Equine Coat Colors
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
light horse breeds
for running, hunting, etc.
Thoroughbreds, Appaloosa, Quarter horse
Characteristics of light horses
Thin coat
Thin legs
Lean muscles
Draft horses
bred for pulling, farm work, and plowing
Draft horse characteristics
Stalky legs
Muscular
Thick shoulders and neck
Pony characteristics
Under 14.2 hands (measure hoof to withers/last hair of their mane)
Round bellies
Middle of stocky and lean
Warm-blood horses
Bred for undersaddle work (athletics)
A cross between a hot-blood and a cold-blood (draft + light horse)
3 basic coat colors
black
bay
chestnut
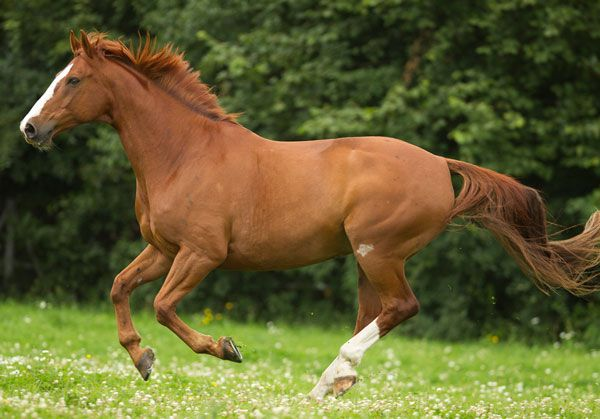
Chestnut
Reddish-brown coat
Main/tail typically matches body color
No black main/tail

