Unit 2: Constitutional Foundations (Part I Rev)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
American Revolution
The war between Great Britain and its American colonies, 1775-83, by which the colonies won their independence.

Declaration of Independence
the document recording the proclamation of the second Continental Congress (4 July 1776) asserting the independence of the colonies from Great Britain authored by Thomas Jefferson

Thomas Jefferson
author of the Declaration of Independence. He borrowed ideas on natural rights from John Locke

no taxation without representation
reflected the colonists' belief that they should not be taxed because they had no direct representatives in Parliament

U.S. Constitution
The government of the United States. A set of principles (guidelines) that describe the duties and powers of the government.

George Washington
led the Continental Army during the American Revolution/1st president of the United States

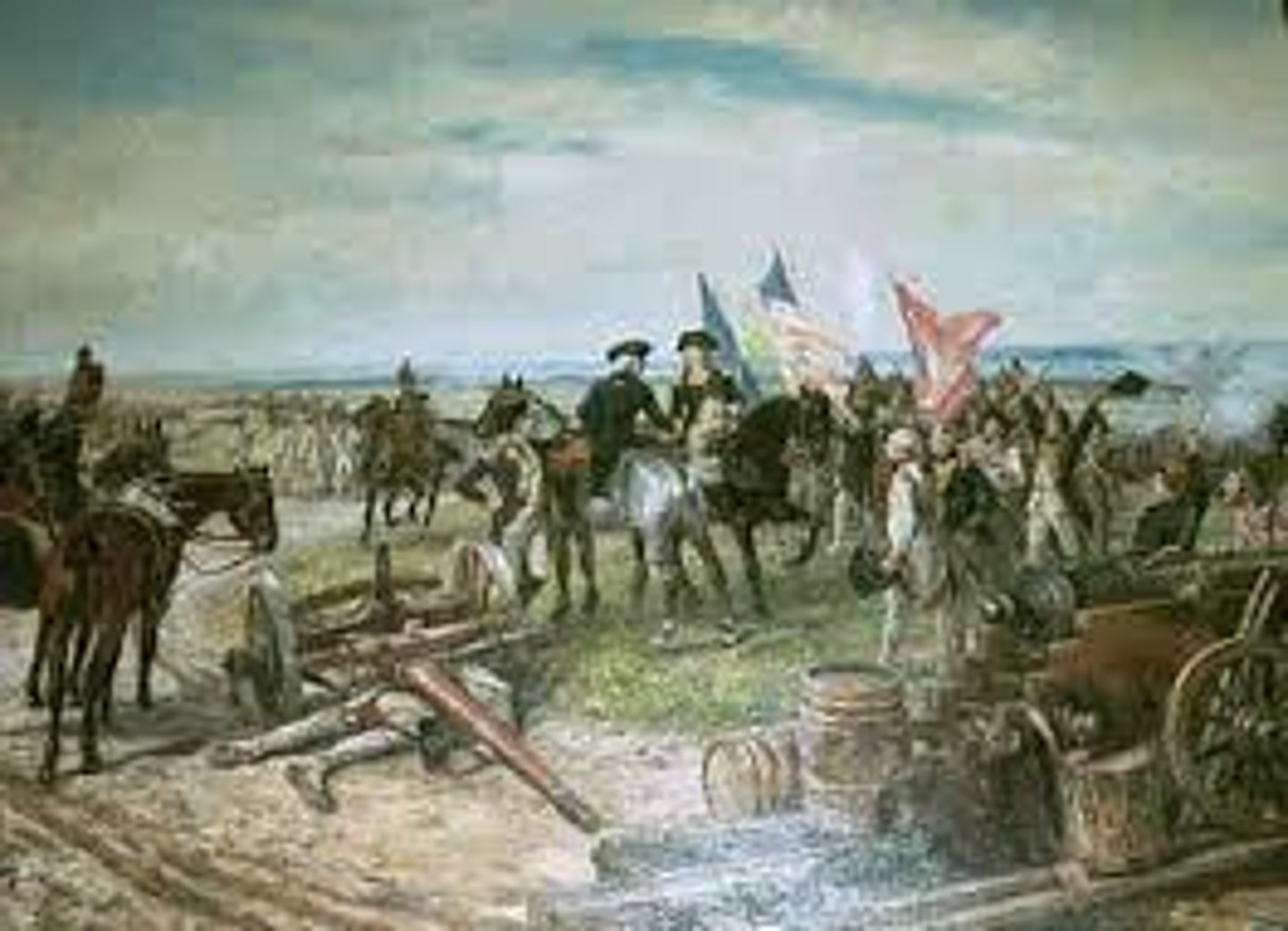
Yorktown
1781; last battle of the revolution; Benedict Arnold, Cornwallis and Washington; colonists won because British were surrounded and they surrended

