Approach to pustues, crusts + scales (secondary infections)
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Recall the definitions of pustule, crust and scale
Pustule: vesicle filled with pus
Crust: dries exudate containing blood, serum, scaled, pus
Scale: desquamated corneocytes visible on surface
What are the potential causes of pustules?
Superficial bacterial pyoderma
Pemphigus folliceus (immune mediated)
What are the potential causes of crusts?
Ruptured pustules
Dried exudate from erosions/ulcerations
What are the potential causes of scale?
Primary cornification disorders
Secondary to any other skin pathology
How should you approach pustules, crusts and scales?
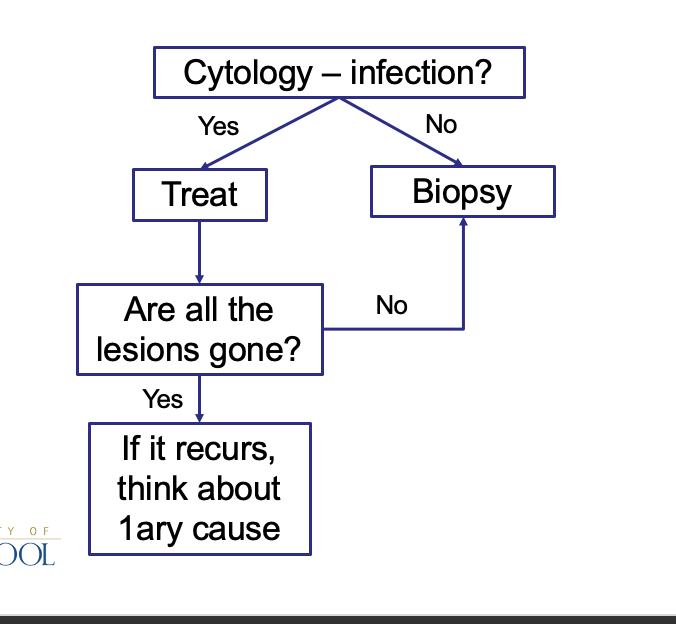
What are the features of skin infections and what are the causes?
Always 2ary to another disease
Allergic skin disease
Ectoparasites
Endocrinopathy
etc.
What are skin infections usually associated with?
Commensals
Take advantage of either a problem with skin barrier or immune system
How do you diagnose skin infections?
Cytology
Culture not diagnostic as present on skin anyways
What is the most common commensal of the skin?
Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius
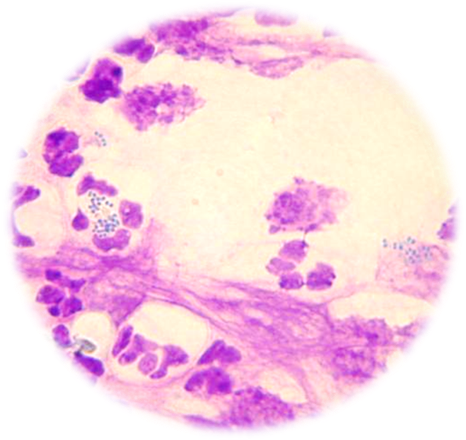
(S. aureus, S. schleiferi and S. canis less common)
What is the most common fungi of the skin?
Malessezia pachydermatis
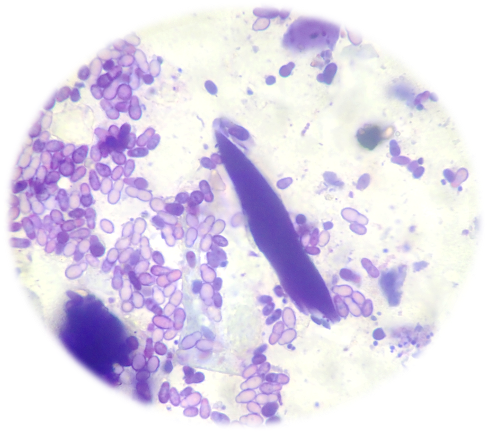
Give an example of primary skin pathogens
Dermatophytes
How are dermatophytes (pathogenic bacteria/not commensal) diagnosed?
Culture
What is bacterial pyoderma?