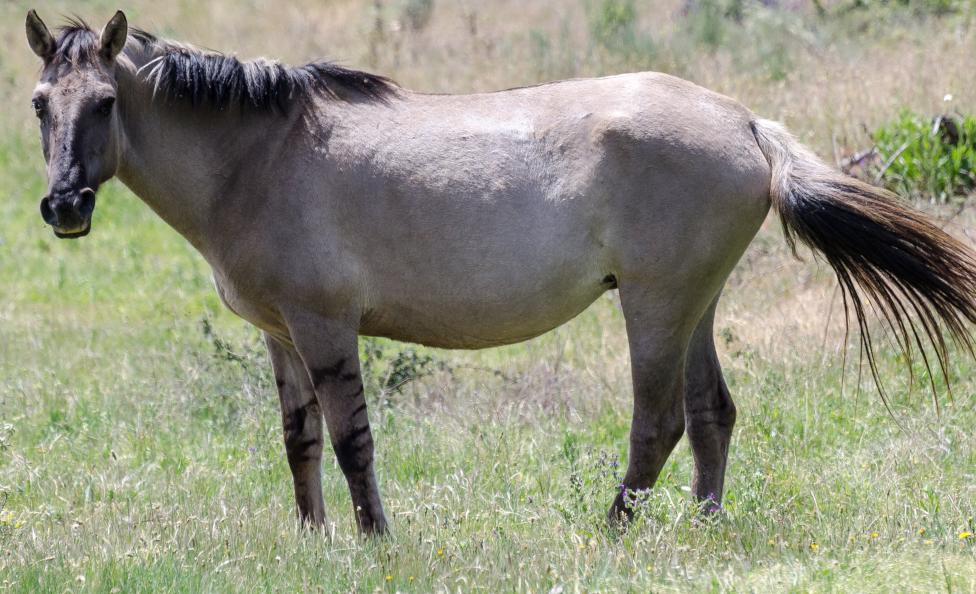
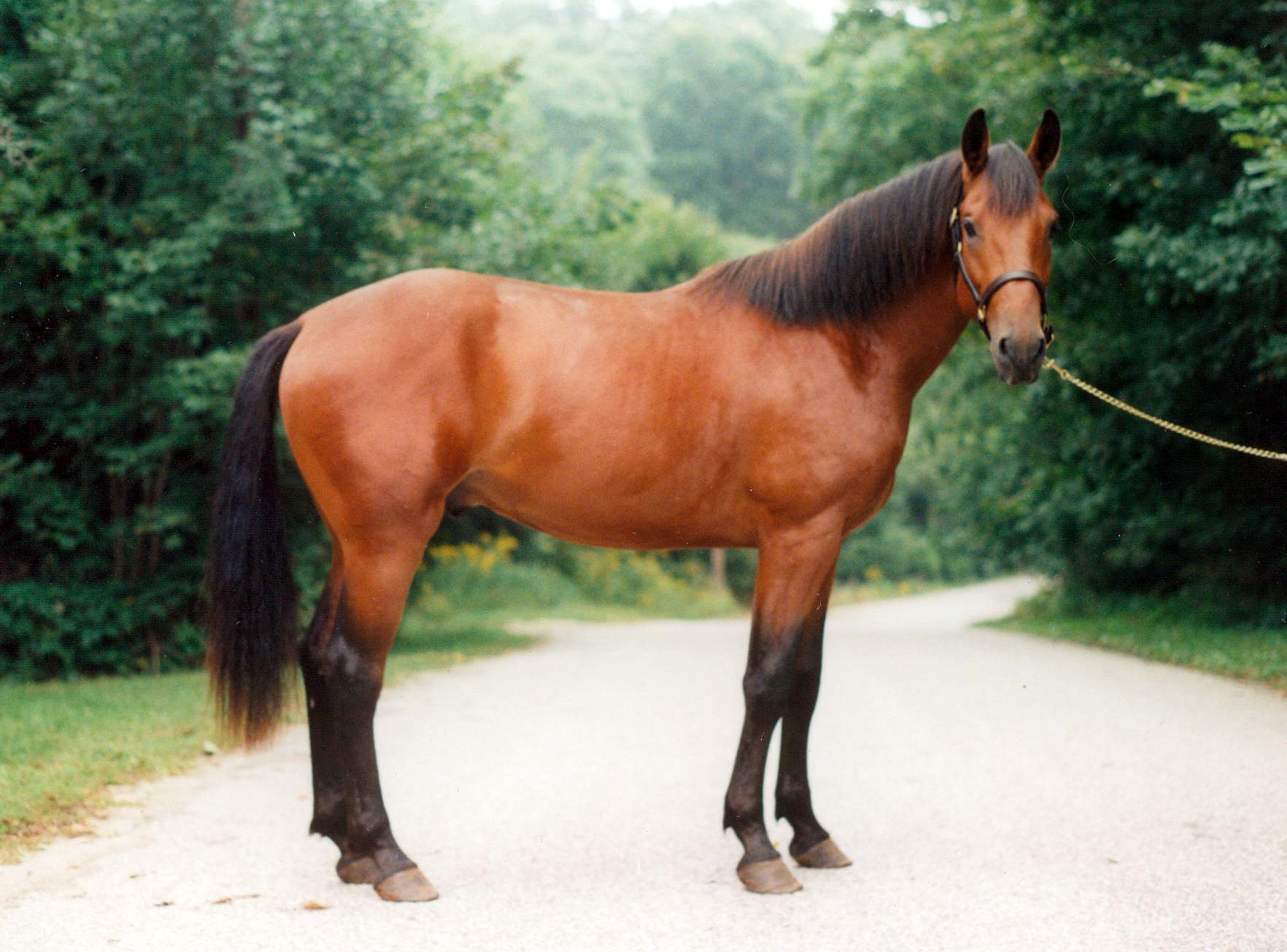
bay
Dark brown with black points (mane/tail, legs, ears)

