BACT LAB: CULTURE & CULTURE MEDIA
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
CULTURE
Growth of microorganism (lots of colonies) in a culture media
CULTURE MEDIA
Mixture of nutrients such as:
Carbon
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Buffers
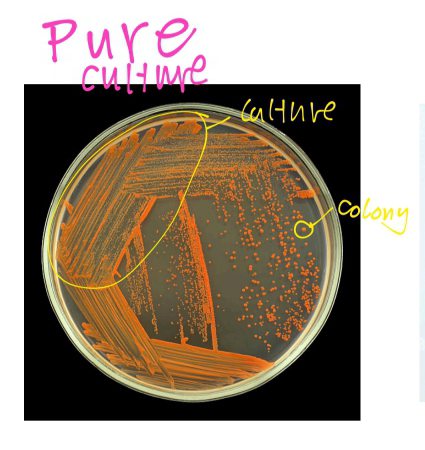
PURE CULTURE
Composed of only 1 species and the goal in bacteriology
MIXED CULTURE
Composed of more than 1 species

STOCK CULTURE
Several culture species contained in separate culture medium (1 species per culture medium)
used for academic & industrial purposes
LIQUID MEDIUM
0% agar; allows growth of aerobes, Also known as “broth”
Brain heart infusion
Trypticase soy broth (TSB)
Thioglycollate
SEMI-SOLID MEDIUM
0.5 - 1% agar; observe bacterial motility and detect presence of indole and sulfide production
Sulfide indole motility medium
COLONY
used to describe a single isolated microorganism in a culture medium
TURBIDITY
Indication of bacterial growth in liquid medium becuase you can’t see colonies
18 - 24 HOURS
This is the average time of using liquid medium as an enrichment broth (to propagate microorganisms)
In semi-solid medium, a microorganism is considered motile when there is __________ outside of the puncture area.
DISPERSION / SIGN OF GROWTH
SOLID MEDIUM
2 - 3% agar; is always plated
Triple sugar iron agar (TSI)
MacConkey agar (MAC)
Blood agar plate (BAP)
Chocolate agar plate (CAP)
SYNTHETIC / DEFINED MEDIUM
Known components
Research purposes
Preferred for isolation of cyanobacterium & chemoorganotrophs
BG-11 medium
NON-SYNTHETIC / COMPLEX MEDIUM
Unknown substances
Peptones
Meat
Yeast extract
Isolation of medically significant bacteria
Nutrient broth medium (NB)
TSB
MAC
TISSUE CULTURE MEDIUM
Used for obligate intracellular bacteria
Rickettsia
Chlamydia
HeLa 299 cells
Human cervical tissue
McCoy cells
Fibroblast
W138 cells.
Fibroblast.
PLATE MEDIA
Distribued into petri dish or plate
TUBE MEDIA
Prepared as butt, slant, or both butt and slant
TSI
SIM
Simmon’s citrate agar
Lysine iron agar (LIA)
STAB
Distribution method for butt, uses needle
ANAEROBIC
FISH TAIL METHOD
Distribution method for slant, uses inoculating loop
AEROBIC
NUTRITIVE MEDIA
Routinely used w/o supplements
Supports growth of most non-fastidious bacteria
Meat & Soy bean extract
Nutrient agar (NA)
NB
TSB
ENRICHMENT MEDIA
Propagate certain group of bacteria from mixed culture
Contains specific nutrients w/o additional supplements
Alkaline peptone water (vibrio)
Selenite F. (salmonella)
Thioglycollate
Tetrathionate
Gram-neg broth
Lim broth (Streptococcus agalactaea)
The RBC in a blood agar plate should be ________ to indicate intact cellular structure.
INTACT
The RBC in a chocolate agar plate should be __________ for hemoglobin and NAD.
LYSED
SHEEP’s BLOOD
Your first choice of blood when preparing a BAP
BAP BLOOD CHOICES
Sheep
Horse
Human
Your first choice of blood when preparing a BAP from a human should be __________.
O+
DIFFERENTIAL MEDIA
Allow visualization of metabolic differences between groups of bacteria
MAC
BAP
Eosin methylene blue (EMB)
Hektoen enteric agar (HEA)
Mannitol salt agar (MSA)
PINK
Color of organism when it has the ability to ferment lactose (MAC)
COLORLESS
Color of organism when it doesn’t have the ability to ferment lactose (MAC)
ALPHA HEMOLYSIS
Partial hemolysis w/ greenish coloration
Escherichia coli
BETA HEMOLYSIS
Complete hemolysis w/ clearing of blood
Streptococcus pyogenes
GAMMA HEMOLYSIS
No hemolysis
Staphylococcus epidermidis
SELECTIVE MEDIA
Incorporated w/ antibiotics, dyes, or chemicals to inhibit growth of other organisms
HEA
MAC
Xylose lysine deoxycholate agar (XLD)
Bismuth sulfate agar (BSA)
MSA
Thayer-Martin agar (TMA)
GENTAMICIN BLOOD AGAR
Streptococcus
BACITRACIN CHOCOLATE AGAR
Haemophilus
BAP W/ AMPICILLIN
Aeromonas
PHENYLETHYL ALCOHOL
Gram + bacteria
COLISTIN-NALIDIXIC ACID AGAR (CNA).
Gram + bacteria.
INHIBITORY SUBSTANCE FOR GRAM ( + ) BACTERIA
Crystal/Gentian violet
Basic/Carbol fuchsin
Bile salt
INHIBITORY SUBSTANCE FOR GRAM ( - ) BACTERIA
Potassium tellurite
Sodium azide
INHIBITORY SUBSTANCE FOR SWARMING BACTERIA
Alcohol
Chloral hydrate
A SWARMING BACTERIA SPECIES
Proteus spp.
HEKTOEN ENTERIC AGAR (HEA)
Inhibits indigenous microbiota of the lower gastrointestinal tract (LGIT)
Recovery of fecal bacteria
Contains Bile salt & dyes
pH indicator = Bromthymol blue
MACCONKEY AGAR (MAC)
Inhibits gram ( + ) bacteria
Recovery of fecal bacteria
Contains Bile salts & Crystal violet
XYLOSE LYSINE DEOXYCHOLATE AGAR (XLD)
For fecal bacteria
Differentiates Shigella & Salmonella
Contains:
Xylose
Lysine
Sucrose
0.25% sodium deoxycholate & sodium thiosulfate
MANNITOL SALT AGAR (MSA)
Supports growth of Staphylococcus aureus (a halophile)
THAYER-MARTIN AGAR (TMA)
Selective for Neisseria sp.
SPECIAL MEDIA
Isolate bacteria w/ specific growth requirements
Lowenstein-Jensen medium (LJ)
Thiosulfate citrate-bile salts-sucrose agar (TCBS)
BLOOD AGAR PLATE (BAP)
Differentiate hemolytic pattern of bacteria
CHOCOLATE AGAR PLATE (CAP)
Recovery of Haemophilus
STEPS IN MEDIA PREP (PLATES)
Weigh
Dissolve (distilled H2O)
Sterilize (autoclave)
Dispense
STEPS IN MEDIA PREP (TUBES)
Weigh
Dissolve
Dispense
Sterilize
Set the autoclave to ______ psi for ______ minutes at ______° C.
15 psi; 15 minutes; 121° C.
Aseptically dispense approx. ____ ___ of agar in sterile petri plates
25 mL
Solve for the agar amount needed for 20 plates
Given: suspend 40g in 1,500mL
13.33g