bacterial skin infection very common in dogs
Not very common in cats except in abscesses from fighting
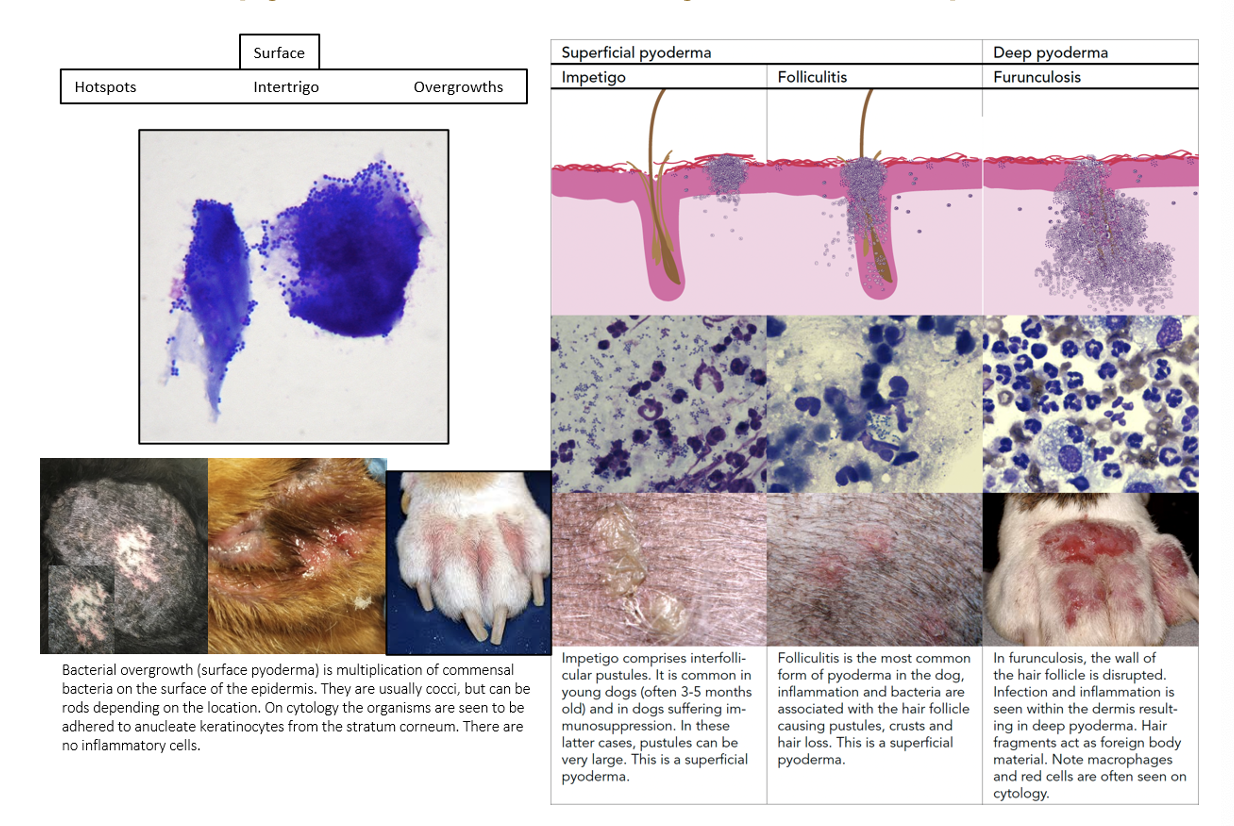
How is bacterial pyoderma classified?
Surface - Superficial epidermis
Superficial - Epidermis and hair follicles
Deep - Epidermis, hair follicles, dermis +/- subcutaneous fat
(according to depth)
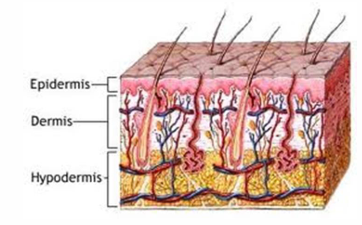
How does surface pyoderma present clinically?
Hotsposts (moist pyotraumatic dermatitis)
Intertrigo (skin fold pyoderma)
Bacterial overgrowth
What bacteria will you see in surface pyoderma?
Coccoid, rod-shaped or mixed bacteria depending on location
Staphylococci most common
May progress to superficial/ focal deep infections
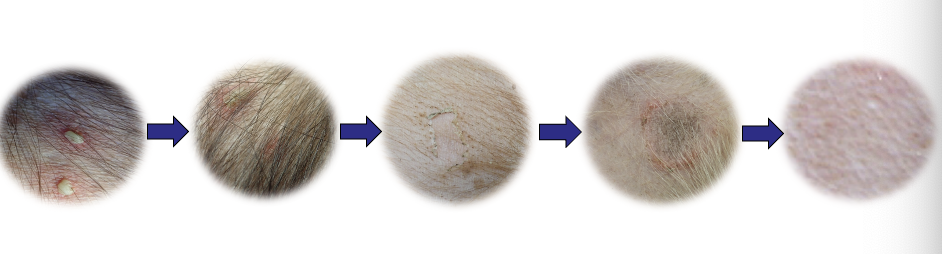
What are the features of moist pyotraumatic dermatitis?
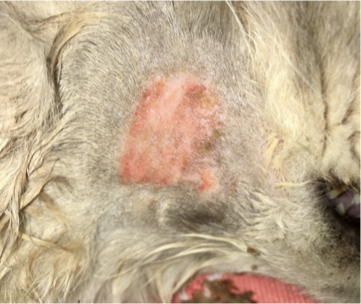
Well demarcated flat eroded moist lesion with erythematous halo
Usually on cheek, neck, rump
Develops within hours due to self trauma
FAD or pruritic/painful trigger
hotspot before + after clipping
What breeds are predisposed to moist pyotraumatic dermatitis?
