Physics aqa gcse paper 1
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
What is a system?
single object/group of object that you’re interested in.
What happens when a system changes?
energy transfered. can be transfer into/away from system between diff object in system/type of energy store.
What happens when energy is transfered to an object?
it’s stored in one of objects energy stores
What are the energy stores, energy can be transfered to?
thermal(internal), kinetic, gravitational potential, elastic potential, elastic potential, chemical, nuclear, electrostatic, magnetic
How can energy be transferred?
mechanically, electrically(work done by moving charges), heating, radiation(light/sound).
How can work be done?
current flowing(work done against resistance), force moving object
How to calculate kinetic energy?
Ek is measure in joules
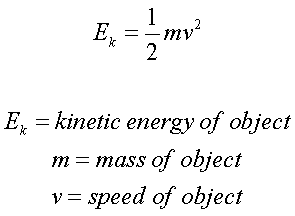
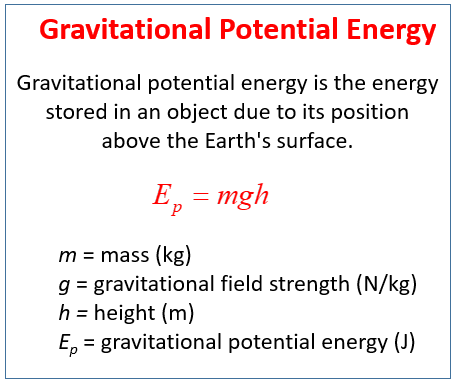
How to calculate gravitational potential energy?
How to calculate elastic potential energy?
only use formula if limit of proportionality hasn’t exceeded.

How to calculate specific heat capacity?
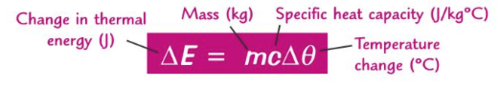
What is specific heat capactiy?
amount energy needed raise temp of 1kg substance by 1 degree celcius.
What store does specific heat capacity involve?
thermal energy
specific heat capacity experiment?
block of material(2 holes in it for heater/thermometer).
measure mass/temp at start, wrap in insulating layer(so energy no much energy transfer to surroundings), set p.d. to 10V(power supply), then start stopwatch, use therm to meas temp every min as block heat up.
ameter current shouldn’t change. After recording results stop.
calculations:calc power to heater(p=vi), then calc energy transfer to heater at time pf each temp read(e=pt) t=time since experiment began.
Plot graph of energy transfer to thermal store of block against temp if assume all energy transfer to heater has gone to block. Find grad of straight line(▲0÷▲E)
Specific heat cap of material=1÷(gradxmass(block))
what is power?
rate of energy transfer/doing work or energy transfer per second
power equation/formula?
power(watts), energy transfer/word done(J), Time(seconds)
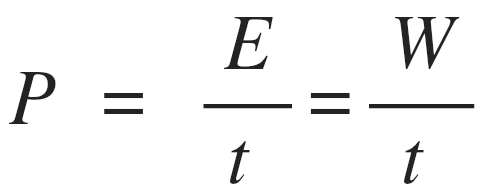
What is 1 watt equal to?
1 joule of energy transferred per sec.
What can energy be used for?
transfer useful/store/dissipated/never created or destroyed.
What’s a closed system?
system where neither matter/energy can enter/leave, net change in total energy is 0.
What happens when energy is transferred between stores?
some always dissipated(wasted energy, because store in a non-useful/unwanted way)
ways to reduce unwanted energy transfers by thermal insulation?
cavity walls(inner/outer wall with air gap in mid reduce conduct)/insulation(air gap fill with foam reduce conduct/convect), loft insulation(laid across loft floor/ceiling fibreglass wool good ins as has pockets of trap air reduce conduct/ convect current), double glazed window(cavity walls), draught excluders(reduce convect), reducing diff between inside/outside house.
ways to reduce unwanted energy transfer by friction?
lubricant(liquid), streamlining, tightening loose parts( prevents unwant virbation wasting energy as sound)
What is thermal conductivity?
measure of how quick energy is transferred through a material.