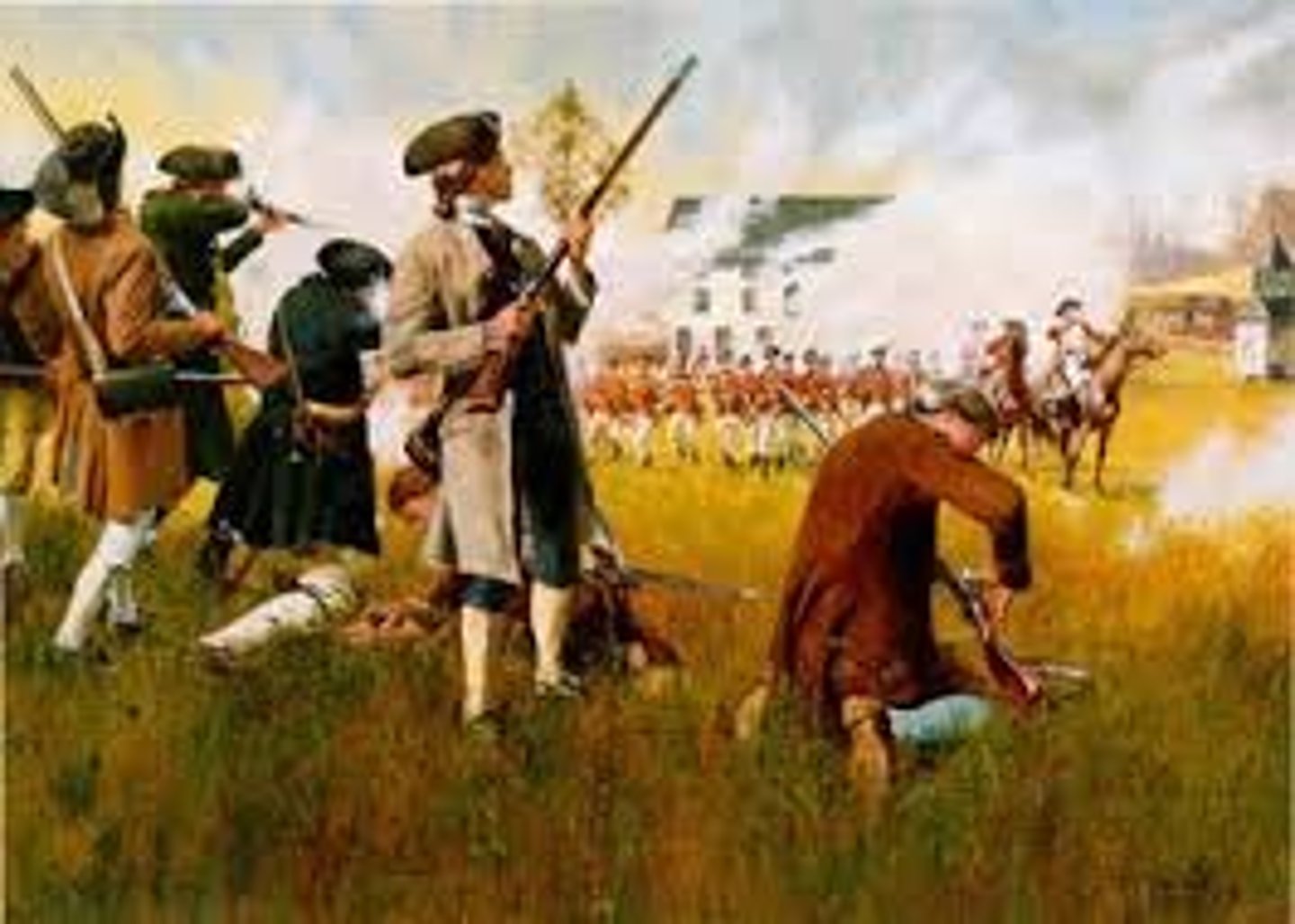
Lexington and Concord
"The Shot Heard Round the World"- The first battle of the Revolution in which British general Thomas Gage went after the stockpiled weapons of the colonists in Concord, Massachusetts.