Rottweiler, Golden Retriever & GSD
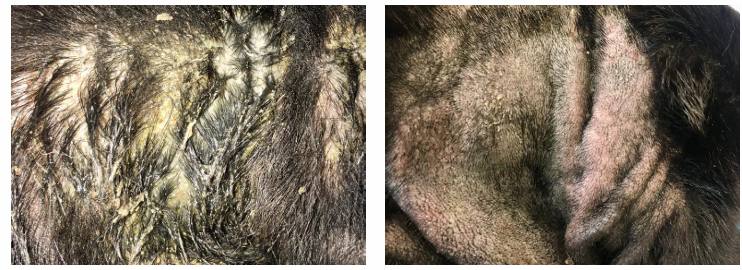
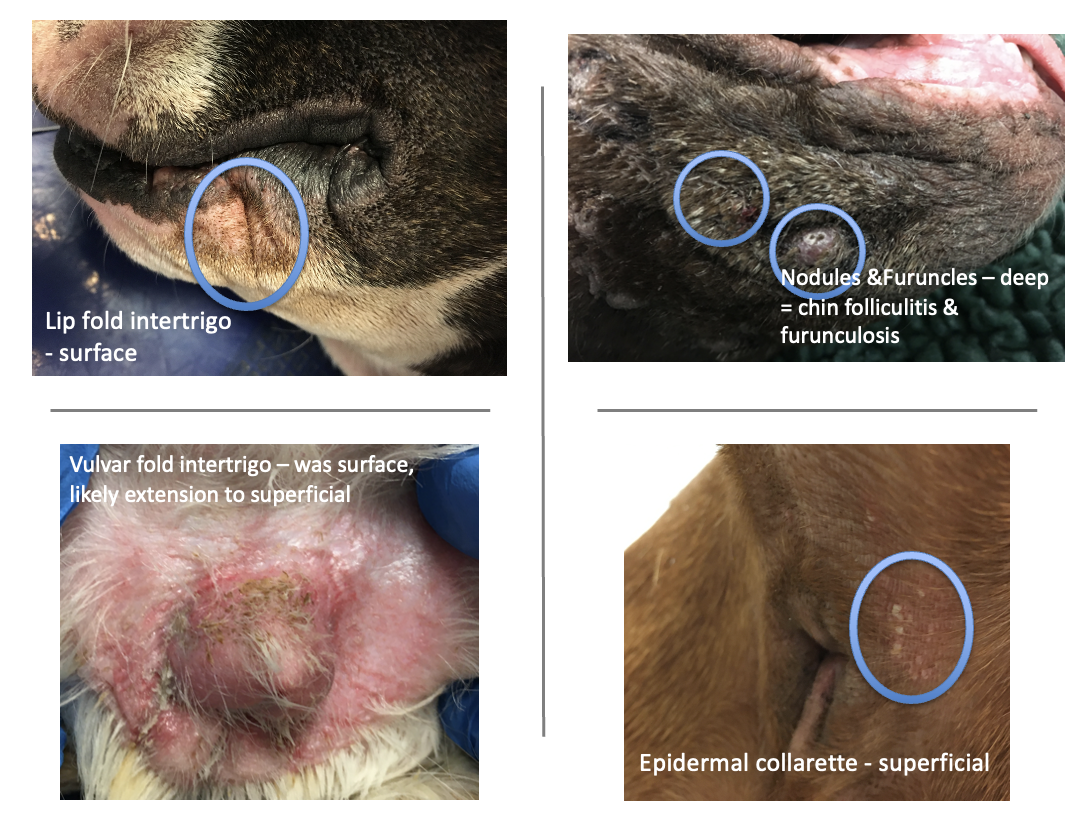
What are the features of intertrigo?
