Hip & Pelvis
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
hip functions
- link between the trunk and lower extremities
- supports the upper body in erect position and sitting
- provides mobility for ambulation
- functions primarily in "closed chain"
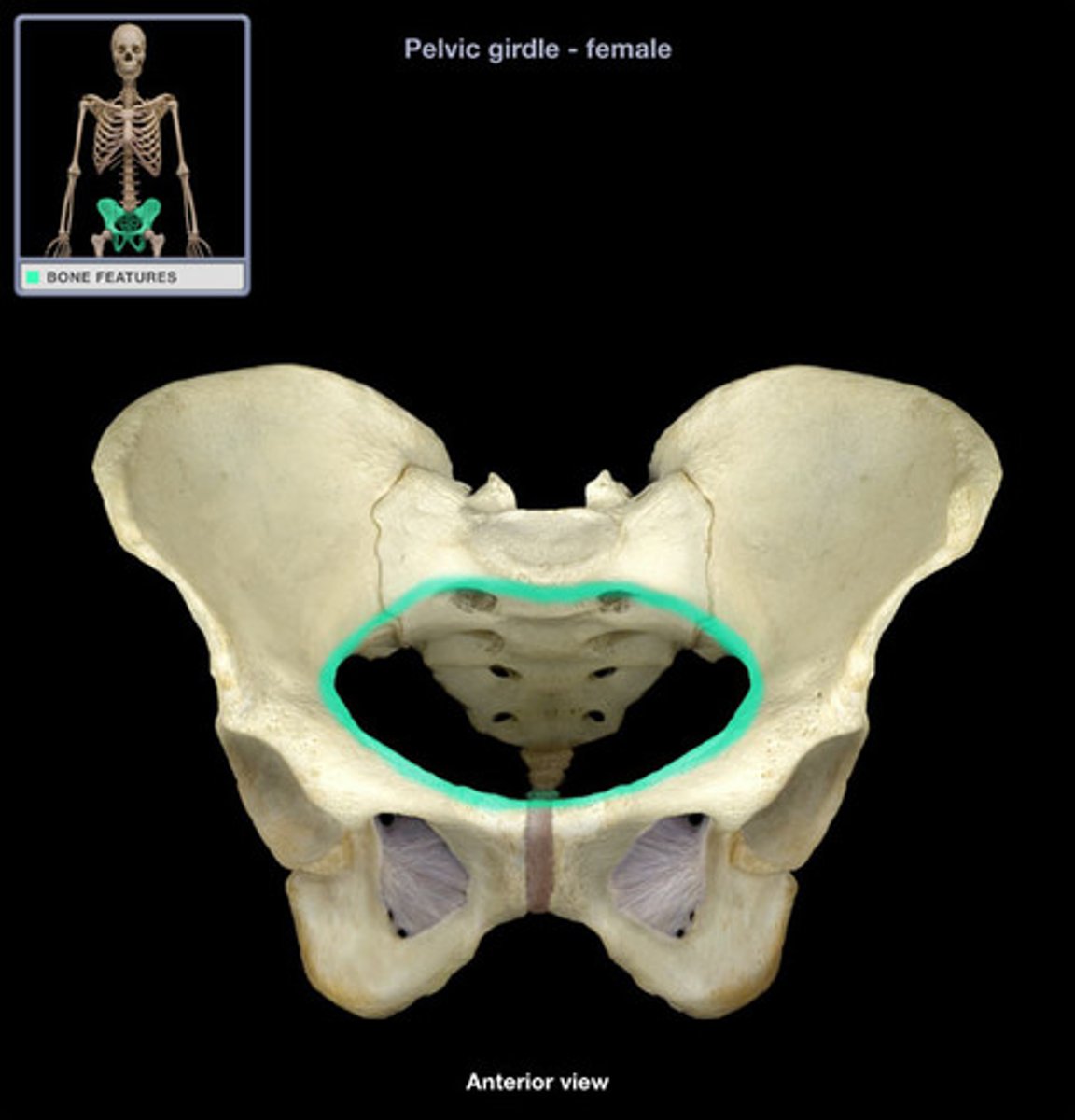
pelvic girdle
comprised of low back (L4 & L5), pelvis, and femur
pelvic ring
"ring" formed by the pelvic girdle
*between the 2 pelvic bones
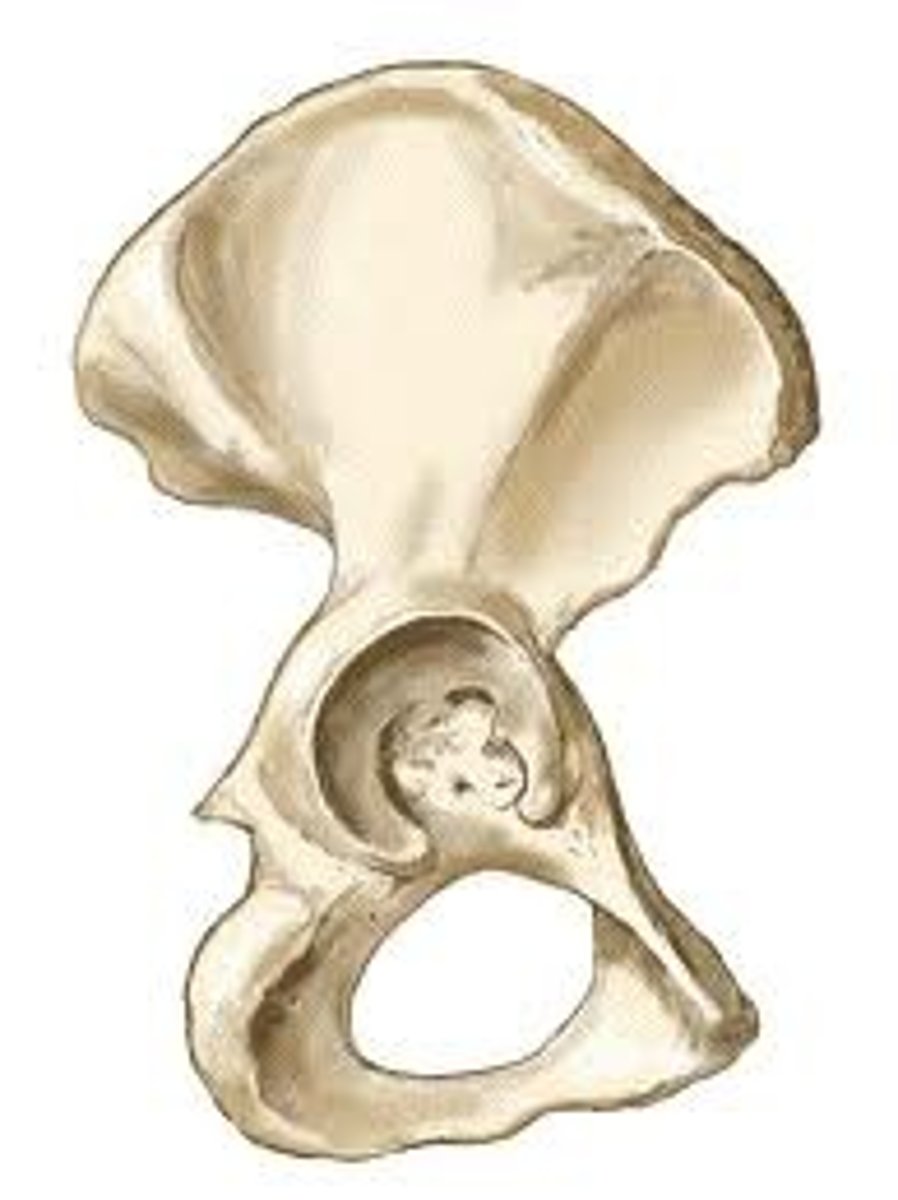
pelvic bone
aka os coxae, coxal bone, or innominate
