Movement across membrane ( Active Transport)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Active Transport
The movement of substances against their concentration gradient from a low to high concentration of that substance across the membrane.
Using ATP and protein carriers
What is a carrier protein ?
These membrane have a regions. That binds to and allows the hydrolysis of a molecule of ATP to release energy = acts as enzyme.
Have specific regions that combine reversibly with only certain solutes molecules/ ions.
The energy helps the carrier protein change its conformation. ~ carry the ion from one side of the membrane to other.
Why is active transport important ?
Kidney : Reabsorption of sugar + ions from the venal filtrate
Nerve Cells : The Na + : K + pump maintain the resting potential
Phloem : loading os sucrose for transport
Bulk Transport
Movement of large quantities of material :
into cell endocytosis out of the cell exocytosis using vesicles
What does endocytosis involve taking of ?
Solids : Phagocytosis / Cell eating / Specialized cell or phagocytes ( WBC + Amoeba )
Liquids : Pinocytosis / Human egg
Bulk Transport - Exocytosis
Movement of large quantities of material out of the cell
This happens in :
Secretory cells : Glandular cell in gut / breast
In phagocytes : after the contents of the phagocytic vesicle have been digested
Plant cells : during cell wall building
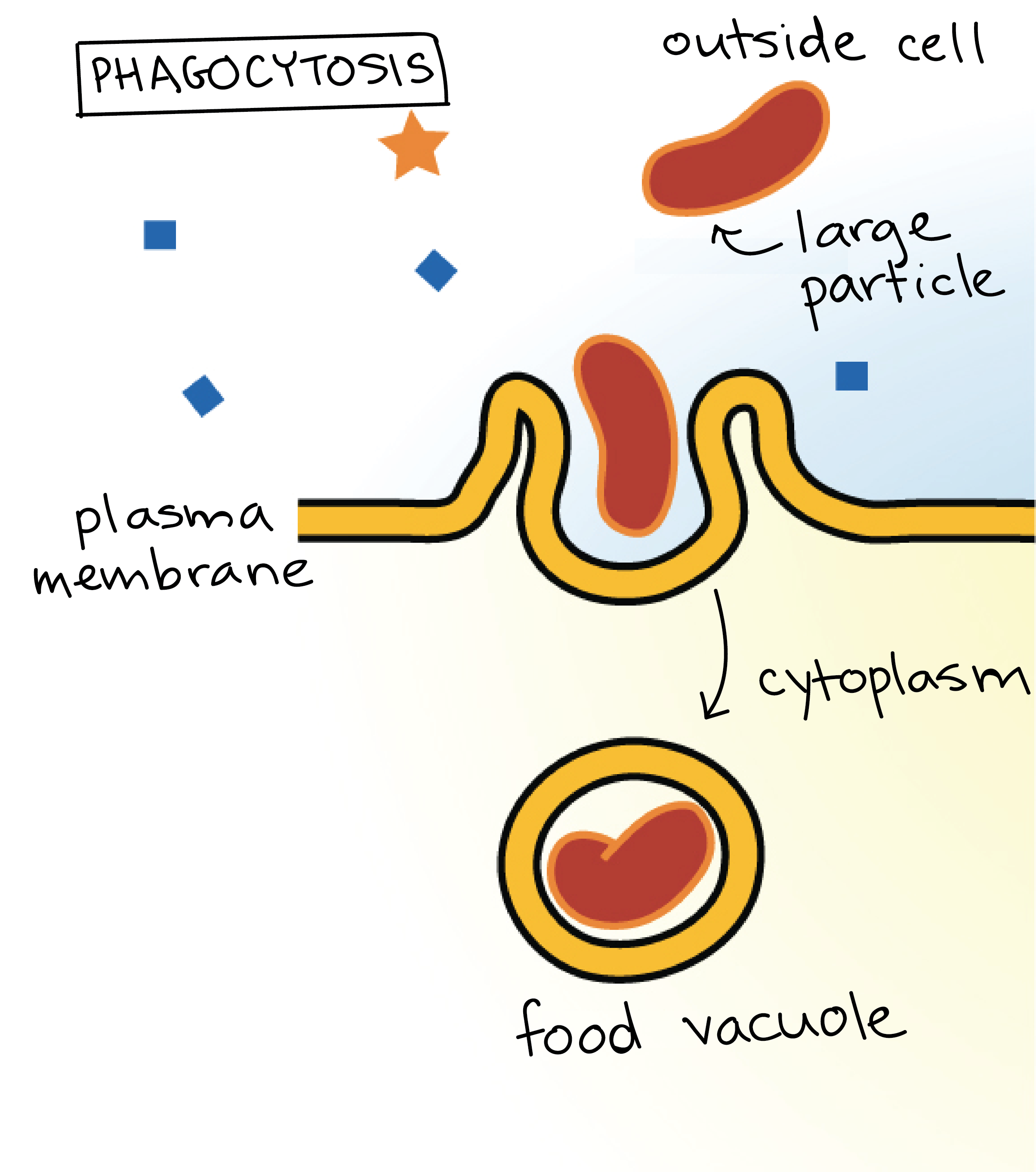
Phagocytosis
Bulk Transport of solids : It takes place in specialized cell * Phagocytes *
Neutrophils are phagocytes white blood cells
Ingest / engulf bacteria as part of body’s defense system
Amoeba
How does bulk transport work ( Phagocytosis )
1) The membrane extends ‘ arms ‘ ( pseudopadia ) around the particle / pathogen which it wants to dissolve.
