chemistry - key concepts in chemistry: atomic structure (1.1 - 1.12)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
1.1 Dalton atomic model
all matter made up of tiny particles called atoms
atoms - tiny, hard spheres, cannot be broken into smaller parts
atoms can’t be created/destroyed
atoms in element are identical
each element has its own type of atom
1.1 development of Dalton atomic model
thought cathode rays contained atoms leaving negative electrode
Thomson found particles in rays were lighter than atoms
so cathode rays contain subatomic particles - electrons
1.2 structure of atom
tiny nucleus in centre containing protons & neutrons
surrounded by fast moving electrons in shells
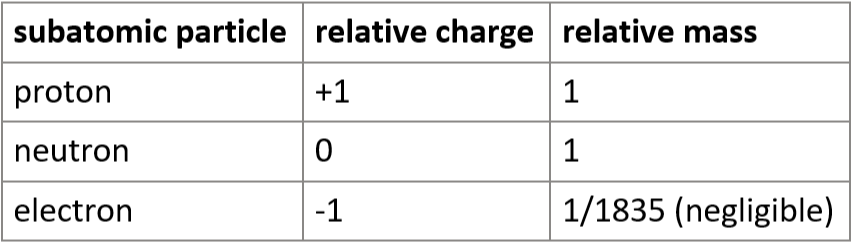
1.3 protons, neutrons, electrons - relative charge & relative mass
1.4 why do atoms contain equal numbers of protons & electrons?
no overall charge - charges cancel out
1.5 size of nucleus
very small compared to overall size of atom
1.6 where is most of atom’s mass?
concentrated in nucleus
1.7 mass number definition
total number of protons & neutrons in atom
atomic number definition
number of protons
1.8 number of protons in atoms of same element
same number of protons
this number (atomic number) is unique to that element
1.9 isotopes definition
different atoms of same element with same number of protons (same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons (different mass numbers)
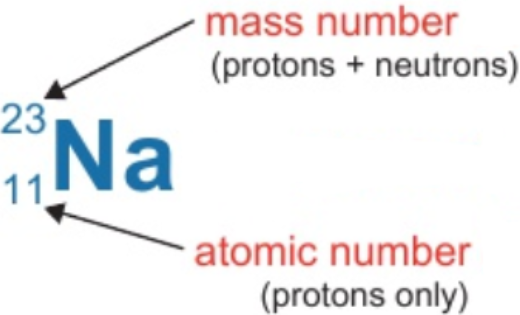
1.10 calculate numbers of protons, neutrons & electrons given atomic number & mass number
protons = atomic number = 11
electrons = protons = 11
neutrons = mass number - atomic number = 23 - 11 = 12
relative atomic mass definition
mean mass of an atom of an element compared with carbon-12
1.11 why are some relative atomic masses not whole numbers?
all elements exist as mixtures of isotopes
RAM takes into account all isotopes of element & amounts of each
1.12 calculate RAM of element from relative masses & abundances of its isotopes
