A&P 9
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Skeletal system
A complex network of bones, joints, ligaments, and cartilage that provides structure, support, and protection to the human body.
Number of bones in the human skeleton
206
Main components of the skeletal system
Bones, joints, ligaments, and cartilage.
Joints
Connect bones and promote movement.
Ligaments
Fibrous connective tissues that connect bones to bones, providing stability.
Cartilage
Smooth, elastic tissue that cushions joints and reduces friction.
Primary functions of the skeletal system
Support and structure, movement, protection, mineral storage, blood cell production, and fat storage.
How does the skeletal system support and structure the body?
It provides a rigid framework that supports organs and muscles.
Hematopoiesis
The process of blood cell production that occurs in the red bone marrow found within bones.
Minerals are stored in bones
Calcium and phosphorus, essential for bone health and overall body function.
What type of marrow is responsible for fat storage?
Yellow bone marrow, found within bones.
Function of yellow bone marrow
Store fat
How does the skeletal system protect vital organs?
The skull, rib cage, and spine protect vital organs like the brain, heart, and lungs.
Divisions of the skeletal system
Axial and appendicular
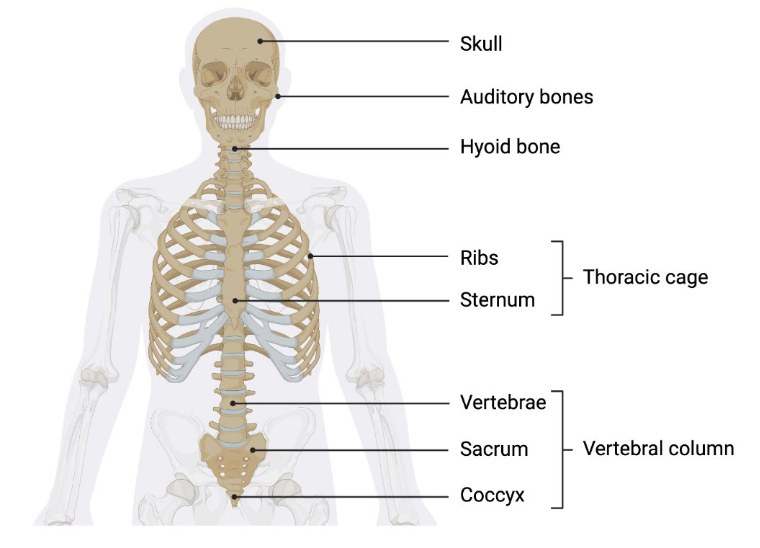
Components of axial skeleton
Skull
Vertebral column
Thoracic (rib) cage
Hyoid bone
Hyoid bone
Unique bone in the throat that doesn't articulate with any other bone but provides attachment for muscles of the tongue and neck
Functions of axial skeleton
Protection
Support
Attachment
Balance and movement
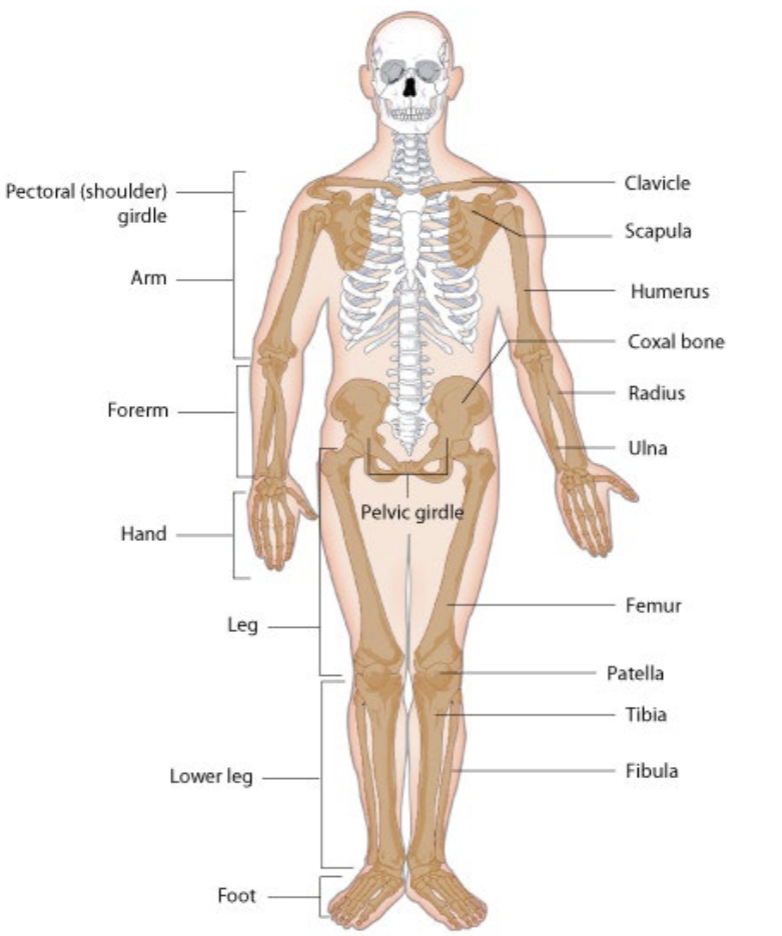
Appendicular skeleton
Comprises bones of the upper and lower extremeties
Number of bones in the appendicular skeleton
126
Functions of the appendicular skeleton
Locomotion
Weight transmission
Muscle attachment
Locomotion
The lower limbs are adapted for standing and walking, while the upper limbs are used for grasping and manipulating objects
Weight Transmission
The pelvic girdle helps to support the body's weight and transmit it to the ground through the lower limbs
Muscle Attachment
Provides attachment points for many muscles, allowing for a wide range of movements