Stamp Act
1765; law that taxed printed goods, including: playing cards, documents, newspapers

Sugar Act
(1764) British deeply in debt partly to French & Indian War. English Parliament placed a tariff on sugar, coffee, wines, and molasses. colonists avoided the tax by smuggling and by bribing tax collectors.

Quartering Act
1765 - Required the colonials to provide food, lodging, and supplies for the British troops in the colonies.

Townshends Acts
Duties (taxes) on glass, lead, paint, paper and tea to help pay for military costs and salaries of colonial governors.

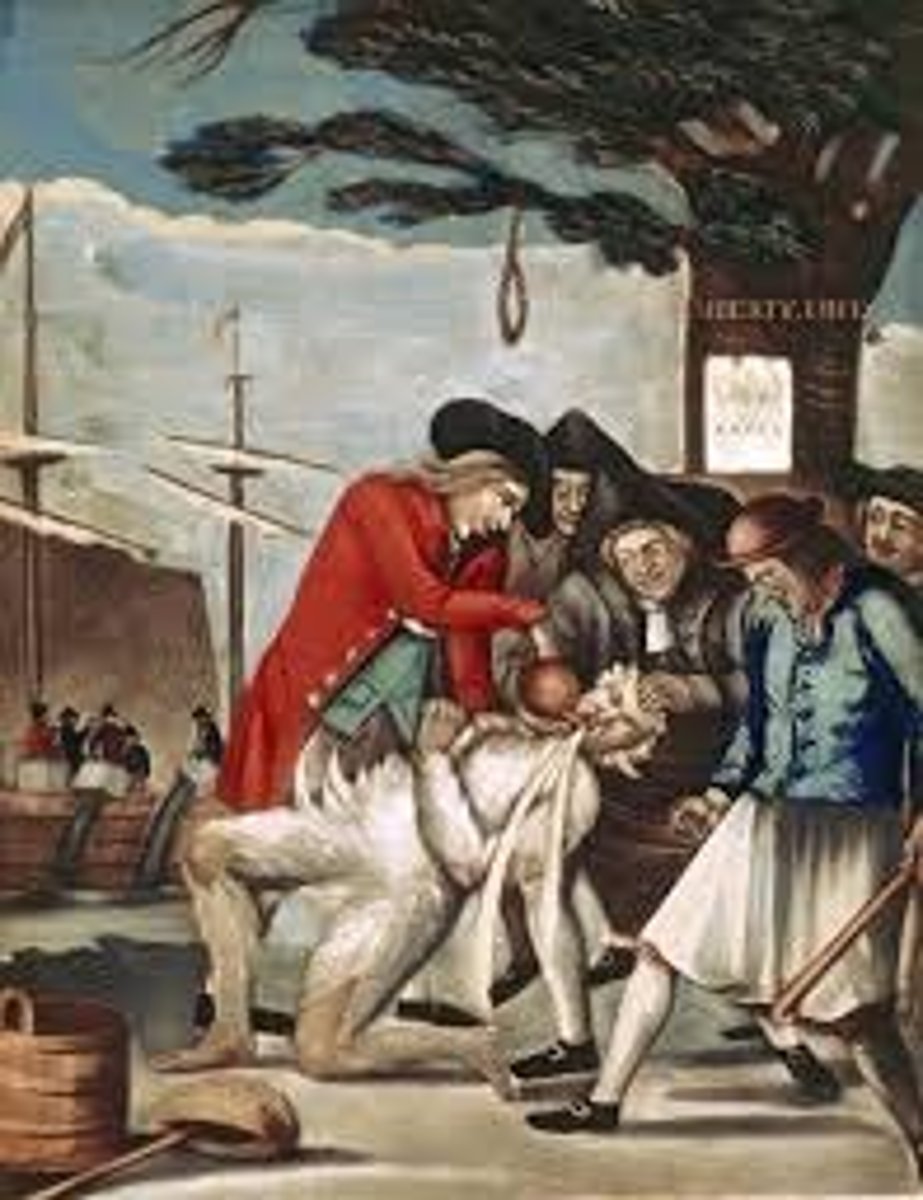
Sons of Liberty
A group of colonists who formed a secret society to oppose British policies before the American Revolution