What is conduction process?
energy transferred to object by heating it’s thermal store. part of the particles in object heated gain energy, and turn thermal to kinetic store, vibrating vigourously, colliding with other particles to transfer this energy onwards.
insulator experiment?
boil water, pour water in sealable conatainer, measure mass/temp of water. Seal contain then leave for 5 mins using stopwatch.
Final: remove lid, measure temp, pour out, allow contain to be room temp, try diff insulator now.
efficiency formula for energy transfer?
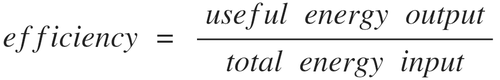
efficiency formula for power
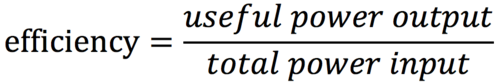
What is a renewable energy resource?
can be renewed as it’s used. will never run out. do damage environment, but less, unreliable, dont generate much energy
The main energy resources?
fossil fuels(coal, oil, gas), nuclear fuel, Wind, water waves, hydro electricity, biofuel, tides. geothermal, sun(solar)
oil energy resource?
petrol/diesel vehicles use fuel from oil. Transport/heat.
disadvantage of oil energy resource?
if spillage can affect mammal/bird live in/around sea. burn release c02/s02(can dam tree/soil/ecosystem)
coal energy resource?
old fashion train boil water to produce steam. burnt in fireplace, Electric/heat/transport, coal mine mess landscape.
disadvantage of coal energy resource?
burn release c02/s02(can dam tree/soil/ecosystem).
gas energy resource?
heat water(pumped into radiators in home to heat).electric/heat/transport.
disadvantage of gas energy resource?
burned release c02.
advantage wind power?
no pollut(except manufacutre), no fuel cost, mini run cost, no perm dam to land. electric generate
disadvantage of wind power?
need a lot in exposed place(moor/roundcoast), imposs increase supply(extra demand), spoil view, noisy, stopping(no wind/wind too big), produce electric(70-85%), initial cost high
Solar power and advantage?
power road sign/satelite. no pollut(except manufacture), energy free, running cost nil. heat/electric generate.
how does a solar water heater work?
(water heat by sun, pump in radiator building)heat generate.
disadvantage of solar power?
initial cost high, gen little electric(sunlight), imposs increase supply(extra demand), remote place where less choice
geothermal power and advantage?
reliable than wind/solar. use energy from underground therm store. gen electric/heat building directly.
process of geothermal power?
cold water pump down earth to hot rock, steam from rock pump up to turbine to generate energy, then steam condense, process start over.
disadvantage of geothermal power?
less suit place for powerplants to be built(cost is often high compare to produce of energy. In volcano area(hot rock lie near surface).
hydro electric power and advantage?
reliable than wind/solar. flood of valley(big dam), rain caught, then through turbine, no pollut, quick response to incease demand of electric, no fuel cost, mini run cost, transfer energy from kinetic store of falling water.
disadvantage of hydro-electric power?
flood(valley):rot vegetation(release meth, c02), loss habitat, reservour(look bad when dry), initial cost high, gen bit electric
wave power and advantage?
no pollut, no fuel cost, mini run cost, like wind power but turbine rely on waves. gen electric.
disadvantage of wave power?
need lots around cost, disturb seabed/habitat of marine, spoil view, hazard(boat), initial cost high, gen bit energy, waves tend to die(wind no).
tidal barrages and advantage?
dam built across river estuary, turbine in them. process:tide fill estuary, water out turbine at control speed. no pollut, near to predict height. no fuel cost, mini run cost. electric gen.