Bone fusing
A baby's body has 270-300 bones at birth, some of which are made entirely of cartilage. These bones eventually fuse to form the 206 bones that adults have.
Long bones
Cylinder-like shape, longer than it is wide; function in leverage. Examples include femur, tibia, fibula, metatarsals, humerus, ulna, radius, metacarpals, phalanges.
Short bones
Cube-like shape, approximately equal in length, width, and thickness; provide stability, support, while allowing for some motion. Examples include carpals, tarsals.
Flat bones
Thin and curved; points of attachment for muscles and protectors of internal organs. Examples include sternum, ribs, scapulae, cranial bones.
Irregular bones
Complex shape; protect internal organs. Examples include vertebrae, facial bones.
Sesamoid bones
Small and round; embedded in tendons; protect tendons from compressive forces. Example includes patellae.
Bone density
The total amount of bone tissue continues to increase slowly until the late 20s.
Bone growth cessation
Bones stop growing in length between the ages of 16 and 18.
Joints/articulations
Connections between two or more bones
Structural classification of joints
Based on the structure of joints.
Fibrous joints
Joints connected by dense connective tissue, which are immovable (e.g., skull sutures) or slightly movable (e.g., radioulna joint).
Cartilaginous joints
Joints connected by cartilage, which are partially movable (e.g., spine).
Synovial joints
Joints with a fluid-filled capsule and ligaments, which are freely movable (e.g., shoulder and hip joints).
Functional classification of joints
Classification based on the function of joints.
Synarthrosis
Immovable joints (e.g., skull sutures).
Amphiarthrosis joint
Slightly movable joints (e.g., between the two halves of the pelvis).
Diarthrosis
Freely movable joints (e.g., shoulder and hip joints).
Sutures
Fibrous joints found between the bones of the skull, allowing minimal movement in infants but not adults.
Gomphoses
Fibrous joints occurring between teeth and their sockets in the jawbone, providing support for teeth.
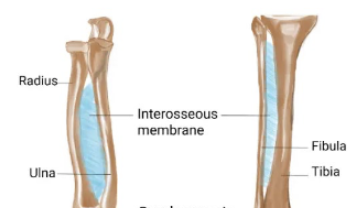
Syndesmoses
Fibrous joints where two parallel bones are joined by connective tissue, allowing slight movement (e.g., tibio-fibula joint).