Skin fold pyoderma
Compromised barrier (friction, altered microclimate, loss of normal ventilation)
Microbes proliferate, produce toxins, create inflammation
May have concurrent skin disorder
Can progress to superficial or deep infection
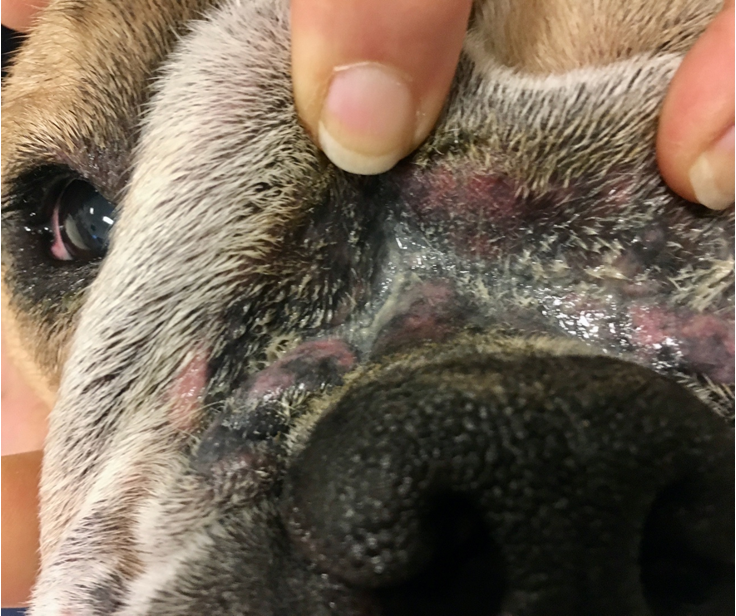
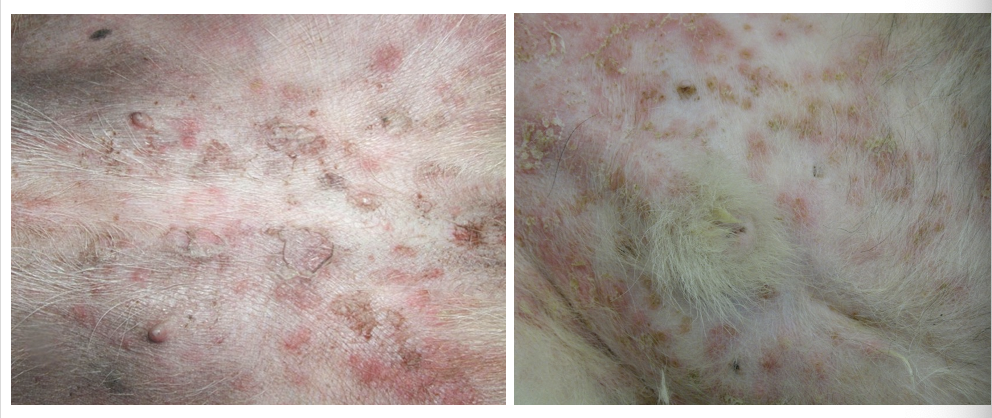
What are the features of bacterial overgrowth as a symptom of surface pyoderma?
Common, usually due to underlying cAD
Ventral trunk and interdigital spaces
Can be very pruritic
Erythema, hyperpigmentation, lichenification, excoriation & alopecia
Ddx Malassezia dermatitis
What is an overgrowth?
Excessive presence of microorganism on skin surface
Not pyogenic - lack of neutrophilic inflam (in infection there is a presence of degenerative neutrophils)
What does superficial pyoderma affect? What is the primary lesion?
Epidermis and superficial hair follicles
Primary lesions: follicular papules & pustules
‘Folliculitis
What does pyogenic mean?
Degenerative neutrophils & phagocytosis of bacteria
What are the symptoms of superficial of pyoderma?
Can be pruritic or non-pruritic; can exacerbate pruritus e.g., cAD
Very variable clinical picture
What aetiological agents usually causes superficial pyoderma?
Usually, staphylococci
S. pseudintermedius dogs and cats
less so, S. aureus or S. schlieferi
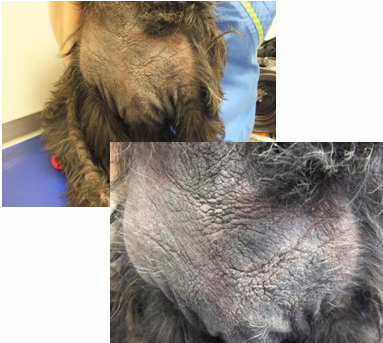
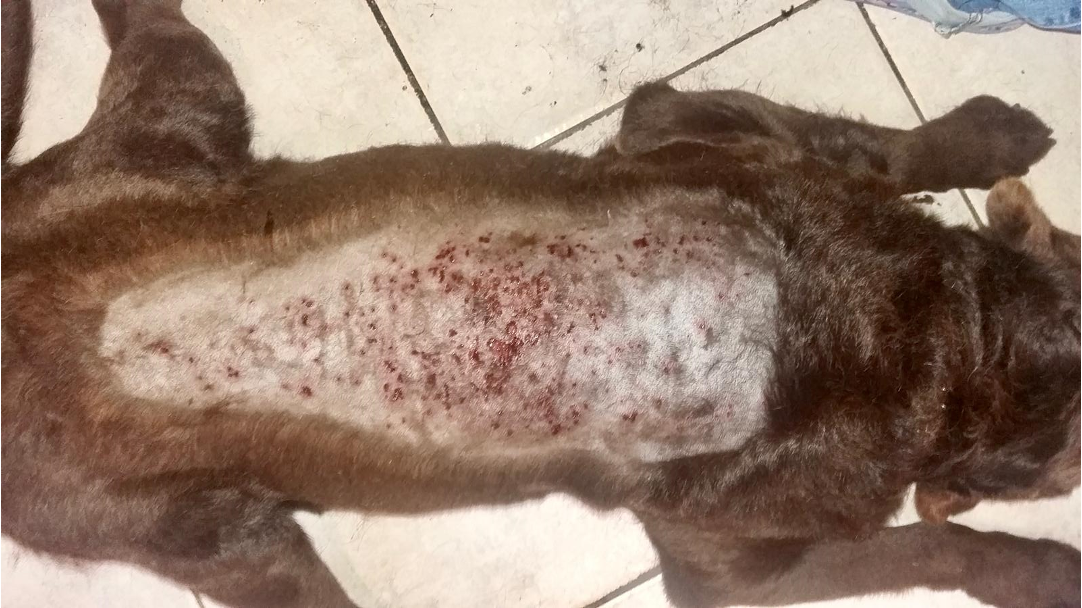
What is being shown here?
