Overview of the Immune, Respiratory, and Urinary Systems
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
How air is humidified in the nasal passages
Air is humidified to 80% and warmed to body temperature.
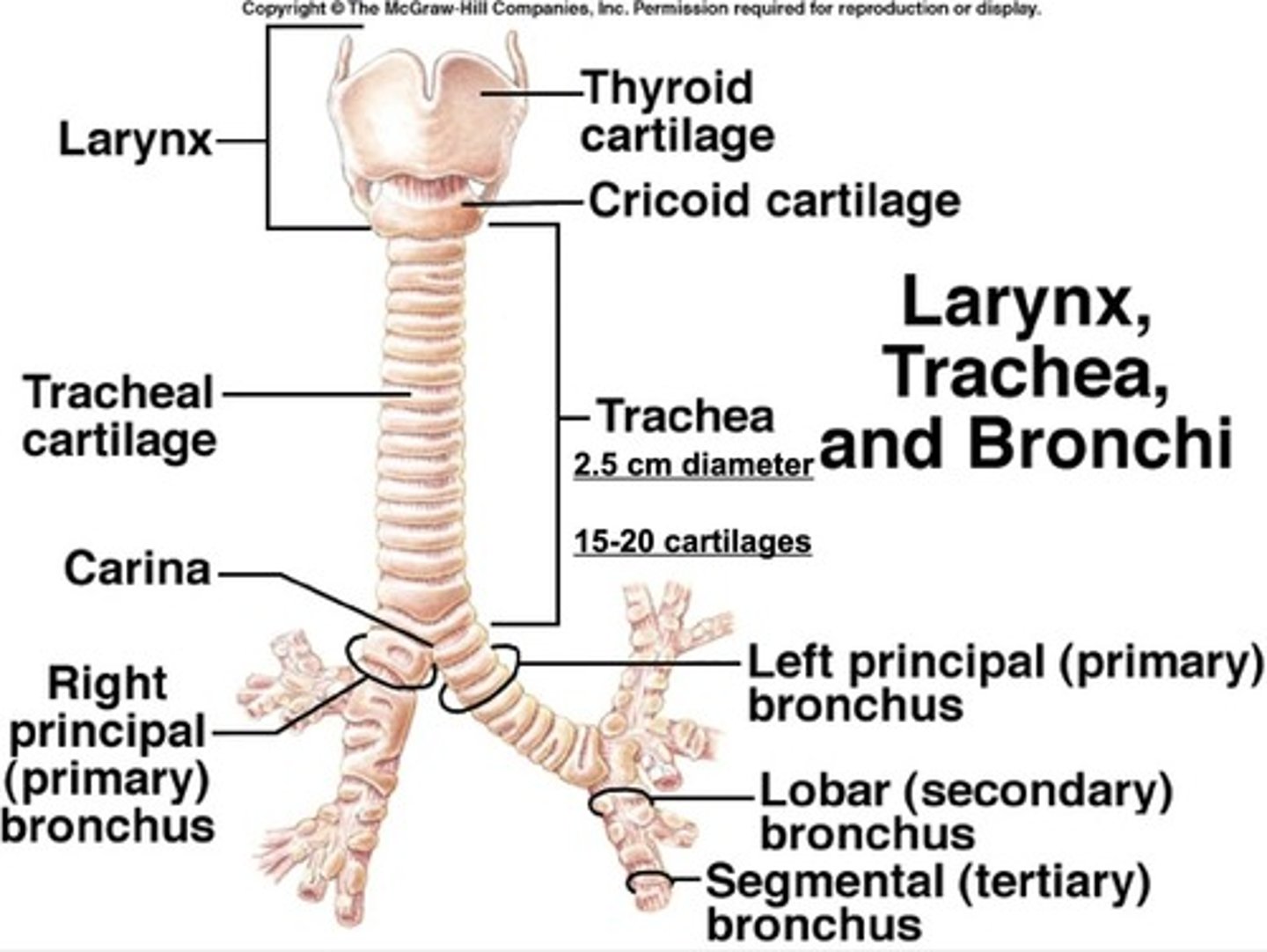
Trachea
Provides a clear and open path for air to travel from the larynx to the bronchi and into the lungs.