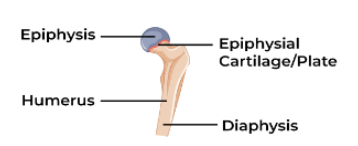
Synchondrosis
A temporary cartilaginous joint formed by hyaline cartilage (e.g., epiphyseal plates in children).
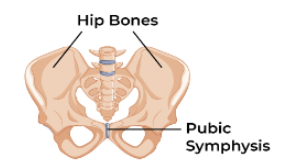
Symphysis
A permanent cartilaginous joint formed by fibrocartilage (e.g., intervertebral discs).
Ball and socket joint
A synovial joint where one bone fits into a socket of another bone (e.g., hip, shoulder).
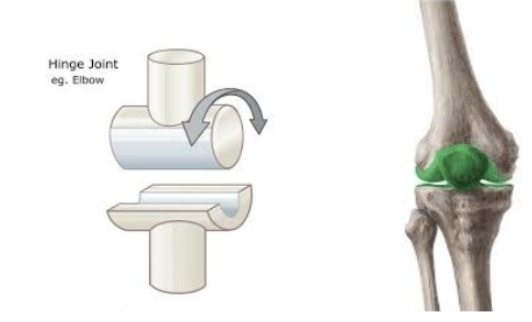
Hinge joint
A synovial joint where one bone moves back and forth on another (e.g., elbow, knee).
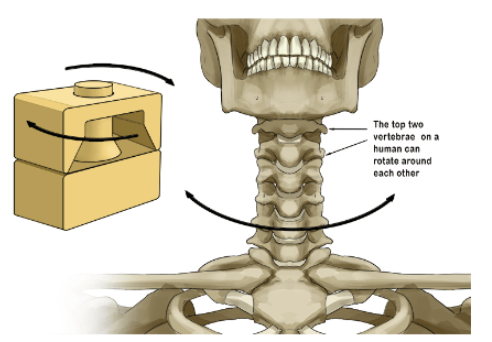
Pivot joint
A synovial joint where one bone rotates around another (e.g., neck).
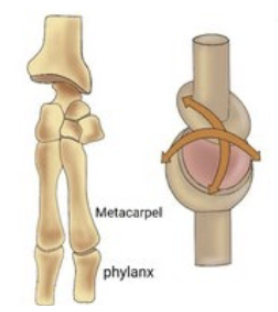
Condyloid joint
A synovial joint where one bone moves in two directions on another (e.g., wrist).
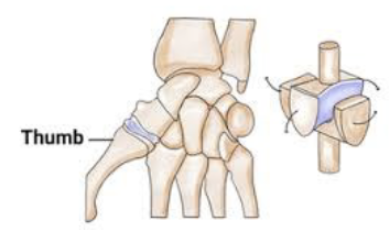
Saddle joint
A synovial joint where one bone moves in two directions on a saddle-shaped bone (e.g., thumb).
Functions of joints
Flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, rotation, and gliding, and provide cushioning, stability, and lubrication.
Why is cartilage considered a slow-healing tissue?
Due to its lack of blood supply.
What conditions can result from damage to cartilage?
Osteoarthritis and joint pain.
Cells that produce cartilage
Chondrocytes, which are produced by chondroblasts.
Main components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) of cartilage
Collagen, proteoglycans, ground substance, elastin fibers, and hyaluronic acid.
What type of collagen is primarily found in cartilage?
Type II collagen.
Function of proteoglycans in cartilage
Retain water and provide cushioning.
Properties of cartilage
Avascular (lack blood vessels) and aneural (lack nerves).
Three main types of cartilage
Hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage.
Hyaline cartilage
Most common type, somewhat flexible, rich in type II collagen, found in joints, nose, ribs, and trachea. Provides smooth, low-friction movement in joints.
Fibrocartilage
A dense network of thick type I collagen fibers, making it the strongest type of cartilage, least flexible. Provides support and shock absorption to intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, and menisci.