How are tides created?
gravitational pull of sun and moon
disadvantage of tidal barrages?
prevent free access(boat), spoil view, alter habitat, height(tide)can effect energy produce:lower(neap)=low energy, spring(big). dont work(water level same both side), init cost high, needs be suitable estuary.
What are biofuels?
renewable, from plant/animal dung, solid/liquid/gas burnt=electric/run vehicles
advantage of biofuel?
carbon neutral, reliable(plant growth=short), no respond to quick energy demand.
disadvantage of biofuel?
high cost(refine biofuel be suitable), insufficient space/water for food crop demand(biofuel produce), area(forest) clear for biofuel crop. decay/burn of this vegetation release c02/meth
What can a mix of biofuel and petrol/diesel do?
run vehicles
main uses of biofuel?
electric/transport generation
fossil fuel/nuclear energy advantage?
enough meet current demand, extracted fast(powerplant fuel in stock), respond quick to change(demand), run/extraction cost(low), cost effective.
fossil fuel/nuclear energy disadvantage?
set up cost(powerplant high), spoilt view
nuclear power pros and cons?
clean, but waste is dangerous(difficult dispose), high cost(powerplant/decomissioning cost), risk:major catastrophe
nuclear fuel advantage?
quite cheap. electric/heating/transport generation
what will have to happen if renewable energy isn’t so efficient?
combination of diff powerplant(expensive), research((reliability)take time/money
how will switching to renewable energy be paid?
customer(bills), government, taxes.