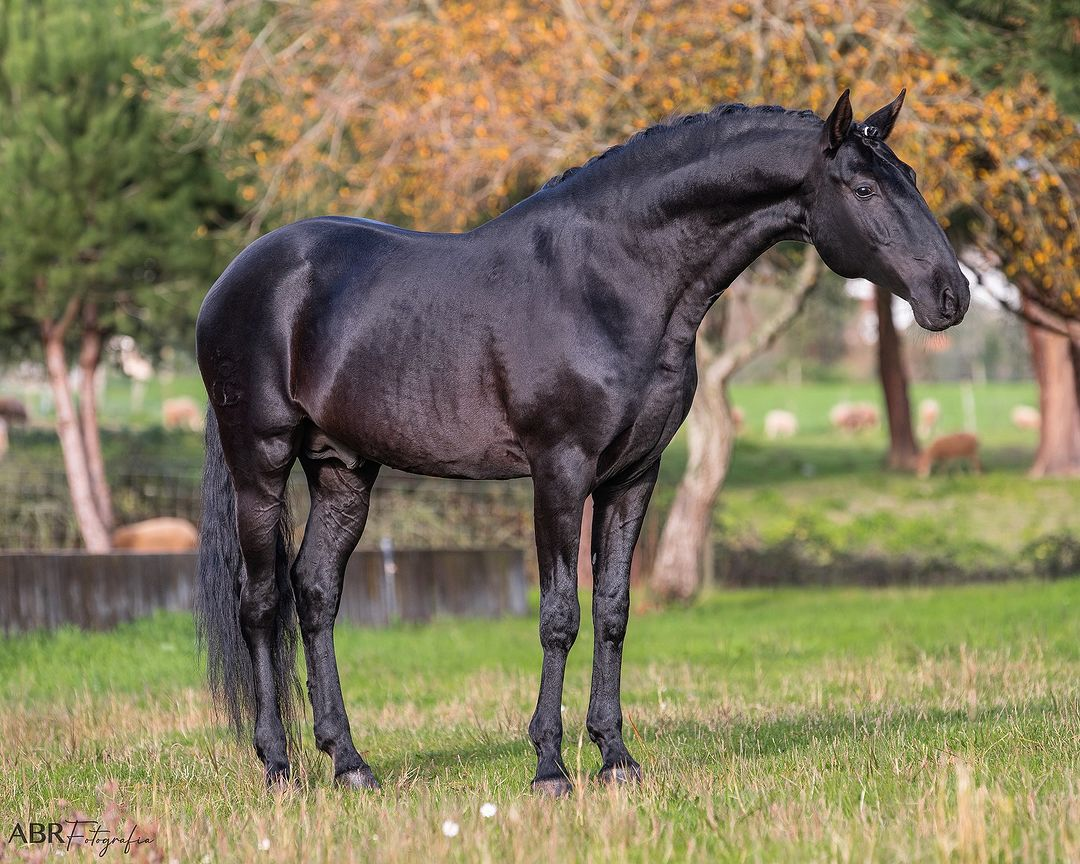
black
Black body and mane/tail
No light points

Grey
Dapples
No pink skin, grey skin instead
As it ages, the coat changes
Could be brown, but then turns grey
Grey turns to white
Prone to benign sarcomas and melanomas
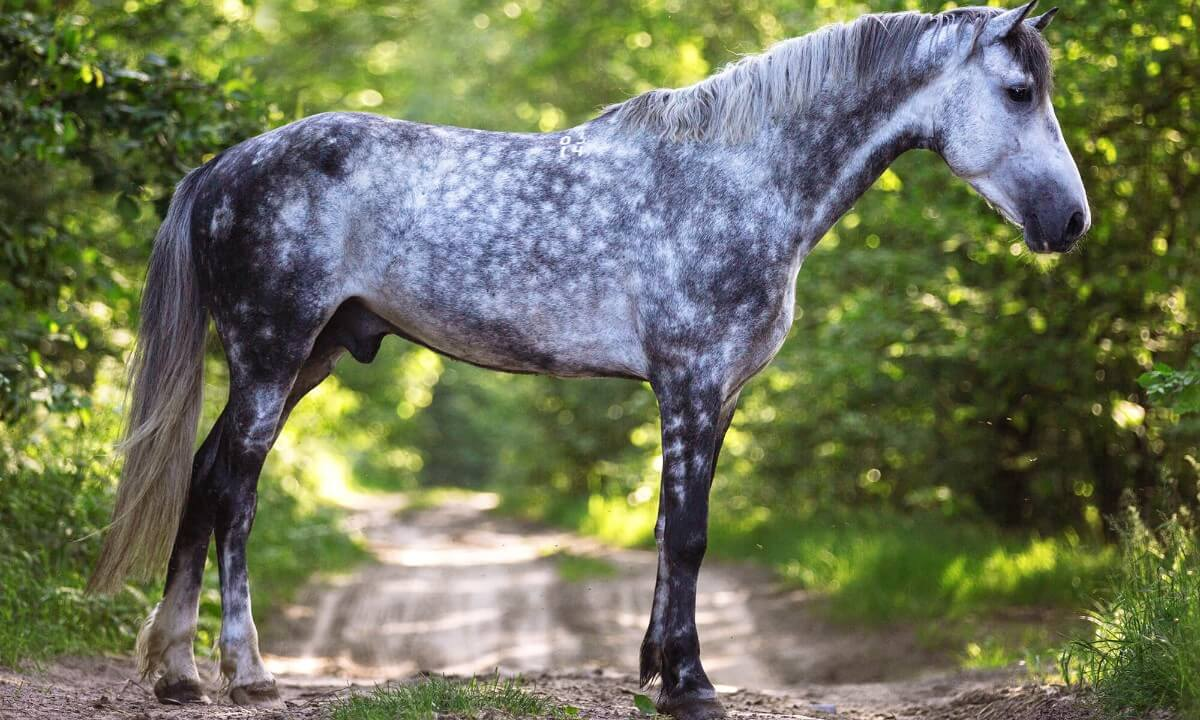