Elastic cartilage
Provides flexibility and support, found in the ear, epiglottis, and larynx.
Fibroelastic cartilage
A type that combines properties of elastic and fibrocartilage, found in the temporomandibular joint.
Functions of cartilage
Cushioning joints, supporting and protecting bones, maintaining joint flexibility, and shaping body structures.
What role does cartilage play in the shape of body structures?
It contributes to the shape and support of structures like the nose, ears, and trachea.
Two parts of long bone
Diaphysis and epiphysis
What does the periosteum contain?
Blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels
What type of cartilage is articular cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage
Flat bone
Consist of a layer of diploe (spongy bone). Protect internal organs.
Facet
Small, flat articular surface
Trochlea
Smooth, grooved articular process
Sulcus
A narrow groove
Sinus
Air-filled space in the bone
Fissue
Deep furrow, clef or slit
Osteoblasts
Responsible for forming new bone tissue and secrete proteins and minerals that mineralize and create bone matrix. Located on surface of bones.
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells that reside within the bone matrix. Maintain bone tissue and regulate mineral content. Connected to each other through a network of channels called canaliculi.
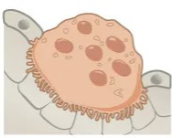
Osteoclasts
Break down and resorb bone tissue. Multi-nucleated cells that release enzymes to dissolve bone matrix. Essential for bone remodeling and repair
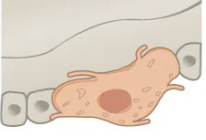
Osteogenic cell
Only bone cells that divide
Two types of bone tissue that make up the human skeleton
Compact bone and spongy bone.
Primary function of compact bone/Cortical
To provide strength and protection to the skeleton.
Compact/Cortical bone location
It forms the hard, dense outer shell of all bones, including long bones, ribs, and flat bones of the skull.
Osteon
The primary functional and structural unit of compact bone, forming a cylindrical structure.
Haversian canal
A central canal within each osteon containing blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels.
Lamellae
Concentric rings of hardened bone matrix surrounding the Haversian canal.
Lacunae
Small spaces where osteocytes are located within compact bone.
Canaliculi
Tiny, branched canals that connect the lacunae, allowing for the transport of nutrients and removal of waste from osteocytes.
Perforating canals
Channels that run perpendicular to Haversian canals, connecting them to the periosteum and endosteum.
Spongy bone
A porous, honeycomb-like tissue found at the ends of long bones and in the middle of other bones, containing osteocytes in a lattice-like network.
Function of trabeculae in spongy bone
Provide strength to the bone by forming along lines of stress and making bones lighter.
Hematopoiesis
The process of blood cell formation that occurs in the red marrow found in some spongy bones.
How do spongy bone and medullary cavity receive nourishment?
Through arteries that pass through the compact bone via nutrient foramina and from blood vessels of the periosteum.
Role of nerves in bone
Sense pain and help regulate blood supplies and bone growth, concentrating in metabolically active regions.
Ossification
The process of bone development that begins in the sixth or seventh week of embryonic life.
Intramembranous ossification
The direct development of bone from mesenchymal connective tissue, forming flat bones like those of the skull.
Steps of intramembranous ossification
Formation of ossification center
Osteoid secretion
Mineralization and osteoblast trapping
Osteocyte formation
Blood vessel incorporation
Spongy bone formation
Compact bone formation.
Bones formed through intramembranous ossification
Flat bones such as the skull bones, clavicle, mandible, and maxilla.
Endochondral ossification
The process where cartilage is converted into bone, occurring in long and short bones.
Stages of endochondral ossification
Formation of cartilage
Maturation of chondroblasts
Hypertrophy and matrix calcification
Death of chondrocytes
Blood vessel invasion
Formation of primary ossification center
Formation of secondary ossification center
Bones are formed through endochondral ossification
Long bones like femur, tibia, humerus, and short bones like tarsals and carpals.
Age do humans typically stop increasing in height
Between the ages of 18 and 20, due to the closure of growth plates.