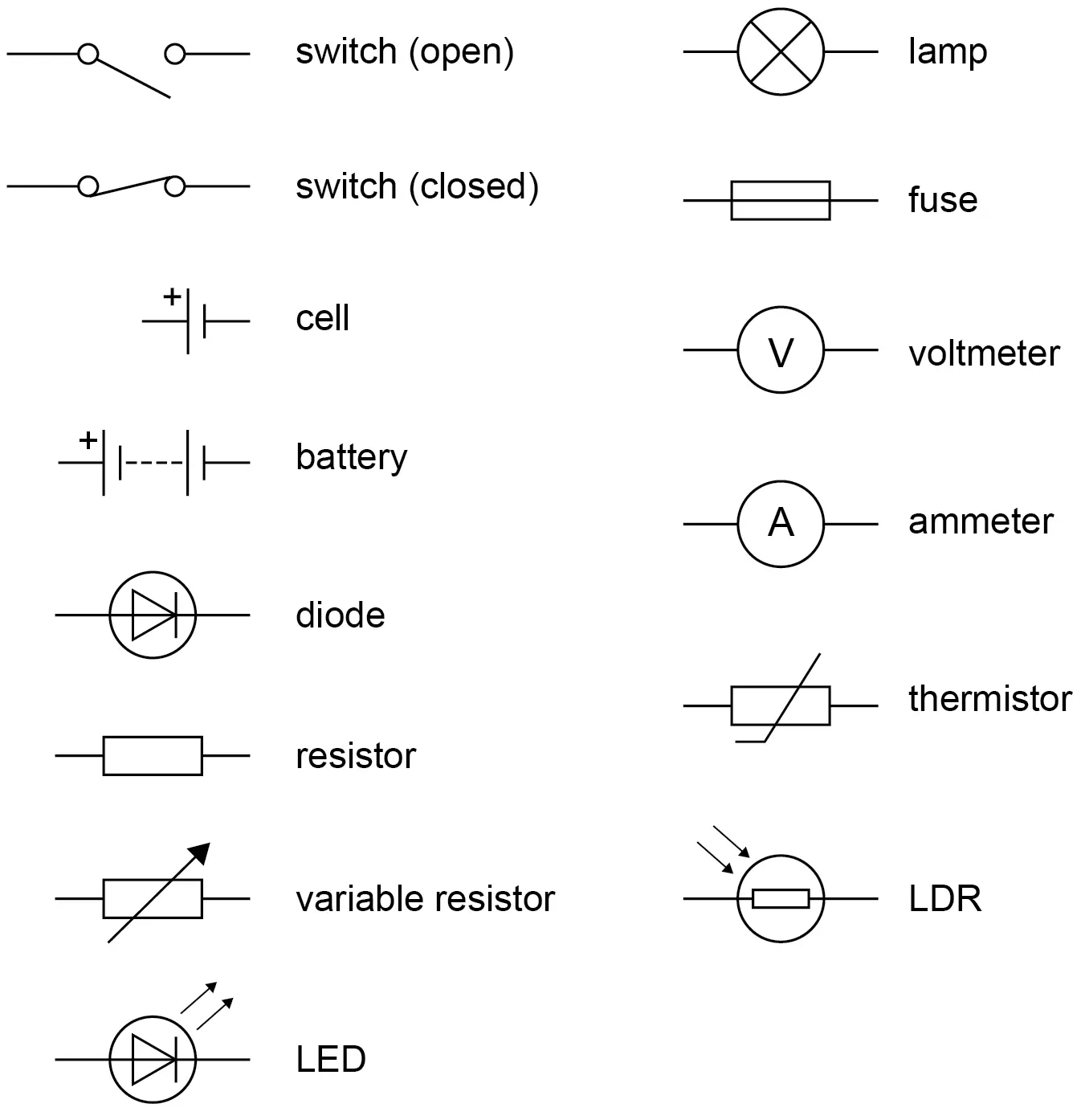
The circuit symbols?
What is current?
flow of electrical charge
What is potential difference?
driving force that pushes the charges around.
What is the size of the current?
rate of flow of electrical charge
How can current flow through a closed circuit?
if there’s a source of potential difference.
Equation linking charge, current and time?
Charge(coulomb C), Time(second S), Current(Amperes/Amps A)
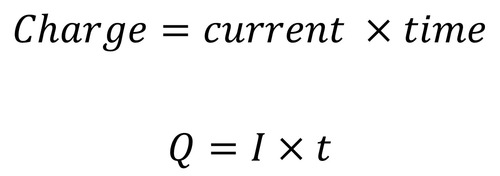
in a single closed loop, what happens to the current?
it stays the same
What does a current flowing through a component depend on?
potential difference, resistance
Equation linking potential difference, resistance and current?
potential difference(Voltage/volts V), Current(Amperes/Amps A), resistance(Ω)

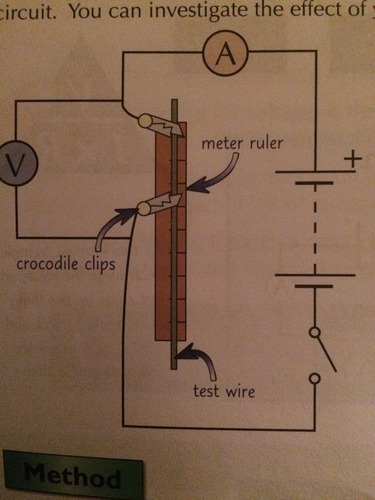
investigating resistance experiment?
attach croc clip to wire of ruler at 0cm, 2nd croc clip 10cm away. record length of wire. close switch then record p.d./current, open switch, then repeat process. use record of p.d./current to calc resistance, then plot graph of resist against length(wire), should be a straigh diag line through origin.
What are ohmic conductors?
wries, resistor
What doesn’t change with the current?
resistance of ohmic conductors(some components)
What does directly proportional mean?
goes up at similiar amounts
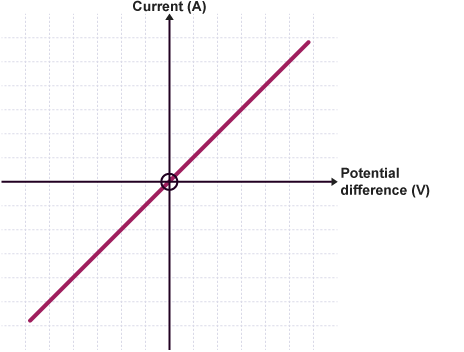
What happens at a constant temperature through an ohmic conductor?
current is directly proportional to potential difference. Resistance(R), remains constant.
