Lab 6 biology (animal support, locomotion, and external protection)
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Latter half of lab 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Fibers
muscle tissue cells that are capable of contraction and relaxation.
Integument
Protective outer covering that prevents inner tissues from being damaged.
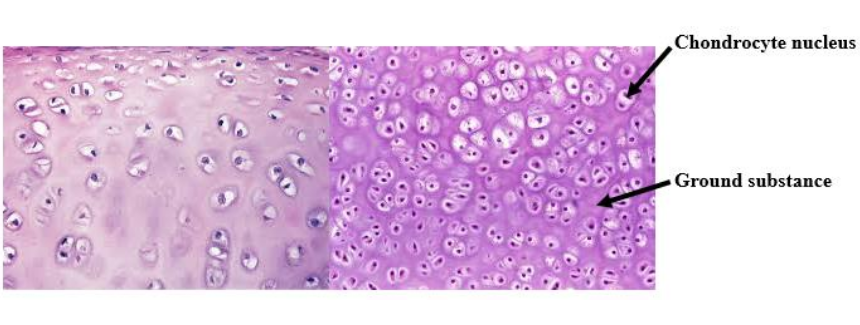
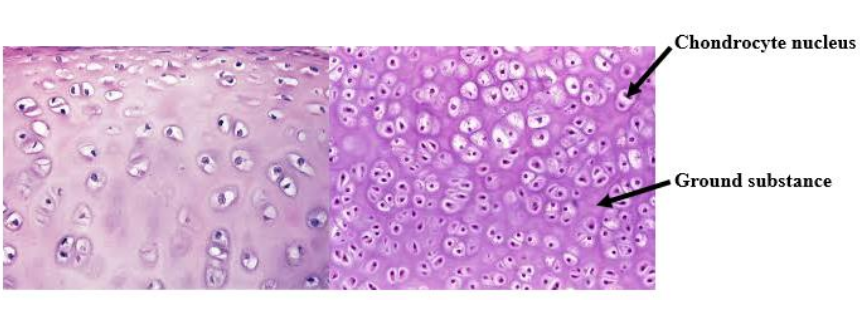
Chondrocytes
Dense connective tissue cells in cartilage.
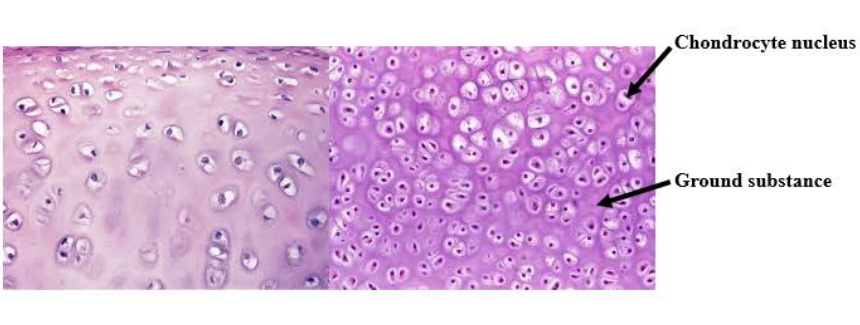
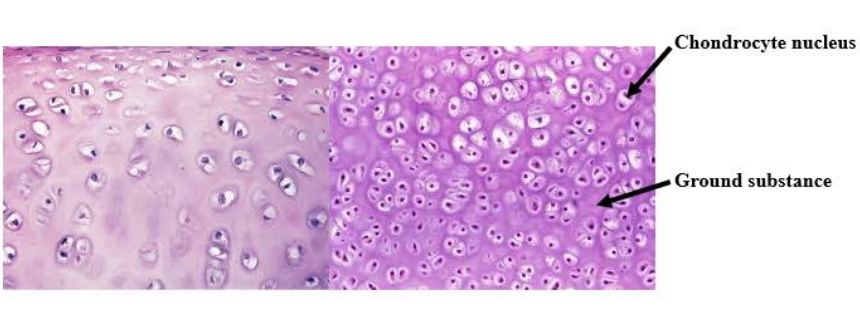
Ground substance
Rubbery protein-carbohydrate that suspends the chondrocytes in cartilage.

Bone connective tissue
tissue found in the endoskeletons and teeth of vertebrate animals.


Osteons
oval-shaped mineralized matrix surrounding a central cavity housing blood vessels and nerves.

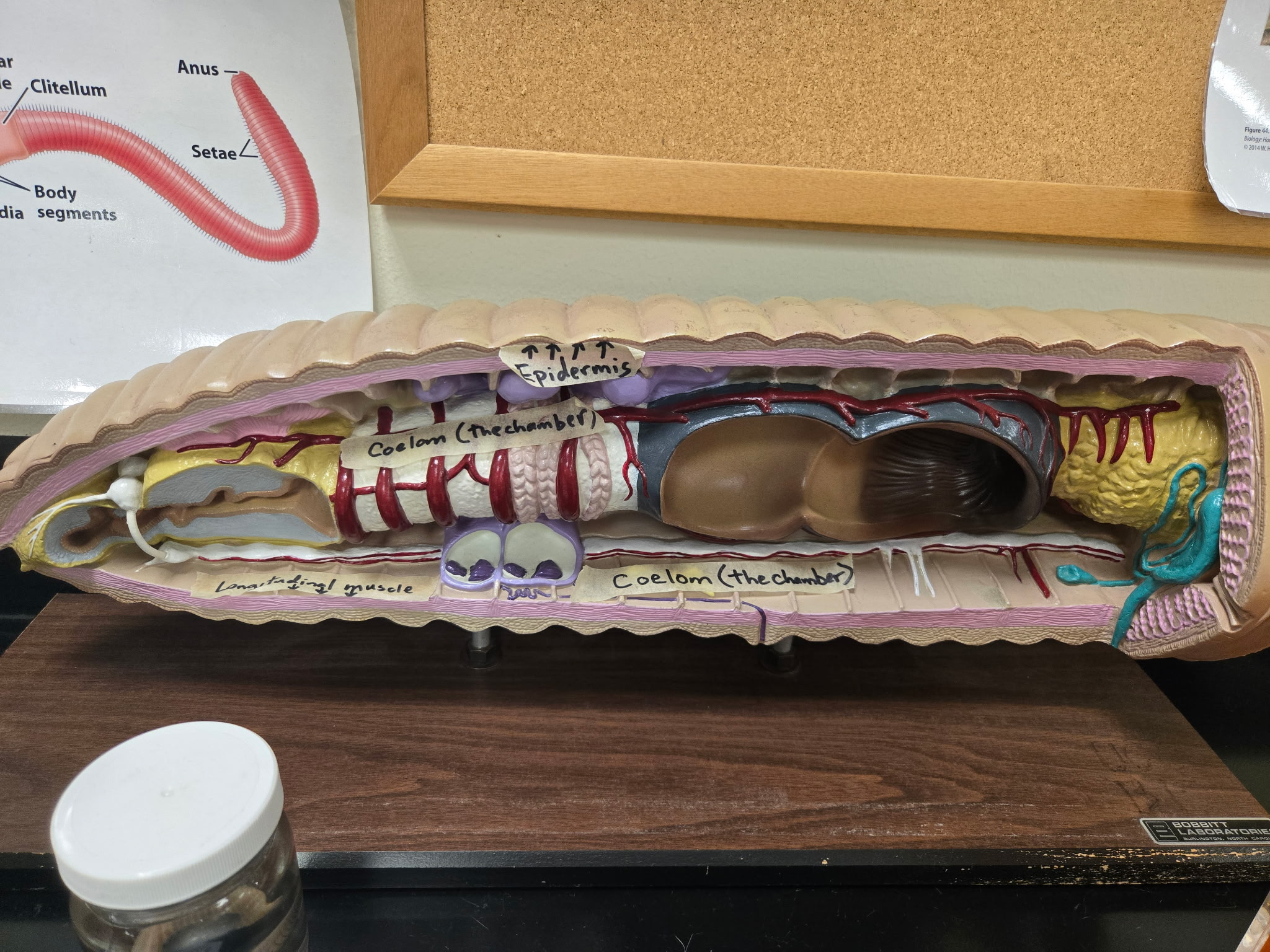
Chaete
short spines of chitin that project laterally and ventrally from each body segment of a worm.

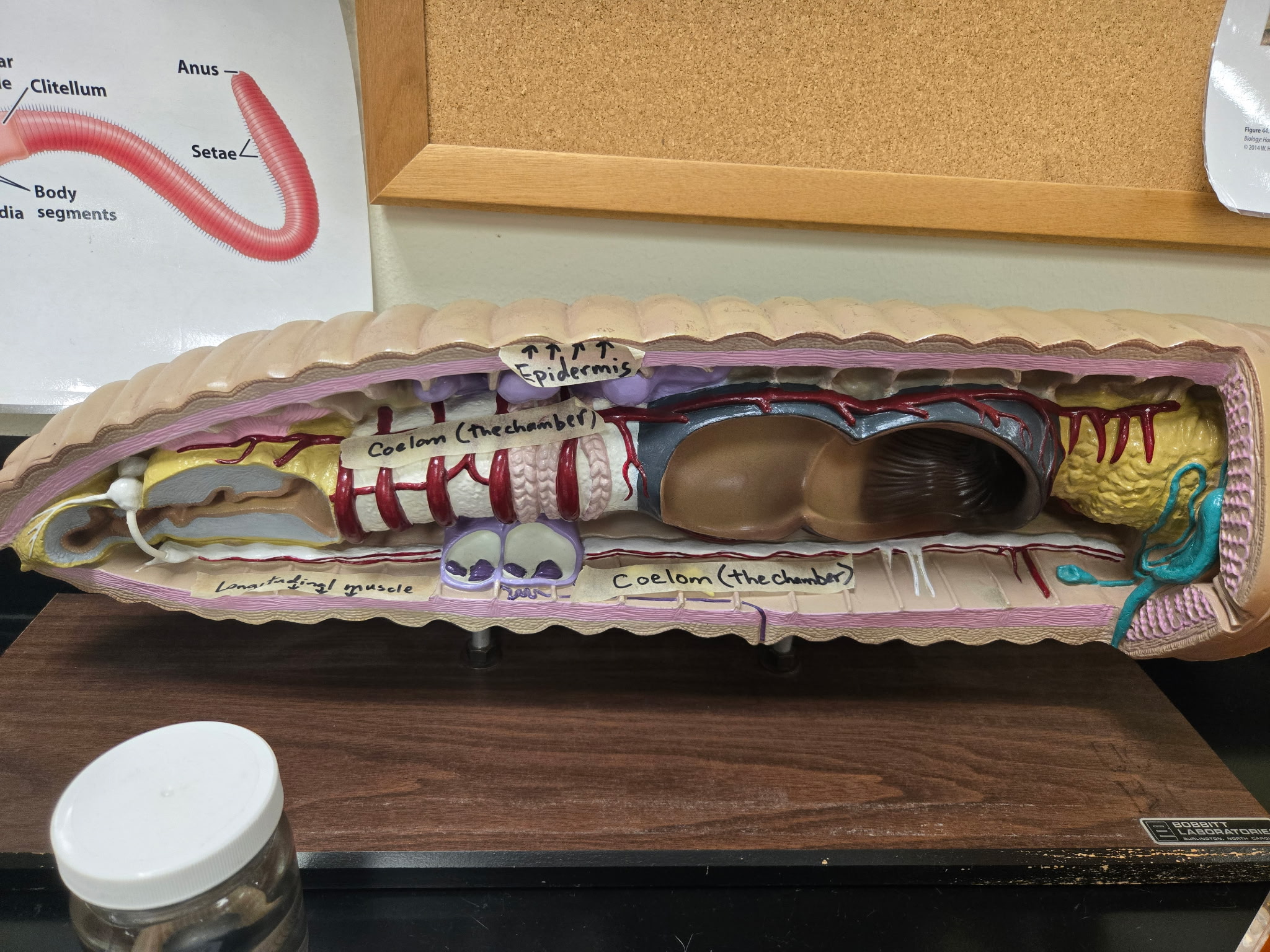