*ilium, ischium, & pubis
**separate bones until skeletal maturity (15-25 years)
iliac crest
upper margin of iliac bones
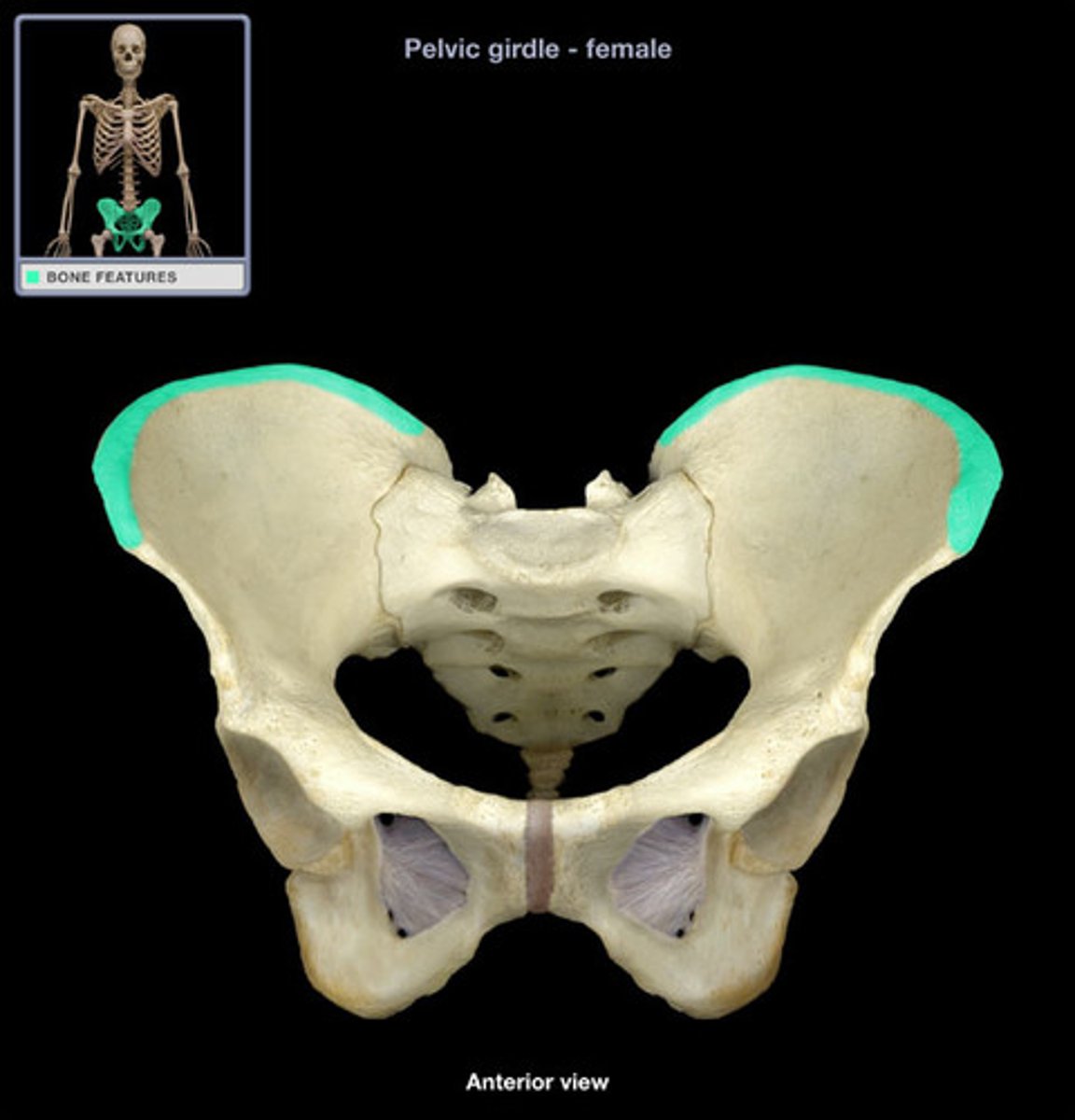
PSIS (posterior superior iliac spine)
the point of the iliac crest in back