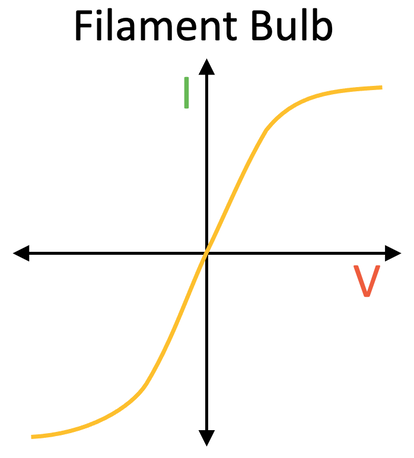
What happens when an electrical change flows through a filament lamp(or resistance of component that changes with current)
trasnfer some energy to therm store(lamp), which design to heat up. Resist increase(heat). A diode works differently.
Examples of resistance in components that change with current?
filament lamp, diode, thermistor, LDR
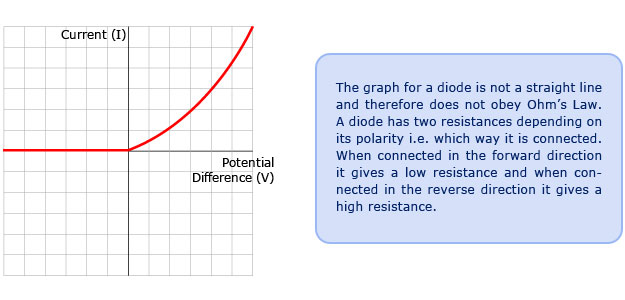
How does resistance change in a diode?
depends on direction of current. allow current in one direction, but not in other(resistance is higher)
What is a thermistor?
temp dependant resistor. hot=resistance falls, cold=resistance rise. Use:thermostat
What is an LDR
light dependant resistor. bright=resistance fall, dark=resistance rise. Use:Automatic nightlights
What is a linear component?
ohmic conductors
What is a non-linear component?
filament lamp, diode
Invesitgating I-V characterisitcs experiment?
vary variable resist(alter currrent/potential diff), record reading of A/V to see how p.d. varies as current changes. repeat enough to see I-V character, swap over wires connected to cell/battery so current flow is reversed. now plot graph(always current against resistance)
What is an I-V characterisitc?
graph showing how current changes as p.d. increase. always current against resistance on graph.
In a series circuit what happens to the current?
stays the same through all components.
What does all the p.d. of components add up to in a series circut?
the total p.d. of the power supply of the circut.
In a series circuit what is the total resistance of 2 components equal to?
the sum of the resistance of each component.
In parallel circuits what is the p.d. of all the components?
the same
What is the total current in a parallel circuit equal to?
the sum of current through each seperate component
What happens if you have 2 resistors in parallel?
The total resistance of 2 resistors is less than the resistor with the smallest resistance of the 2 resistors.
What is the mains electricity supply(electricity in your home)?
ac(alternating current) supply
How many volts is supplied to your home by an ac supply in the UK?
230V
What is the frequency of the ac supply?
50Hz(cycles per second)
What does direct potential difference create?
direct current(flows in same direction)
What does alternating potential difference create?
alternating current(posotive/negative ends keep alternating meaning current flow keeps changing direction).
What are most electrical appliances connected to the mains supply by/using?
3 core cables
What are the cables covered in?
colored insulation to show it’s function.
What colour is the live wire?
brown
What colour is the earth wire?
green and yellow
What colour is the neutral wire?
blue
What is the live wire?
provides alternating potential difference from mains supply.