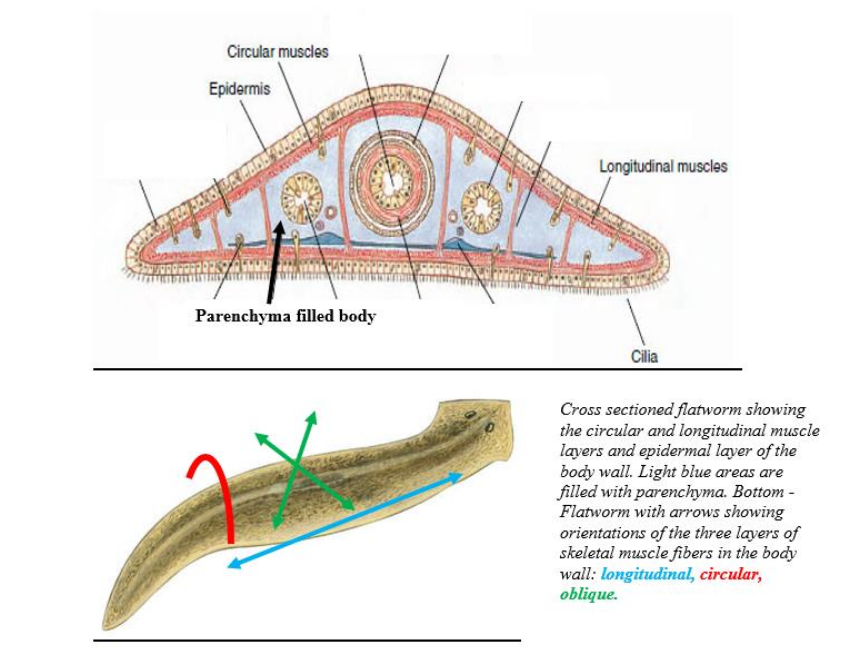
circular muscle
muscle directly beneath the epidermis of a worm
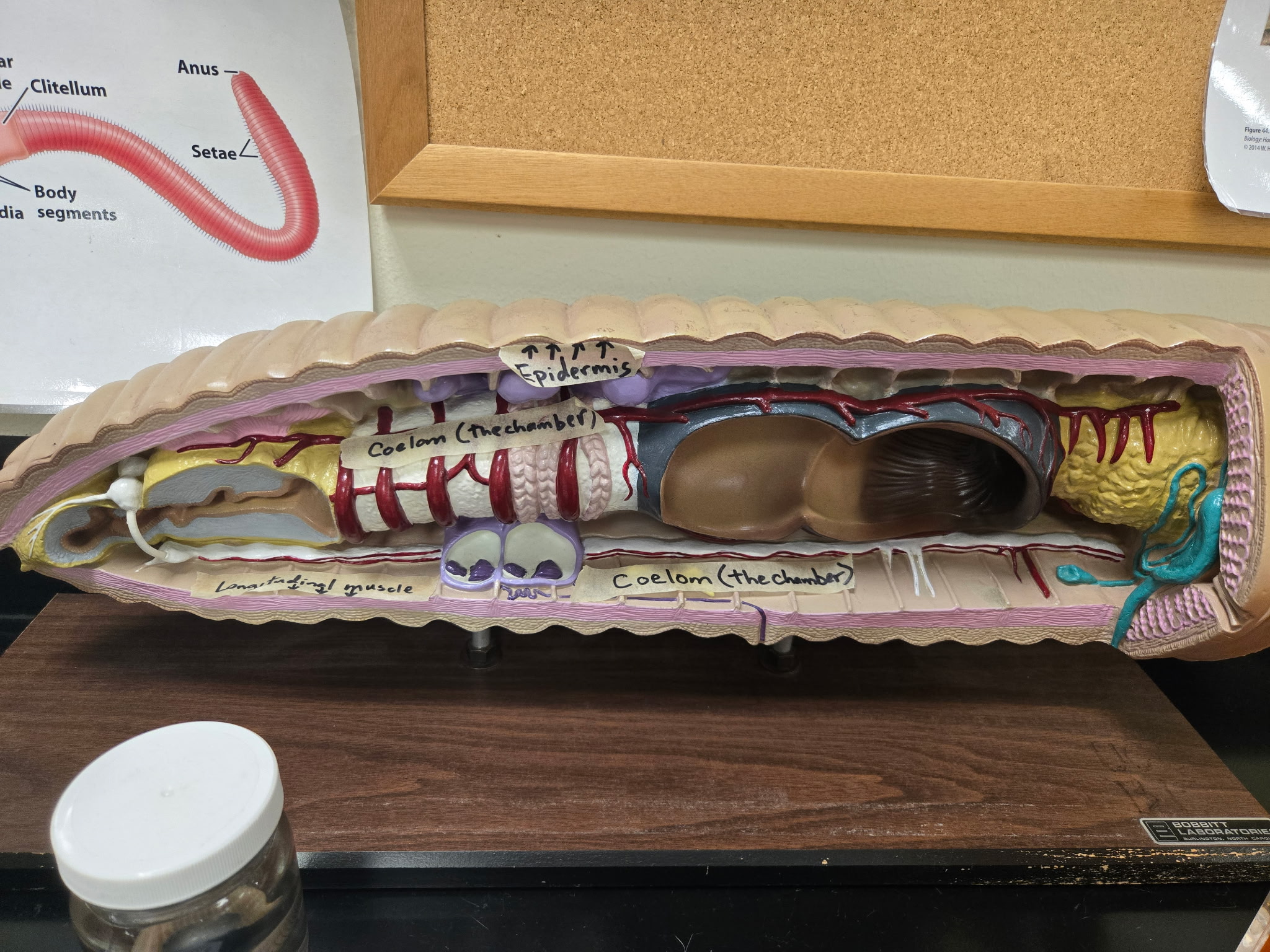
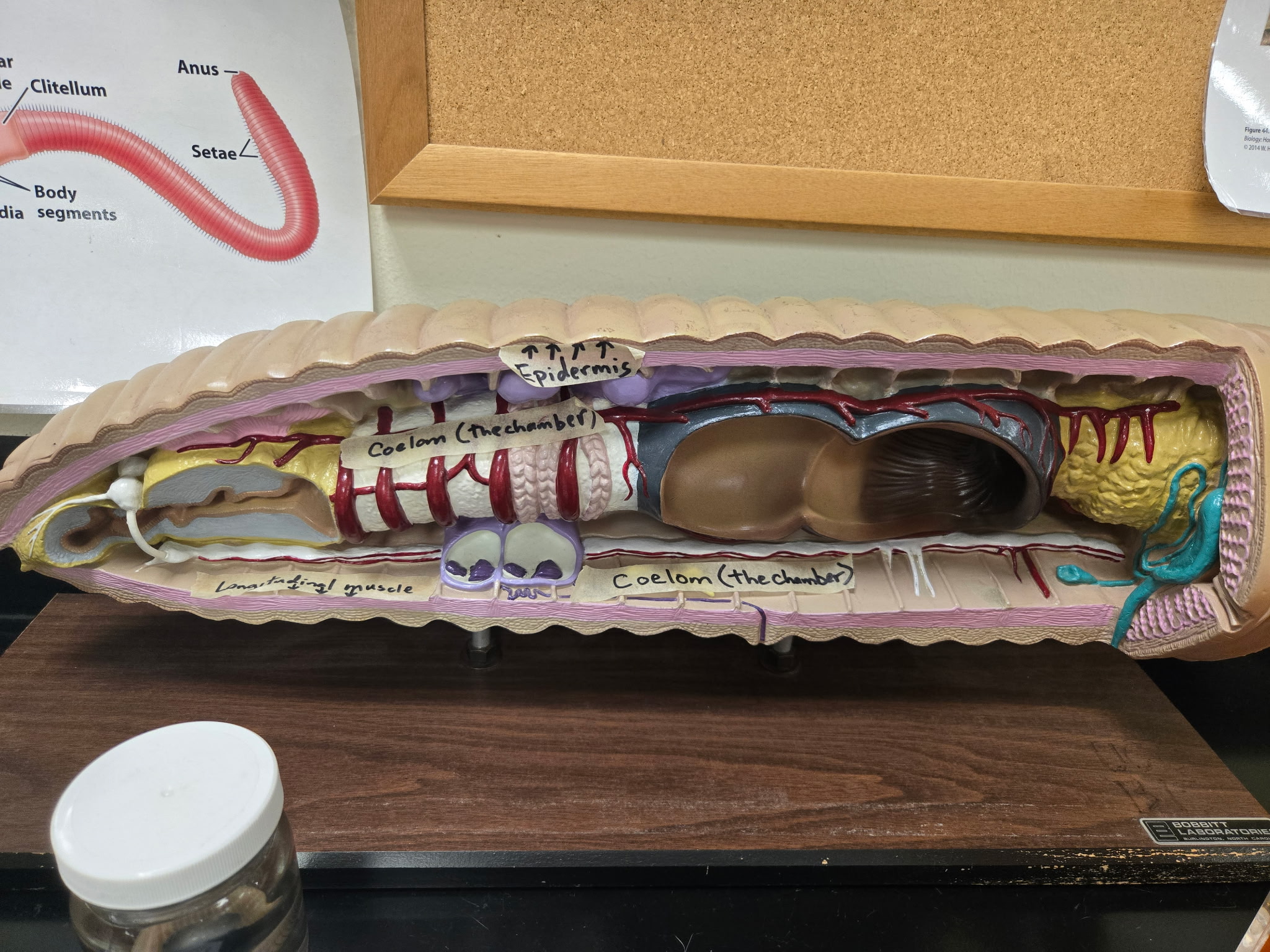
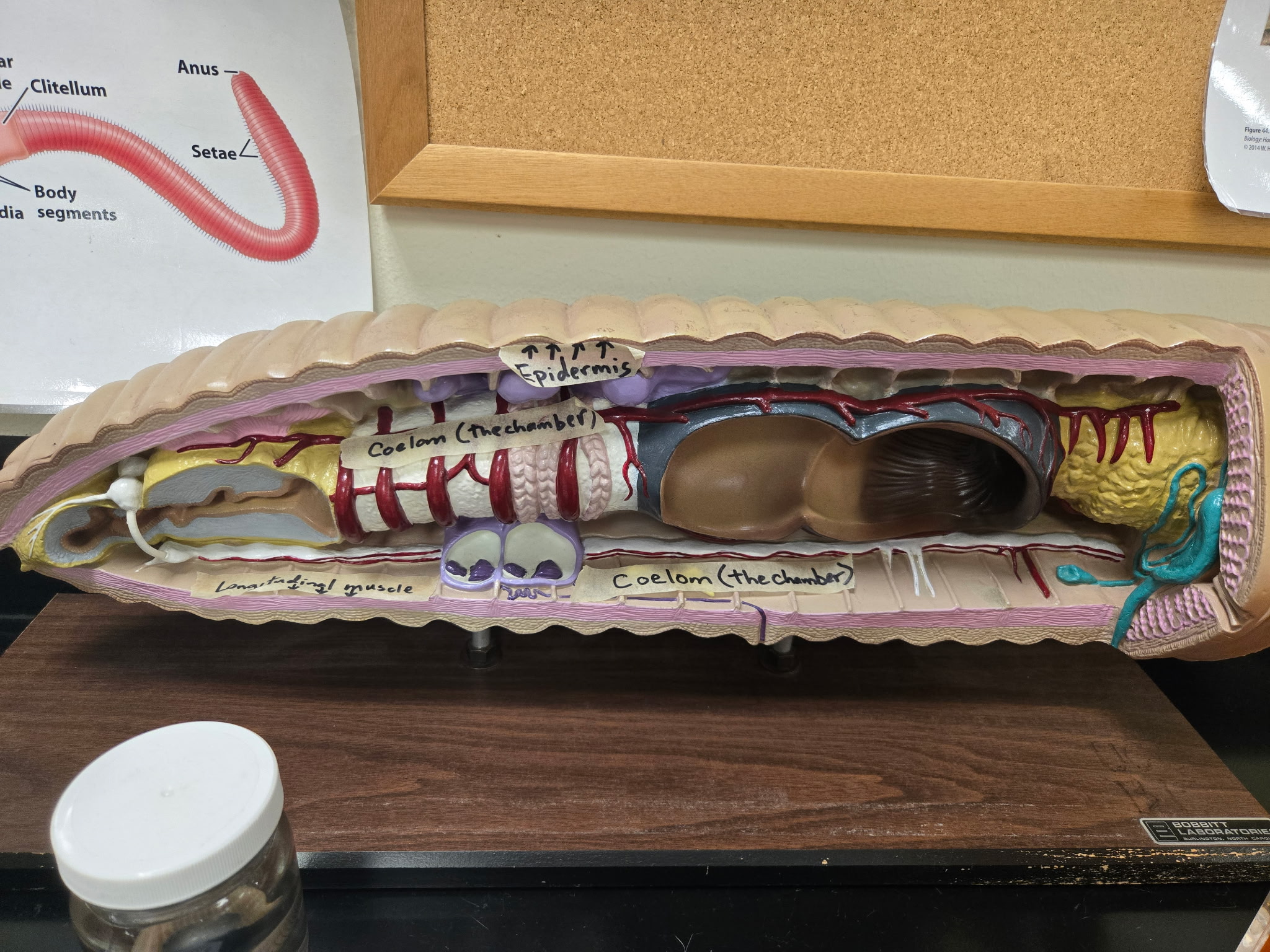
Longitudinal muscle
Muscle beneath the circular layer of a worm with a longitudinal arrangement.
Endoskeletons
consist of hardened, fibrous skeletal elements embedded within soft tissues. found in sponges, corals, echinoderms, and chordates
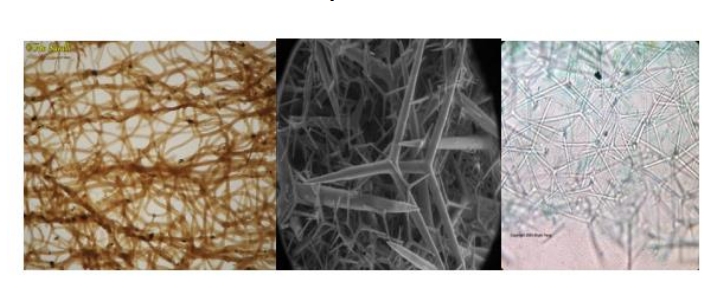
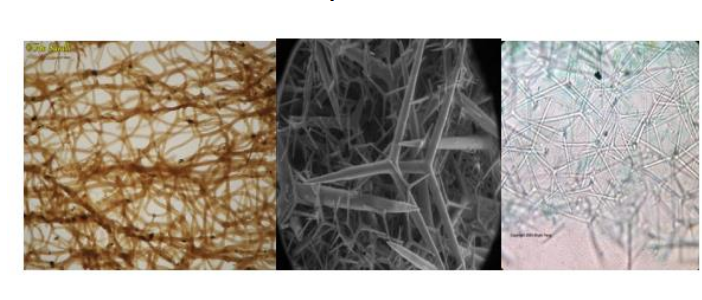
Fibers and spicules
What the endoskeleton of sponges are made of. consist of proteins, calcium, carbonate, and silica.
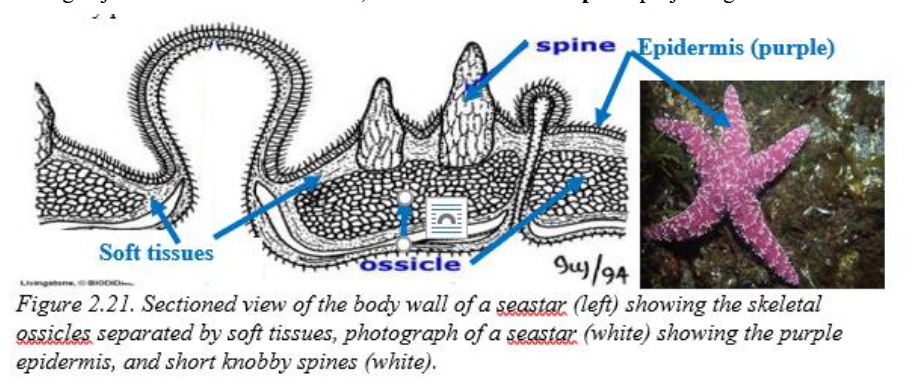
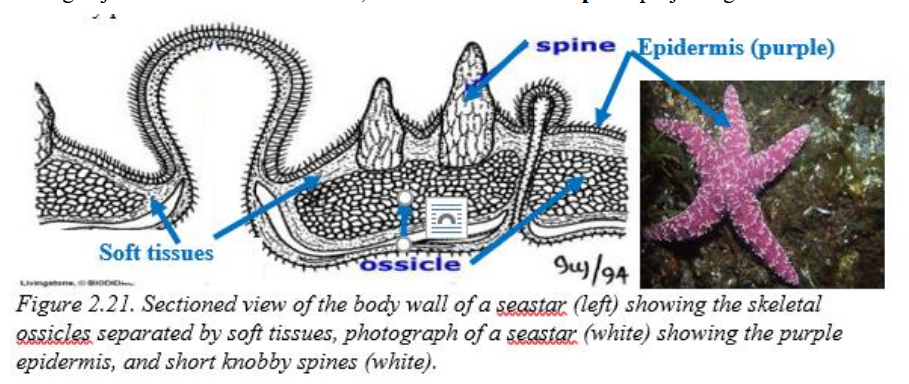
endoskeletal ossicles
calcified plates that lie beneath the epidermal layer of echinoderms
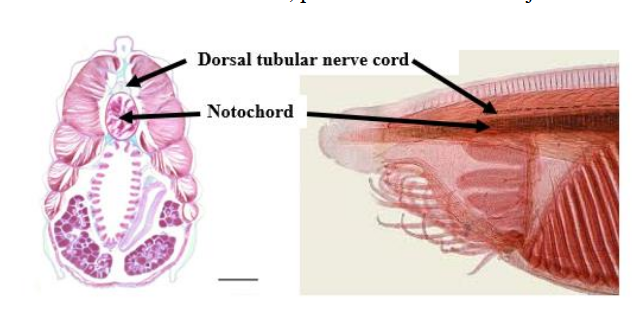
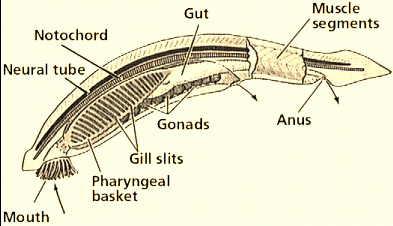
Notochord
an internal skeletal rod in chordates, that is the evolutionary pre-cursor of the vertebral column.
