2. 8.1b Antifungal Agents
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is the overview of antifungal agents?
Many target the cell membrane or cell wall
Some are fungistatic (e.g. griseofulvin = inhibits growth rather than kill) or fungicidal (e.g. echinocandins = kill fungi by cell wall lysis)
Severe infections occur mainly in immunocompromised patients (e.g. disease or chemotherapy)
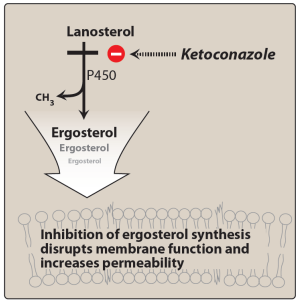
What are azoles and their key features?
Azoles inhibit ergosterol synthesis by blocking cytochrome P450-dependent 14α-lanosterol demethylation
Ketoconazole largely replaced due to side effects
Itraconazole safer, broader activity (Candida, Cryptococcus, Aspergillus, dermatophytes); needs food and acid for max absorption
Fluconazole has narrower spectrum, treats Candida and Cryptococcus, used for prophylaxis in immunosuppressed patients
Give key clinical points for voriconazole and posaconazole?
Voriconazole broad-spectrum; active vs Candida, Aspergillus, molds; 1st line for aspergillosis
Posaconazole broadest azole; oral only, take with food; active vs yeasts and molds; used for thrush and prophylaxis; fewer interactions
Azoles may promote hepatitis (rare) and have specific drug interactions, requiring monitoring
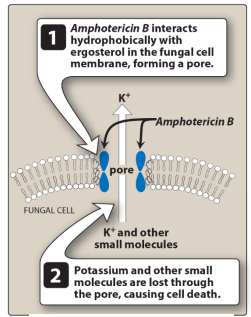
What are the mechanism, action, toxicity, and main agents of polyenes?
Bind ergosterol in fungal cell membranes
Increase membrane permeability causing leakage
Fungicidal in action
Toxicity due to weak cholesterol binding
Main agents Nystatin (topical) and Amphotericin B (systemic)
What are the main uses, absorption properties, and administration methods of Nystatin?
Nystatin is used as a ________ ________ for the treatment of ________ ________; it is poorly absorbed from the ________________ _____ so has limited ________ ______; administration methods include “ _____ __ _______” or “ _____ ___ ____”.
Nystatin is used as a topical agent for the treatment of oral Candida; it is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract so has limited toxicity issues; administration methods include “swish and swallow” or “swish and spit”.
What are the formulation, toxicity, and spectrum of activity of Amphotericin B?
Only available as an ____________ – colloidal suspension with ________ ____________ due to poor water solubility
Binds serum lipoproteins, penetrates poorly into ___ and other fluids
Causes _____________, ____, and infusion reactions – fever, chills, nausea, myalgias; slow infusion required
Lipid-based formulations (________) reduce toxicity
Broad-spectrum activity – ______, _________ ___, ___________ ___, molds including __________
Only available as an intravenous – colloidal suspension with sodium deoxycholate due to poor water solubility
Binds serum lipoproteins, penetrates poorly into CSF and other fluids
Causes nephrotoxicity, anemia, and infusion reactions – fever, chills, nausea, myalgias; slow infusion required
Lipid-based formulations (liposomes) reduce toxicity
Broad-spectrum activity – yeasts, Candida spp., Cryptococcus spp., molds including Aspergillus
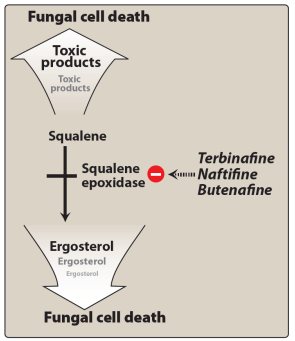
What is the mechanism, formulation, activity, and key features of Allylamines such as Terbinafine?
Inhibit __________ __________ blocking __________ synthesis in the fungal cell membrane. Key example is __________.
Available in both ______ and ______ formulations – active against __________ that cause skin and nail infections; generally active against __________ __________.
Reserved for infections unresponsive to other agents; not for __________ infections; therapy usually lasts ___ months. With oral use, drug distributes to skin, nails, and fat – long half-life up to ___ hours.
Common adverse effects involve the _______________________ ______.
Inhibit squalene epoxidase blocking ergosterol synthesis in the fungal cell membrane. Key example is Terbinafine.
Available in both oral and topical formulations – active against dermatophytes that cause skin and nail infections; generally active against Candida albicans.
Reserved for infections unresponsive to other agents; not for systemic infections; therapy usually lasts 3 months. With oral use, drug distributes to skin, nails, and fat – long half-life up to 400 hours.
Common adverse effects involve the gastrointestinal tract.
What is the mechanism, examples, formulation, and key features of Echinocandins?
Inhibit beta-(1,3)-D-glucan in the fungal cell wall = lysis and death
e.g. caspofungin, micafungin, anidulafungin
Caspofungin only available IV, should not be co-adm with ciclosporin
Not metabolised by, nor inhibit, CYP450 enzymes
Used for many Candida infections and for aspergillosis, either combined with voriconazole or used in succession
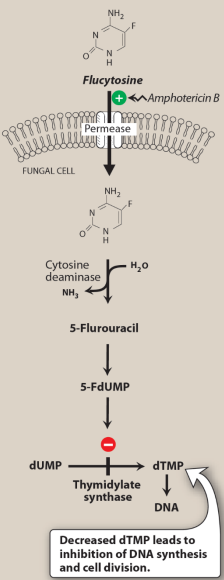
What are the mechanism, limitations, and clinical use of Pyrimidine Inhibitors, (Flucytosine is the only member of this class)?
Converted to - ___________ in fungal cells = disrupts protein and DNA synthesis; fungistatic
High _______ _______ ∴ only used with other antifungals, e.g. amphotericin B
Resistance occurs due to ____________ of enzymes modifying flucytosine to active form
Dose-related bone marrow and __________; caution with chemo/radiotherapy that leads to bone marrow depression
Used for systemic mycoses and meningitis caused by _______ _______ and _______ _______
A:
Converted to 5-fluorouracil in fungal cells = disrupts protein and DNA synthesis; fungistatic
High mutational resistance ∴ only used with other antifungals, e.g. amphotericin B
Resistance occurs due to downregulation of enzymes modifying flucytosine to active form
Dose-related bone marrow and hepatotoxicity; caution with chemo/radiotherapy that leads to bone marrow depression
Used for systemic mycoses and meningitis caused by Cryptococcus neoformans and Candida albicans
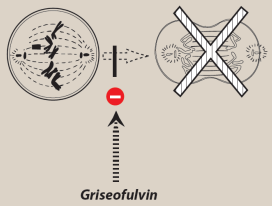
What is Griseofulvin’s mechanism, use, and key features?
Oral agent
Disrupts microtubules = prevents spindle formation = inhibits mitosis
Accumulates in newly synthesized keratinized tissue; used for dermatophytic nail infections
Treatment duration up to 1 year
Induces hepatic cytochrome P450, ↑ metabolism of other drugs, e.g. anticoagulants
Largely superseded by terbinafine and itraconazole; still used for skin and hair fungal infections