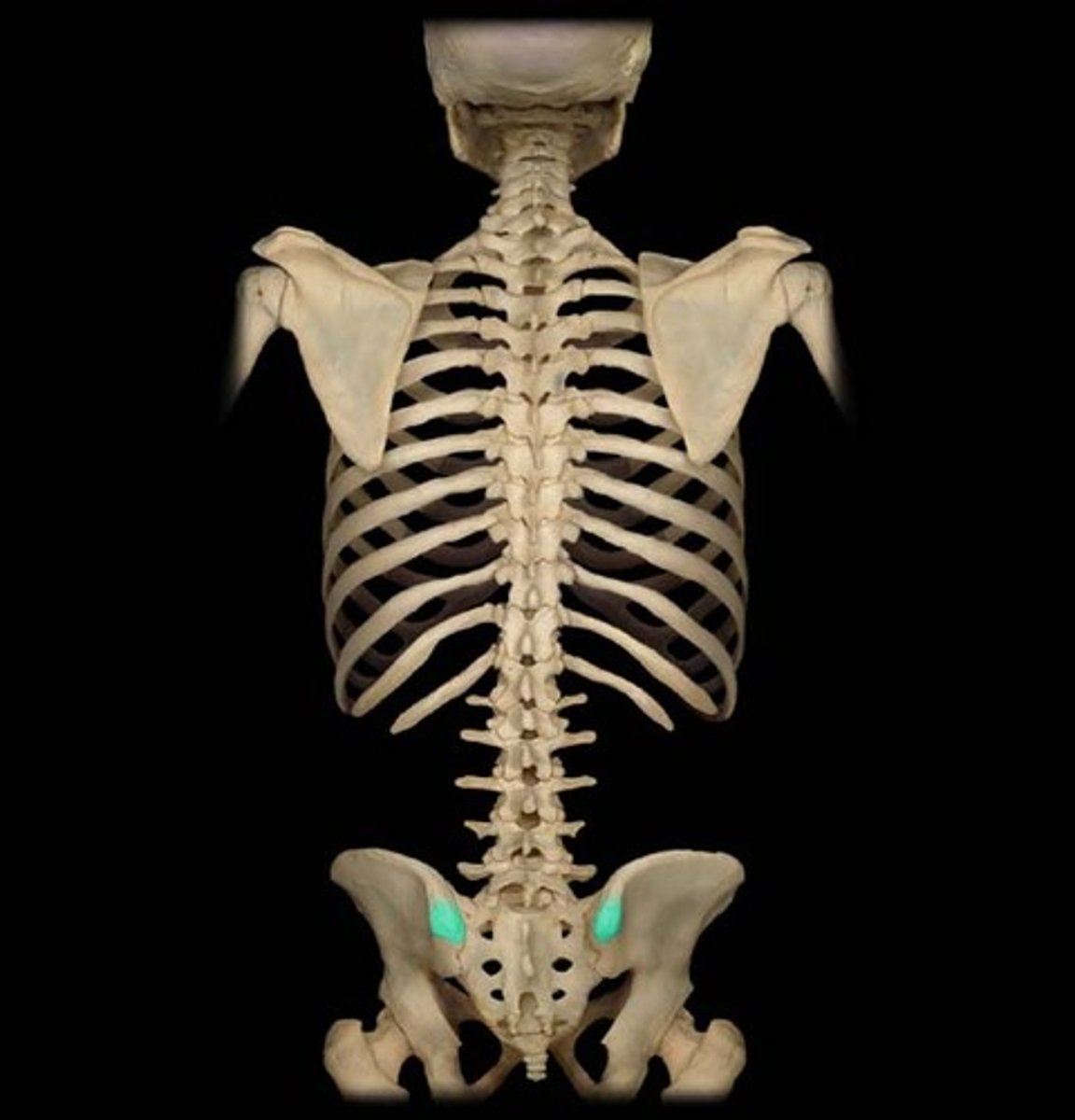
ASIS (anterior superior iliac spine)
the point of the iliac crest in front
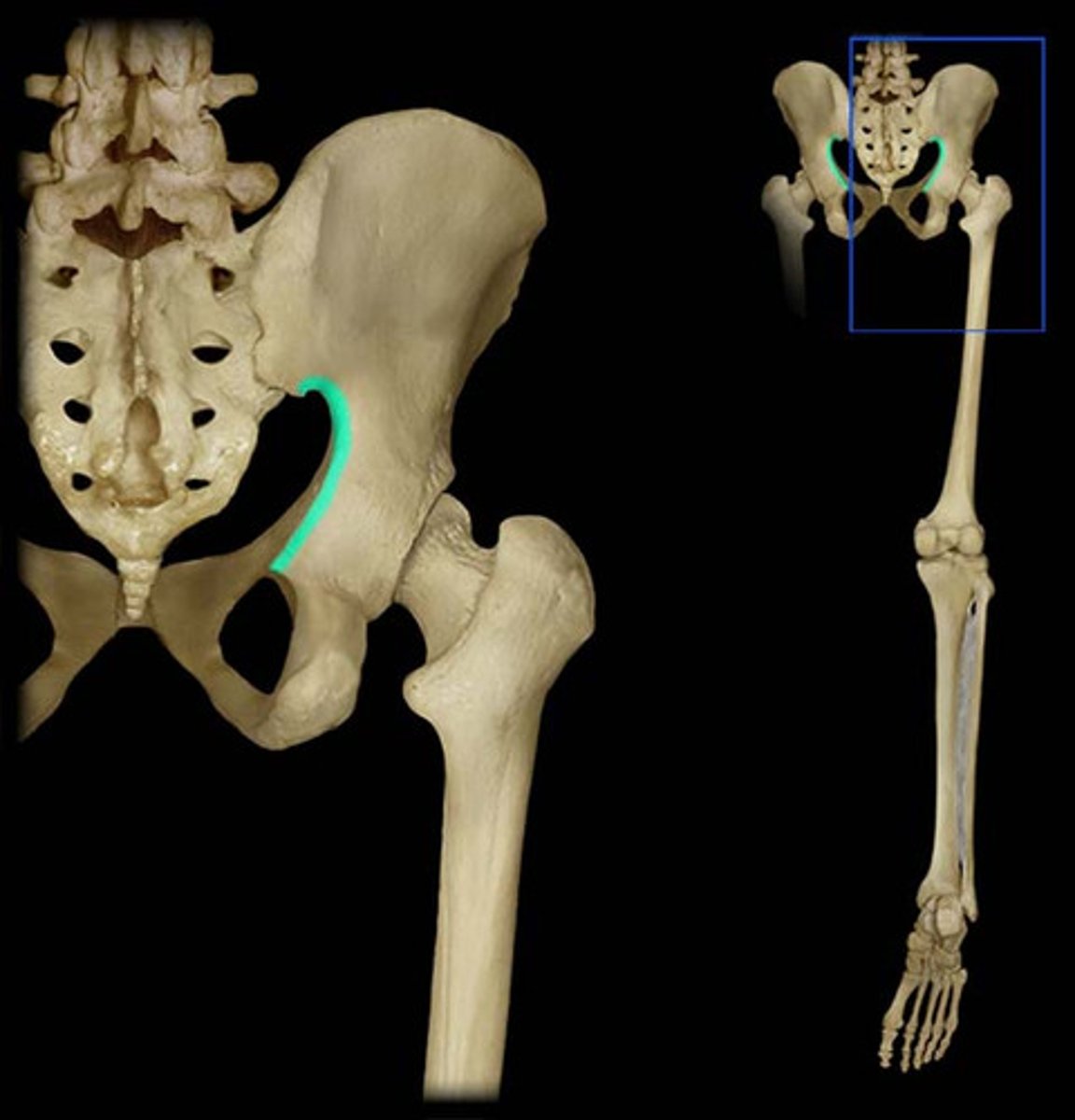
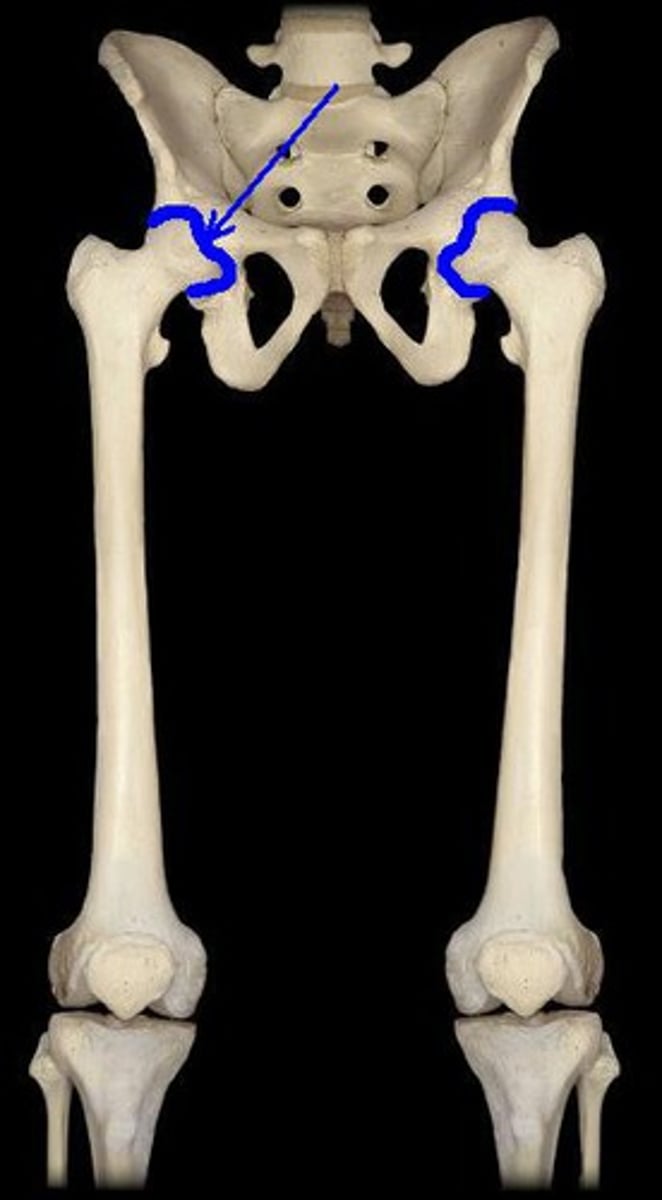
greater sciatic notch
Name this specific part of the pelvic bone.