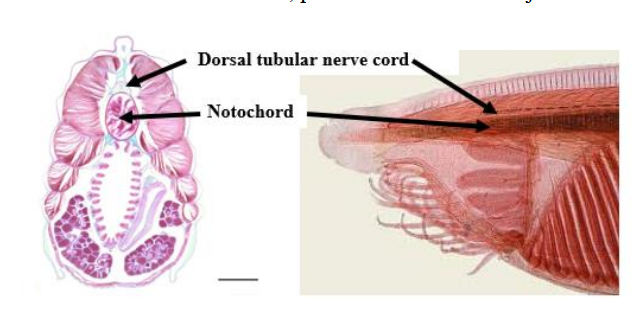
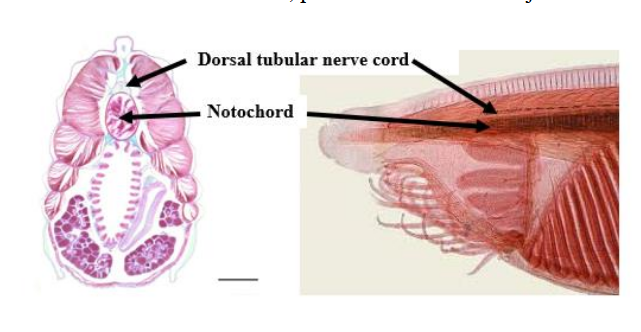
nerve cord
tube on the top side of a chordate, develops into the central nervous system
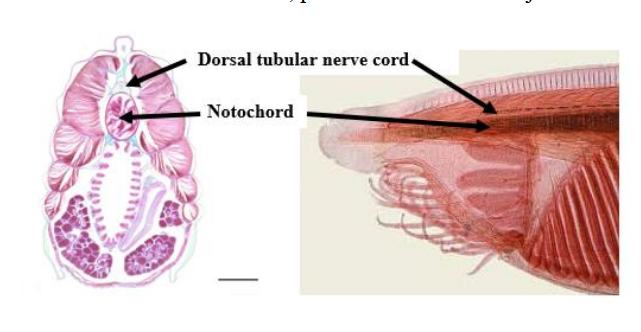
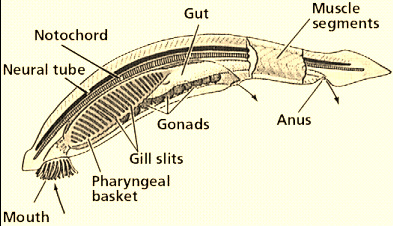
pharyngeal basket
a complex structure of the pharynx containing slits or pouches that function in feeding and respiration, filtering food from water and absorbing oxygen. (like gills)
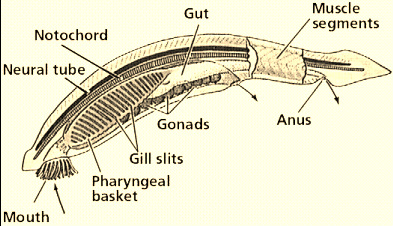
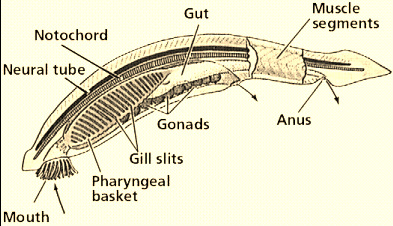
post-anal tail
a posterior elongation of the body that extends beyond the anus, containing muscle and skeletal elements
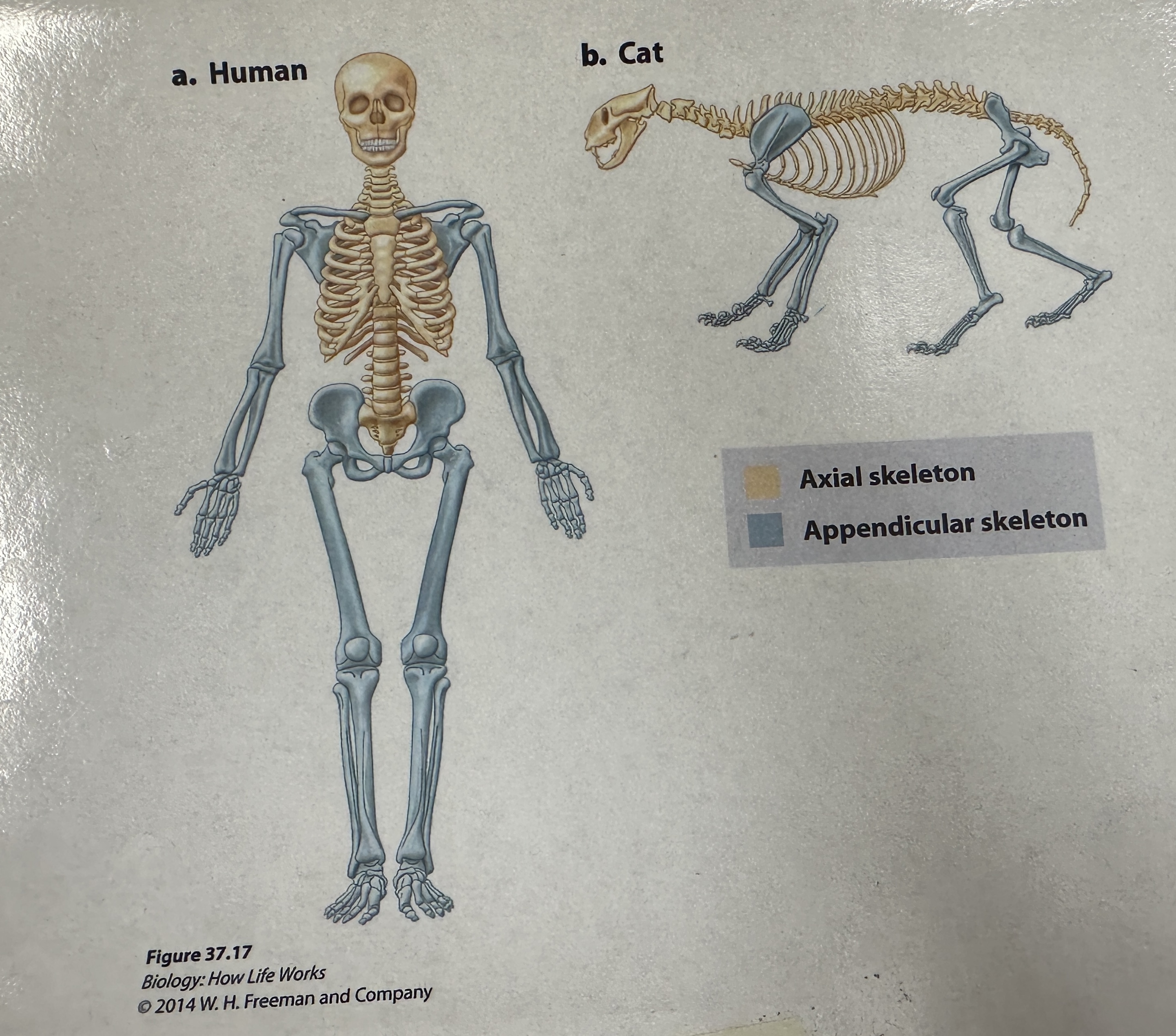
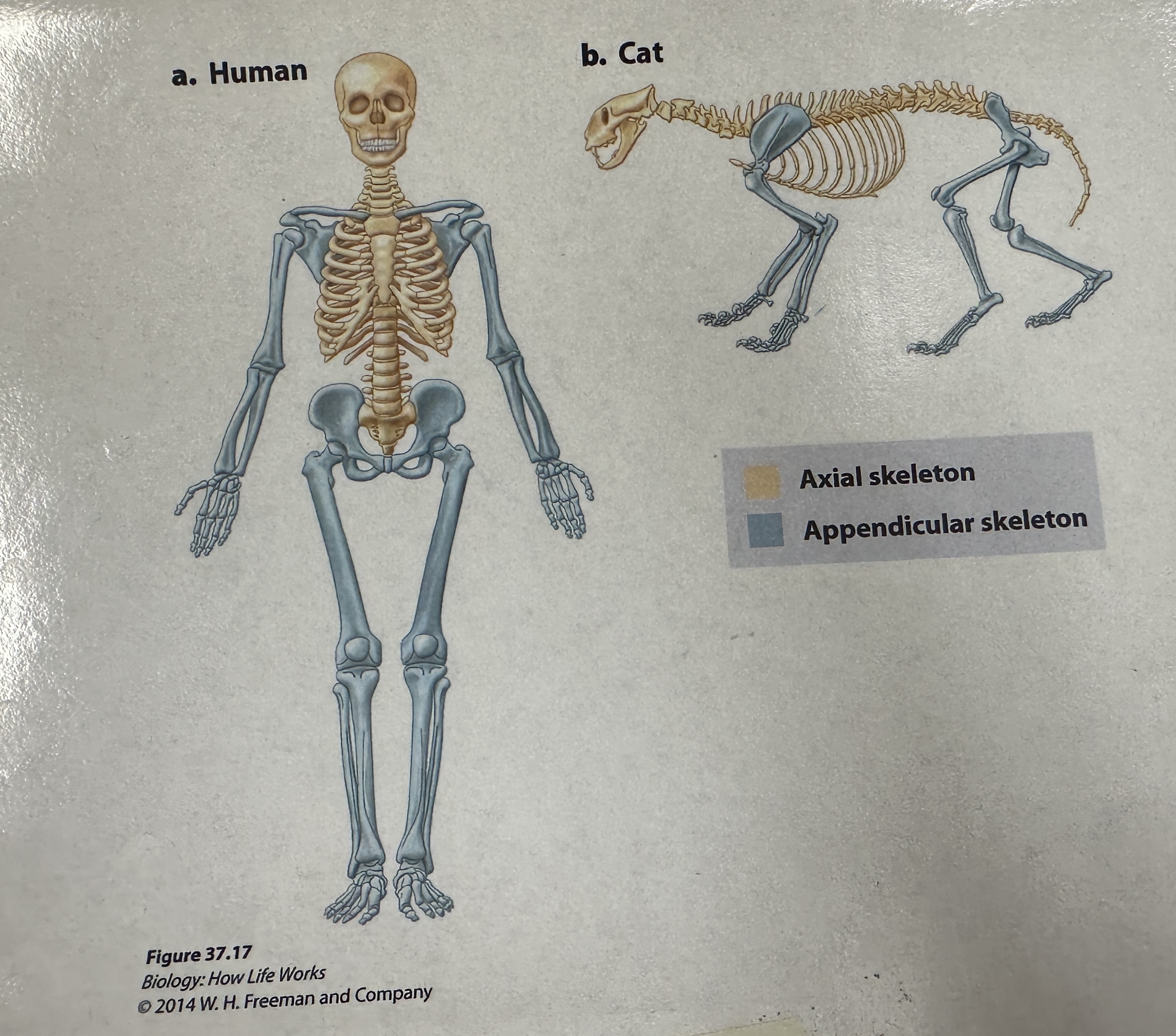
Axial skeleton
endoskeleton division that consists of the cranium and the vertebral column
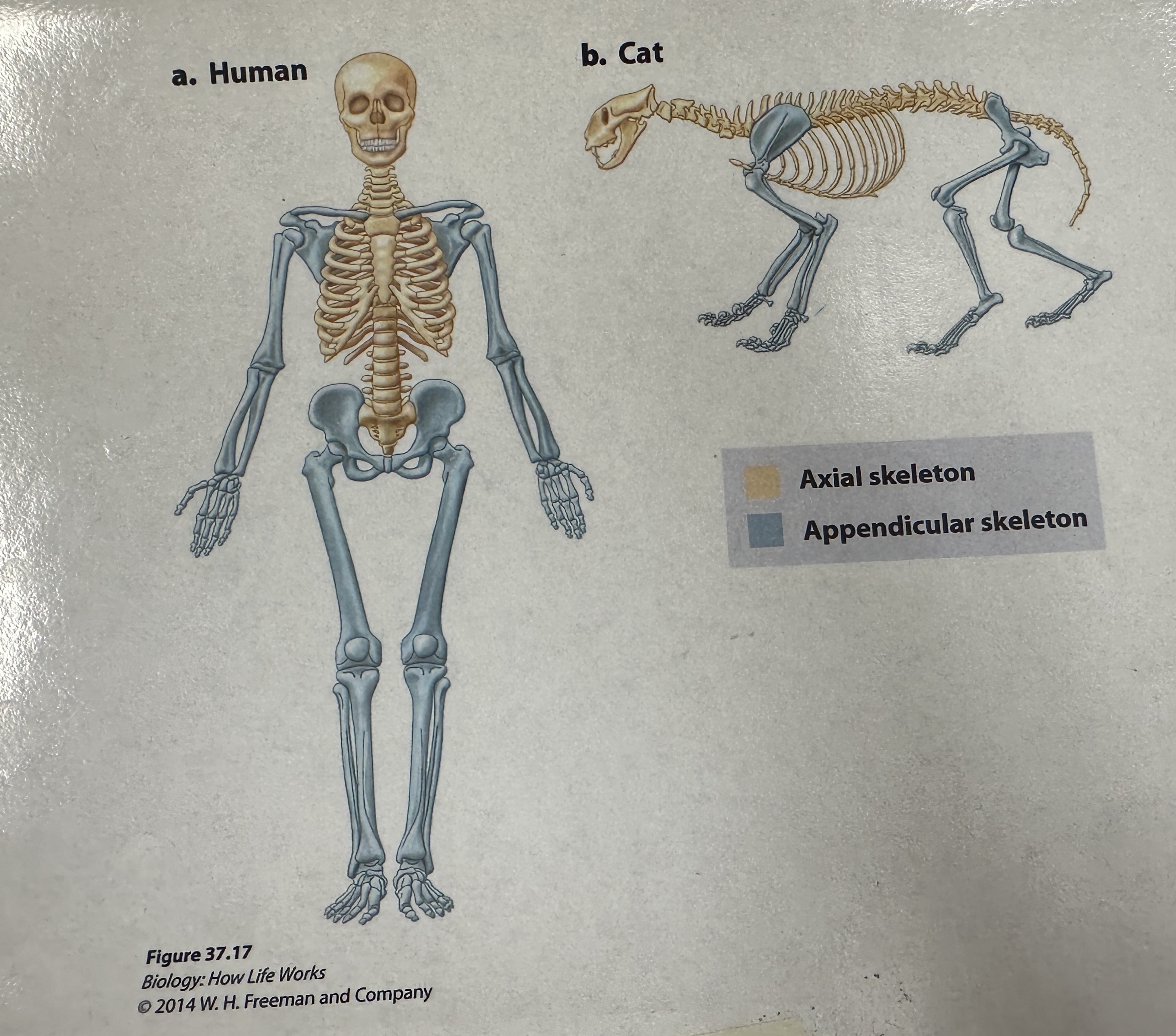
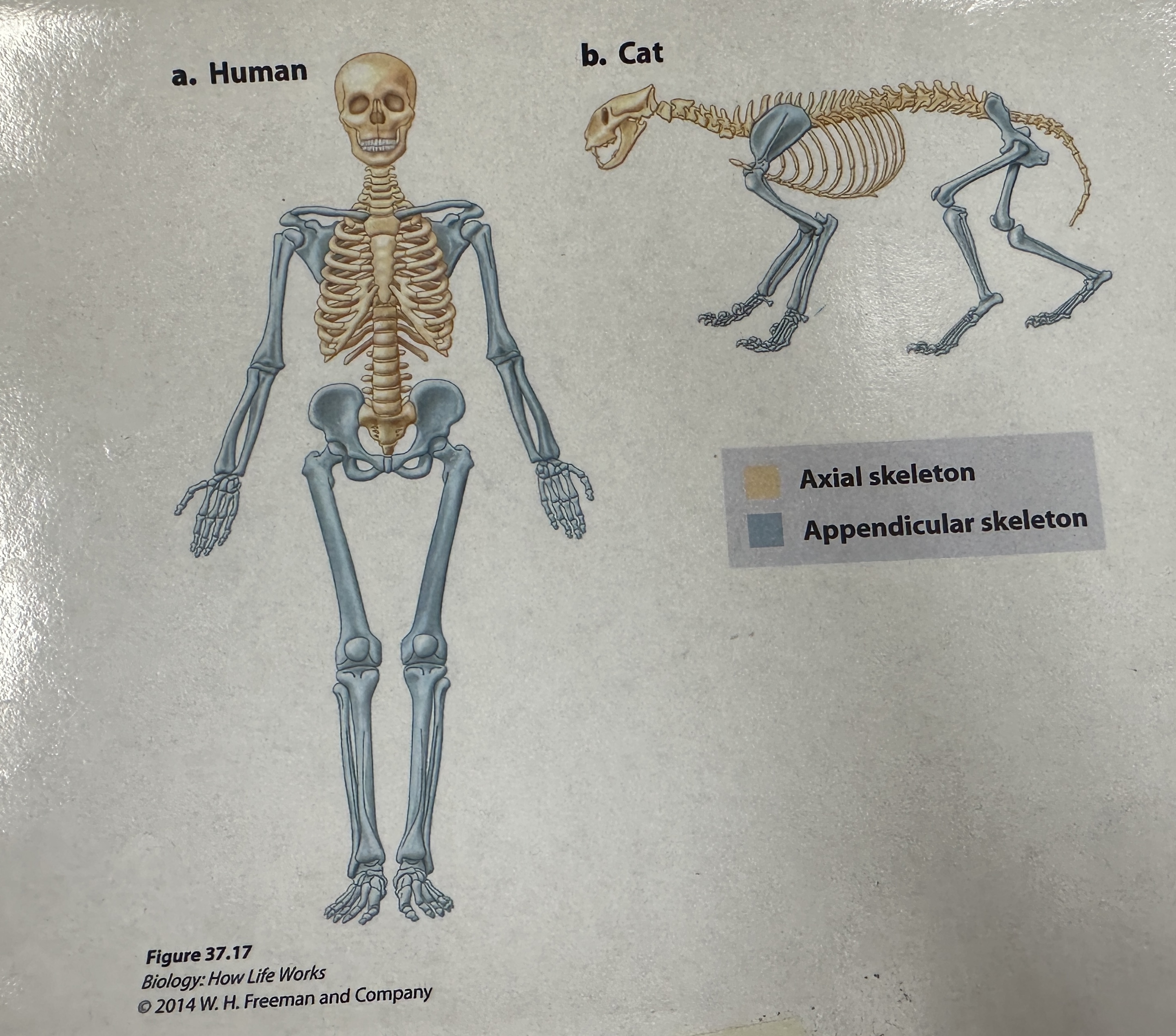
Appendicular skeleton
Endoskeleton division that consists of pectoral girdle which supports the skeletal elements of the forelimbs, and the pelvic girdle which supports the skeletal elements of the hindlimbs
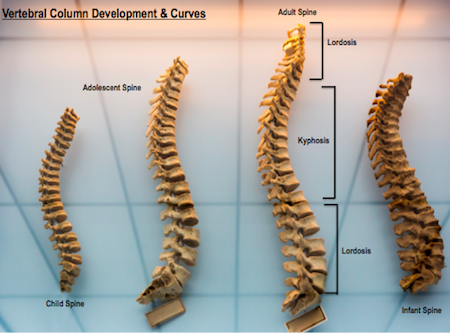
vertebral column (spine)