Superifical pyoderma
Erythema, follicular papules & pustules, crusts, epidermal collarettes, erosions & hyperpigmented macules
What are epidermal collarettes?
Rims of scale
How does superficial pyoderma present differently in different breeds?
Moth eaten look in short coated
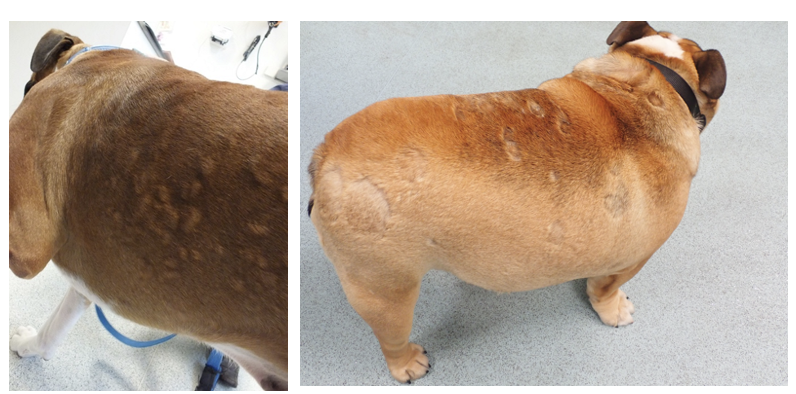
Long coated- disheveled look (crusts and scales)
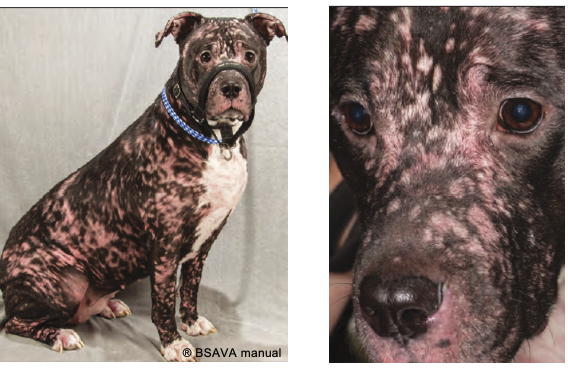
What is superifical pyoderma a main DDx for?
Spontaneous multifocoal alopecia
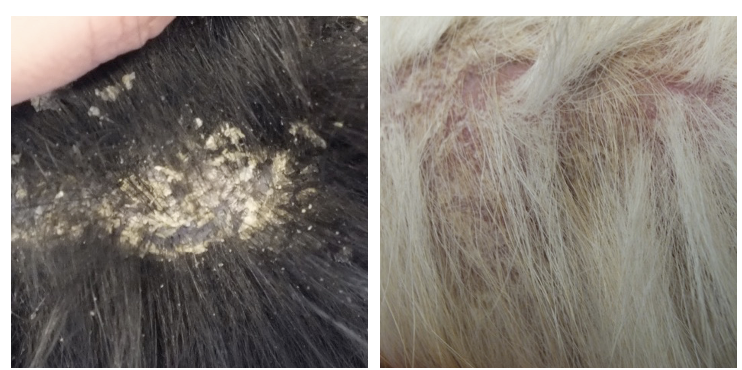
What is impetigo?
Type of superifical pyoderma
Non follicular pustules —> not centred around hair follicles
What is the pathogenesis of deep pyoderma?
Epidermis
Folliculitis (entire hair follicle) -> Furunculosis (follicle rupture) -> Dermis +/- subcutaneous fat
Folliculitis & furunculosis
What are the clinical signs of deep pyoderma?
Heat, swelling, erythema, furuncles, nodules, bullae, plaques, sinus tracts, ulcers, exudation and crusts
Lesions usually haemorrhagic to haemo-purulent (as BV in dermis)
Pain, systemically ill, fever, lymphadenopathy
how does deep pyoderma present in cytology?
Gram-negative or atypical bacteria
E.g., E. coli, Proteus spp., Pseudomonas spp.
How does deep pyoderma present grossly?