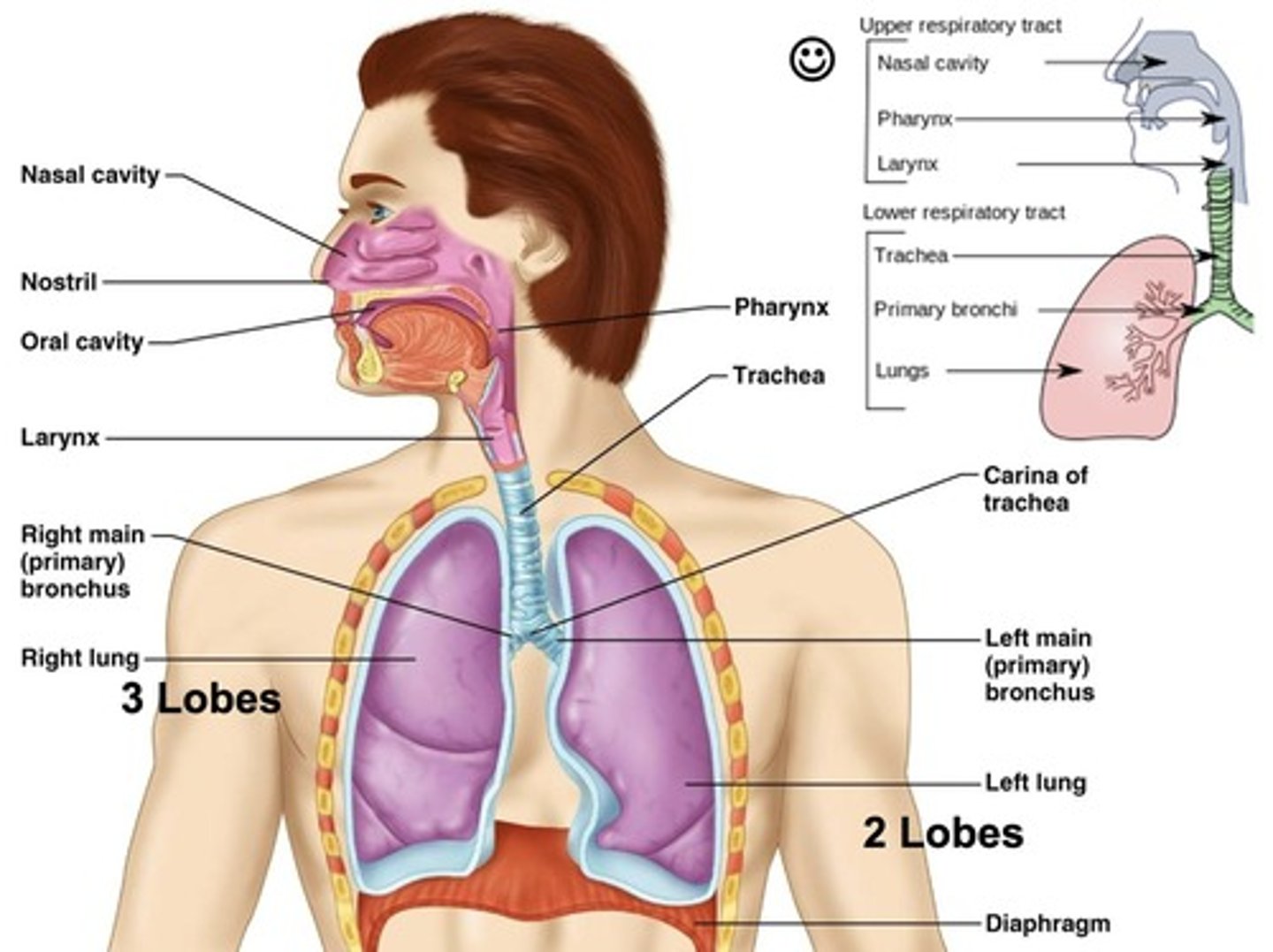
Filtration and Protection
The trachea is lined with ciliated epithelial cells and mucus-producing goblet cells that trap dust, microbes, and debris.
Mucociliary Escalator
The cilia move the mucus upward toward the throat to be coughed out or swallowed.
Structural Support
C-shaped cartilage rings keep the trachea open at all times, preventing collapse during breathing.
Cough Reflex
The trachea helps trigger a strong cough reflex if something irritating enters it, helping to protect the lower airways.
Inspiration (Inhalation)
The diaphragm contracts and moves downward, creating negative intrapleural pressure.
External Intercostal Muscles
Contract to pull the ribs up and out, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity and lungs.
Air Flow
Air flows from high pressure to low pressure.
Expiration (Exhalation)
The diaphragm and external intercostals relax, allowing the lungs to deflate due to elastic recoil.
Lung Volume and Pressure
Decreased lung volume increases pressure inside the lungs, causing air to flow out.
Respiratory Control Centers
Located in the brainstem, specifically in the medulla oblongata and pons.
Medulla Oblongata
Main control center for respiration, containing the dorsal and ventral respiratory groups.
Dorsal Respiratory Group (DRG)
Controls basic rhythm of breathing, especially inspiration.
Ventral Respiratory Group (VRG)
Kicks in during forced breathing, like exercise or talking.
