Econ final exam
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Prices
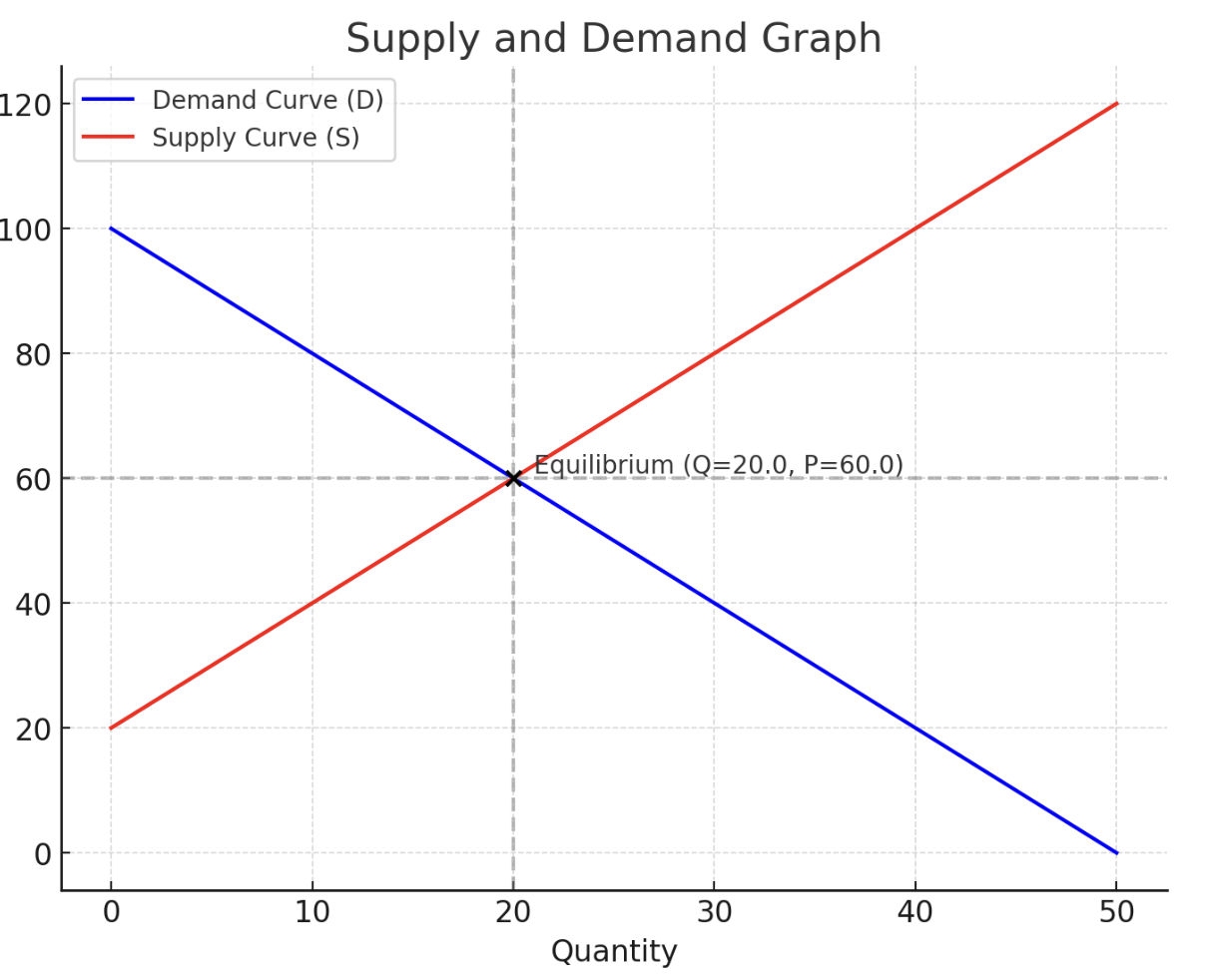
Prices fluctuate depending on the movement of buyers and sellers.;Price correlates with quantity when there is equilibrium
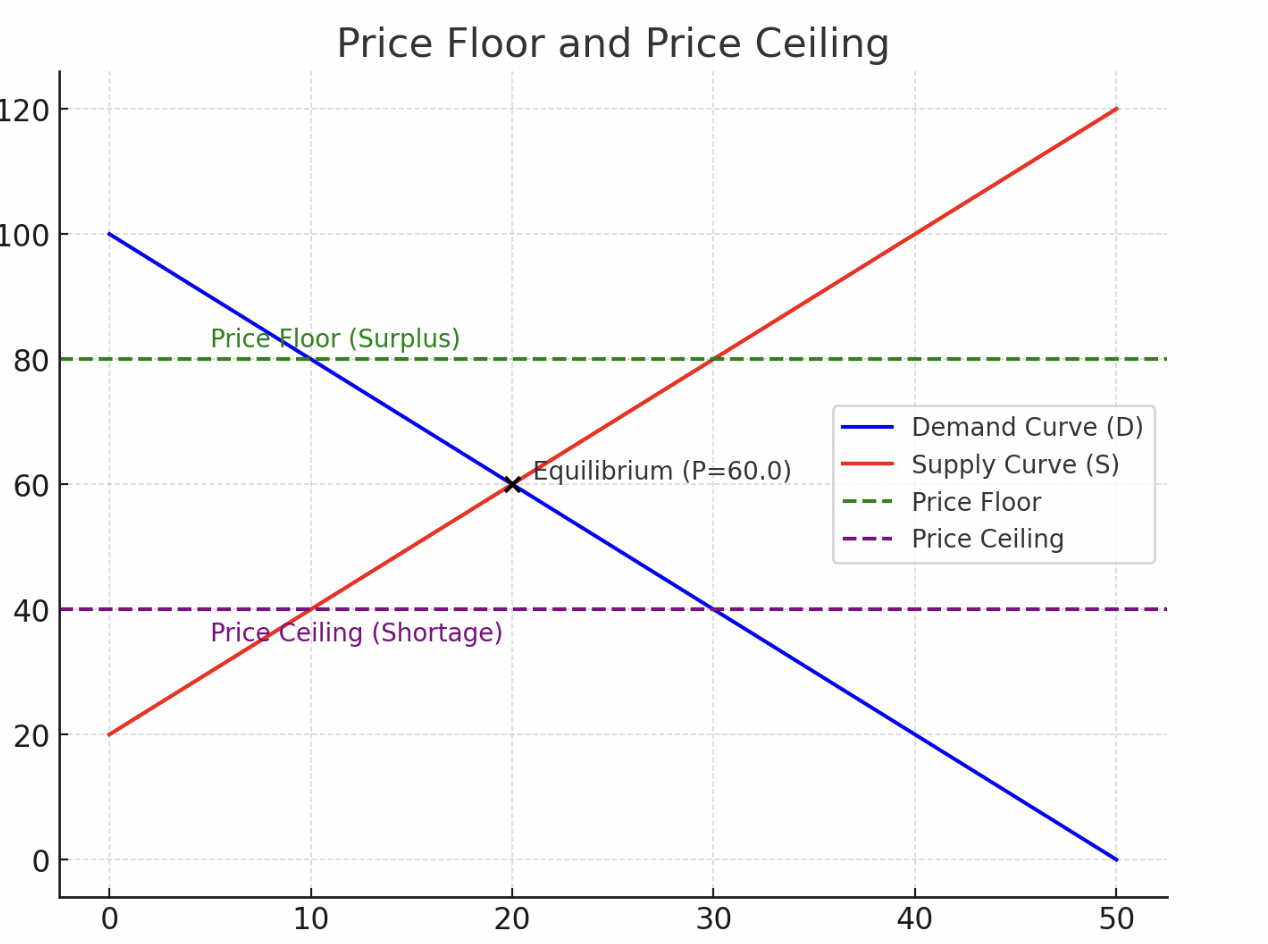
When there is more of a good than there is the demand for it;there is a surplus of a good if it is one cent above the equilibrium
When a stockholder sells an investment for more than they paid.
When a stockholder sells an investment for less than they paid.
When the stock market falls over time
When the stock market rises over a period of time.
Thinking at the margin
the process of deciding how much more or less to do
Land
all natural resources used to produce goods and services
Labor
Workers, people who make the products
Entrepreneur
Use these things to make money, most entrepreneurs fail or take a long time to turn a profit.