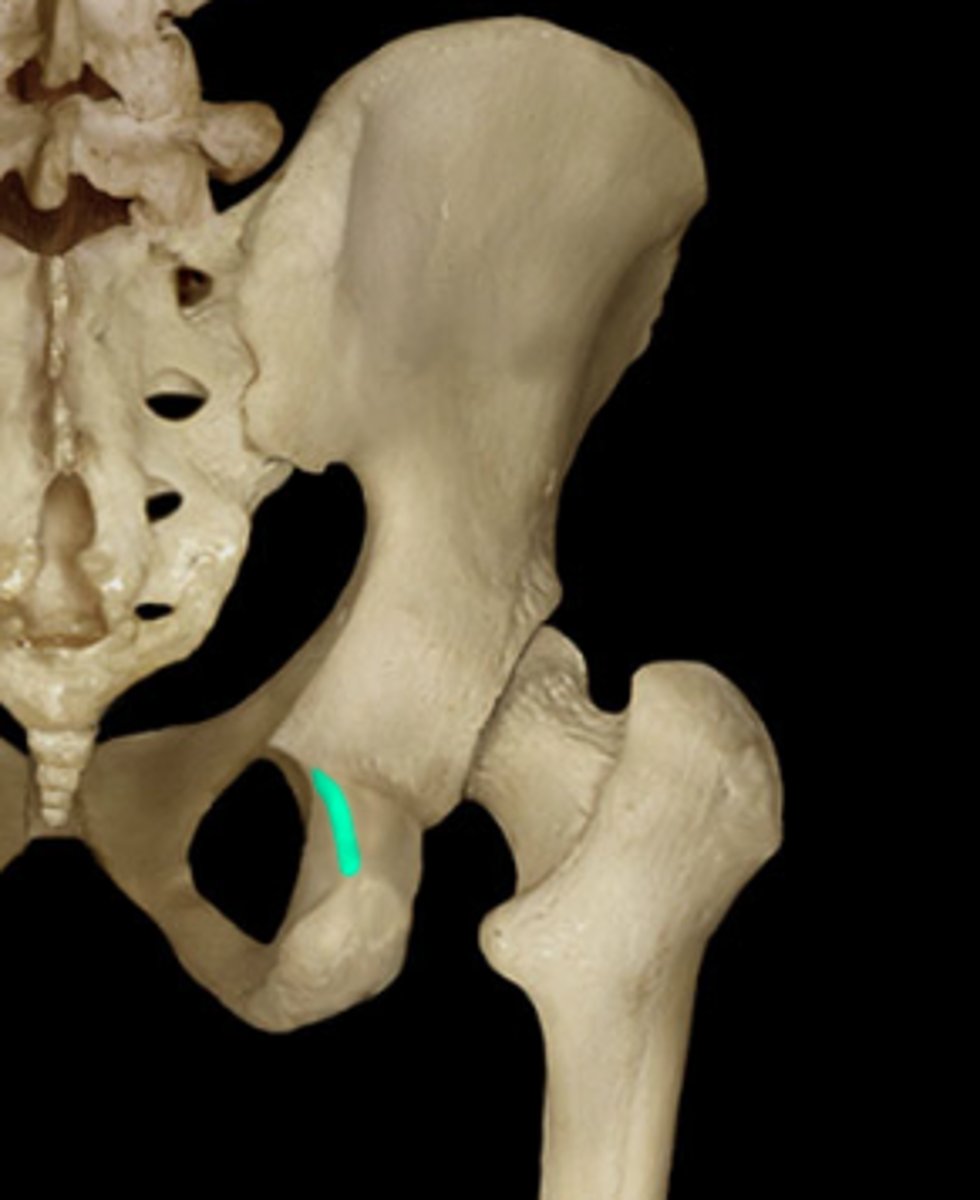
lesser sciatic notch
Name this specific part of the pelvic bone.
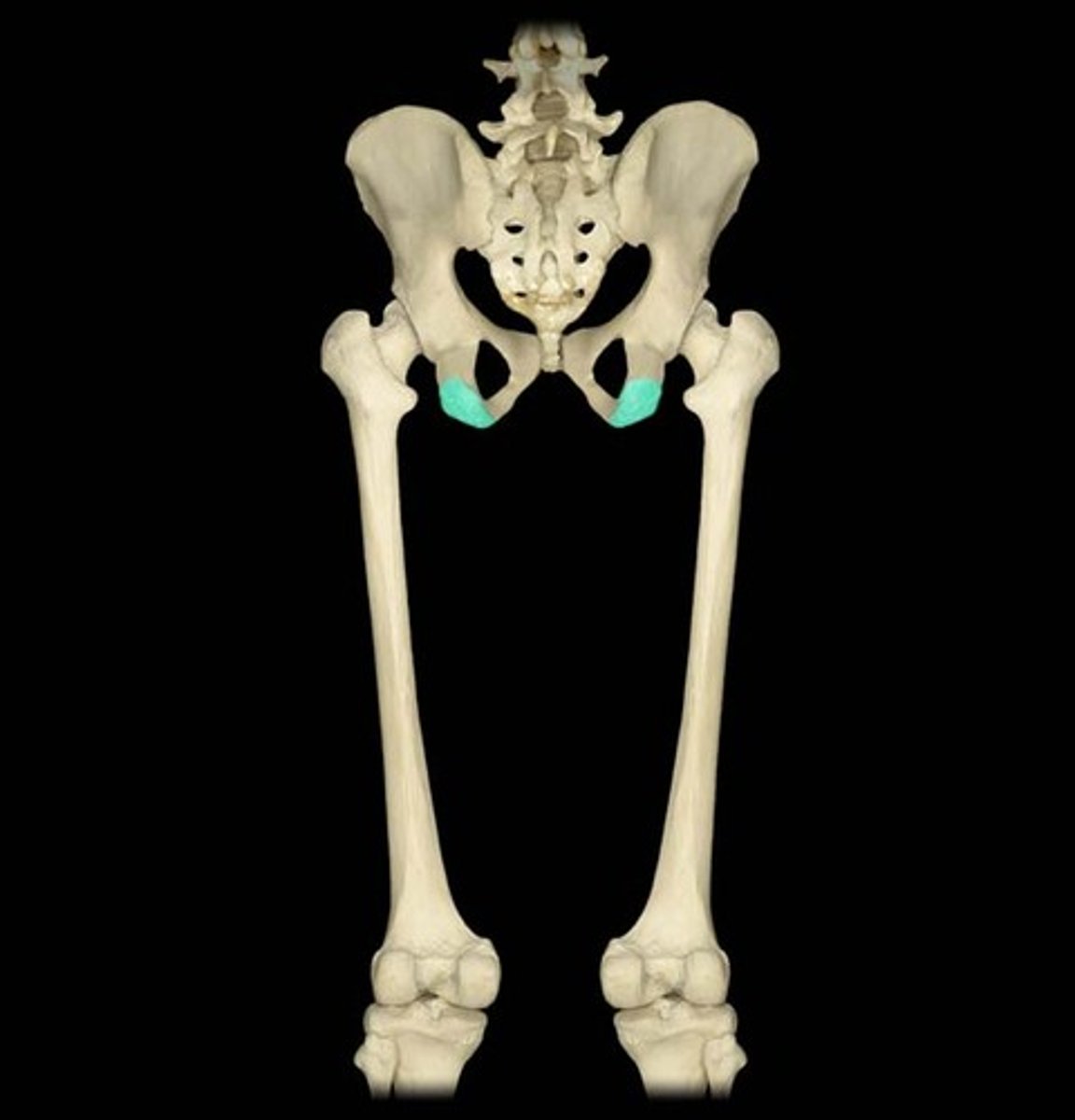