notochord becomes segmented during development to form this column. it consists of segmented vertebrae
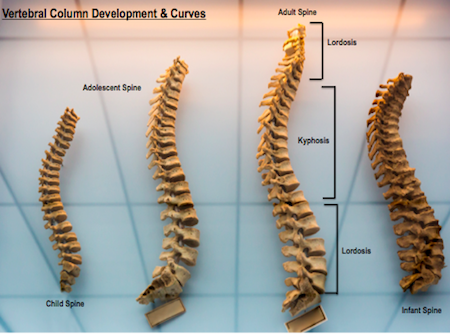
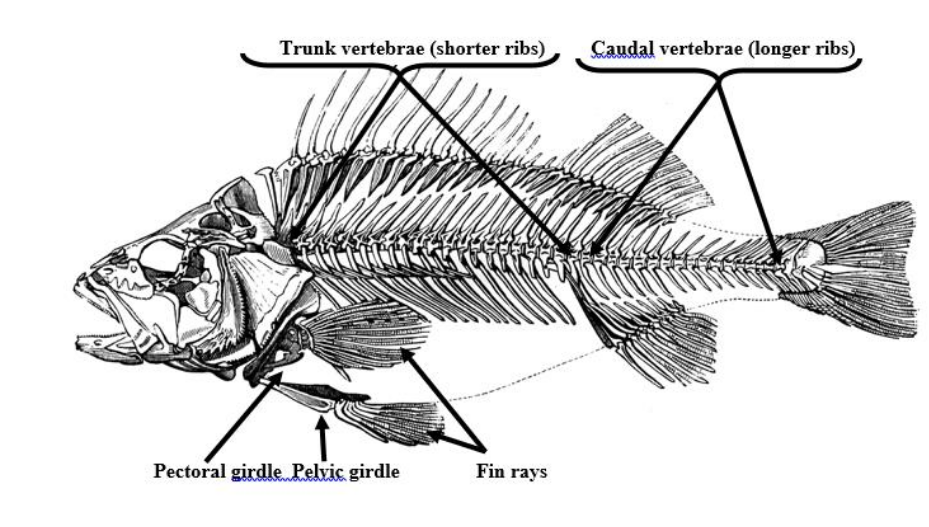
Trunk vertebrae
Shorter ribs, bones that make up the upper section of the vertebral column
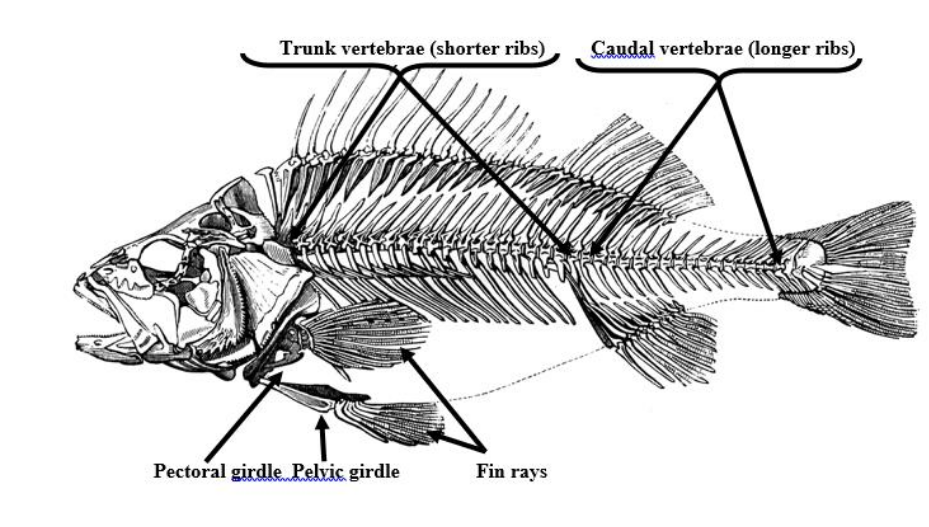
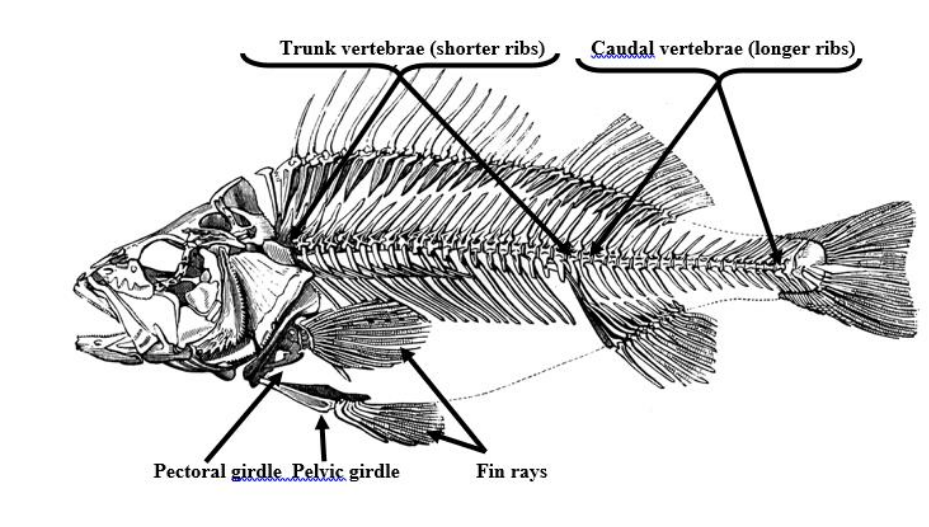
Caudal vertebrae
longer ribs, bones that make up the lower section of the spinal column
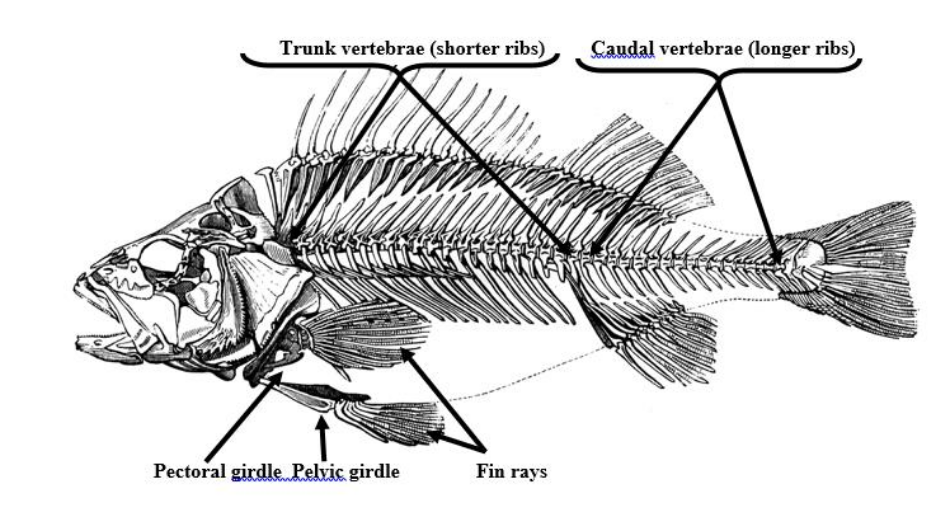
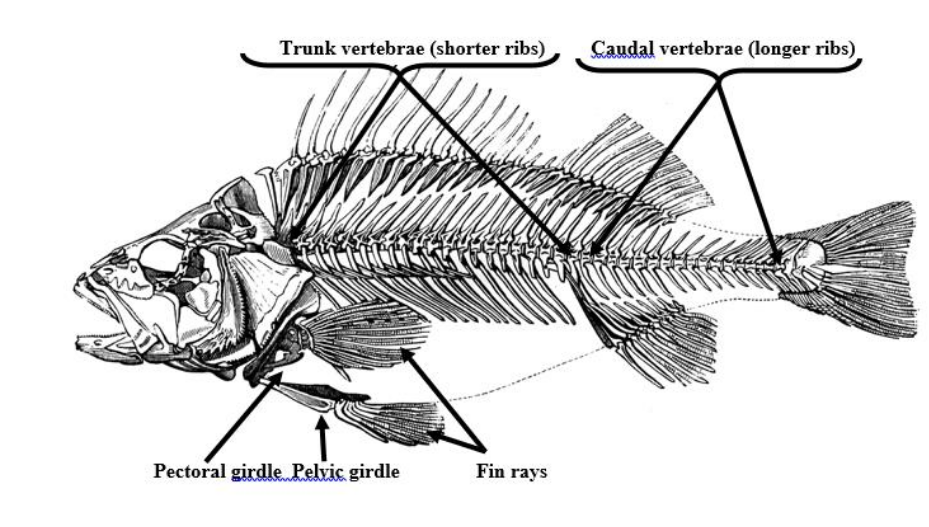
Pelvic girdle (synsacrum)
a ring of bones that forms the lower part of the trunk and supports the weight of the upper body
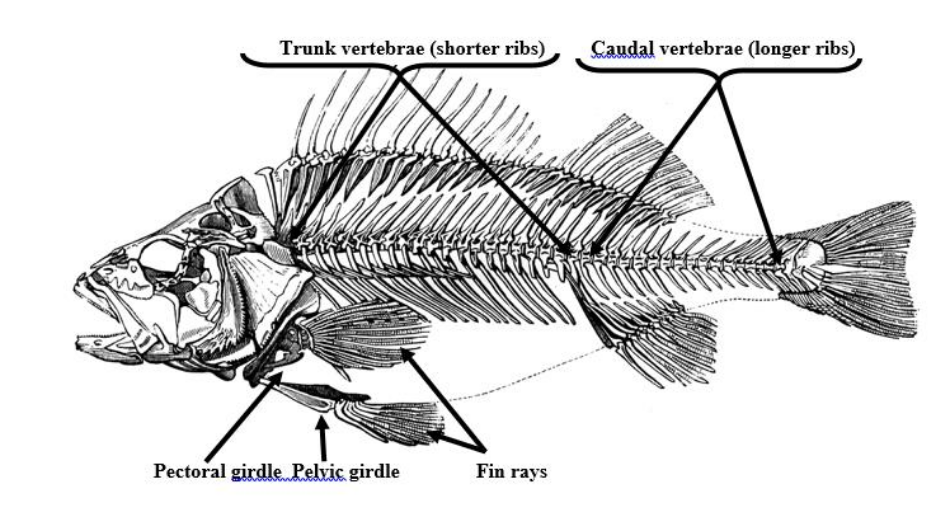
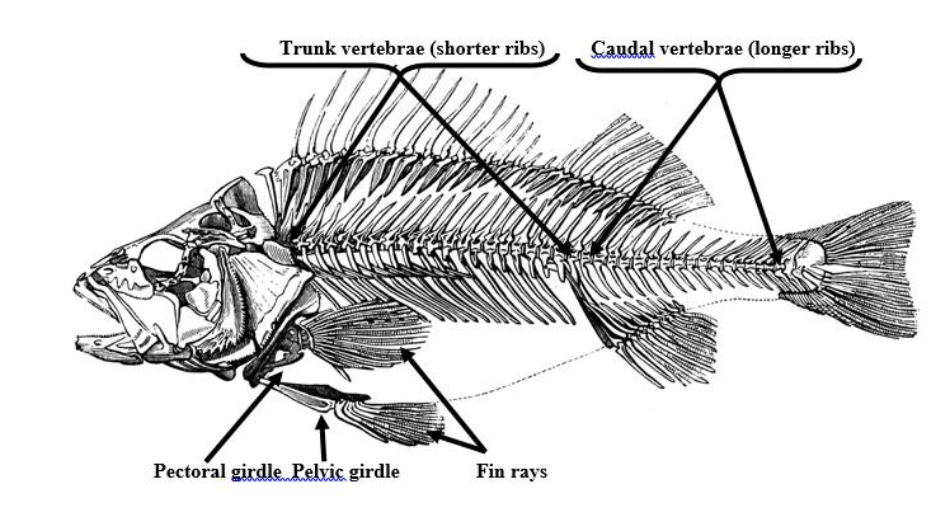
Pectoral girdle (clavical)
the skeletal framework which provides attachment for the forelimbs or pectoral fins.
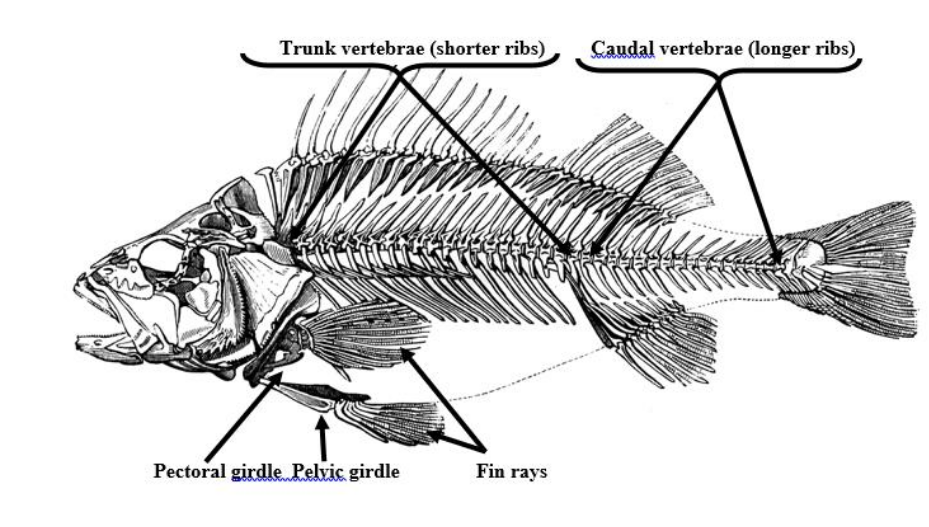
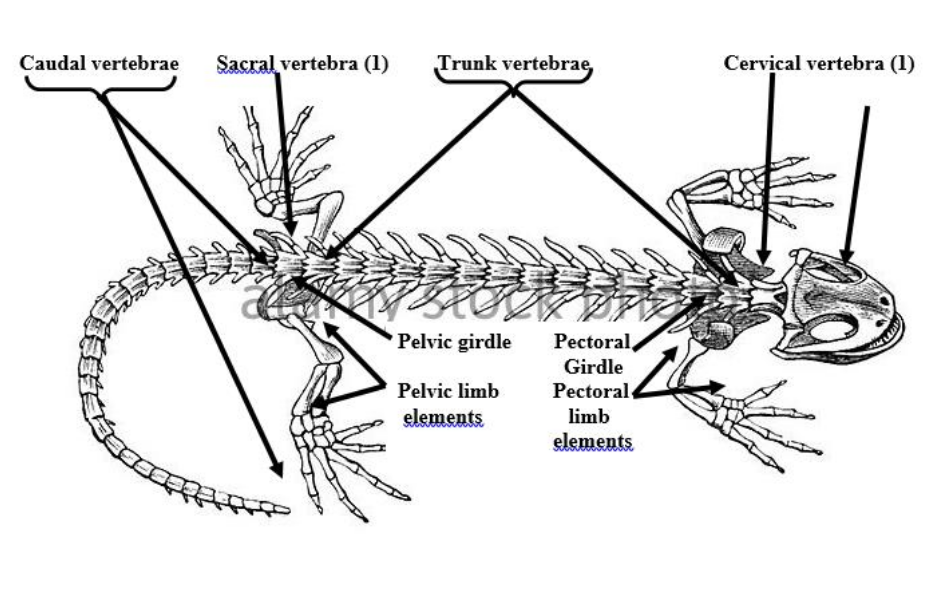
cervical vertebrae
highly mobile bones in the neck that support the head, protect the spinal cord, and facilitate head movement
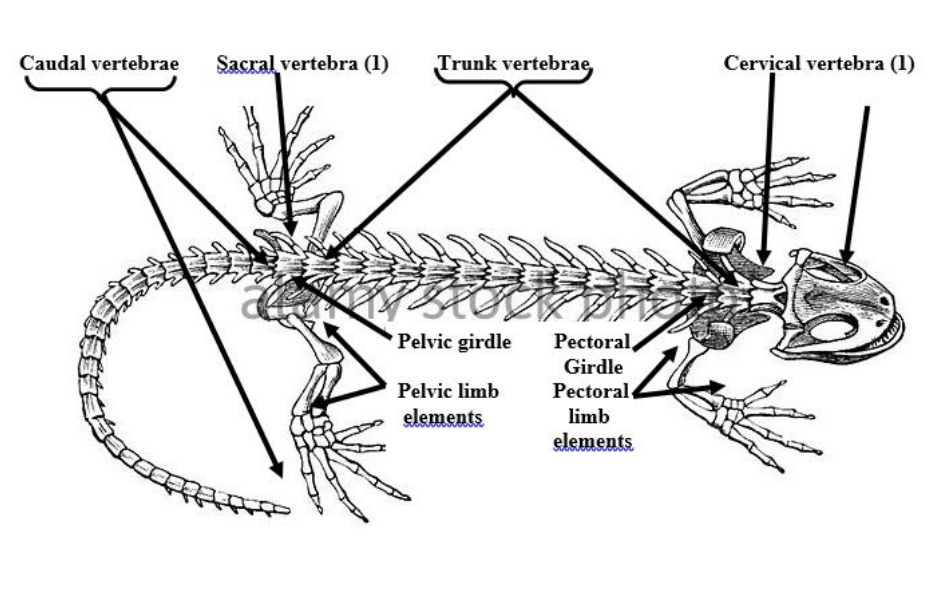
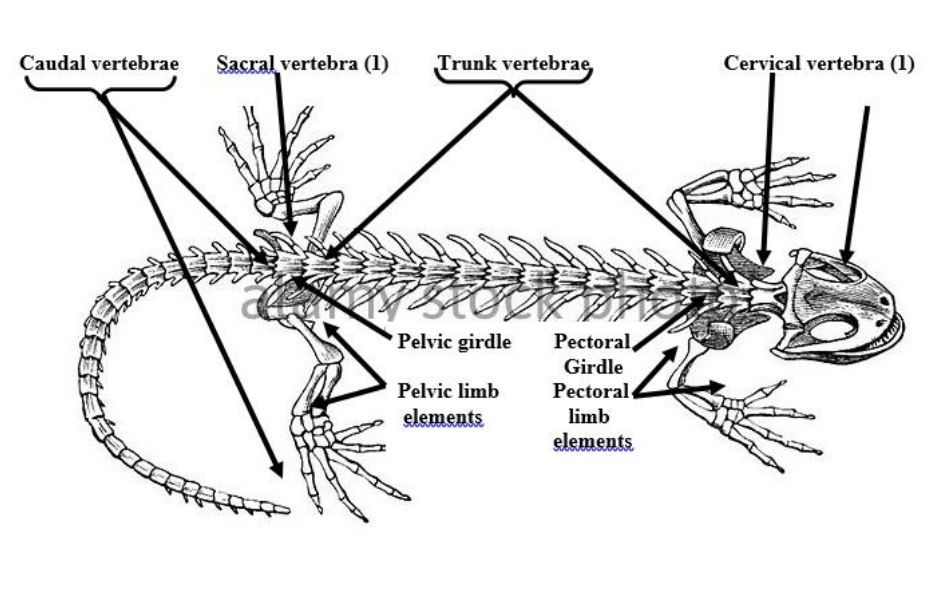
sacral vertebrae
There is a single one of these vertebra in salamanders and ancestral tetrapods. has a slender sacral rib.
