Chemical Equilibria, Le Chatlier’s Principle and Kc
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
what is a reversible reaction? how are they represented?
when a reaction can proceed in both directions simultaneously, at the same rate, represented by this symbol:
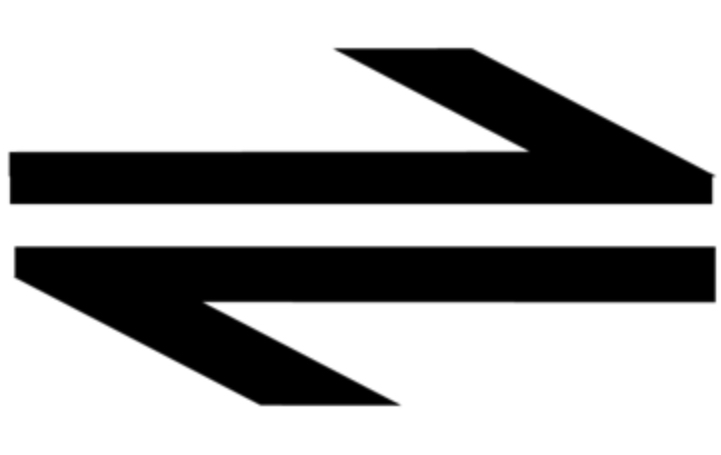
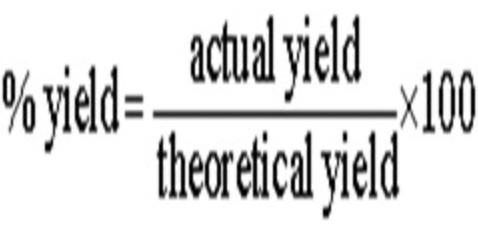
if a reverse reaction is favoured, we will never run out of products, this helps explain why (if a reaction is reversible) the ? yield will always be less than the ? yield
this helps explain why the actual yield will always be less than the theoretical yield
what is rate of reaction?
how quickly reactants are turned to products in a reaction in a specific time period
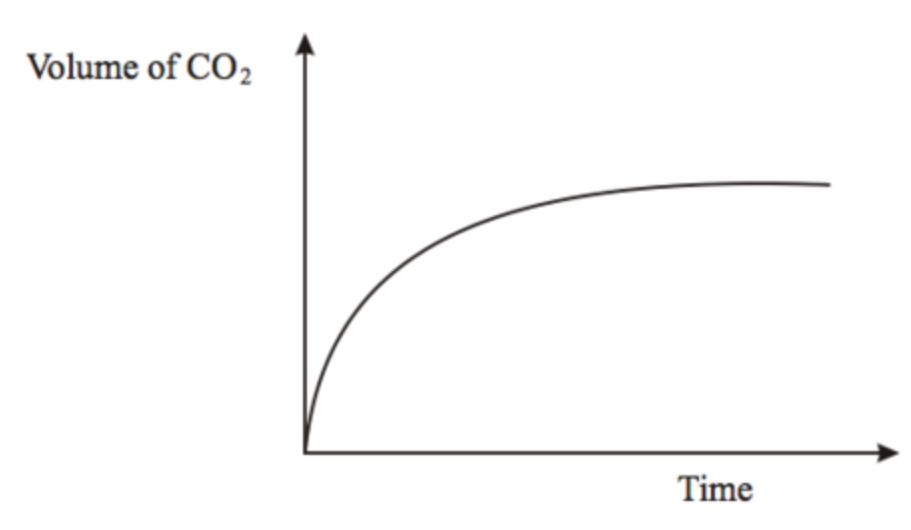
rate of reaction graph? y and x axis?
starts at origin: vol. of reactants is high (rate is high), then it slows as reactants are used up (rate decreasing), when it levels off it shows the reaction is finished
how do the axis differ for a reversible reaction on a graph?
instead of volume on the y axis, we use concentration;
there are 2 curves, one for products and one for reactants
when forward reaction is favoured, how are the graph curves for each presented?