Pontine Respiratory Group
Helps fine-tune the breathing rhythm, smoothing out transitions between inhalation and exhalation.
Main Driver for Breathing
Carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the blood, not oxygen.
Carbonic Acid
Formed when CO2 levels rise, lowering blood pH.
Central Chemoreceptors
Detect the drop in pH and stimulate the medulla to increase the rate and depth of breathing.
Minute Ventilation (VE)
The total volume of air breathed in or out per minute.
Ventilation Formula
Minute Ventilation (VE) = tidal volume (TV) x Respiratory Rate (RR).
Tidal Volume
The amount of air inhaled or exhaled in one breath, average is about 500 mL at rest.
Respiratory Rate
Number of breaths per minute, average is about 12-20 breaths/min at rest.
Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve
X-axis = partial pressure of oxygen (mmHg), Y-axis = hemoglobin saturation with oxygen (%).
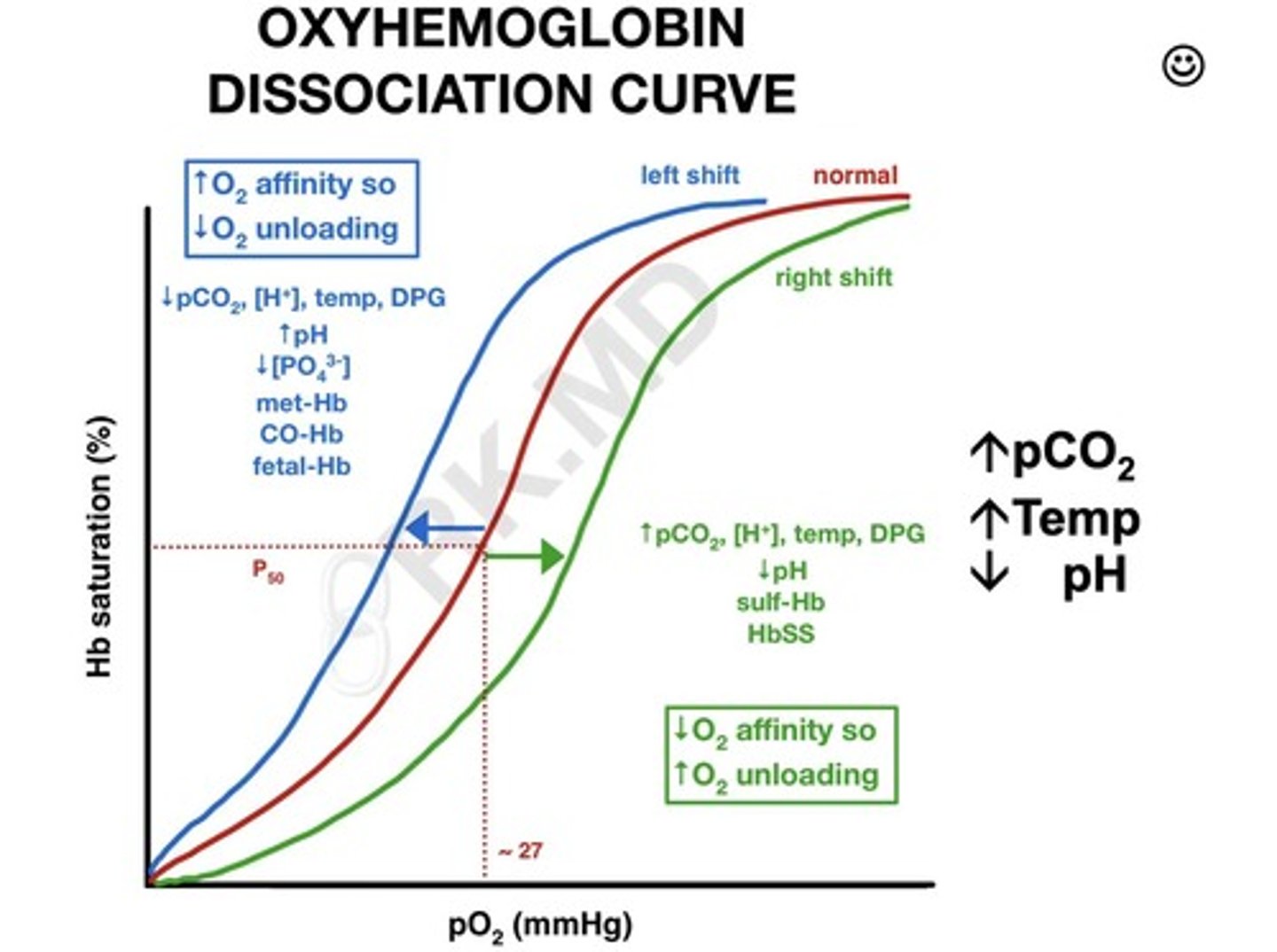
Cooperative Binding
Once one oxygen binds to hemoglobin, it's easier for the next ones to bind.