Declaratory Act
(1766) The British Parliament emphasized its authority to make binding laws on the American colonies.

The French and Indian War
A war with the French and Indians versus the British and other Indian tribes over the Ohio River Valley.

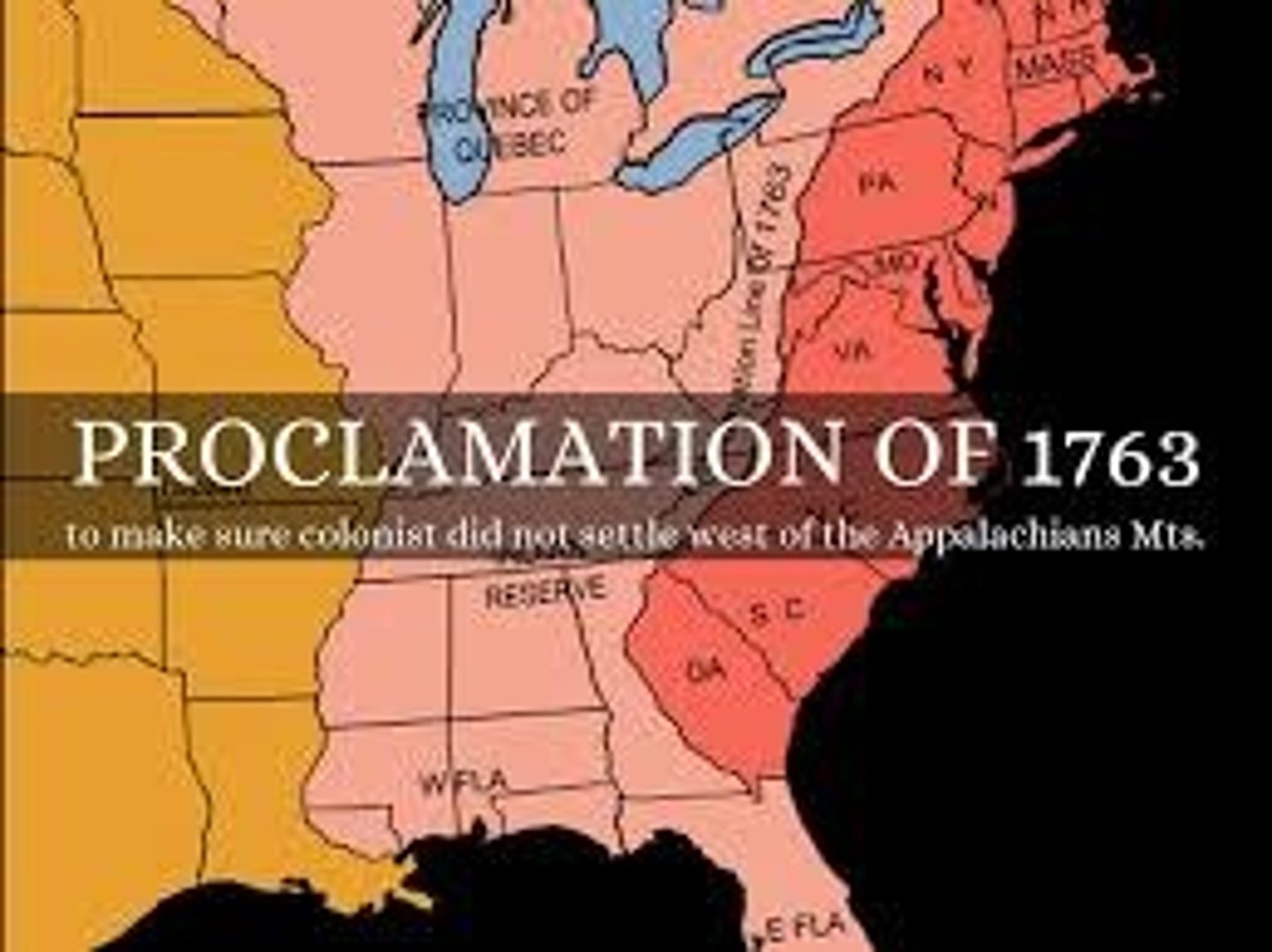
The Proclamation of 1763
Boundary set up between colonies and the Native American lands East of the Appalachian Mountains.
The Boston Massacre
Incident on March 5, 1770 where the redcoats killed eleven colonists. This is significant because it added to the resentment of the British by the colonists.