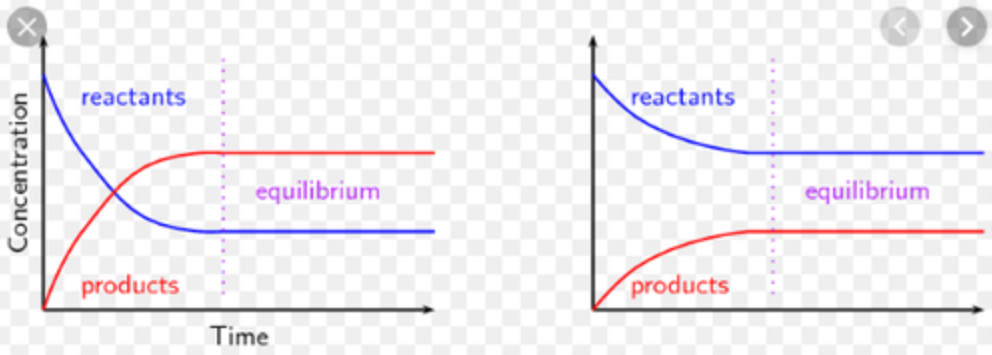
why do concentration of reactants not decrease to 0 when the forward reaction is favoured?
the increase in conc. of products, increases rate of the backwards reaction, but they will level off (happens until conc. becomes constant)
what is dynamic equilibrium?
where both forward reaction and backward reactions are occurring simultaneously, at the same rate, in a closed system with a fairly constant concentration
what is a closed system in terms of reactions?
no reactants are added, no products are lost
e.g. conc. of reactants and products remain the same
what is static equilibrium?
state where bodies are at rest
what is dynamic equilibrium?
state where bodies are moving at a constant velocity/rate
what does Le Chatelier's Principle state?
if an external condition is changed the equilibrium will shift to oppose the change
what is Le Chateliers principle used to work out?
how changing external conditions affect the position of equilibrium
do exothermic reactions make the system hotter or cooler?
hotter: energy is released
chemical energy -> heat energy = hotter
do endothermic reactions make the system hotter or cooler?
cooler: energy is taken in
heat energy -> chemical energy = colder
how would equilibrium oppose an increase in temperature when the forward reaction is endothermic and backwards is exothermic?
equilibrium position moves to oppose increase in temperature, by moving in the endothermic direction, increasing yield of products
does endothermic give a negative or positive enthalpy?
positive
does exothermic give a negative or positive enthalpy?
negative
how would equilibrium oppose increase in pressure?
equilibrium will shift to the side with less gas molecules to oppose increase in pressure
how does equilibrium oppose increase in concentration?
equilibrium moves to oppose the increase in conc., by moving in the other direction to use it up, decreasing conc.
what do square brackets [ ] mean?
concentration
Kc equation?
conc. of products/conc. of reactants
what is Kc?
equilibrium constant
acronym to remember how to find concentration for kc?
ICE
Initial moles
Change in moles
Equilibrium - amount of moles at equilibrium
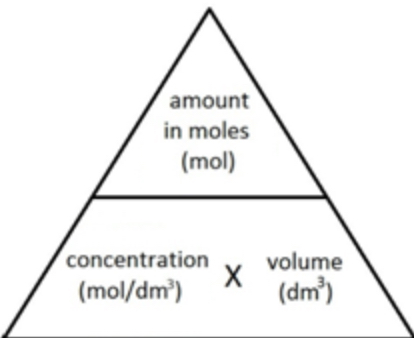
concentration, moles and volume equation?
concentration = moles/volume
concentration, mass and volume equation?
concentration = mass/volume

indice rules for:
a) multiplication - a^b x a^c
b) division - a^b / a^c
c) brackets - (a^b)^c
d) power of 0 - a^0
e) dividing by number with an indice 1/a^b
a) add indices - a^2 x a^3 = a^5
b) subtract indices - a^2/a^3 = a^-1
c) times indices - (a^2)^3 = a^6
d) always equal 1 - 5^0 = 1
e) becomes negative - 1/a^3 = a^-3
true or false: Kc is affected by concentration and catalysts
false
why doesnt changing conc. affect Kc?
equilibrium constant, Kc, is the ratio of rate constants for the forward and reverse reactions.
Since concentration doesn't directly appear in the rate constants, it doesn't affect Kc.
Even if concentrations change due to volume adjustments or gas additions, the rate constants remain constant, preserving Kc
why doesnt a catalyst affect Kc?
the ratio of product concentrations to reactant concentrations ([products] to [reactants]) remains unchanged, so Kc remains constant
how is Kc affected by temperature?
as the equilibrium position changes it results in different concentrations of reactants and products,
in endothermic reactions: Kc increases
exothermic: Kc decreases