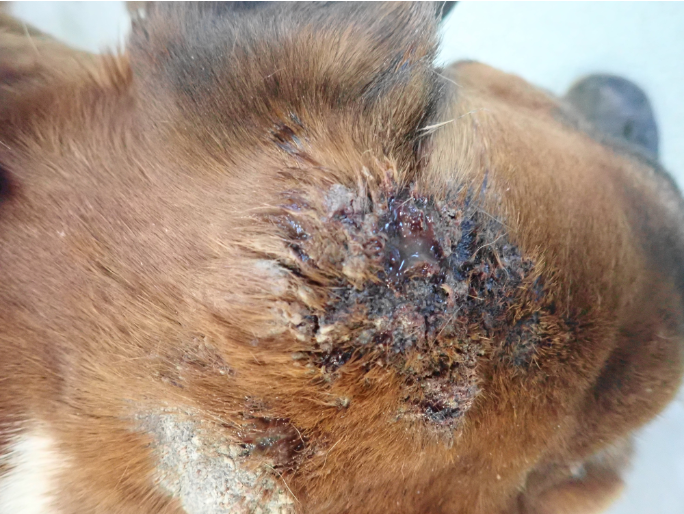
Heat, swelling, erythema, furuncles, nodules, bullae, plaques, sinus tracts, ulcers, exudation and crusts
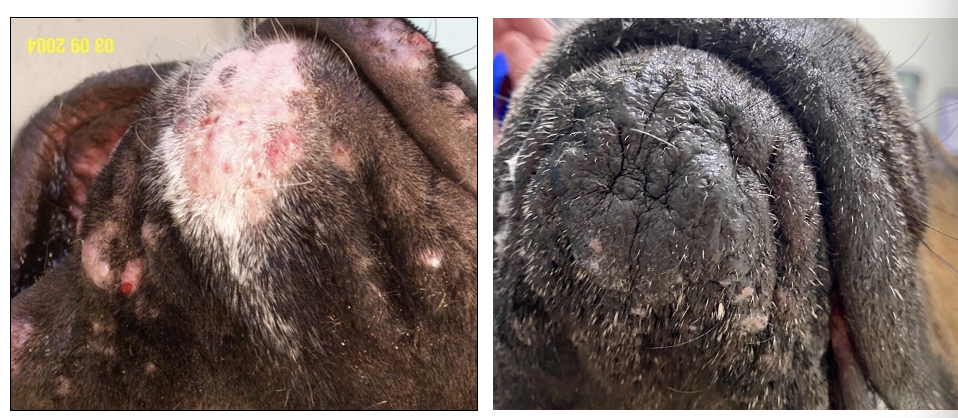
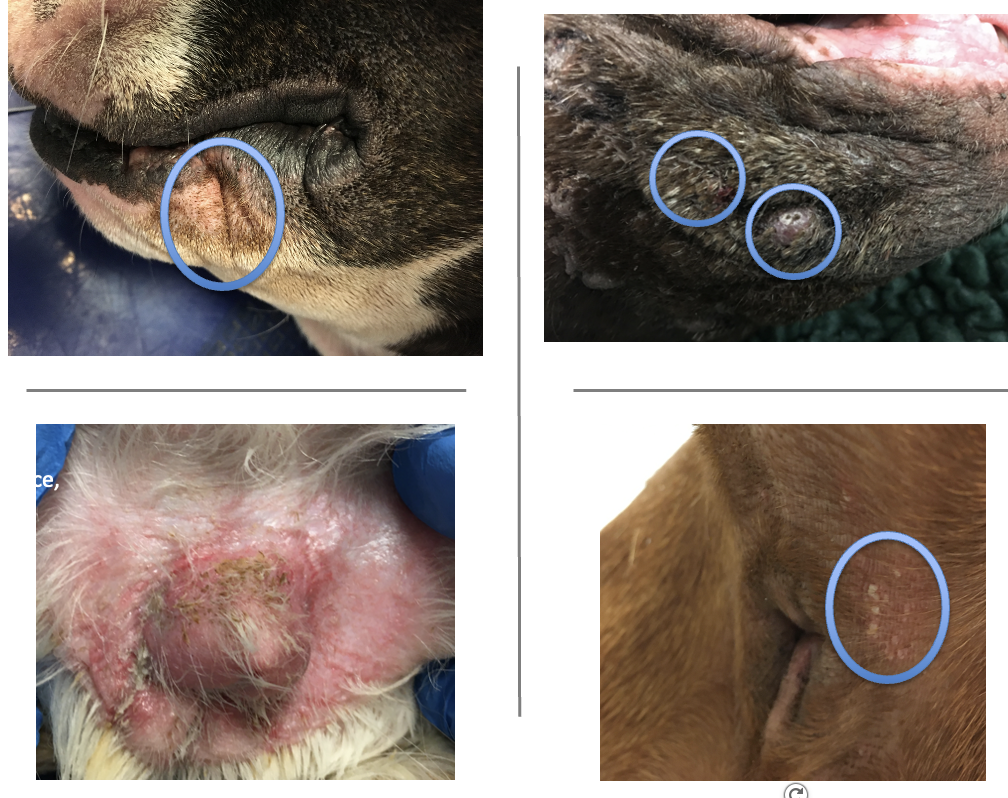
Give some examples of deep pyoderma
Chin folliculitis and furunculosis
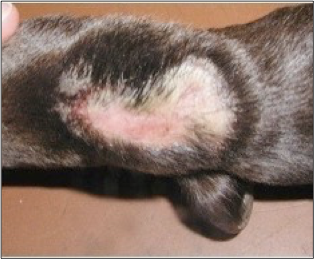
Acral lick granuloma
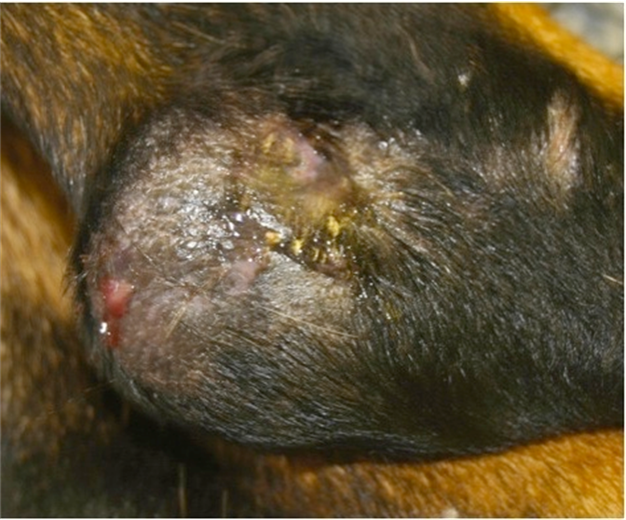
Pressure point deep pyoderma
Post grooming furunculosis
Summarise the clinical presentations of pyoderma
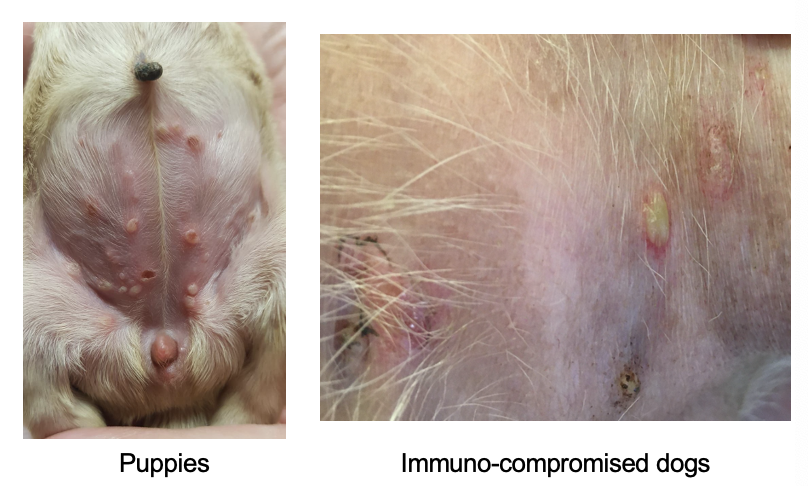
What are these lesions showing?
What are the features of malassezia dermatitis and how does it present clinically?
Overgrowths 2ary to underlying disease
Erythema, greasy exudate, scaling, crusting