2) Once the membrane has fully engulfed the particle, it buds off creating a vesicle inside the cell.
3) The vesicle will usually fuses with lysosomes, and its; content will be dissolve / digested.
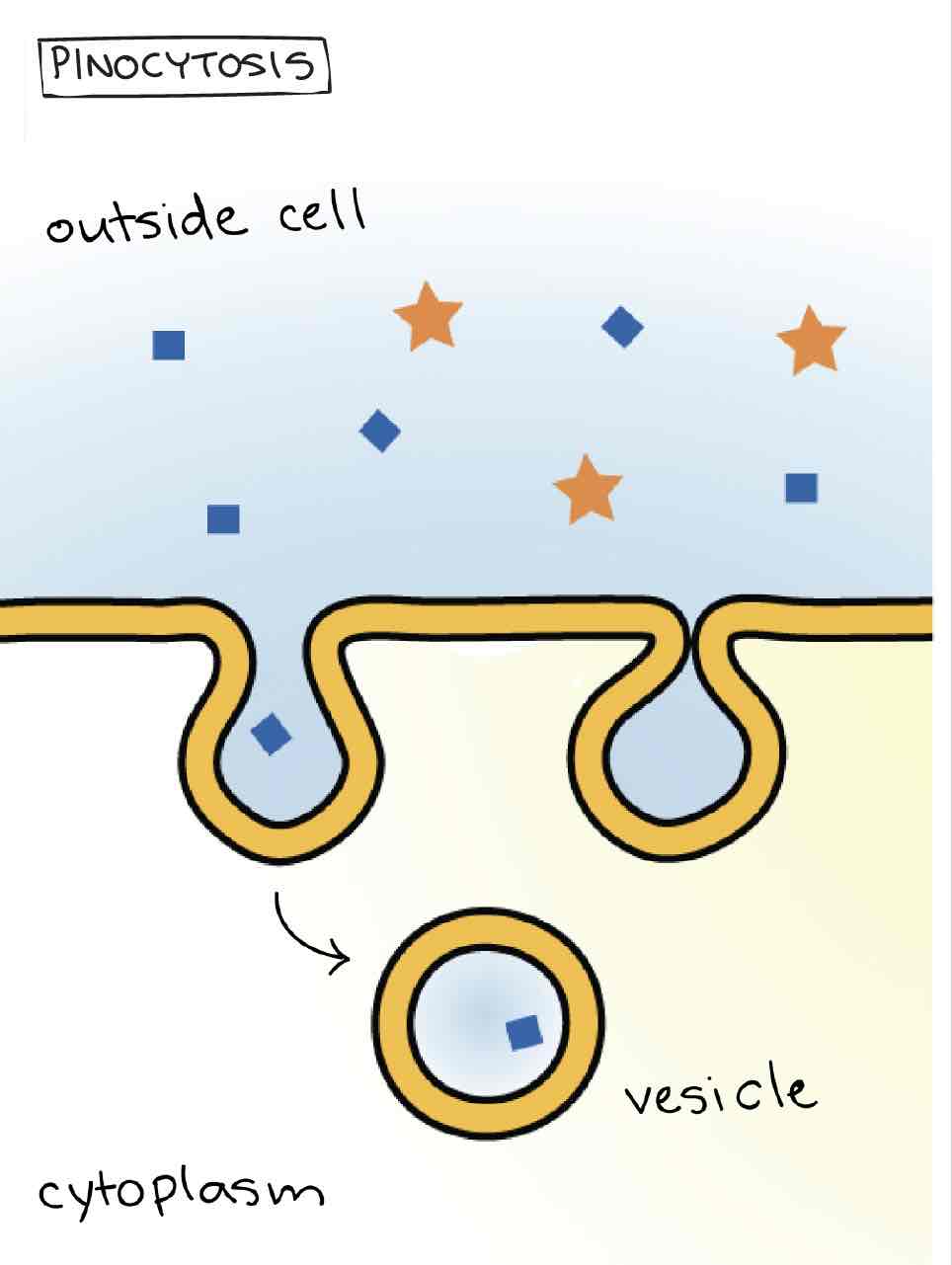
Bulk Transport - Pinocytosis
Bulk Transport of Liquid : cell drinking
If the vesicles pinched off are very small called micro pinocytosis *
The human egg cell ( ovum ) take up the nutrients by pinocytosis from the collide cell that surround it.