Roan
Red or strawberry, or blue
Tend to be lighter in warmer weather and darker in colder weather
Will have a solid color head with a mixture of white on the body

dun
Primitive markings must be present

primative markings

red dun

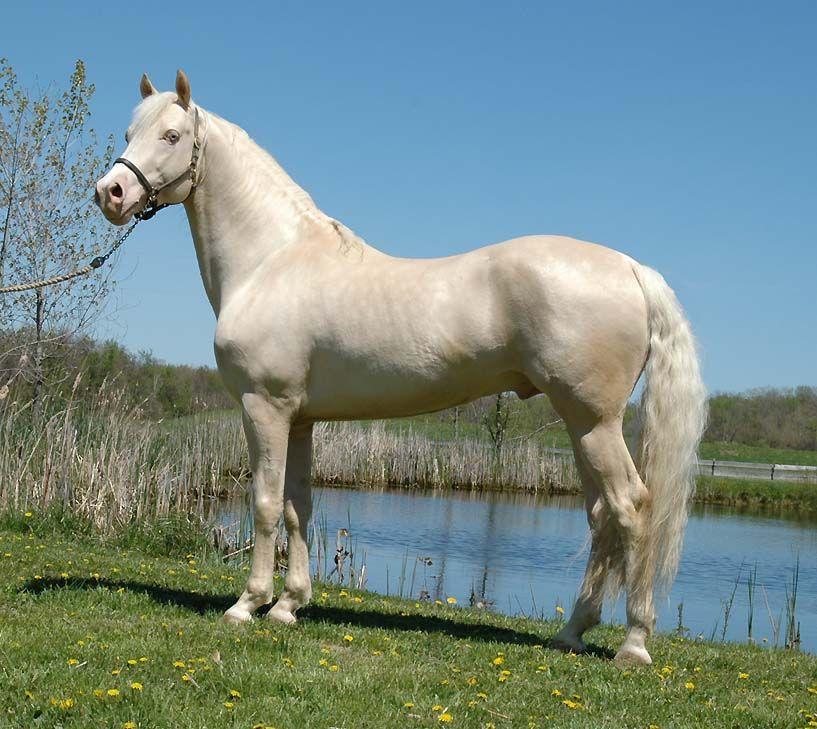
Cream
The dilution gene acts on a chestnut coat, lessening the color of the hair, not mixing in white hairs