When chronic: Greasy alopecia, lichenification & hyperpigmentation
Extremely pruritic
Atopic dogs become sensitised to malaessezia allergens
Creates resistance to anti inflammatories
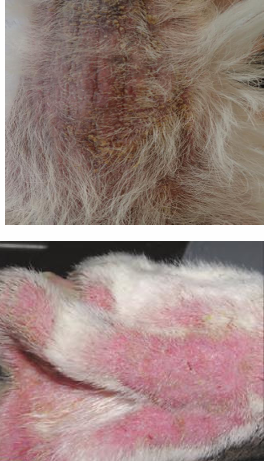
What dog breeds are predisposed to Malaessezia dermatitis?
Basset hounds
WHWT
Cockers
What cat breeds are predisposed to Malassezia dermatitis?
Devon Rex
What can malaessezia dermatitis be secondary to in cats?
Chin acne
Idiopathic facial dermatitis of Persians
Feline Atopic Skin Syndrome
Thymoma-induced exfoliative dermatitis
Paraneoplastic alopecia
How does malassezia dermatitis present grossly in cats?
Brown sebaceous discharge, follicular casting, greasiness
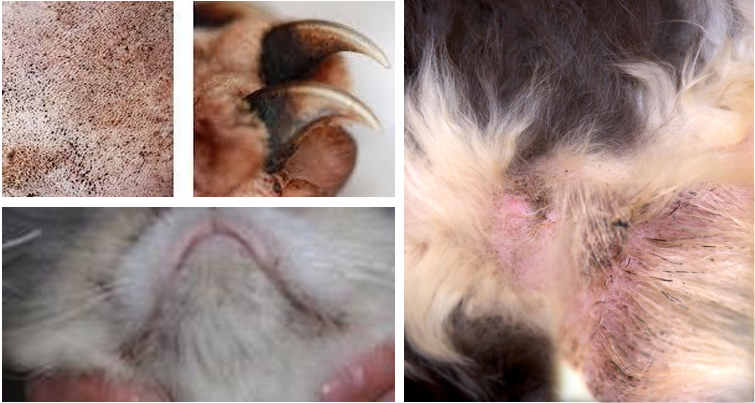
How are skin infections diagnosed?