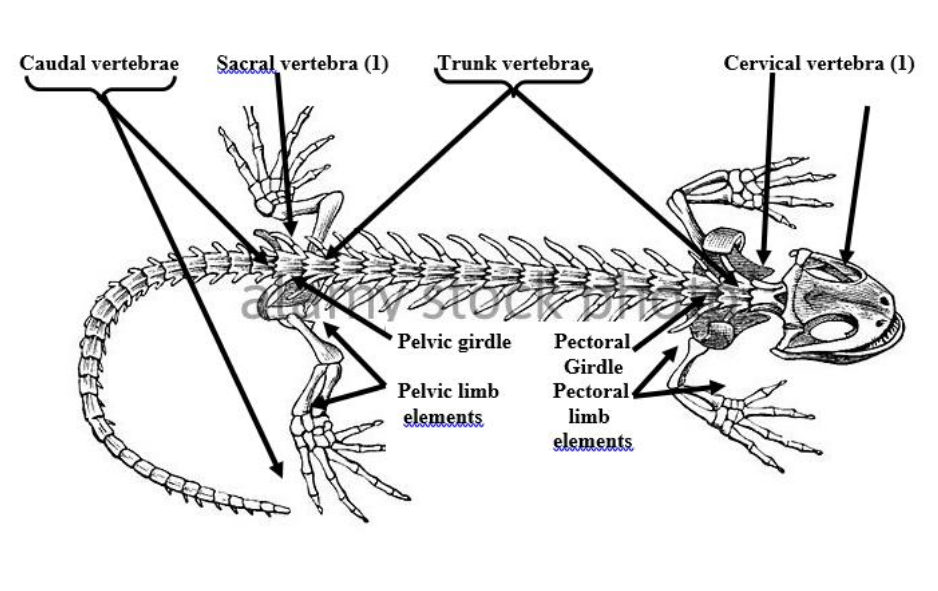
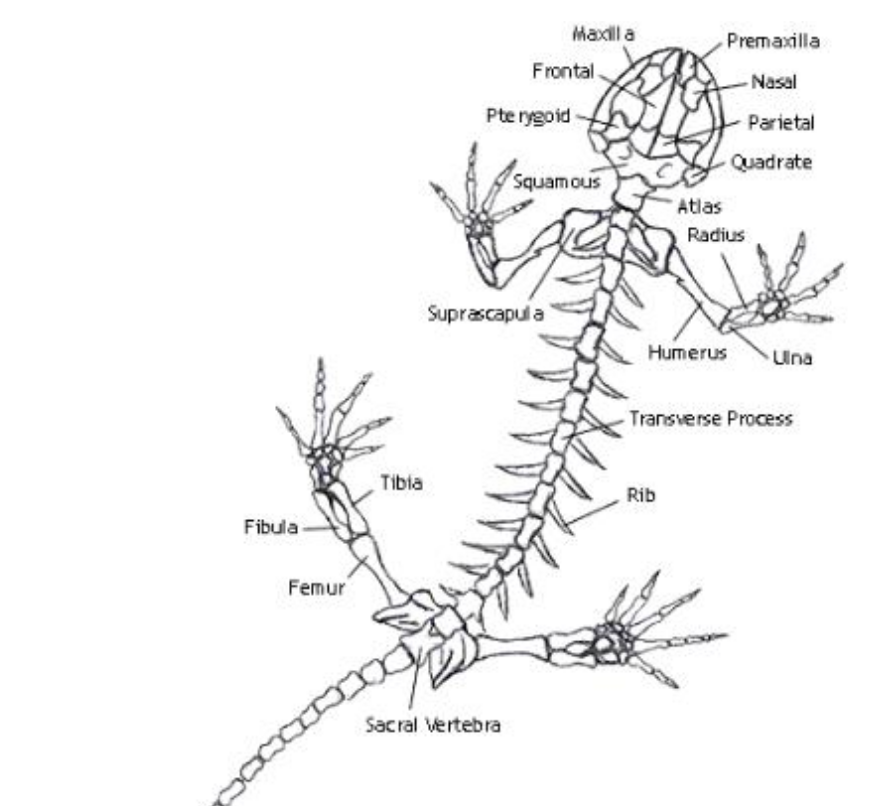
Humerus
the single, long bone of the upper arm that extends to the elbow.
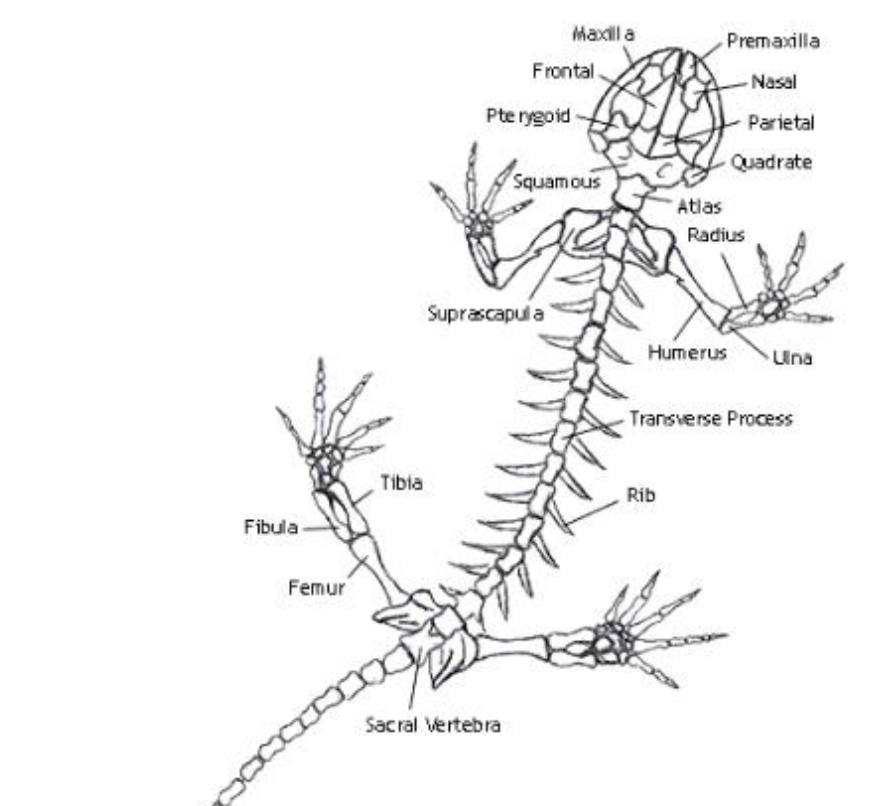
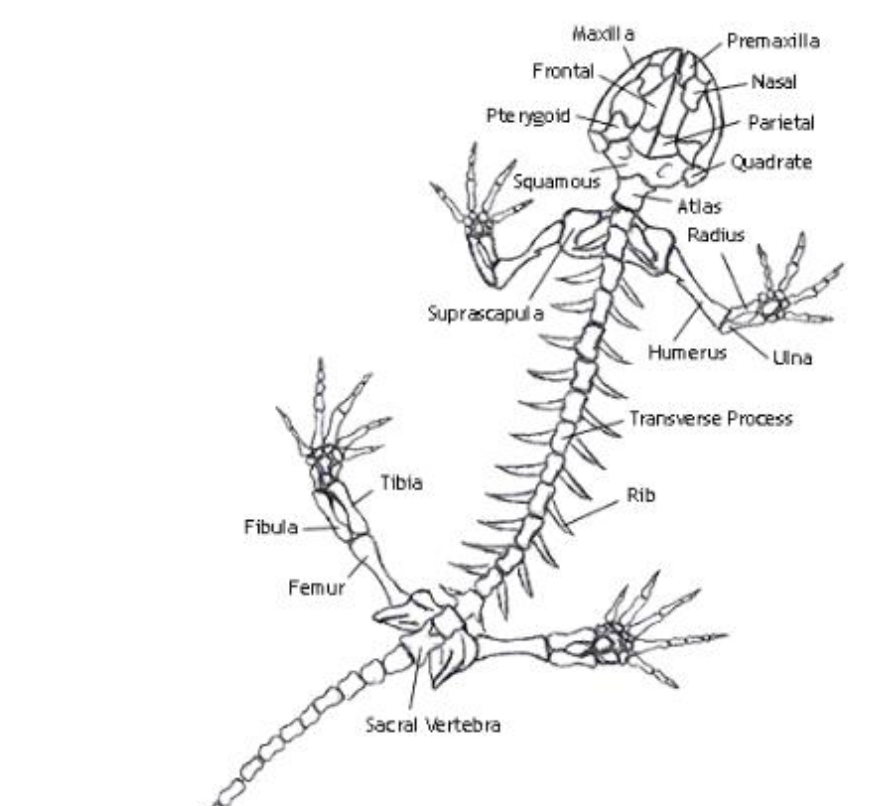
radius
one of the two main bones in the forearm, alongside the ulna. It extends from the elbow to the wrist on the thumb side
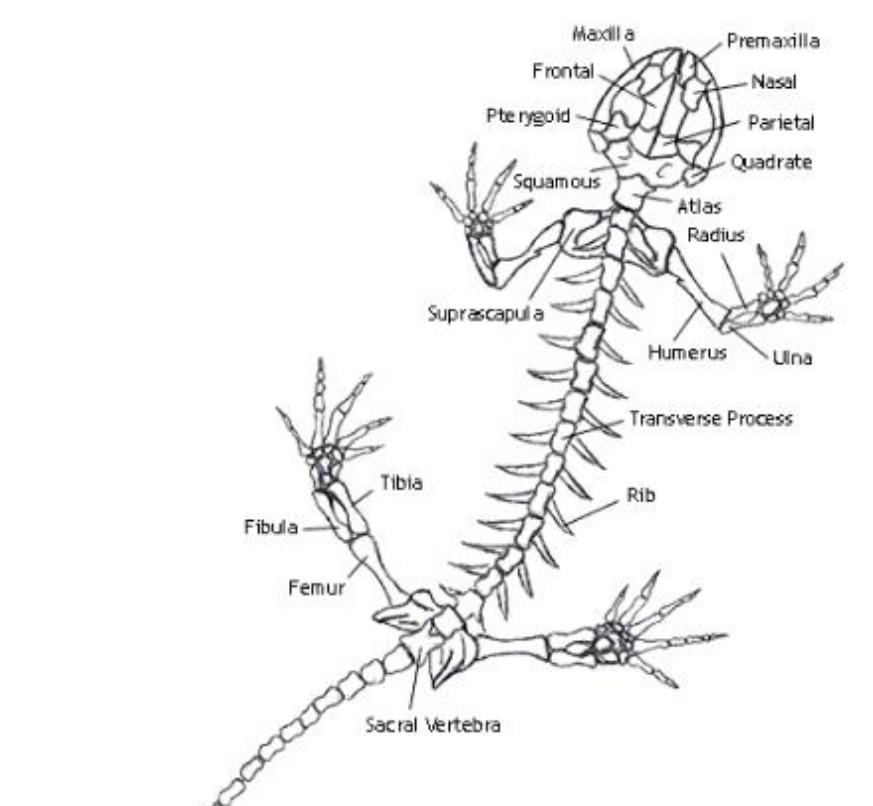
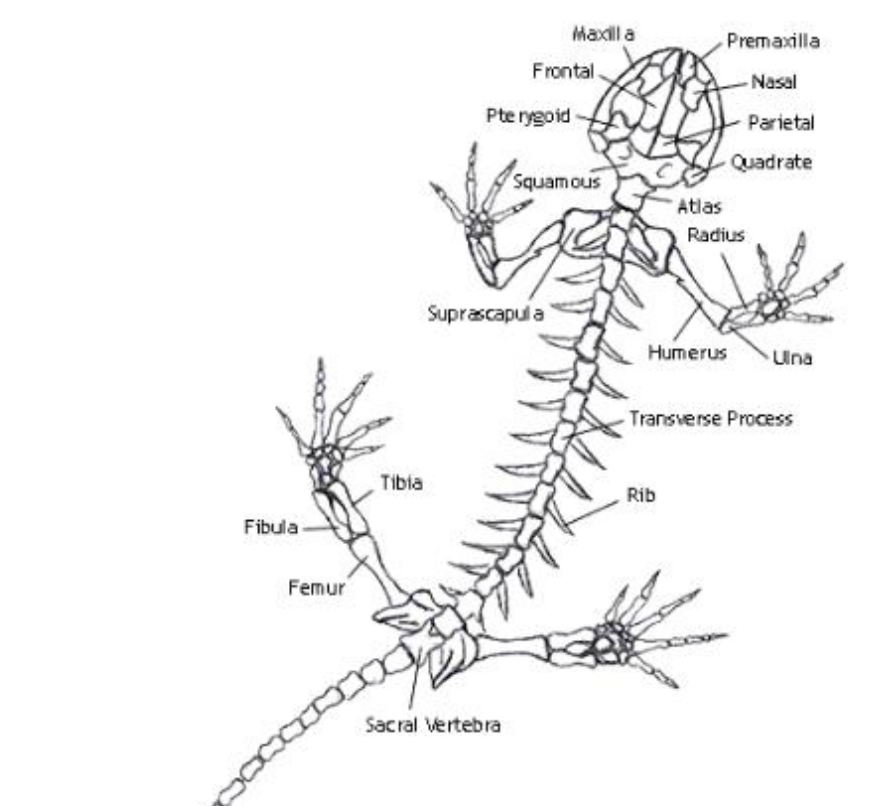
ulna
the longer of the two bones in the forearm, located on the pinky finger side
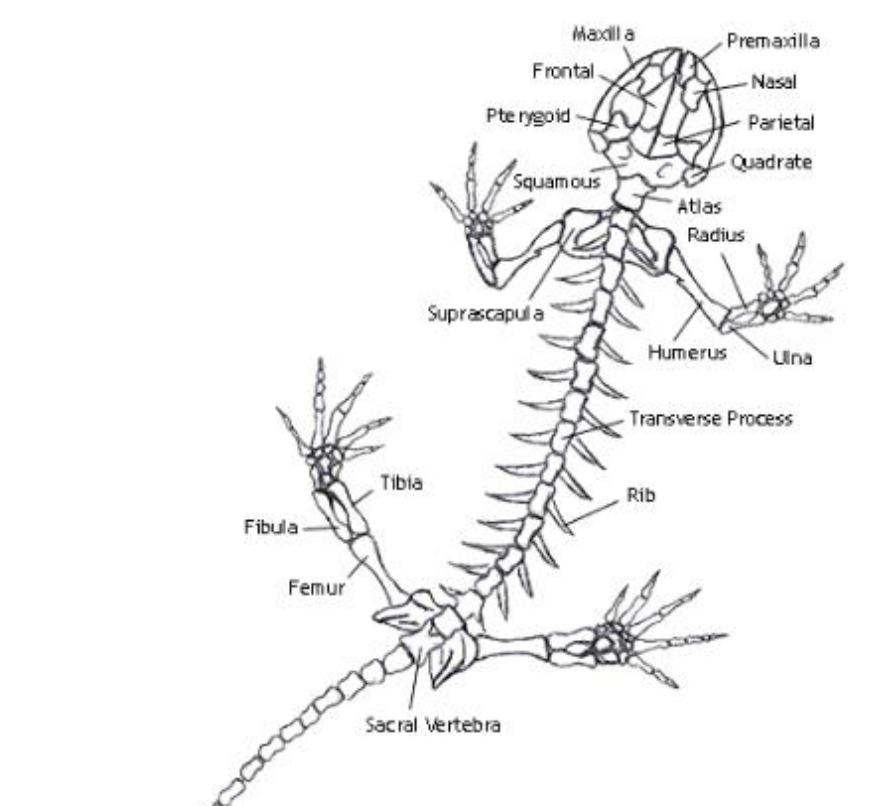
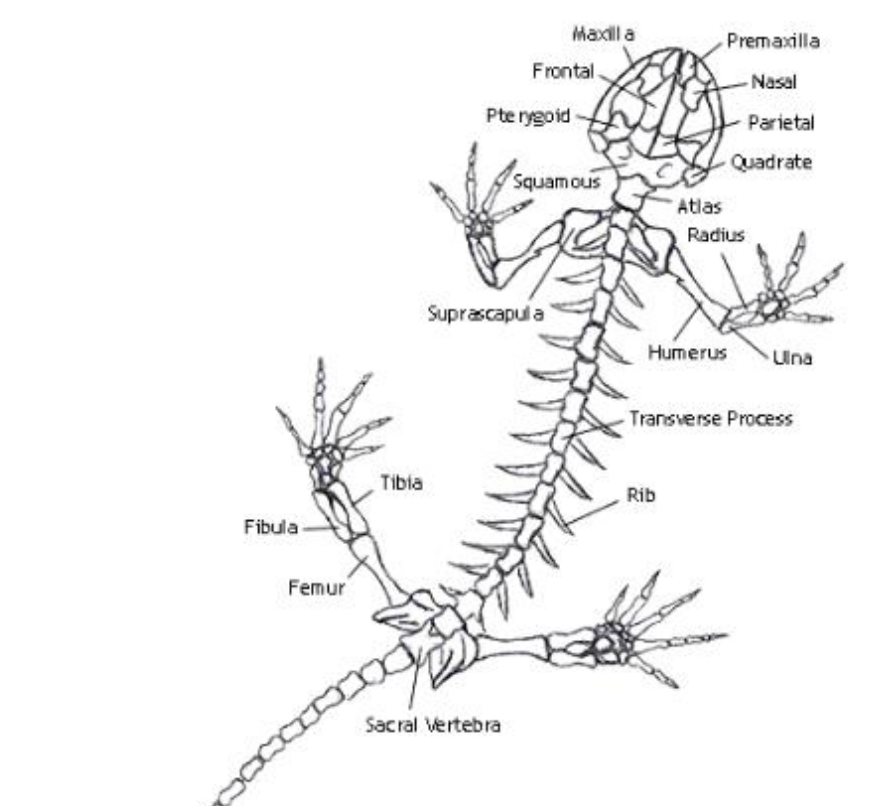
femur
bone located in the upper leg, generally very strong.