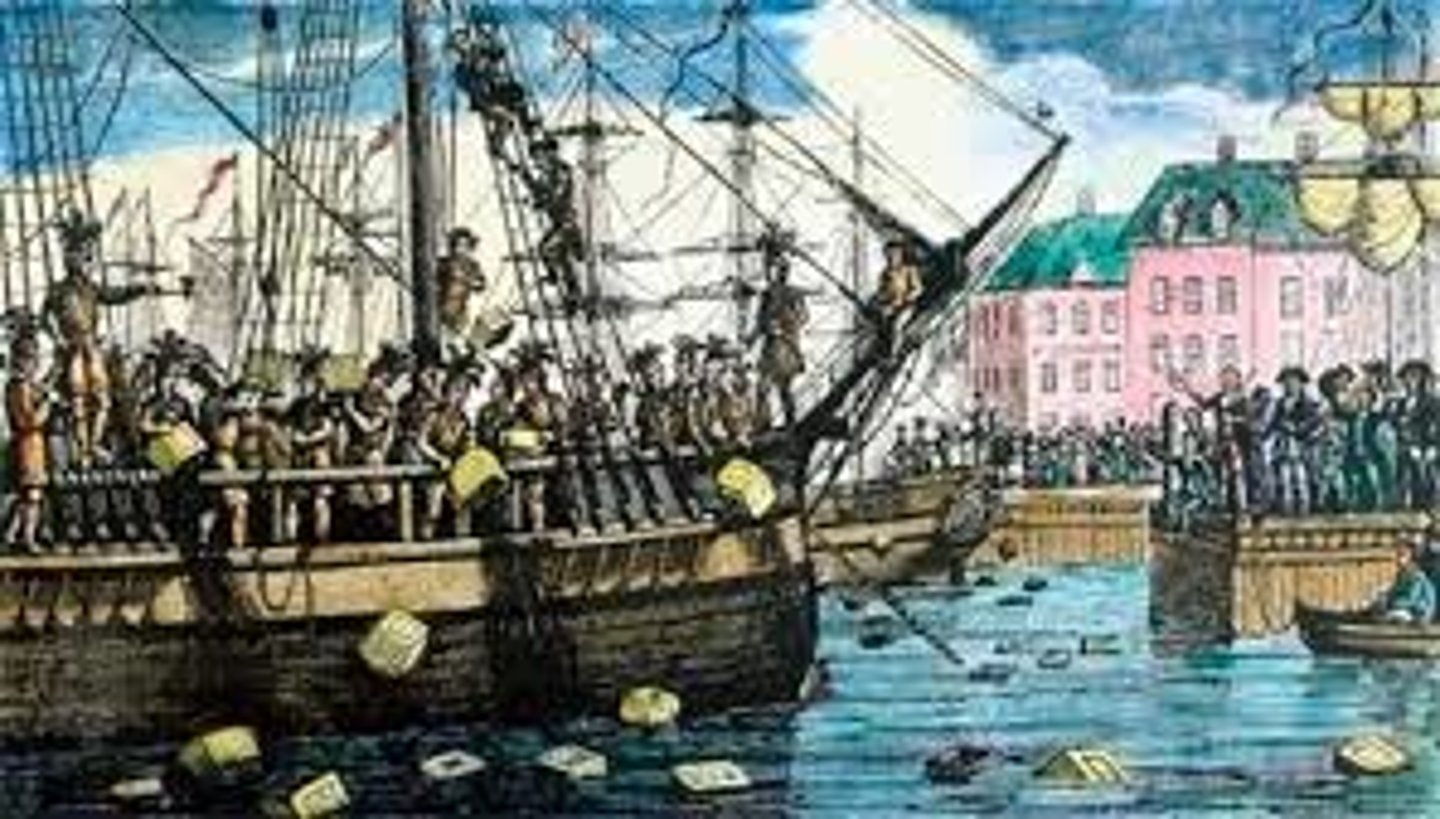
The Boston Tea Party
(1773) Colonists in Boston throws millions of dollars of tea off of British ships in protest of their Tea Tax and Boston Massacre.