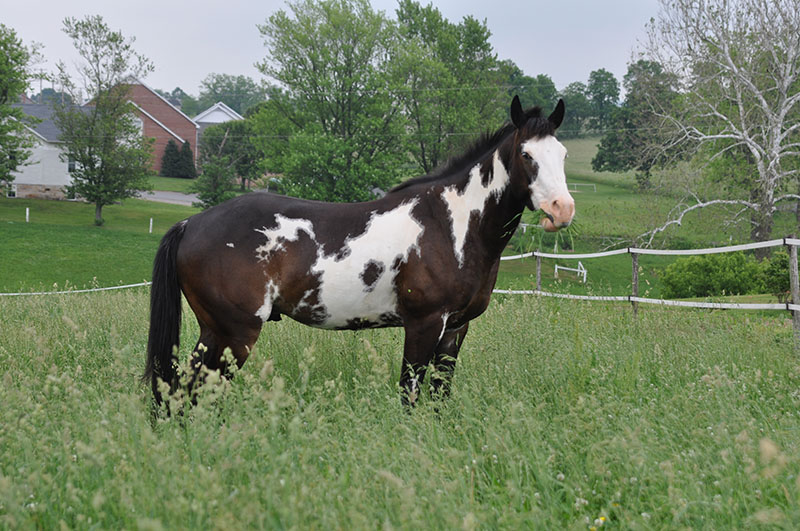
Pinto
Can be any breed
Various color patterns are named
Leopard patterning (Appaloosa) is not permitted
Paint- specific to pedigree, must have one parent as a recorded QH or TB

Palomino
Golden horses with silver manes and tails
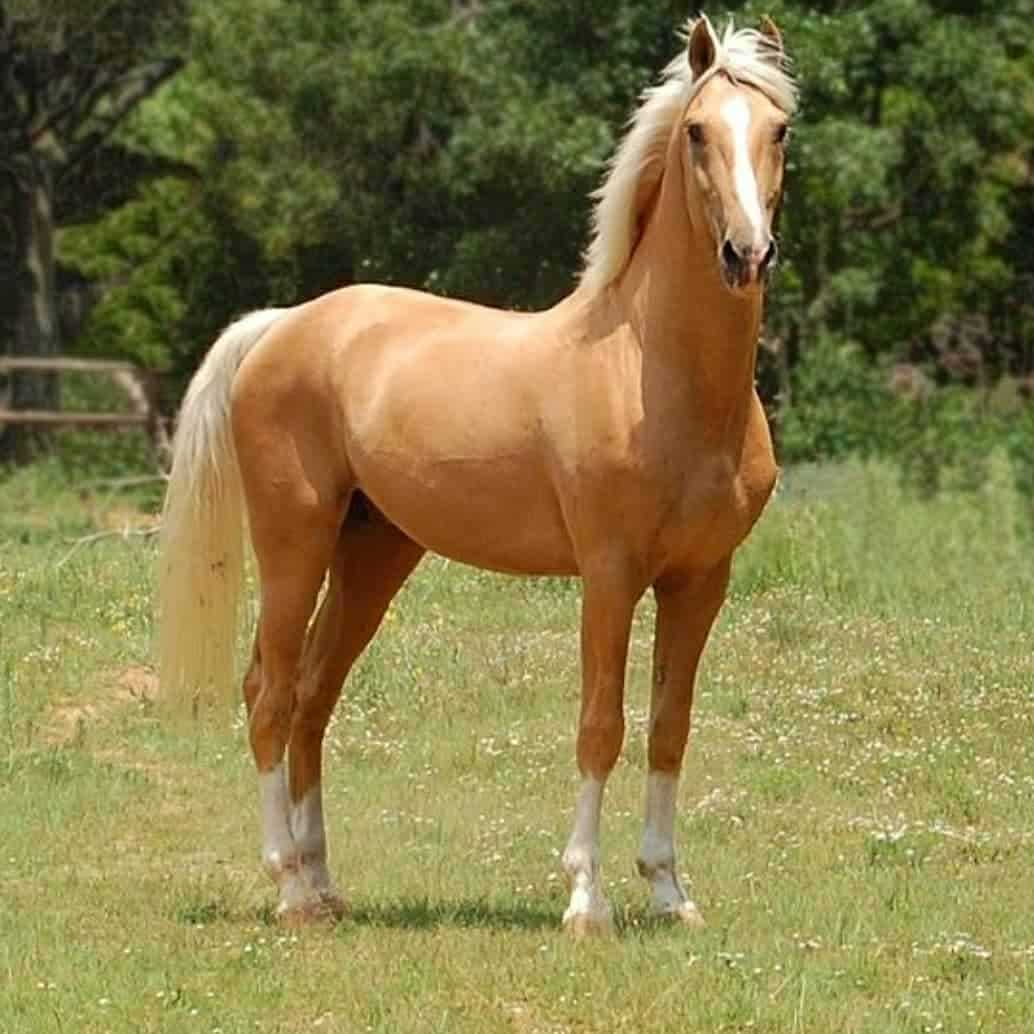