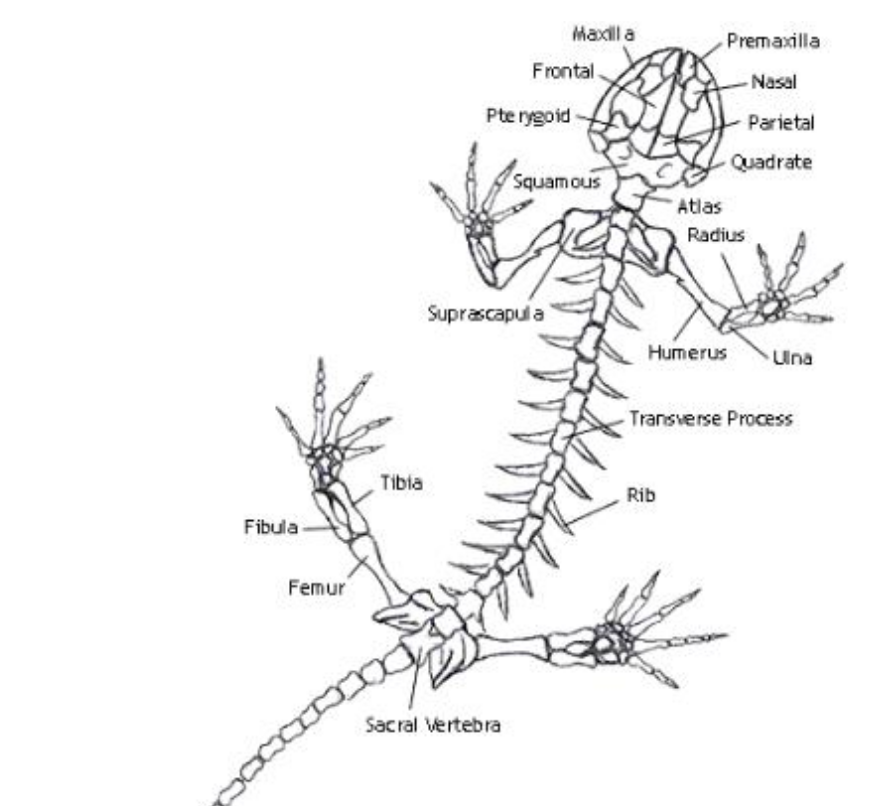
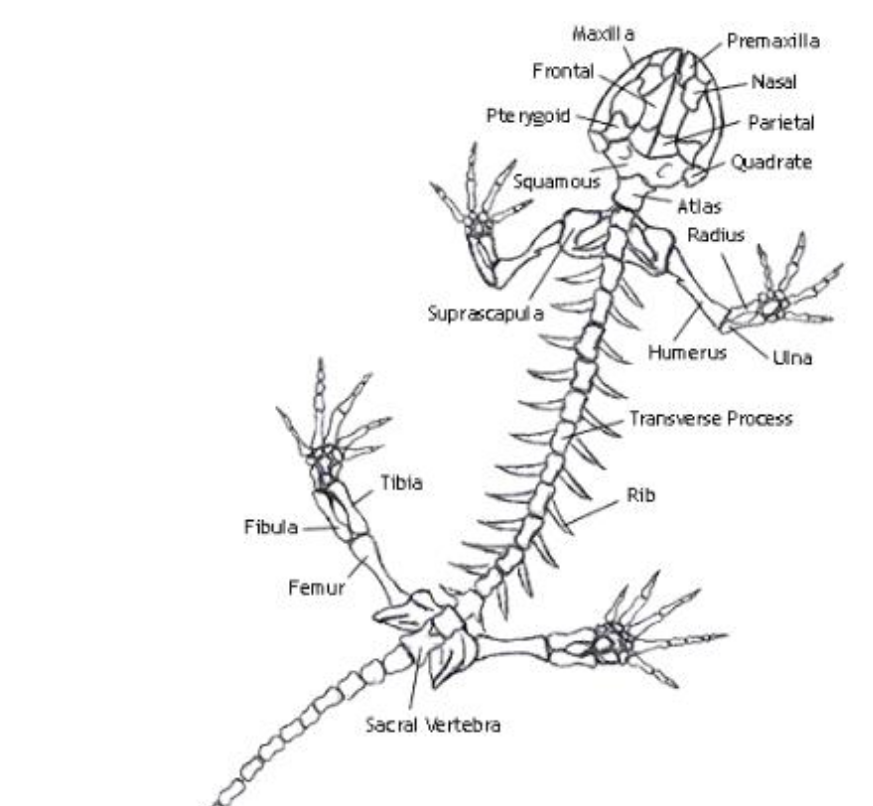
tibia
a long, weight-bearing bone located in the lower leg.
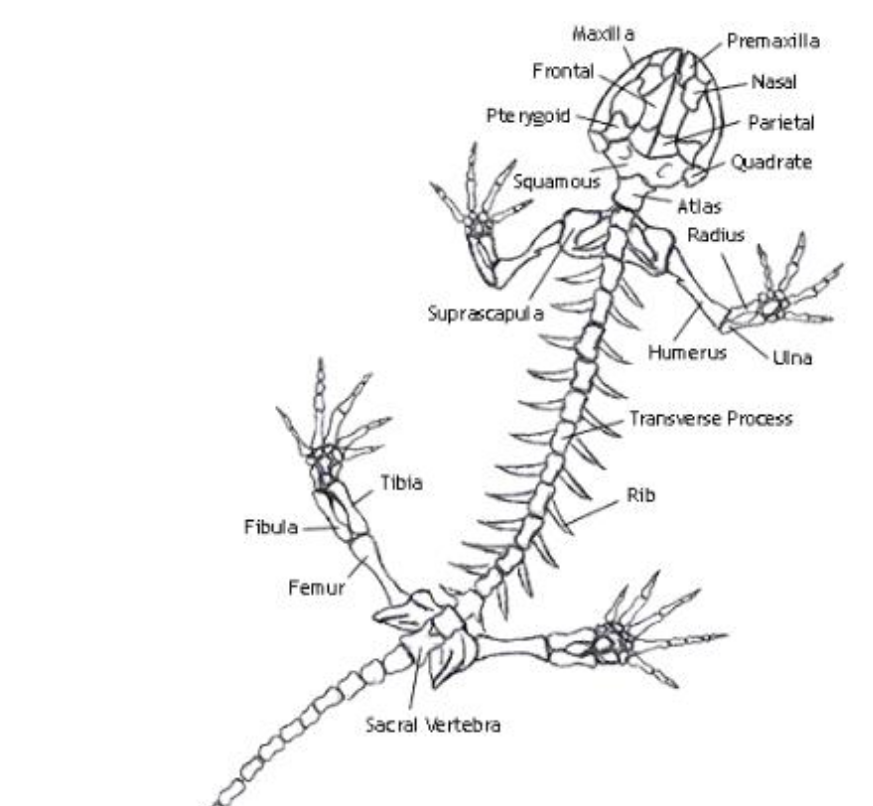
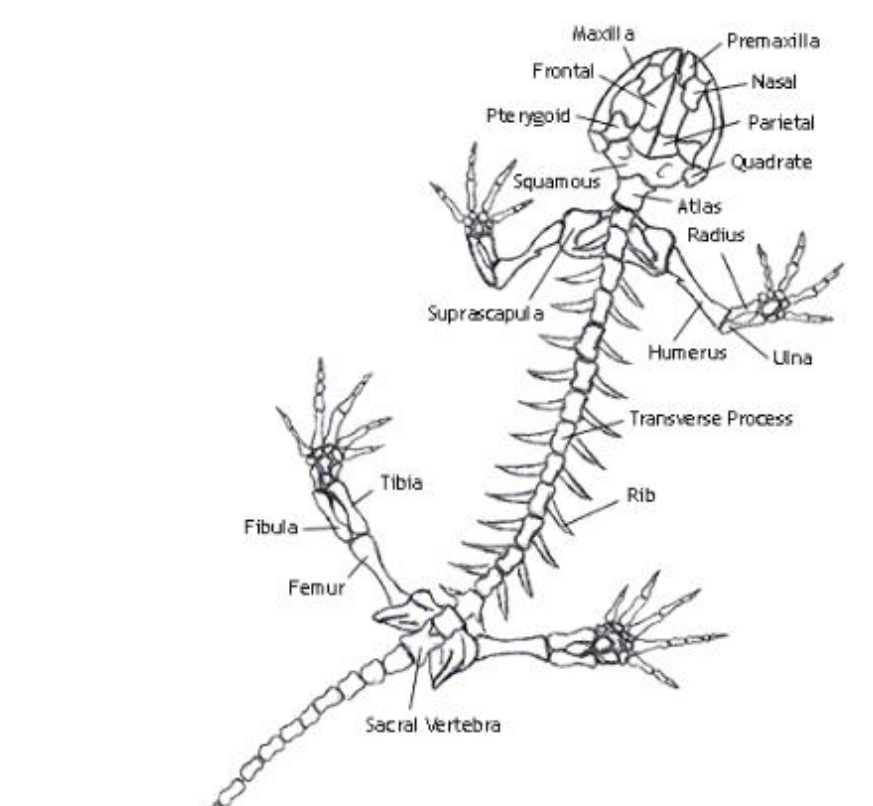
fibula
slender bone located on the lateral (outside) side of the lower leg, parallel to the tibia.
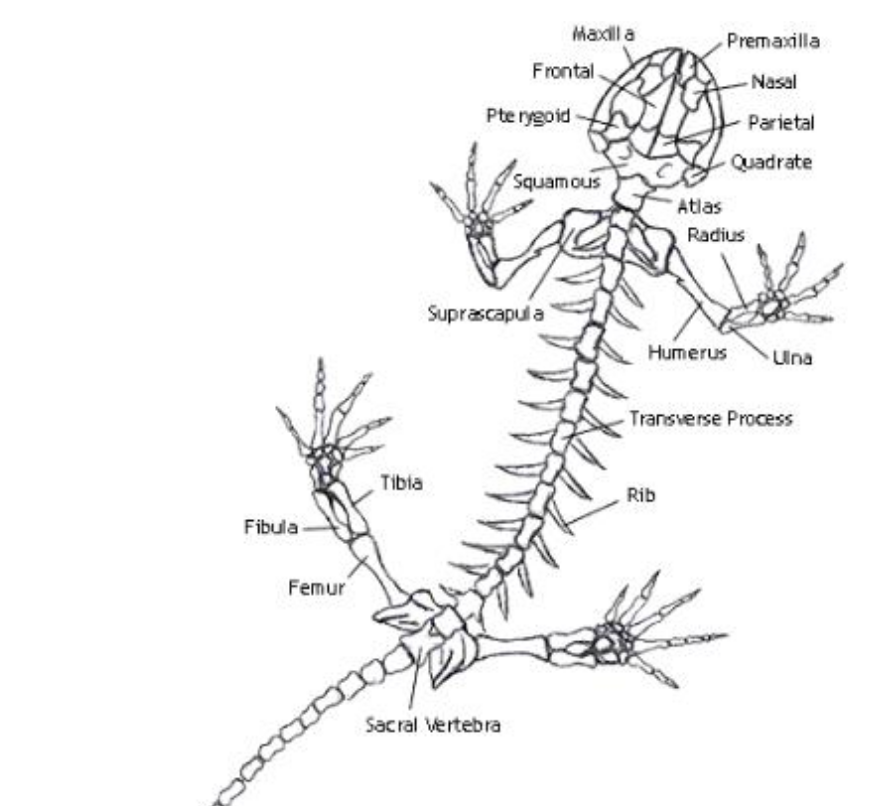
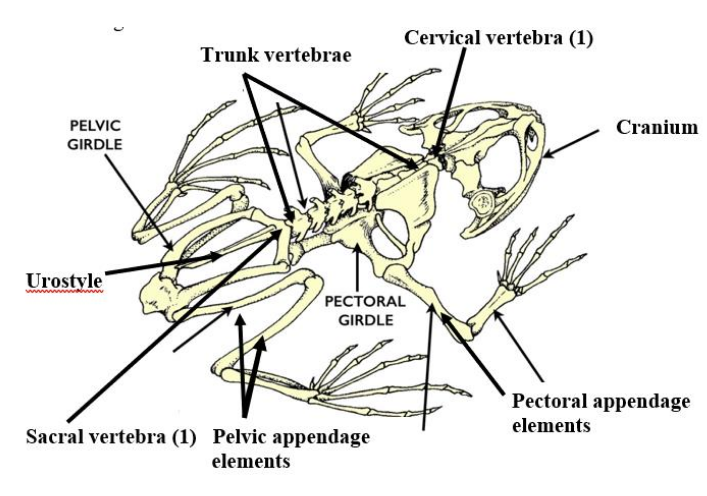
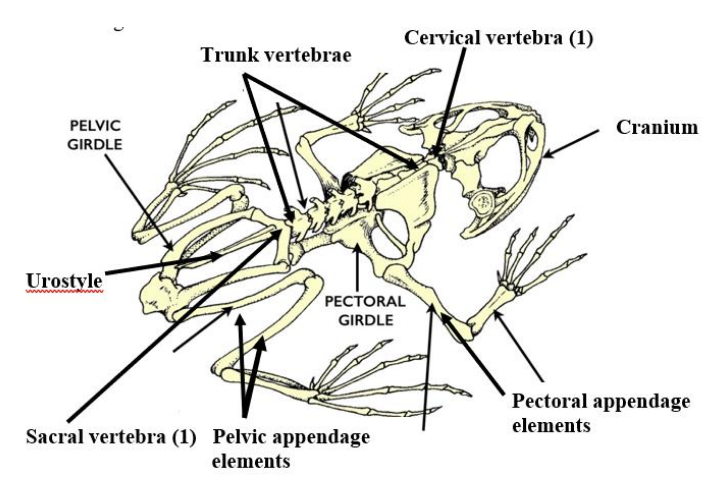
Urostyle
an enlarged, firmly fused pelvic girdle, and caudal vertebrae that are fused into this long rod-shaped bone.
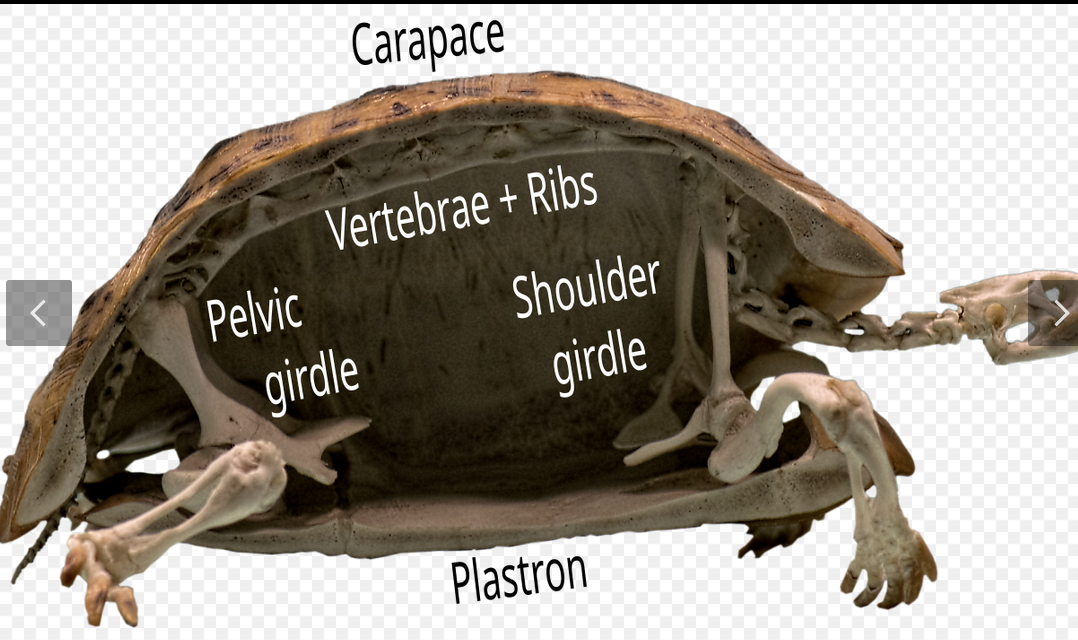
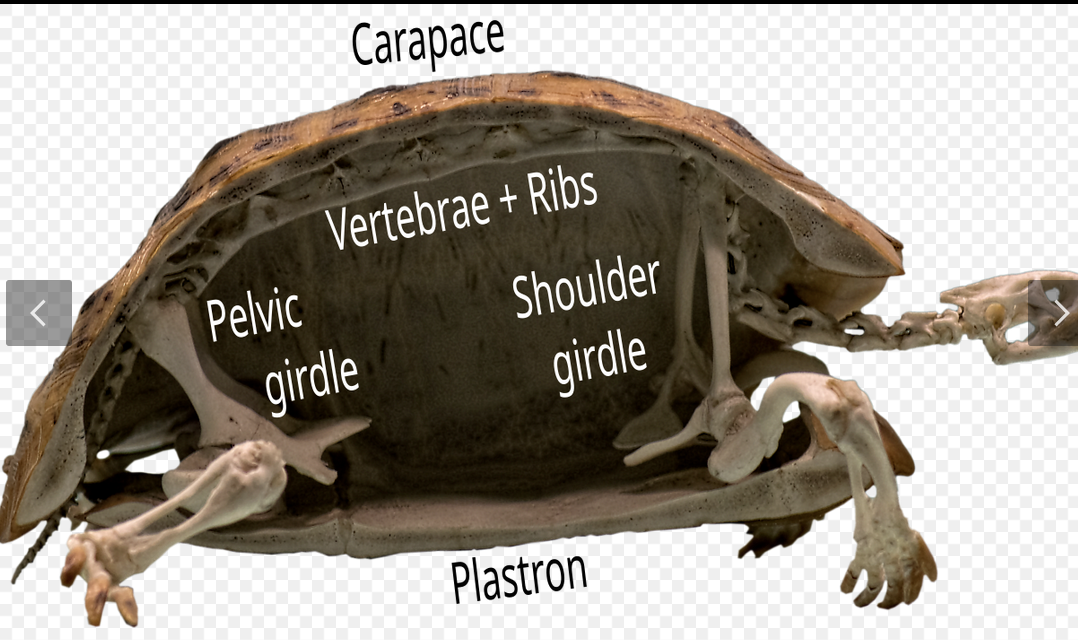
Carapace
dorsal part of turtle shell.