Oxygen Transport in Blood
About 98.5% of oxygen is transported bound to hemoglobin as oxyhemoglobin.
Dissolved Oxygen in Plasma
About 1.5% of oxygen is dissolved directly in plasma, contributing to Pao2 in blood gases.
Gas exchange
Occurs in the alveoli of the lungs.
Alveoli
Tiny, thin-walled air sacs at the end of the respiratory bronchioles.
Pulmonary capillaries
Surround the alveoli.
Oxygen diffusion
Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood.
CO2 diffusion
CO2 diffuses from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled.
Simple diffusion
The exchange of gases driven by partial pressure gradients.
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
The additional amount of air that can be exhaled after a normal breath.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
The additional amount of air that can be inhaled after a normal breath.
Residual Volume (RV)
The amount of air that remains in the lungs after a maximal exhalation.
Tidal Volume (TV)
The amount of air inhaled or exhaled during a normal breath.
Vital Capacity (VC)
The sum of TV, IRV, and ERV, representing the maximum amount of air that can be exhaled from the lungs after a maximal inspiration.
Anatomic Dead Space
The volume of air in the respiratory system that doesn't take part in gas exchange.
Minute Ventilation
The total volume of new air that enters respiratory passages per minute.
Minute Ventilation Formula
MRV = Vt x Respiratory Rate.
Minute Ventilation Value
500 x 12 = 6,000ml/min or 6L/min.
Alveolar Ventilation
The rate at which new air reaches alveoli and other gas exchange areas.
Alveolar Ventilation Formula
Va = Freq x (Vt - Vd).
Va
Volume of alveolar ventilation per min.
Vt
Tidal volume.
Vd
The physiologic dead space volume.
Alveolar Ventilation Calculation
Va = 12 x (500-150) = 4,200 ml/min.
Normal blood gases
Values that indicate the acidity/alkalinity and gas levels in blood.
pH Normal Range
7.35 - 7.45, indicating blood acidity/alkalinity.
PaO2 Normal Range
80 - 100 mmHg, indicating partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood.
PaCO2 Normal Range
35 - 45 mmHg, indicating partial pressure of carbon dioxide (respiratory).
HCO3- Normal Range
22 - 26 mEq/L, indicating bicarbonate level (metabolic).
SaO2 Normal Range