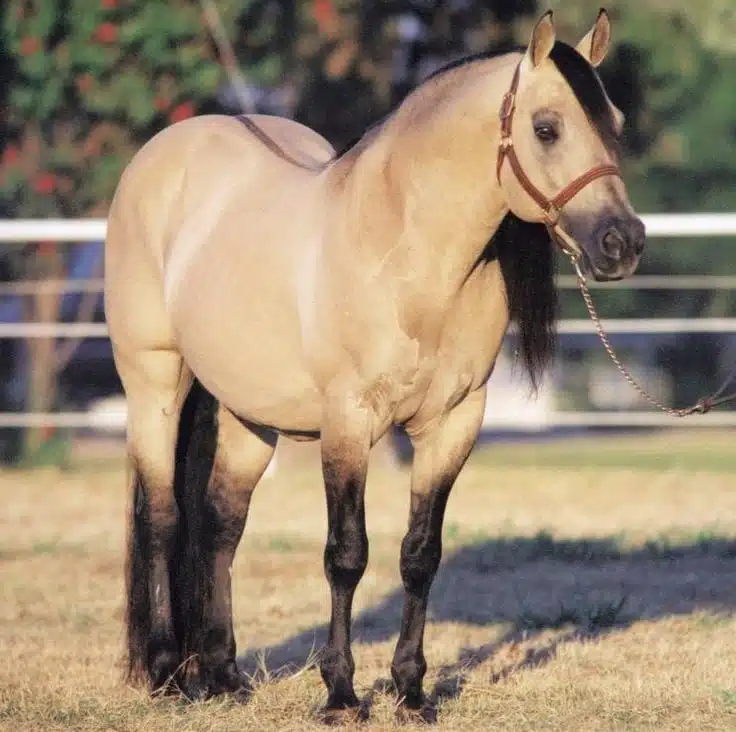
Buckskin
Bay horse with one copy of the cream dilution. Body is predominantly a shade of yellow (gold to nearly brown) with black points. No dorsal strip or other primitive markings.
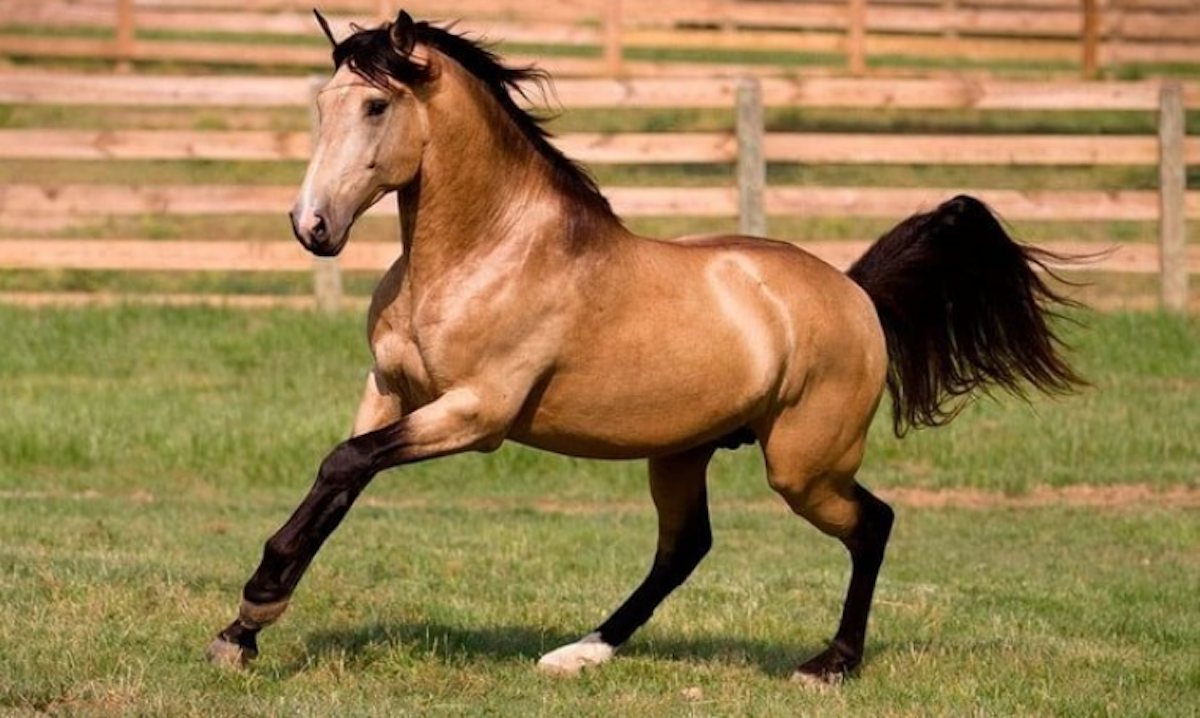