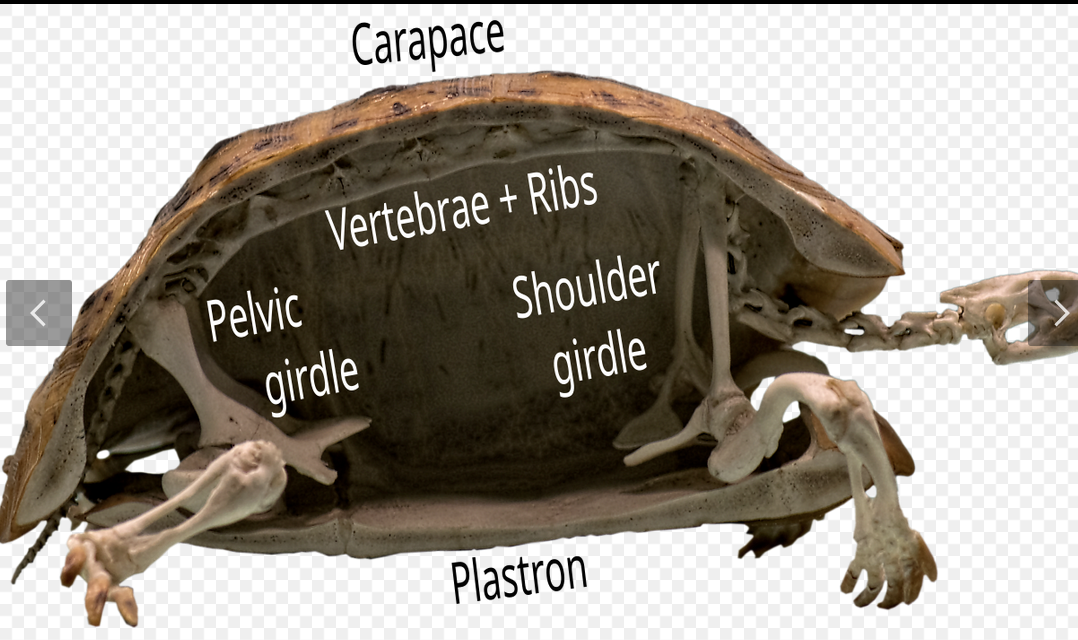
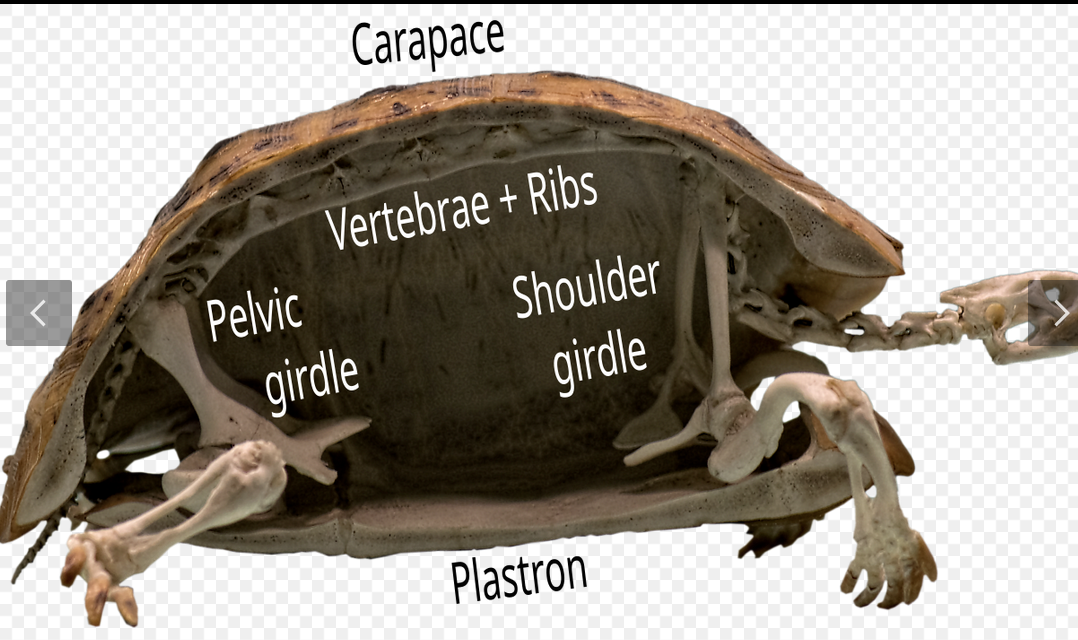
plastron
ventral part of turtle shell
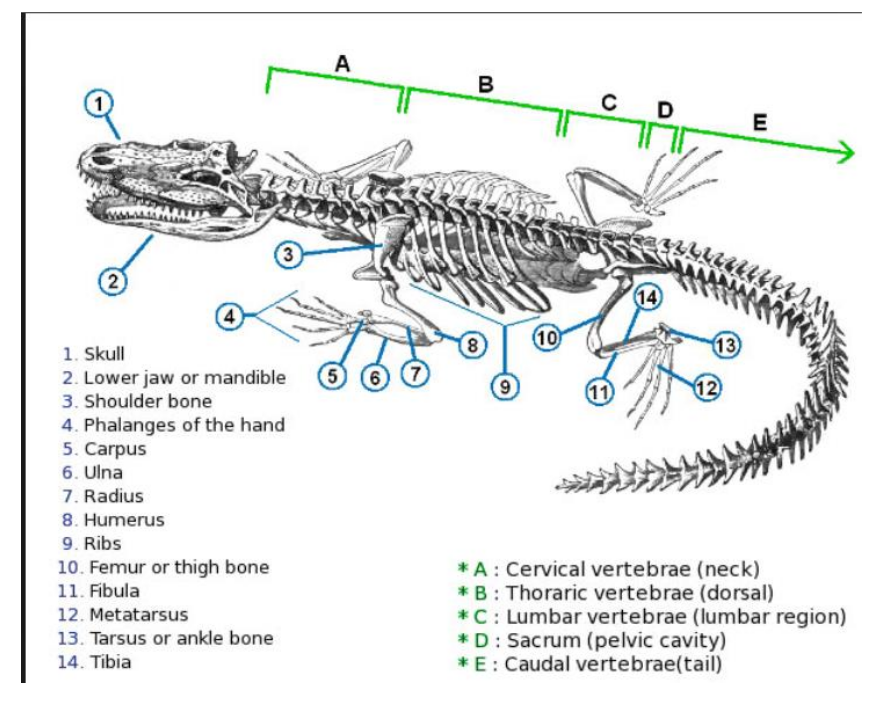
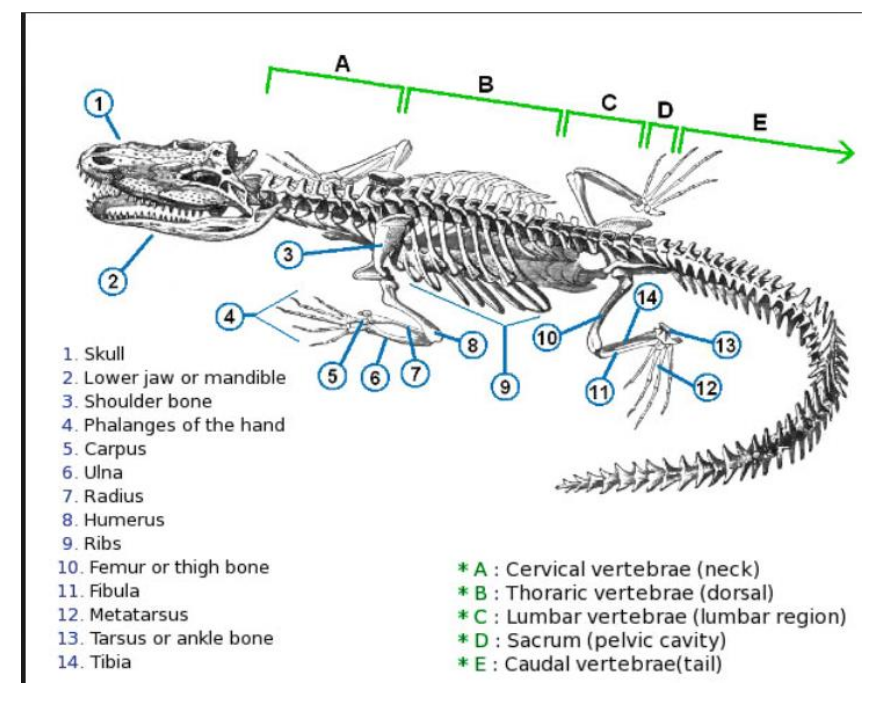
Thoriac vertebrae
vertebrae that support the ribs, on the dorsal section
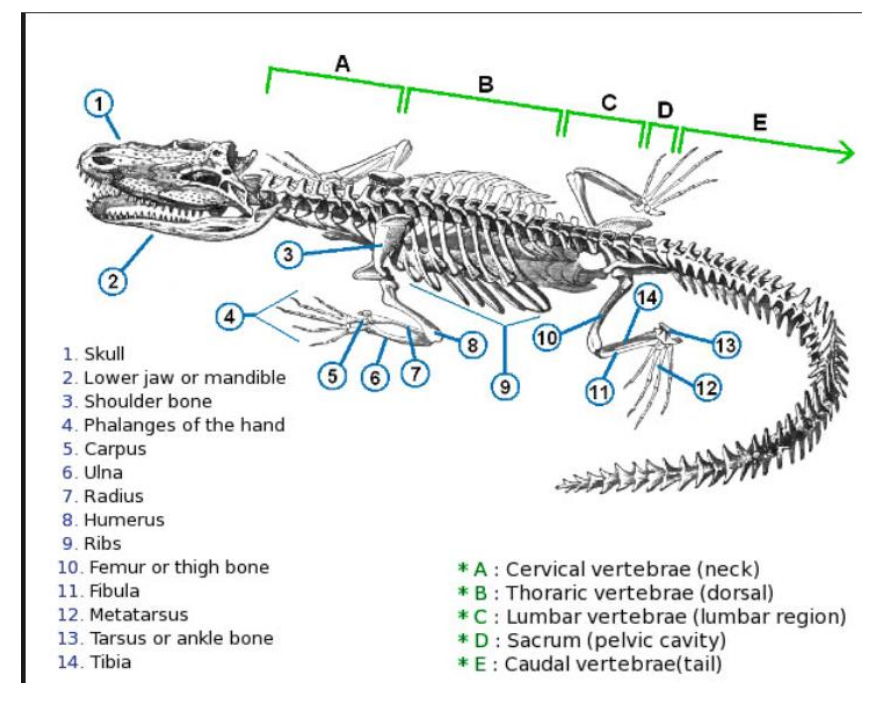
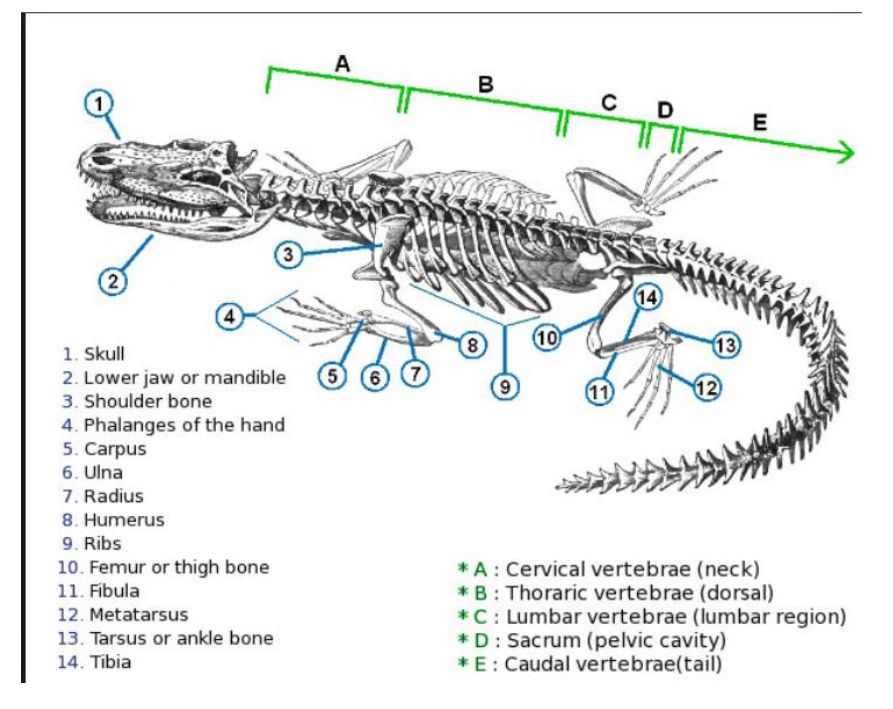
lumbar vertebrae
vertebrae that do not support the ribs, in the lumbar region
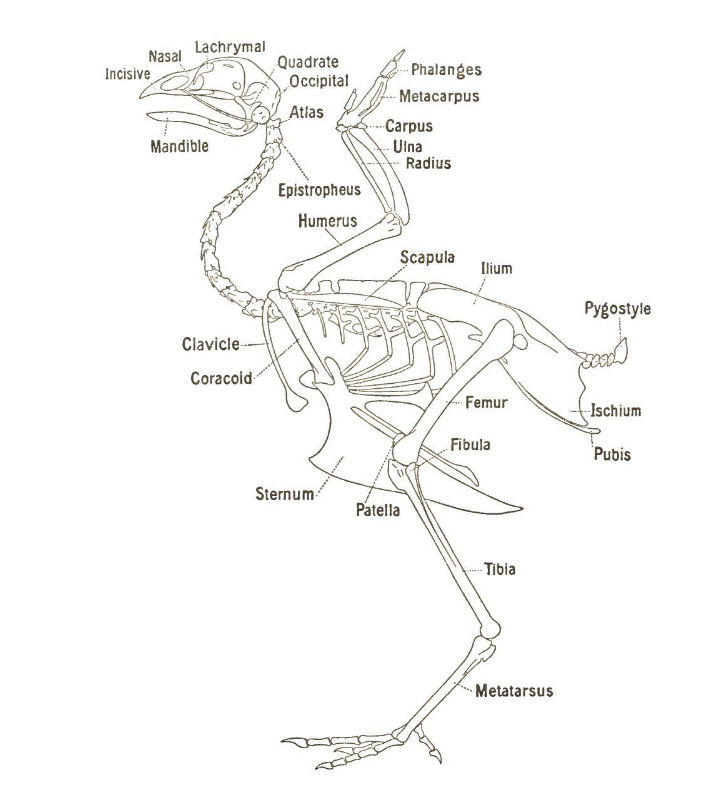
Sternum
a flat, elongated bone located in the center of the chest.