95 - 100%, indicating oxygen saturation of hemoglobin.
Hyperventilation
Increase in alveolar ventilation leading to hypocapnia and increased pH.
Hypoventilation
Decrease in alveolar ventilation leading to hypercapnia and decreased pH.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Chronic, progressive lung disease causing airflow limitation that is not fully reversible.
Emphysema
A condition where alveoli are damaged and enlarged, leading to less surface area for gas exchange.
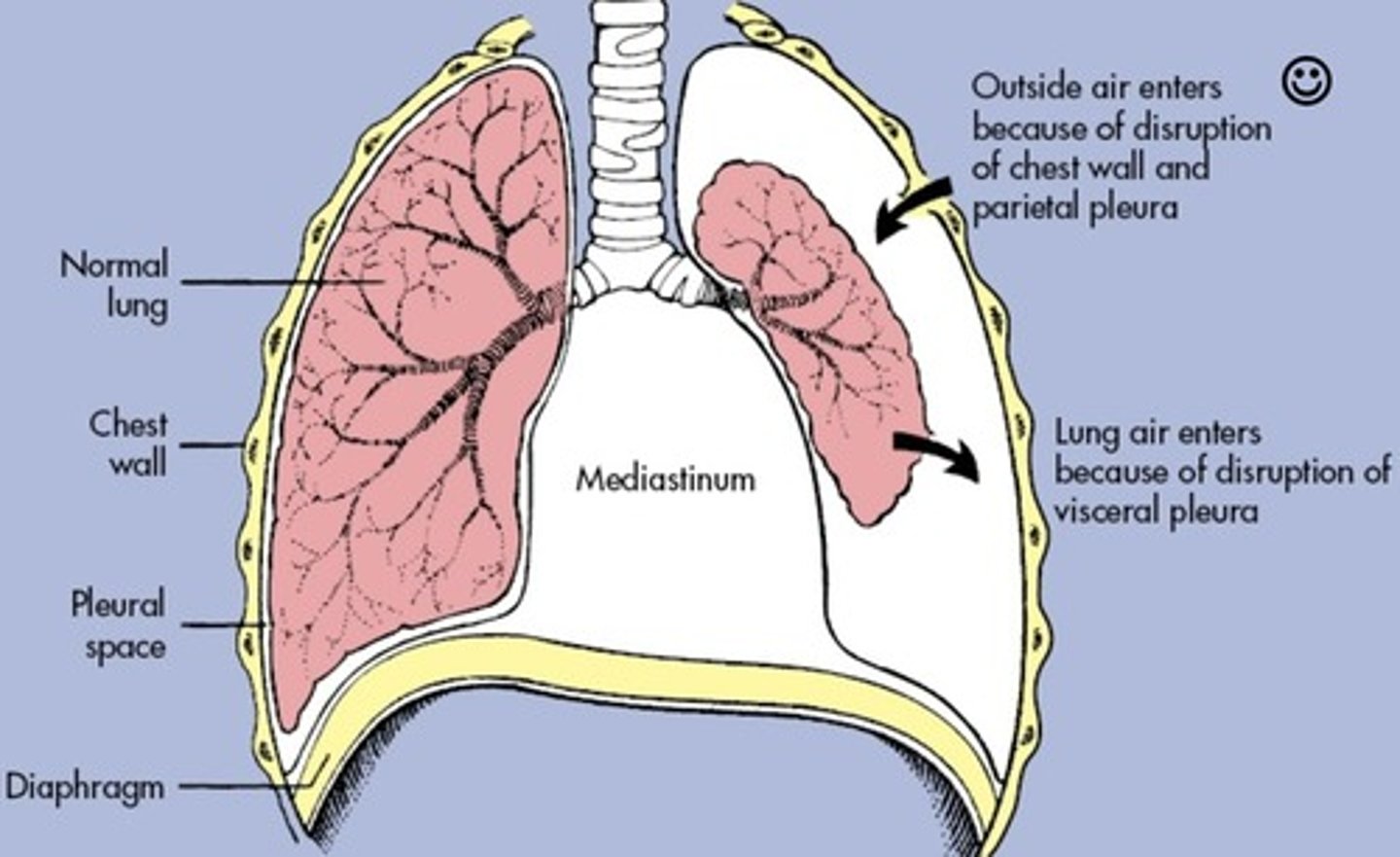
Pneumothorax
Condition where air accumulates in the space between lung and chest wall.
Asthma attack
Characterized by airway inflammation, intermittent airflow obstruction, and bronchial hyperresponsiveness.
Urinary system functions
Excrete metabolic wastes, regulate acid-base balance, secrete hormones, and regulate pH, blood volume, and osmolarity.
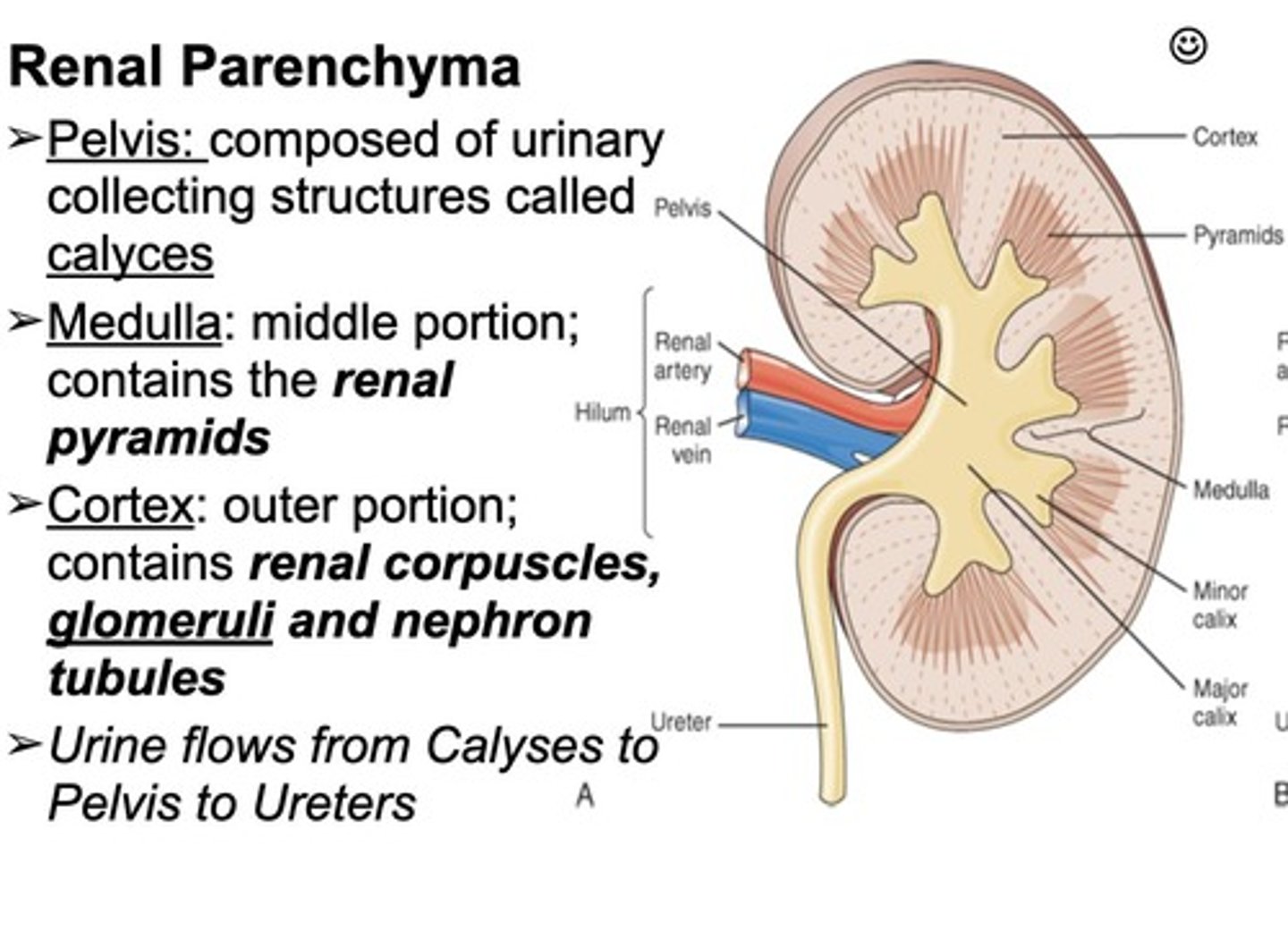
Kidney Anatomy
Includes cortex, medulla, and renal pelvis.
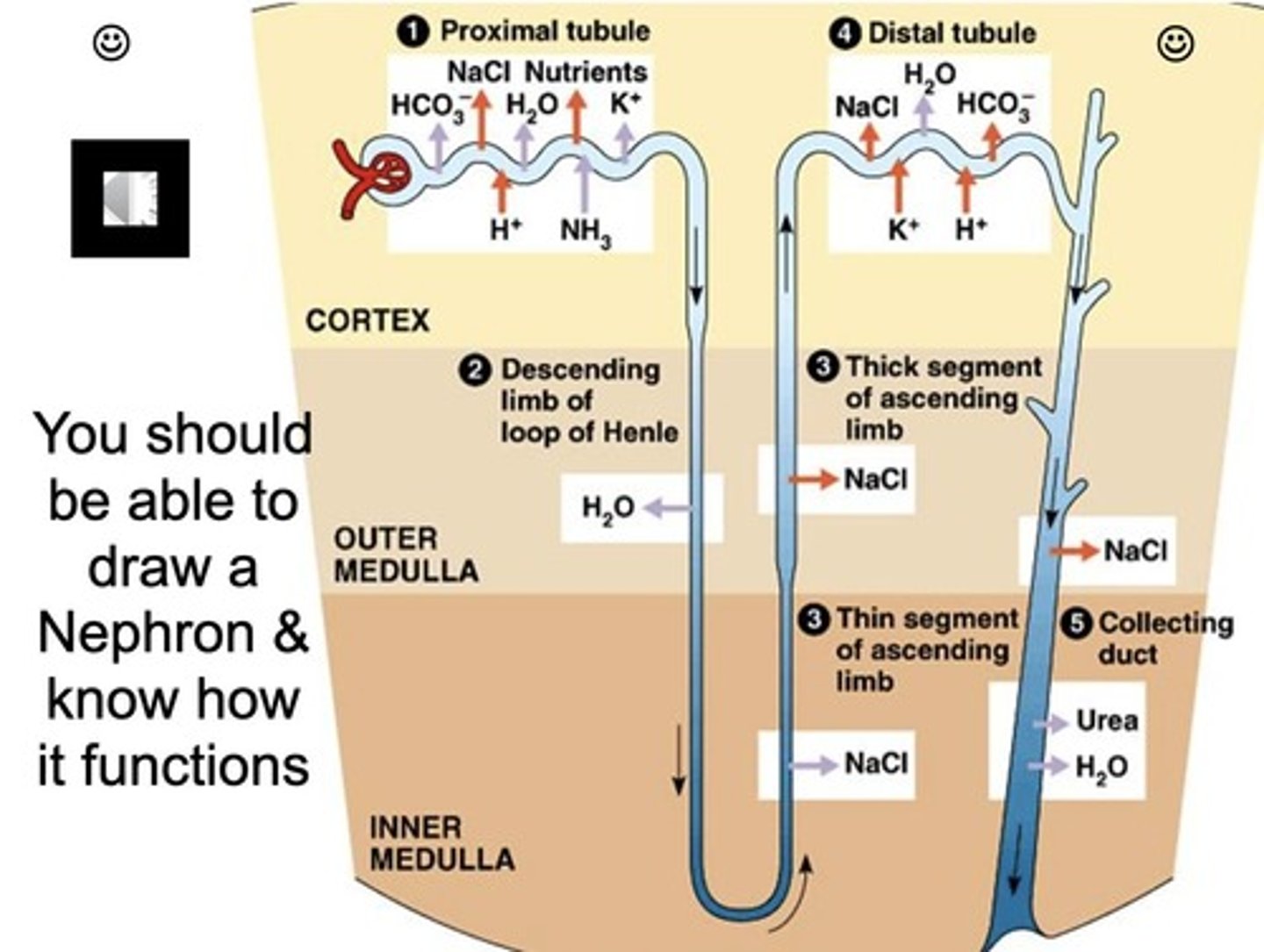
Nephron
The functional unit of the kidney, with about 1 million in each kidney, filtering blood to form urine.
