Chem H Unit 1
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Chemistry
The study of matter (what it’s made of & how it changes)
Matter
Anything that takes up space & has mass (even if it’s so small that you can’t see it)
Scientific Method
A process/series of steps scientists use to study and find solutions to problems
First Step of Scientific Method
Make an Observation [Observations can be qualitative (do not involve measurements) or quantitative (involve measurements)]
Second Step of Scientific Method
Form a Hypothesis (Possible explanations of observations)
Third Step of Scientific Method
Test Hypothesis with an Experiment
Measurement
Must have two parts: a number and a unit
Accuracy
How close a measurement is to a theoretical value (“correct value”)
Precision
How close a series of measurements are to each other
Significant Figures
Established by all known w/certainty PLUS one final digit with uncertainty; Indicate the precision of experimentally measured values (the more sigfigs in a measurement, the more precise the measurement)
Known Digits
With certainty and come from the markings on a tool (balance, ruler, etc.)
Uncertain Digit
Comes from estimation of the measurement that is in-between the markings (even if the estimated value is a “0”)
Density
The ratio of an object’s mass to its volume (an intrinsic value) — it does not depend on the size or shape of a particular matter
Graduated Cylinder
A tall, narrow laboratory container with measurement markings along its side, used for accurately measuring the volume of liquids
Beaker
A flat-bottomed, cylindrical container, typically made of glass or plastic, with a lip for pouring, used in science laboratories for holding, mixing, and heating liquids and solids
Electronic Balance
A modern laboratory or kitchen instrument that precisely measures the mass of an object by converting the downward force of its weight into an electrical signal, which is then displayed as a numerical value on a digital screen
Ring Stand
A common piece of laboratory equipment consisting of a heavy base and an upright rod used to support various apparatus like glassware and other equipment during experiments
Burette
A long, thin, graduated glass tube with a stopcock (a valve) at the bottom, used to accurately measure and deliver variable amounts of liquid in experiments like titration
Counting Significant Figures: Rule #1
All non-zero digits are sigfigs (1.35 cm = 3 sf; 37 = 2 sf)
Counting Significant Figures: Rule #2
Zeros between sigfigs are sigfigs (2.09 cm = 3 sf; 20098 km = 5 sf)
Counting Significant Figures: Rule #3
All zeros in front of the first nonzero digit are NOT sigfigs (0.095 cm = 2 sf; 0.0009 mg = 1 sf)
Counting Significant Figures: Rule #4
Zeros at the end of a number AND to the right of a decimal point are sigfigs (21.00 cm = 4 sf; 9000 g = 1 sf)
Counting Significant Figures: Rule #5
A physical decimal point ending a number makes all preceding zeros sigfigs (500. cm = 3 sf; 500 = 1 sf)
Counting Significant Figures: Rule #6
Only coeffecients in scientific notation are counted as sigfigs (2.50 × 10^12 atoms = 3 sf; 3.050 × 10^-11 m = 4 sf)
Counting Significant Figures: Rule #7
Sigfigs rules are not applied: when counting (5 books), to definitions (1 in. = 2.54 cm), and to constants (pi)
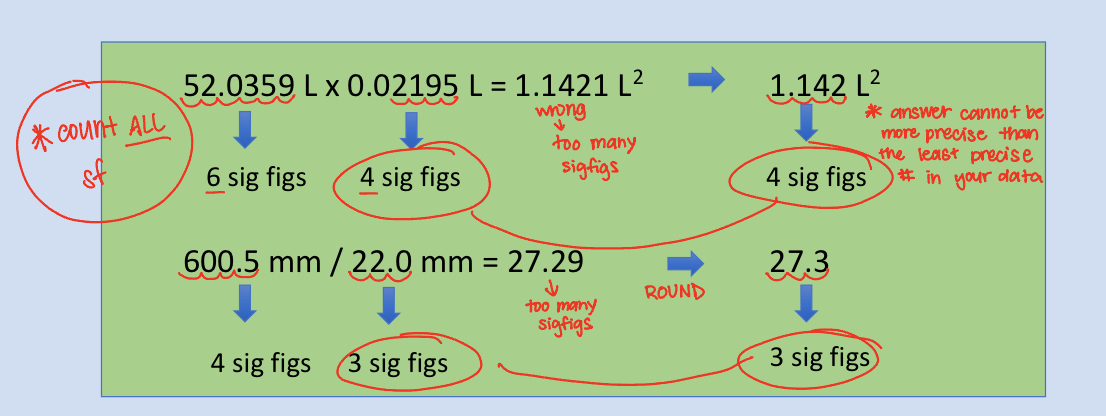
Rules for Rounding Sigfigs From Multiplication & Divison Equations
The answer should have the same number of sigfigs as the measurement in the problem with the fewest number of significant digits
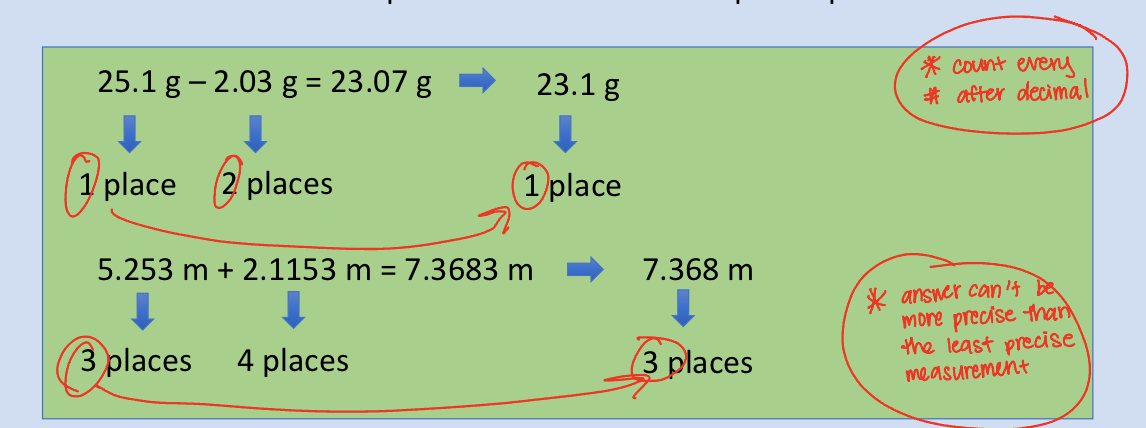
Rules for Rounding Sigfigs From Addition & Subtraction Equations
The answer should have the same number of decimal places as the measurement in the problem with the fewest places past the decimal
Scientific Notation
A method used to write extremely large and small numbers so that they are easier to work with (written with a single nonzero digit before the decimal followed by a power of ten expression: 3.56 × 10^9)