Grulla
A black horse with a dominant dun dilution.
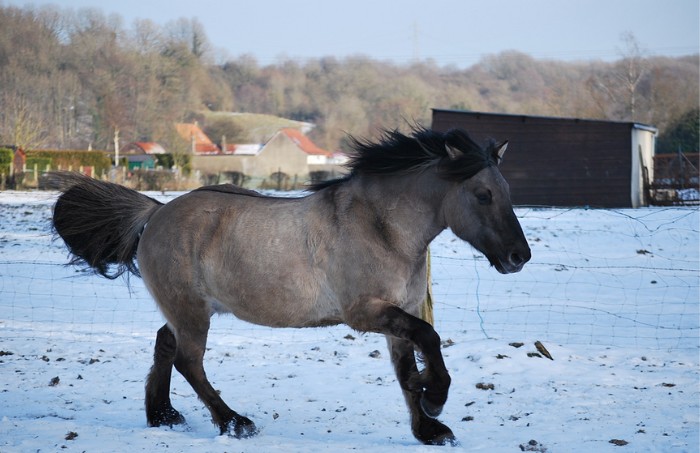

Lethal whit syndrome
genetic disease primarily reported in paint breeds
Leapord Complex or Appaloosa Spotting
genetic disease
Horse homozygous for the leopard complex also have congenital stationary night blindness, or the inability to see in low-light conditions
Lavender Foal Syndrome
genetic disease
A neurological condition that affects Arabian foals with dilute coat colors
Foals are born with a variety of neurologic abnormalities, including limb rigidity, ocular strabismus, and exaggerated spinal reflexes
Foals are euthanized shortly after birth
blaze
A broad vertical white stripe down the center of the horse’s face
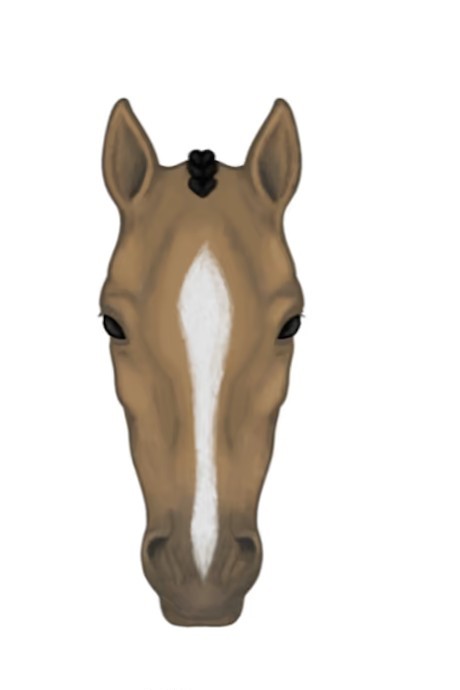