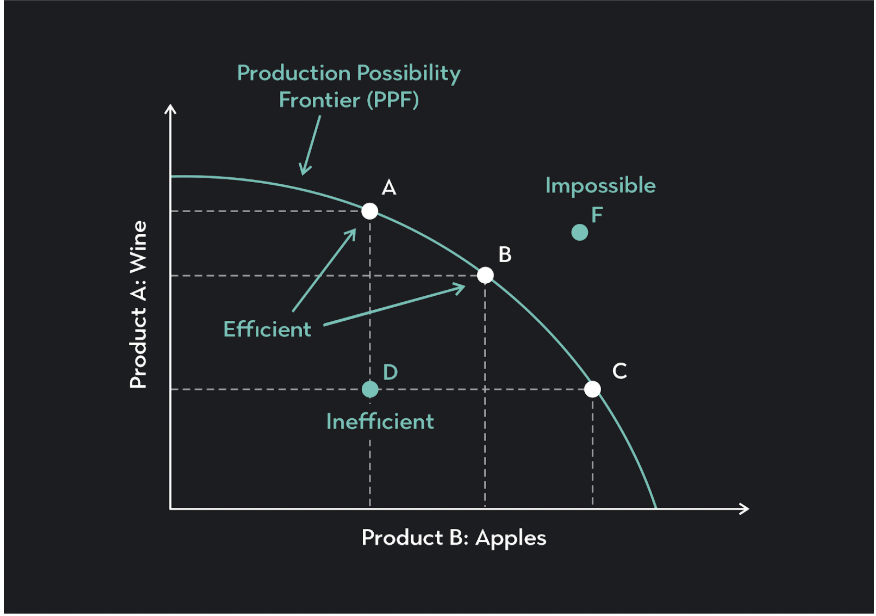
productions possibility curve
demand
the want and ability of consumers to buy something/ will pay for goods and services
Causes of Demand Curve shifts
income
Consumer expectations
Population
Consumer tastes
Income effect
People's income detriment to their demand
As people's income goes up, they will buy more goods
normal goods Income up Demand up, Income down Demand Down
inferior goods Income up Demand down, Income down Demand up
Supply
Supply is seen in the eyes of the producers and is the incentive that as price increases so does supply; Total amount of good/ service at each price point
Causes of the Supply Curve to shift prices can cause the supply curve to shift
Left shift-decrease
Right shift-increase
As input price increases supply decreases
Causes for supply to shift(determinants)
supply determinants.
Price of the good or service (law of supply)
Technology can reduce input cost increasing supply
The global economy sets the relative price
Natural conditions such as weather or natural disasters can slow production
shortage
when there is less of a good than there is the demand for it; If the price is lower than the equilibrium it is a shortage
Money
Anything that a person can use to purchase goods or services. Replaces the need for bartering.
6 characteristics of money
durability, uniformity, limited supply, divisibility, acceptability, portability
uniformity
People must be able to count and measure money accurately;$1=$1 in every marketplace
limited supply
Money would lose its value if there was an unlimited supply of it so it must be regulated and only have a certain amount
divisibility
Can easily be divided into smaller denomination
acceptability
Everyone in the economy must be able to accept the objects used as money
portability
Easy to carry around with you
fiat money
money that has value since the gov. says it has value
representative money
exchanged money for something else of value;:Personal checks/ debit card (checking account) / gold/ silver / IOU note/gift cards
commodity money
Any money that his value in of itself
Banking System
a group or network of institutions that provide financial services for us.
How do banks create a profit?
Banks earn profits by lending money at higher interest rates than they pay on deposits/ex. Checking/ saving accounts
Investment
the process of investing your money in an asset with the objective to grow your money in a stipulated time period; Not consuming today in hopes of growth in the future
Diversification
spreading out of investments to reduce risk
Stock
Stocks consist of all the shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided. A single share of the stock means fractional ownership of the corporation in proportion to the total number of share; Partial ownership in a firm in hope that the firm will gain money
Share
A portion of a stock
Risks involved with investment
Purchasing stock is risky because the firm selling the stock may encounter economic downturns that force dividends down or reduce the stock’s value. It is considered a riskier investment than bonds.
Dow Jones Industrial average
an index that shows how stocks of 30 companies in various industries have changed in value.
S & P 500
an index that tracks the performance of 500 of the top stocks
Brokerage account
A brokerage account is a type of investment account opened with a brokerage firm. You can deposit money into a brokerage account and the brokerage firm will execute investment orders at your request. Many investors use brokerage accounts to purchase stocks, bonds, mutual funds or exchange-traded funds online
What gives cryptocurrency its value?
Both scarcity and its demand due to its increasing price are what give cryptocurrency its value.
Supply vs demand
price floor and price ceiling