Glomerulus
A ball of capillaries that filters blood — water, ions, glucose, amino acids, and wastes pass into nephron; large proteins & blood cells stay in the blood.
Bowman's Capsule
Surrounds the glomerulus and collects the filtrate (aka the fluid that will become urine).
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
First tubule after the capsule that reabsorbs ~65% of filtered water and electrolytes (Na⁺, K⁺, Cl⁻), reabsorbs glucose, amino acids, and nutrients, and secretes some wastes/drugs into the tubule.
Loop of Henle
Has a descending limb and an ascending limb; the thin descending limb is permeable to water, while the thick ascending limb is impermeable to water and contains powerful Na+ - K+ - 2Cl- cotransporters that pump ions into the interstitium.
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Fine-tunes electrolyte balance, responds to aldosterone (reabsorbs Na⁺, secretes K⁺), and allows for some water reabsorption if needed.
Collecting Duct
Collects urine from multiple nephrons and responds to ADH (antidiuretic hormone) — reabsorbs water if the body is dehydrated; final urine concentration happens here.
Electrolytes
Sodium (Na+), Potassium (K+), Chloride (Cl-), Bicarbonate (HCO3-) that are reabsorbed in the Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT).
Amino Acids
Nearly 100% reabsorbed in the Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT).
Glucose
Normally 100% reabsorbed in the Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) unless blood glucose is too high.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect high osmolarity and release ADH from the pituitary gland, increasing the permeability of the collecting tubule to water.
Hydrogen Ions
Secreted from the blood into the nephron tubule to help maintain normal blood pH (7.35-7.45) and get rid of excess acid.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) - H⁺ Secretion
Secretes most of the H⁺ using the Na⁺/H⁺ antiporter (sodium in, hydrogen out).
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) - H⁺ Secretion
Also secretes hydrogen ions to help maintain pH.
Collecting Duct - H⁺ Secretion
Important for fine-tuning pH; intercalated cells use active proton pumps to secrete H⁺ and reabsorb bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) to help buffer the blood.
Afferent Arteriole Constriction
Decreases glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Efferent Arteriole Dilation
Decreases glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Afferent Arteriole Dilation
Increases glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Efferent Arteriole Constriction
Increases glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Normal Constituents of Urine
Water (about 95% of urine), Urea (waste product from protein breakdown), Creatinine (from muscle metabolism), Uric acid (from nucleic acid breakdown), and Electrolytes (Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca2+).
Countercurrent Mechanism
A key process in the nephron that helps regulate water and salt balance in the body, occurring primarily in the loop of Henle and crucial for producing concentrated urine.
Aldosterone
Stimulates tubule cells to reabsorb sodium and water.
Renin
An enzyme released by the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney in response to low blood pressure, low sodium levels, or sympathetic nervous system activity.
Renal Clearance
A measure of the kidney's ability to clear substances from the blood.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
A measure of how much blood is filtered by the kidneys' glomeruli per minute; a key indicator of kidney function.
Normal GFR for a healthy adult
Typically around 90 to 120 mL/min/1.73 m² (adjusted for body surface area).
Chronic Kidney Disease Indicator
A GFR lower than 60 mL/min/1.73 m² for three months or more.
Factors Modulating GFR
Age, gender, body size, blood pressure, and hormonal signals can alter GFR.
Composition of Glomerular Filtrate
Differs from plasma primarily because the filtration process selectively allows certain substances to pass while retaining others.
Urea
A waste product produced when the body breaks down proteins, key component of urine, excreted by the kidneys to eliminate excess nitrogen.