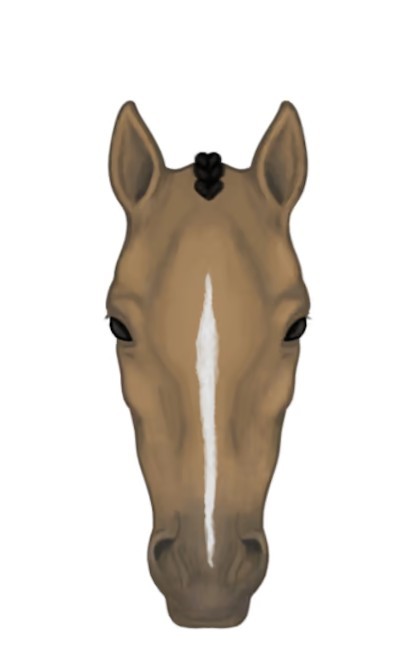
stripe
Thin white stripe down face

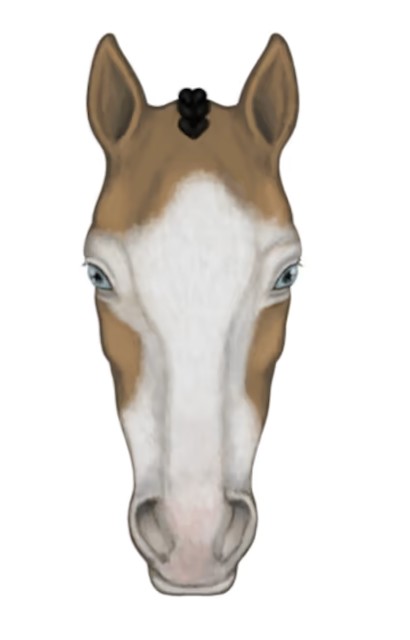
bald
White goes over the eyes

star
A white diamond or splotch between the eyes

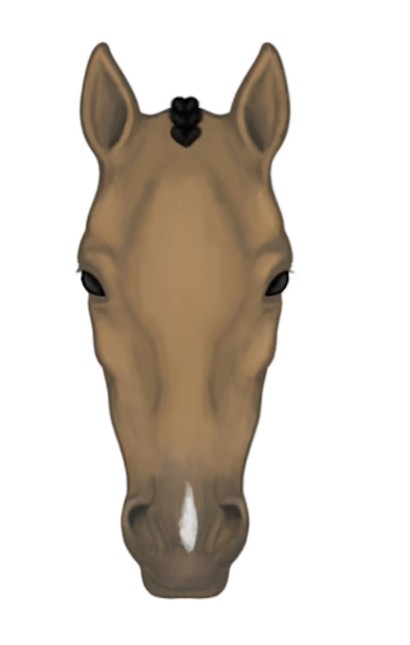
snip
A white mark on the nose between the nostrils

Lip marking
White on lip, usually the bottom

cornet band
white on feet

Pastern
White up to the fetlock

sock
White goes up canon

Stocking
White extends above the knee

dorsal stripe
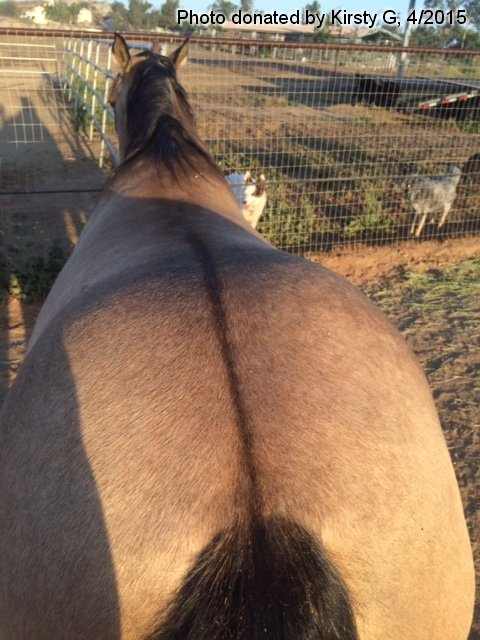
Shoulder stripe

leg stripes / zebra leg markings