Coercive Acts/Intolerable Acts
These acts were laws that punished the colonists for the Boston Tea Party. Called the Coercive Acts in England. The Americans called them Intolerable.

boycott
A refusal to buy or use goods and services.

Loyalists
American colonists who remained loyal to Britain and opposed the war for independence
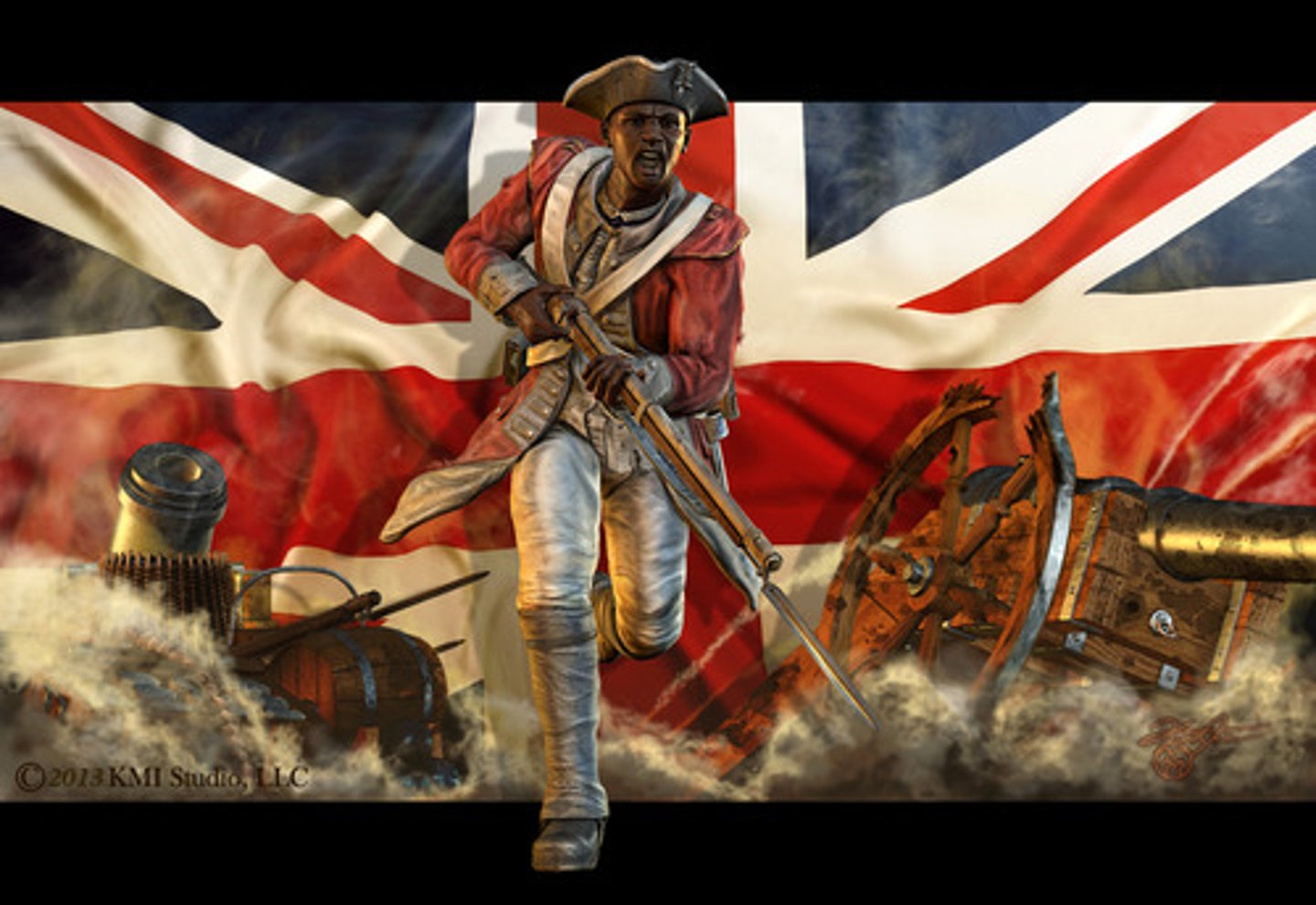

Patriots
American colonists who were determined to fight the British until American independence was won