ischial tuberosity
Name this specific part of the ischium.
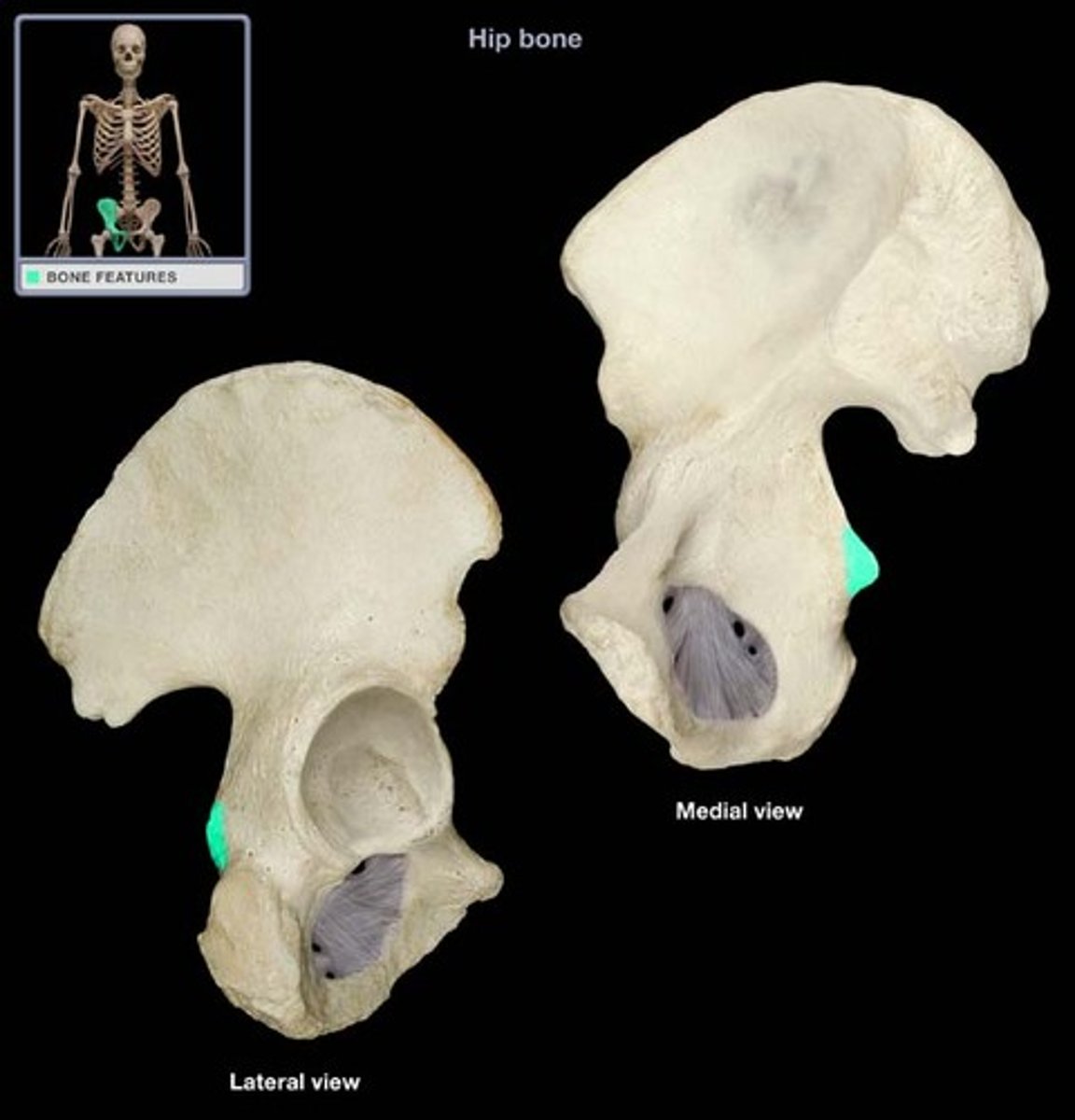
ischial spine
Name this specific part of the pelvic bone.
