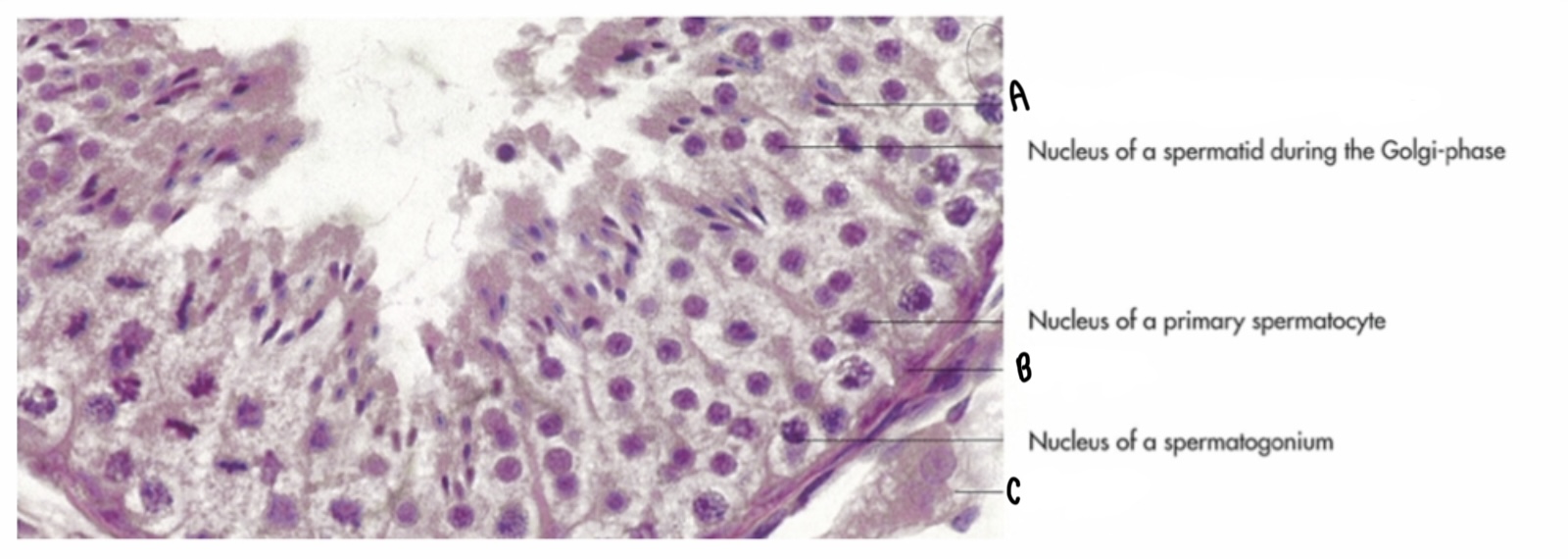
What type of cell is labeled A?
Spermatid cell
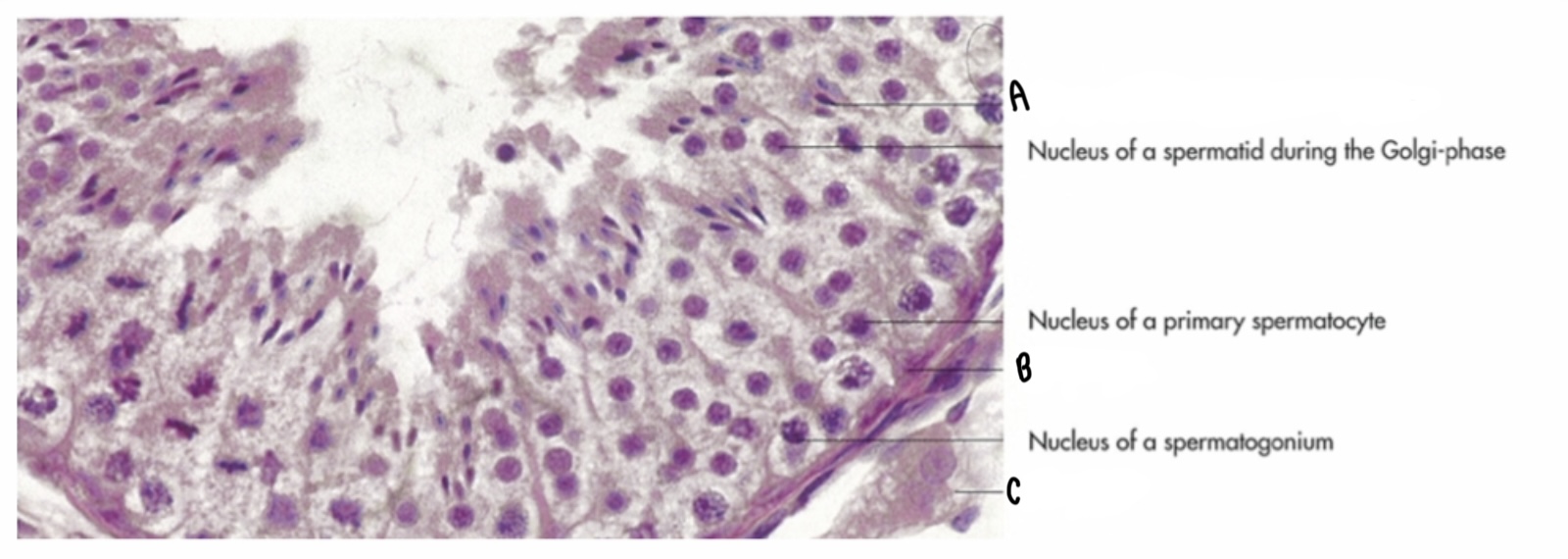
What type of cell is labeled B?