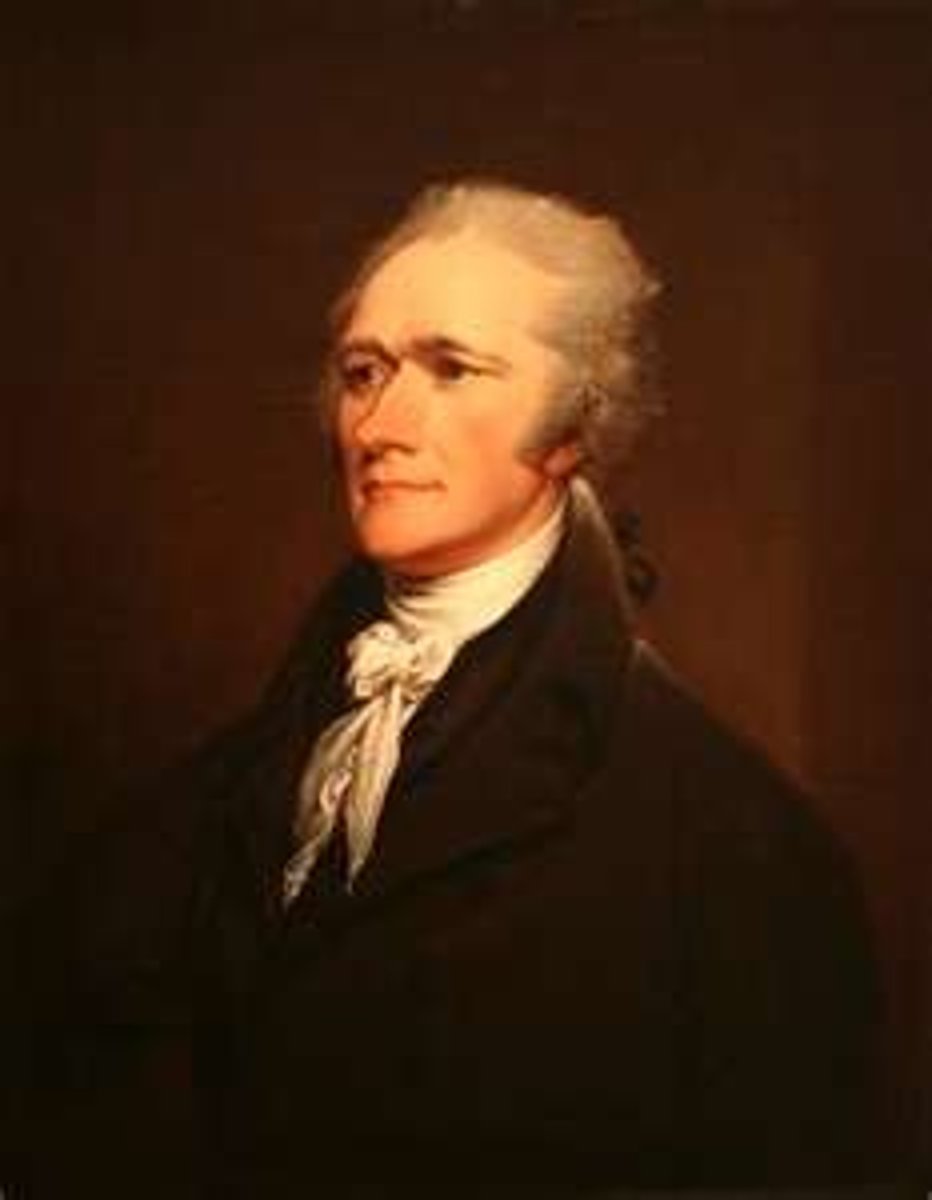
Alexander Hamilton
Helped organized the colonists in the Revolution, 1789-1795; First Secretary of the Treasury. He advocated creation of a national bank, assumption of state debts by the federal government, and a tariff system to pay off the national debt.

1st Continental Congress (1774)
colonial meetings, asked Great Britain to repeal harsh taxes and overturn other harsh actions

Women in the American Revolution
support roles, maintained structure in the home, and developed important resources in support of the war effort, participated in the political discussions of the period, a few fought in revolutionary battles

Native Americans in the American Revolution
- had to choose to fight for the loyalist or patriot cause.
- Some sided with the Americans because they promised neutrality. (most new england indians) they volunteered as minute men before the war started.
- Others sided with the British in hopes of protecting their homelands from further American expansion. (Indians near frontier settlements)
- At the end of the war despite siding with Americans colonists took the Indian land anyway by treaty or by force.
Enslaved People in the American Revolution
primarily from the Southern colonies, participated in the war by fighting alongside the Continental Army, often with the promise of freedom in exchange for their service, though many were not granted that freedom after the war; others chose to escape to the British side, who offered freedom to slaves who joined their forces, creating a complex dynamic where enslaved people were caught between fighting for a nation that still allowed slavery or seeking freedom by siding with the British
Thomas Paine
A British citizen, he wrote Common Sense, published on January 1, 1776, to encourage the colonies to seek independence. It spoke out against the unfair treatment of the colonies by the British government and was instrumental in turning public opinion in favor of the Revolution.
