Pathophysiology Lecture 3: Chromosome Abnormalities
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Chromosome Aberrations
changes in chromosome structures, most commonly occur as breaks that are incorrectly repaired during replication
examples of deletions, duplications, inversions, translocation, and reciprocal translocation
Deletion
removal of a chromosomal segment, which can be identified by sequencing or PCR
Homozygous deletion
lethal deletion
Heterozygous deletion
deletion that causes severe developmental delays and can allow a mutant recessive allele to appear (pseudodominance)
Terminal Deletion
end is lost
Interstitial Deletion
where two breaks occur and the middle is lost
Tandem Duplication
adjacent duplication
Dispersed Duplication
Spread out duplicate
Duplication
repeating a segment; change in gene dosage which can impact a pathway
Inversion
reverses orientation of a segment within a chromosome
Pericentric inversion
inversion that includes the centromere
Paracentric inversion
inversion that does not include the centromere
Translocation
moves a segment from one chromosome to another
-can be balanced or unbalanced
-balanced will have no phenotypic effect but may be dangerous for future generations
9, 22
Philadelphia Chromosome results from translocation between chromosome _ and __
Reciprocal translocation
exchange of segments between nonhomologous chromosomes
Somatic mosaicism
changes in chromosome structure and number can also occur in somatic cells during mitosis, resulting in a mosaic since not all of the cells in the body will be affected
Germline mosaicism
when some egg or sperm cells carry a mutation and others do not
-parents will have no phenotype typically as the mutation would only have an impact on somatic cells
-depending on which gamete is fertilized, offspring may be affected (mom vs dad)
-example of osteogenesis imperfecta
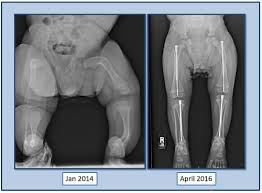
5, 50
Frequencies of chromosomal abnormalities:
_% of sperm
__% of oocytes
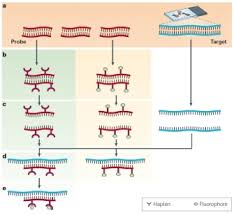
FISH
fluorescent in situ hybridization
-uses a probe containing a fluorescent marker of a complement of a known genetic sequence, which are mixed with patient DNA. If hybridization occurs, it can be detected by fluorescence
-advantages: can help detect deletions and duplications, chromosome painting, and cells do not have to be dividing
-Prader willi and Angelman syndrome can be detected using this
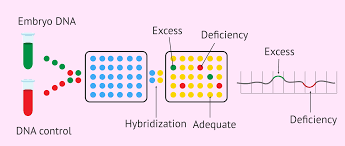
Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (aCGH)
compares sample DNA to known reference DNA, used to identify deletions and duplications
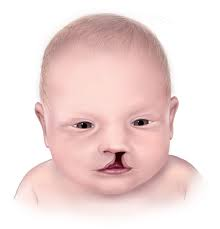
deletion, 4
Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome is caused by a ______ in the terminal end of chromosome _. The displayed phenotypes are microcephaly, cleft lip, and possible cleft palate
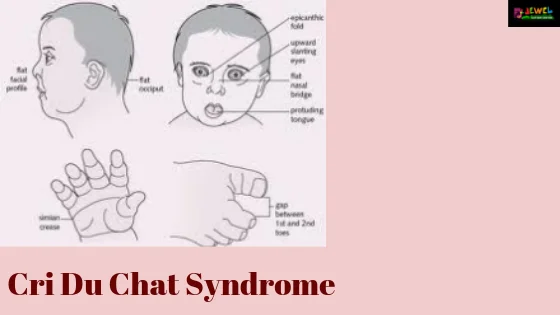
deletion, short, 5
Cri-du-chat is caused by a ______ of terminal end of the ____ arm of chromosome _. Phenotypes include distinctive cry, low birth weight, microcephaly, hypertelorism, round face, micrognathia, and severe cognitive impairment
Contiguous gene syndrome