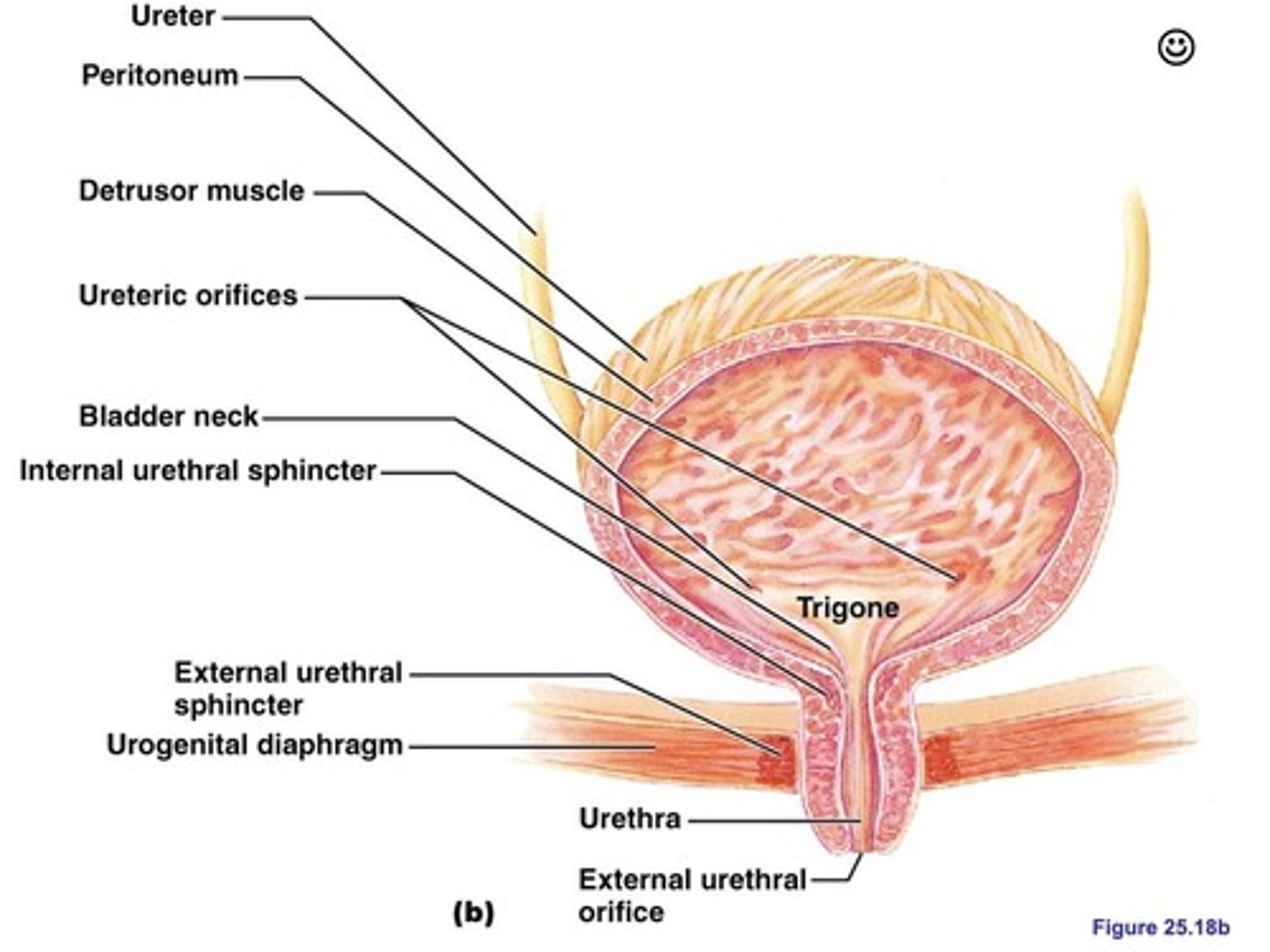
Micturition Reflex
The process by which the body controls the expulsion of urine from the bladder, involving the bladder, nervous system, and sphincter muscles.
Initiation of Micturition Reflex
Initiated when the bladder fills with urine and stretches its walls.
Flow of Urine from Nephron to Urethra
Nephron (glomerulus, Bowman's capsule, proximal tubule, loop of Henle, distal tubule, collecting duct) → Papillary ducts → Renal papilla → Minor calyx → Major calyx → Renal pelvis → Ureter → Bladder (storage) → Internal urethral sphincter → External urethral sphincter → Urethra → External urethral orifice (urine excretion).
Higher Risk of Urinary Tract Infection in Females
Due to a shorter urethra, proximity to the anus, hormonal changes, sexual activity, use of certain hygiene products or contraceptives, urinary retention, and structural or functional abnormalities.
Factors Contributing to UTI Risk
Shorter urethra, anatomical proximity to the anus, hormonal influences, sexual activity, and certain hygiene or contraceptive practices.
Prevention of UTIs
Proper hygiene, hydration, and timely urination after sexual activity can help reduce the risk.