Sertoli-cell
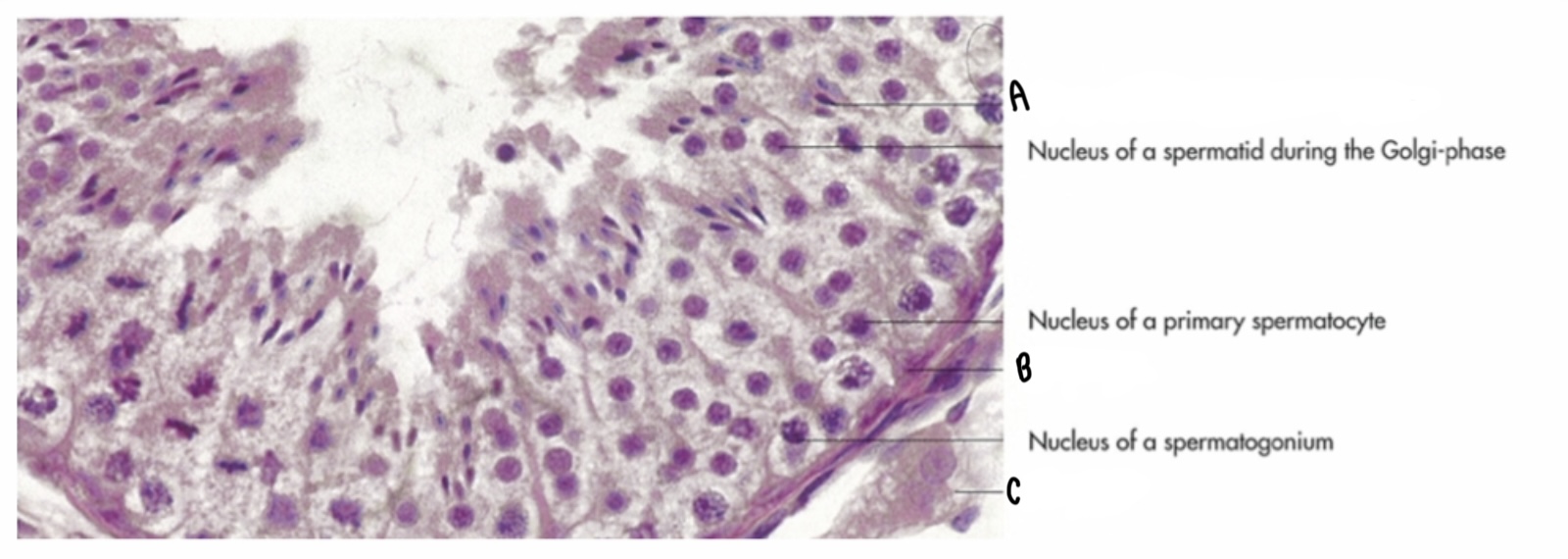
What type of cell is labeled C?
Leydig cell
What blood vessels are found in the spermatic cord?
Testicular artery and vein
What other structures are found in the spermatic cord?
Lymphatic vessels, nerves and vas deferens
What is the pampiniform plexus found in the spermatic cord?
A meshwork of veins that surrounds the testicular artery to keep the testicle cool and to warm blood when it goes up to the abdomen.
What are the two portions of the urethra?
Pelvic portion and penile portion
Briefly describe the pelvic portion of the urethra:
Entry point of deferen duct and accessory reproductive glands
Briefly describe the penile portion of the urethra:
Contains spermatozoa from vas deferens and secretions from reproductive glands as well as urine from the urinary bladder outside the body. Urine flow is temporarily blocked when ejaculation occurs.
What are two accessory reproductive glands?
Ampullary and prostate
What is the ampullary gland?
A widening of the vas deferens
What is the role of the prostate?
Produces alkaline fluid that helps counteract the acidity of the female reproductive tract and provides energy to the sperm.
In what species are cowpers glands found? (Bulbourethral)
Cats and stalions
What is the role of cowpers glands?
Secrete a thick mucous substance that forms part of the seminal fluid. Clears the urethra of debris prior to full ejaculation.
What are the two erectile tissues in the penis?
Corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum
What is the role of the erectile tissues?
Expand proximally when engorged with blood along the penis and is known as the bulb of the penis.
What is the function of the penis?
To convey sperm and fluids from the testis into the female reproductive tract and to convey urine from the bladder to outside via the urethra.
What is the function of the prepuce?
To protect the penis
What is the role of the hypothalamus is sperm formation?
Creates increasing amounts gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH.)
What does GnHR trigger the release of?
Interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH) and LH from the anterior pituitary gland.
What is ICSH and LH responsible for?
Stimulation of cells of Leydig
What does the stimulation of the cells of Leydig lead to?
Production of testosterone which makes the tests start to produce spermatozoa and is responsible for male characteristics and behaviors.
Briefly describe the cycle of hormone control for spermatozoa production:
Hypothalamus releases GnRH which leads to the release of FSH and ICSH. This stimulates the sertoli cells whcih support and nourish spermatozoa and creates osetrogen. Inhibin creates a negative feedback loop on the production of FSH.
Briefly describe the process of sperm formation:
Testosterone produced in interstitial space due to ICSH. This stimulates production of sperm in the seminiferous tubules. Secretions from sertoli cells nourish sperm due to FSH. Sperm grow, mature, detach and travel to epididymis for storing.
What is the role of testosterone?
Produced by the cells of leydig prompted by ISCH. Responsible for sperm production and development of male characteristics.
What is the role of oestrogens?
Produced by the testes from the sertoli cells stimulated from FSH from anterior pituitary gland. Responsible for the maturation of spermatozoa.