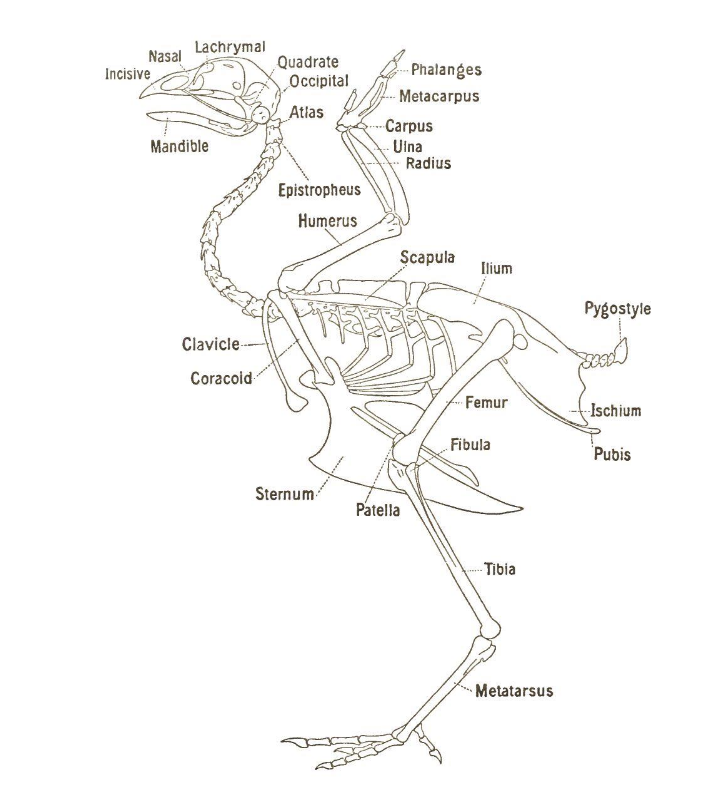
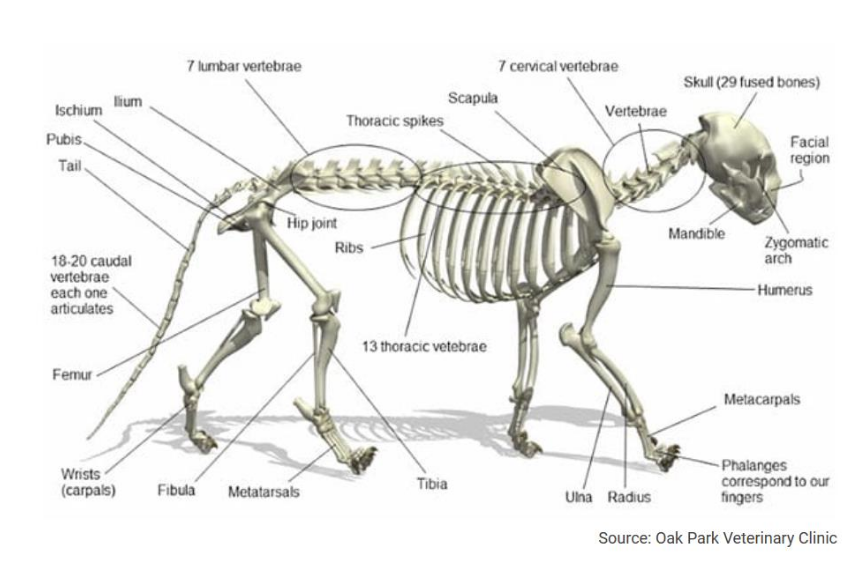
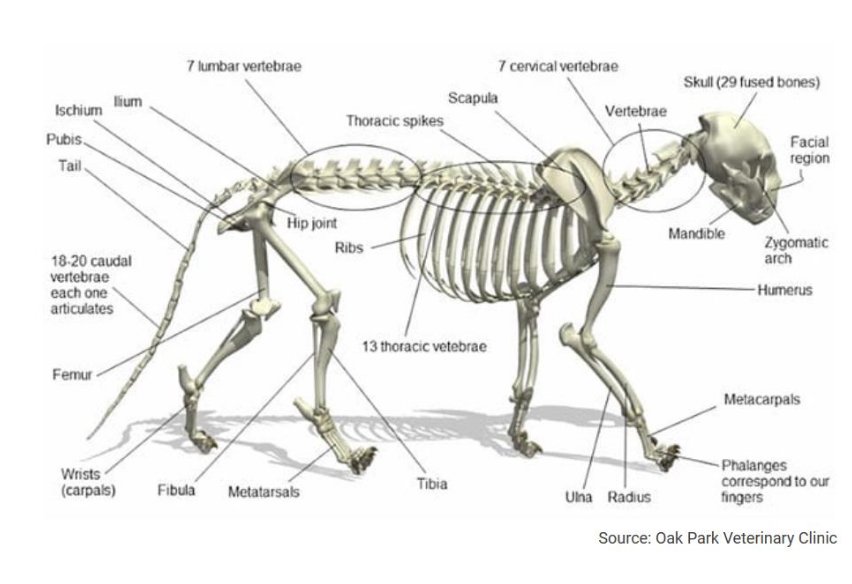
Thoracic vertebrae
Vertebrae that support ribs, there’s differing numbers depending on the species
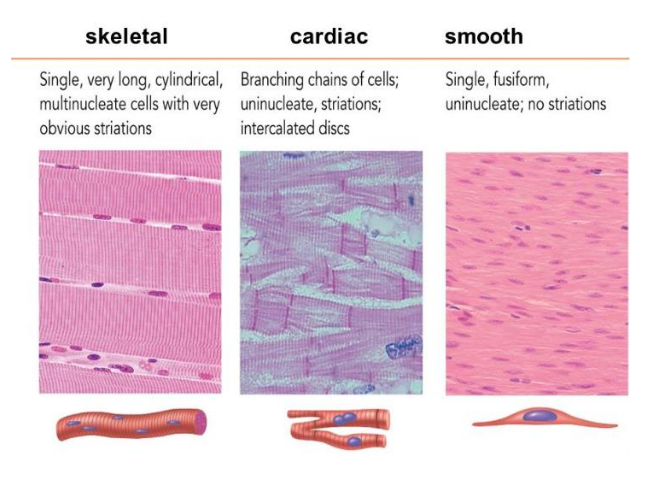
Skeletal muscle
muscle that is enervated by the voluntary portion of the nervous system and are the muscles that move animal body parts to accomplish locomotion
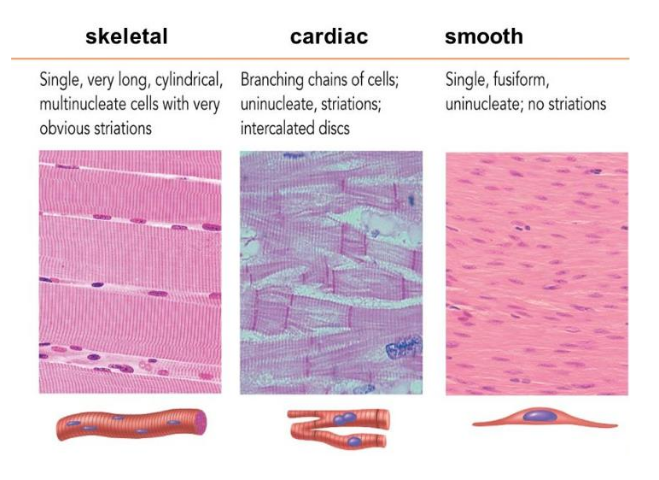
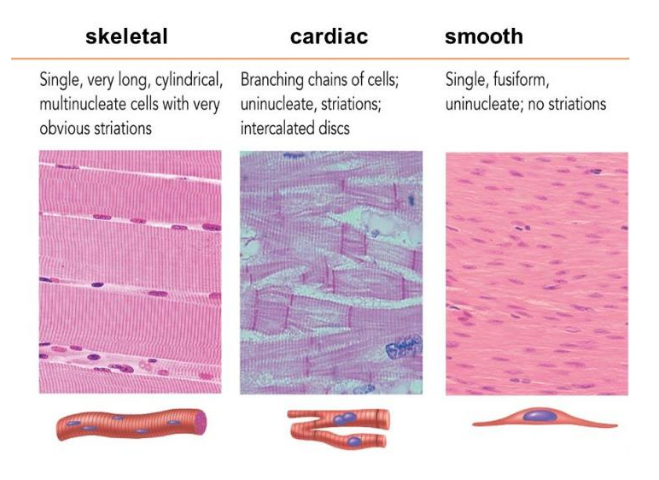
Smooth muscle
muscle incorporated in the walls of internal organs, controlled by the autonomic nervous system, the involuntary portion of the nervous system
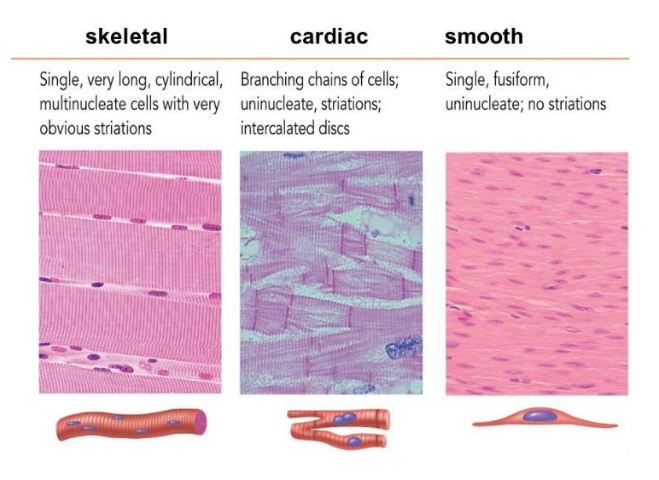
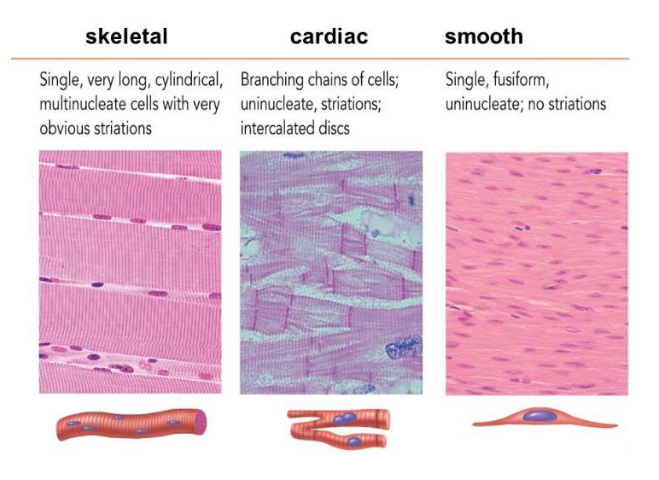
Cardiac muscle
This muscle is associated with blood propulsion.
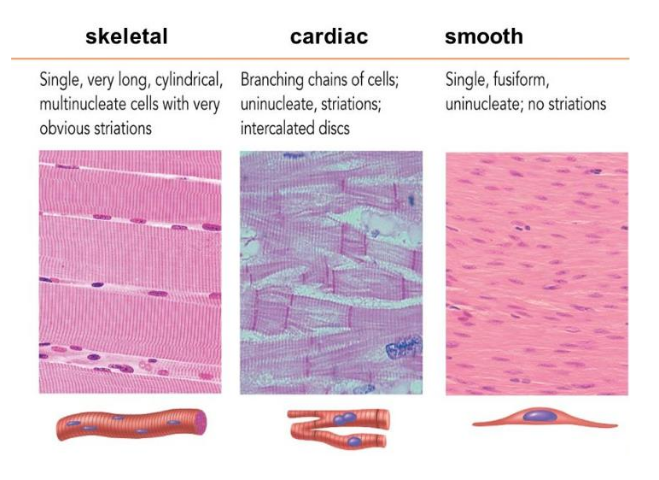
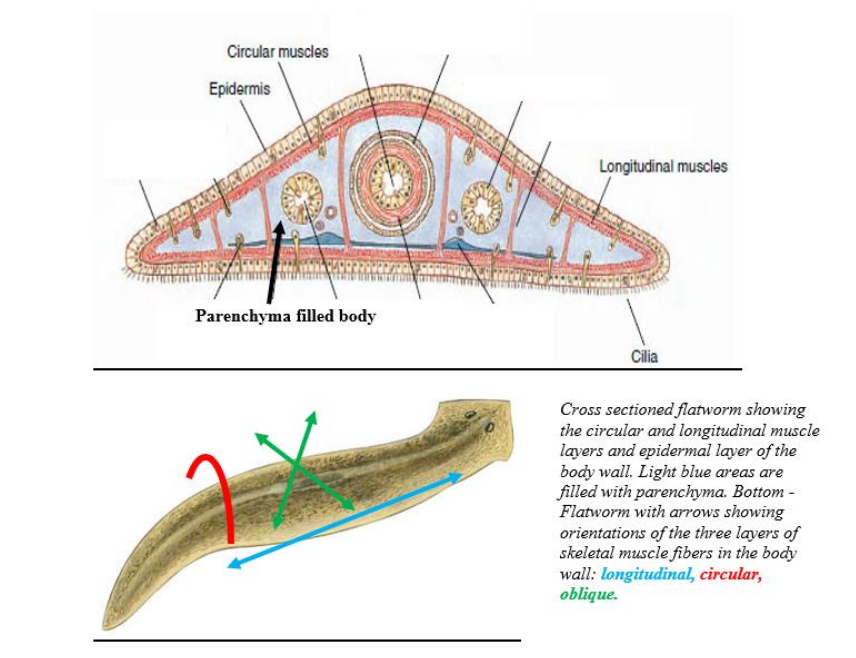
study this image
be able to identify both longitudinal and circular muscles as well as epithelium (epithelial tissue)
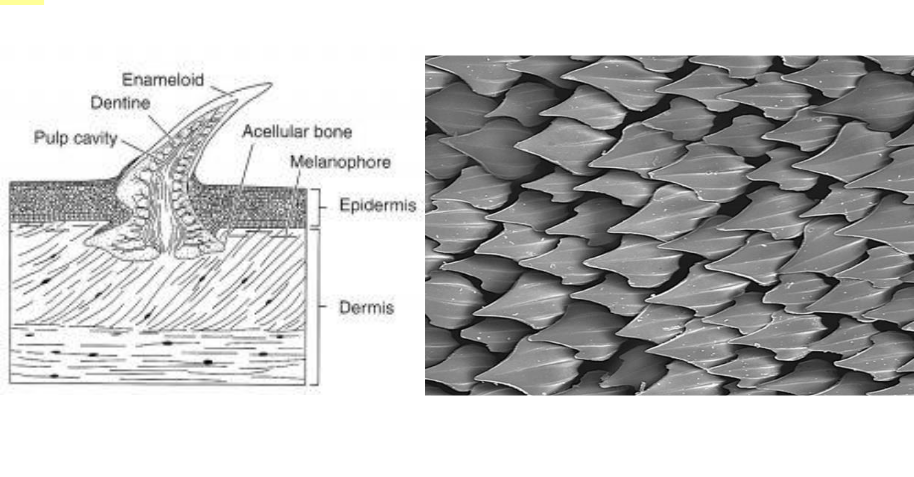
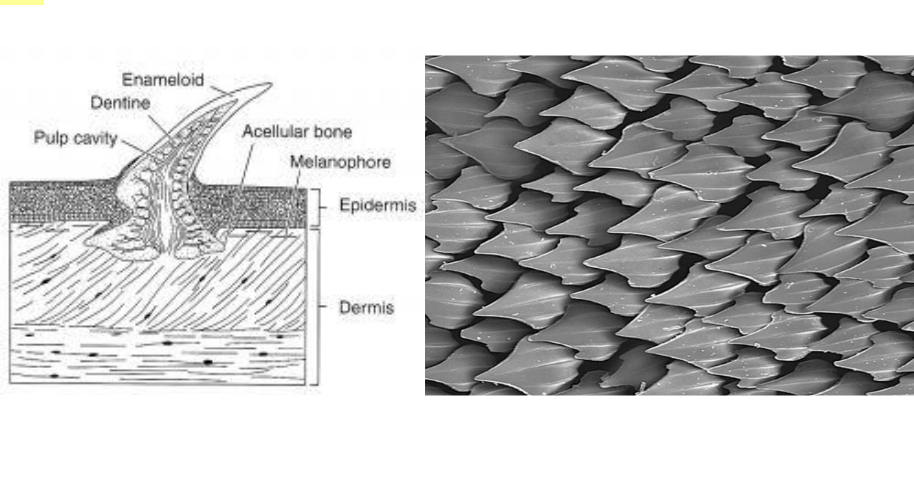
placoid scales
Cartilaginous fish are covered in this type of scale.
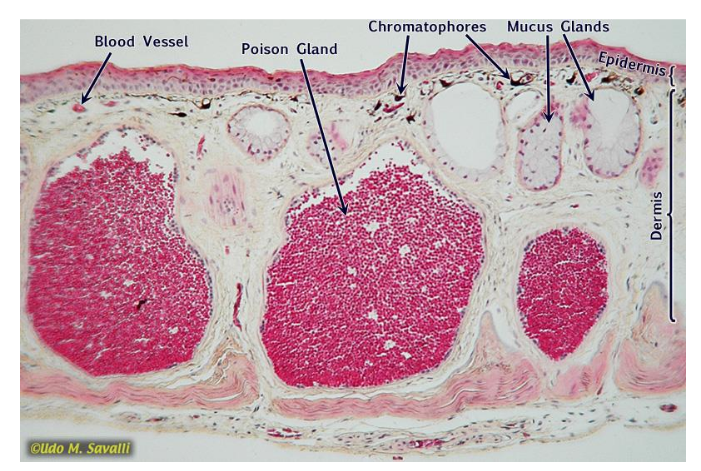
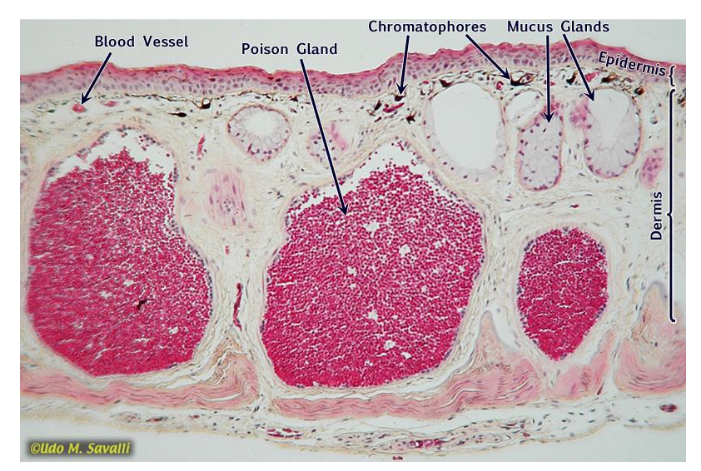
study this frog integument
Be able to identify the following: blood vessel, poison gland, chromatophores, mucus glands, stratum corneum, epidermis, and dermis.