disorders with a recognizable phenotype that are associated with a specific chromosomal abnormality, changes can be identified using FISH or karyotype
characteristics:
-recognizable phenotype
-individual is typically heterozygous
-condition is familial typically in a Mendelian nature
-typically show variable expression
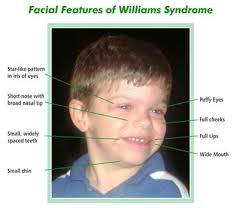
Williams Syndrome
an example of a contiguous gene syndrome
-caused by deletion 7q11.23, which is the elastin gene that codes for elastin protein in connective tissue
-phenotype: short statue, elf like features, satellite iris pattern, hypercalcemia, and vascular changes
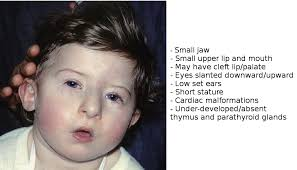
DiGeorge Syndrome
a condition caused by a deletion in 22q11.2
phenotypes:
-hypoplasia or aplasia of the parathyroid glands resulting in a T-cell deficiency
-defect in 3rd and 4th developmental field resulting in congenital heart malformations
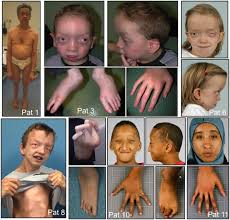
Shprintzen Syndrome
caused by a deletion in 22q11.2
phenotypes:
-cleft palate
-velvo-palatal insufficiency
-heart malformations
-learning disabilities
Uniparental disomy
when an individual inherited both copies of an allele or chromosome from one parent. Important when a patient inherits two recessive alleles from one parent
-example of cystic fibrosis
Imprinting
when gene expression is determined by whether the gene comes from mother or father
-gene that is not being expressed is typically methylated
Prader Willi and Angelman Syndrome
What conditions are examples of imprinting?
Prader Willi Syndrome
-cause: deletion at 15p1113, inherited from father
-phenotypes: hypotonia, cognitive deficits, typical facial changes, obesity, and small hands and feet
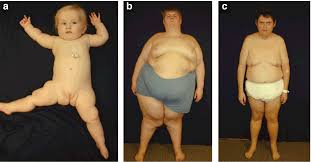
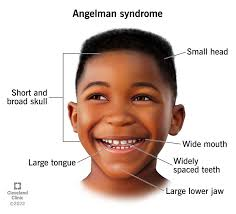
Angelman Syndrome
cause: deletion at 15p1113, inherited from mother
phenotype: seizure, abnormal gait, happy behavior
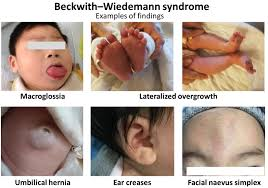
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
What is an example of uniparental disomy?
-caused by inheriting two copies of chromosome 11 from the father
-phenotype: overgrowth, heightened risk of cancerous tumors, large tongue at birth, creases on earlobes, omphalocele
Russell-Silver Syndrome
-a condition caused by maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 11
-phenotypes of slow growth, small triangular shaped face
Compound Heterozygosity
having mutations on both inherited genes, but at different points of the gene
Digenic inheritance
mutations occurring at two different genes
Infant Hearing Loss
What is an example of a condition that can be caused by compound heterozygosity or digenic inheritance?
Multi locus inheritance
phenotype is the result of mutations at more than one locus
-Example of modifier genes, which influence the expression of other genes
van der Woude Syndrome
caused by a mutation in IRF2 gene on chromosome 1
phenotypes: lower lip pits and cleft lip/palate with variable expression
the variable expression is controlled by another mutation on chromosome 17
Epigenetics
ability to change gene expression without altering genetic code
mechanism: chromatin modification, DNA methylation, histone acetylation, RNA associated silencing, and imprinting X inactivation