Cytology
Culture and susceptibility is not diagnostic but can help confirm diagnosis can guide therapy
Name some cytology techniques
direct impression smear
cotton tip/swab smear
adhesive tape strip
fine needle aspirate
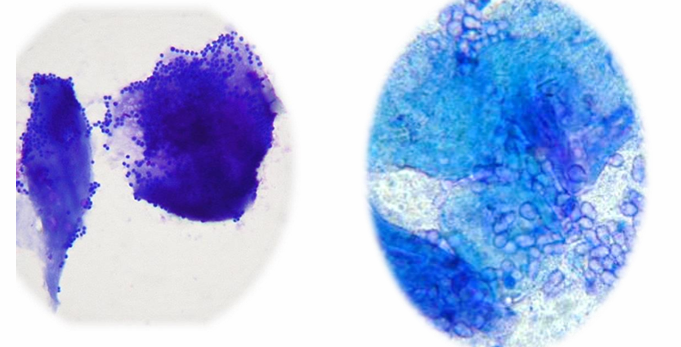
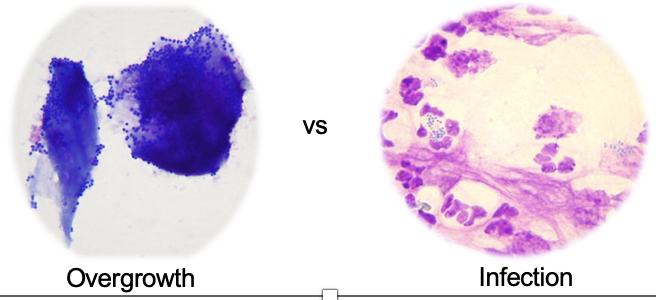
What is being shown in this histology?
LHS = cocci overgrowth
RHS = malassezia overgrowth
both examples of surface infections
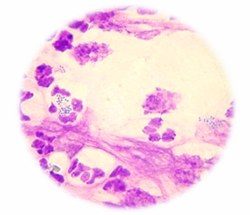
What is being shown in this cytology?
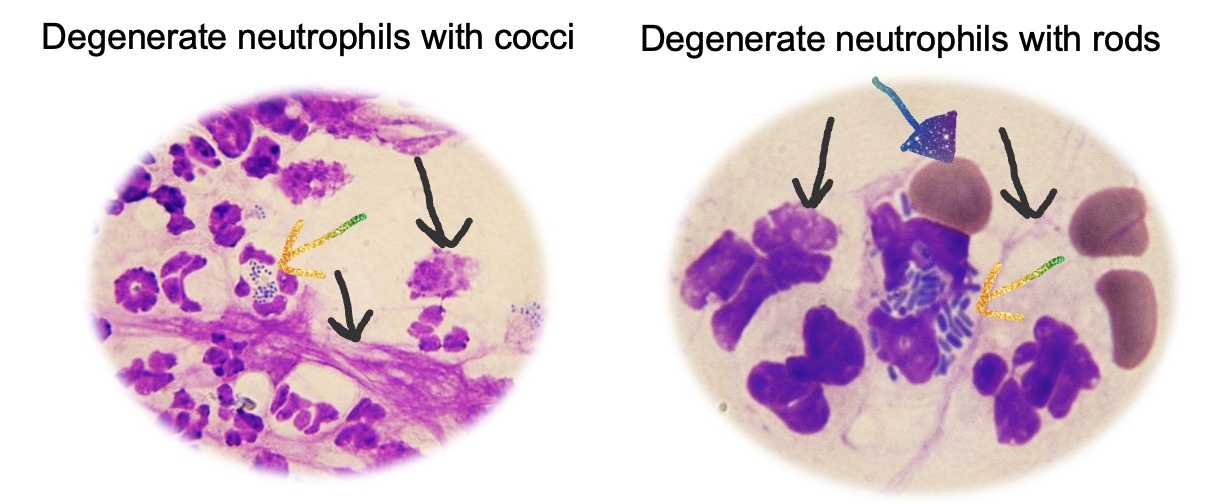
Superficial pyoderma (Left)
Deep pyoderma (Right)
When should you perform culture and suscpetibility for a skin infection?
When there are risk factors for antimicrobial resistance (prev/multiple corses of AB, poor response to empirical therapy)
Rod shaped or unusual organisms on cytology
Deep infections
Degenerate neutrophils but no bacteria
Non-healing wounds
Post op or nosocomial infection
Life threatening infection
How does sampling for culture differ in superifical and deep infections?
Superficial: (crust/pustule)
Rupture and sample intact lesion if present
Sample erosion under a crust or at the edge of a collarette
Deep: (nodular, purulent bloody discharge)
Biopsy (fresh tissue sample)
Rupture intact lesion if possible and use swab
Swab into deep sinus tract- last resort