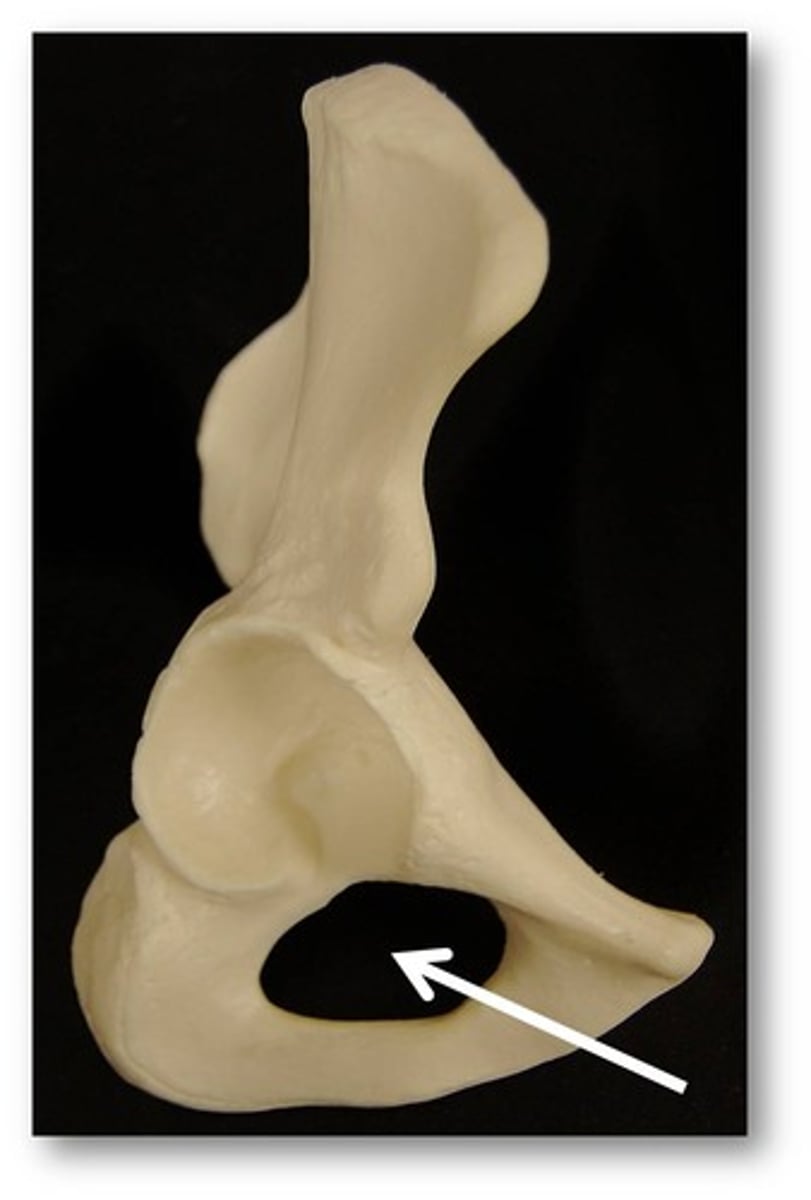
obturator foramen
Name this specific part of the pelvic bone.
HINT: obturator VAN runs through here
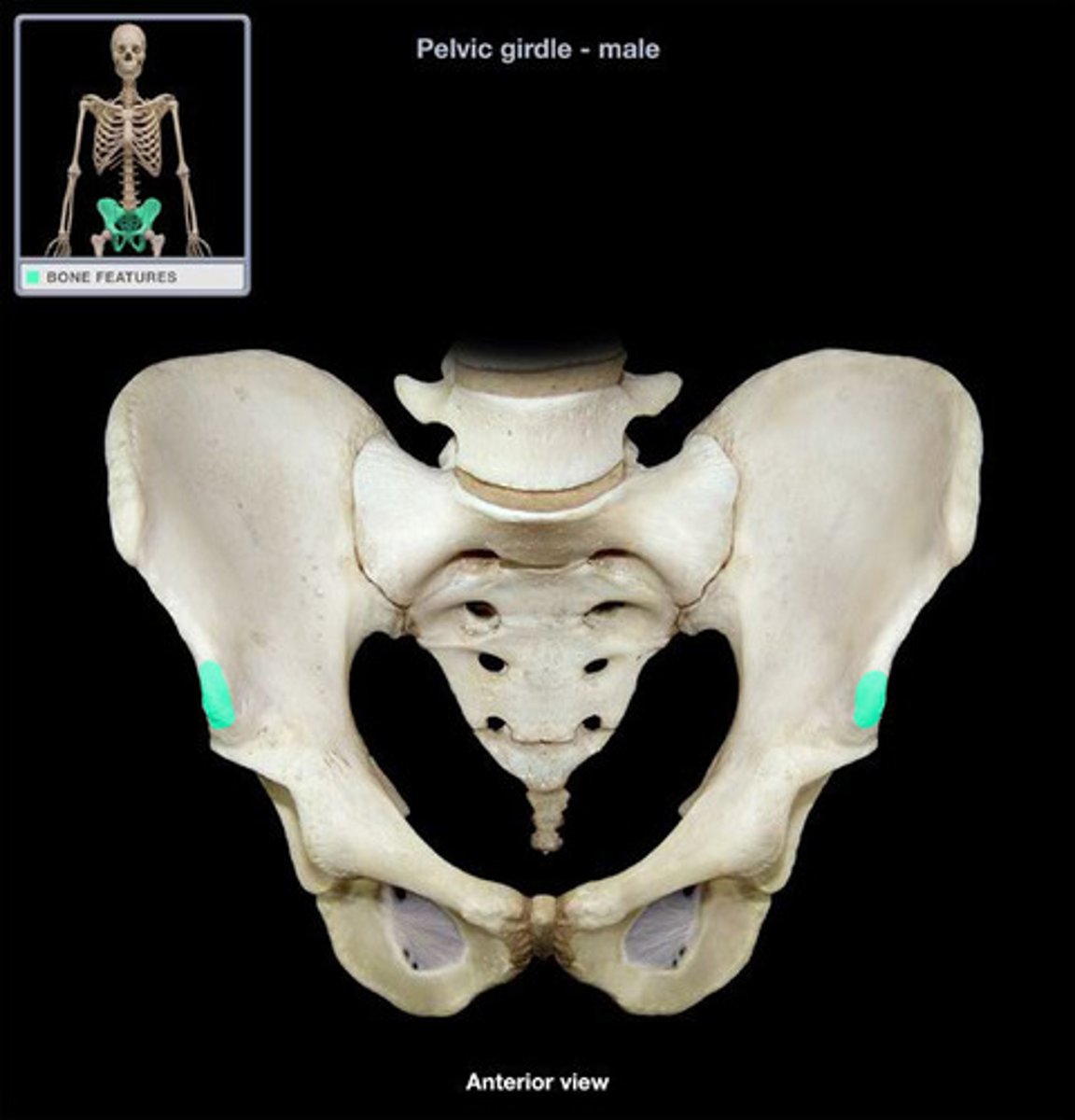
AIIS (anterior inferior iliac spine)
a bony projection on the ilium below the ASIS
ilium, ischium, pubis
The acetabulum is composed of what 3 bones?
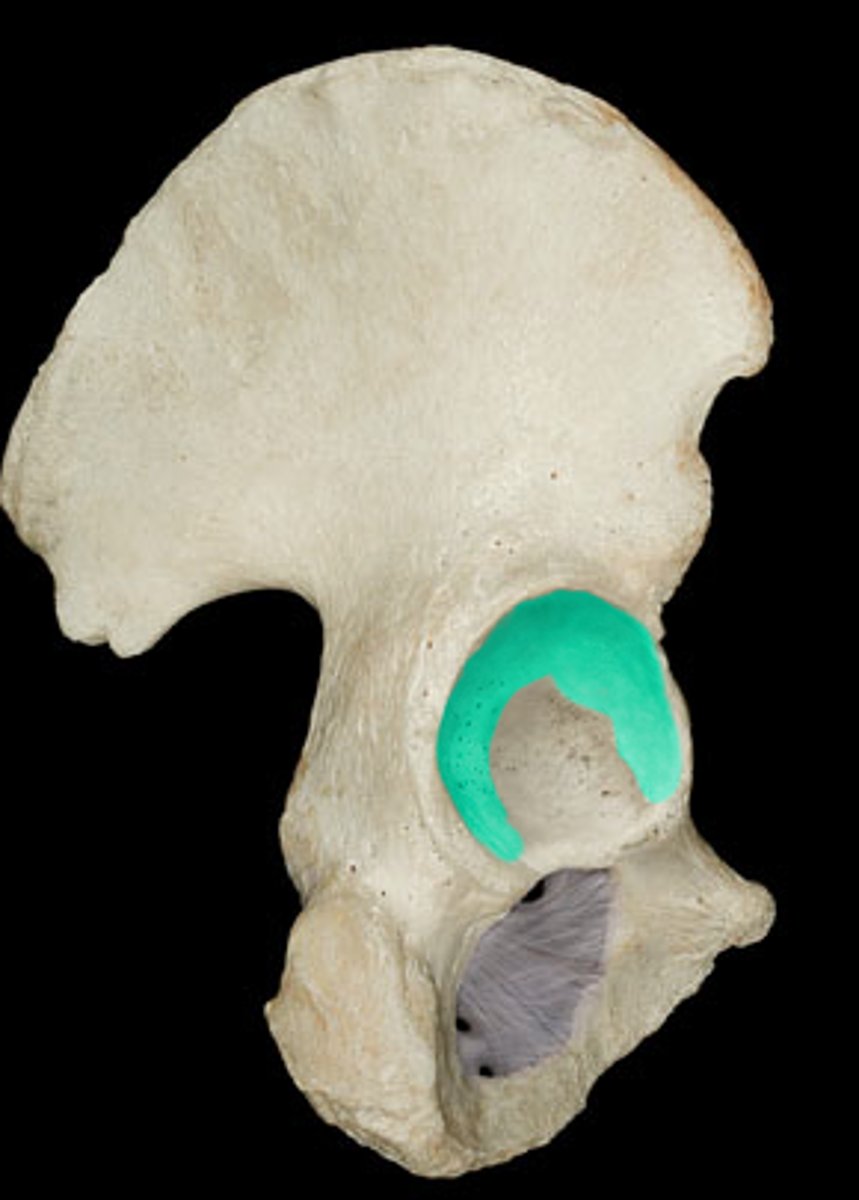
articular surface of acetabulum
horseshoe shaped "lunate surface"
*faces anterior, inferior, lateral (50 degrees inferior, 20 degrees anterior)
pubic symphysis, sacroiliac joint, coxofemoral joint
What are the 3 articulations of the innominate bone?
pubic symphysis
two pubic bones covered with hyaline cartilage, with a fibrocartilaginous disc
*synarthrodial or amphiarthrodial joint
**some motion occurs (2 mm of translation, 3 degrees of rotation)
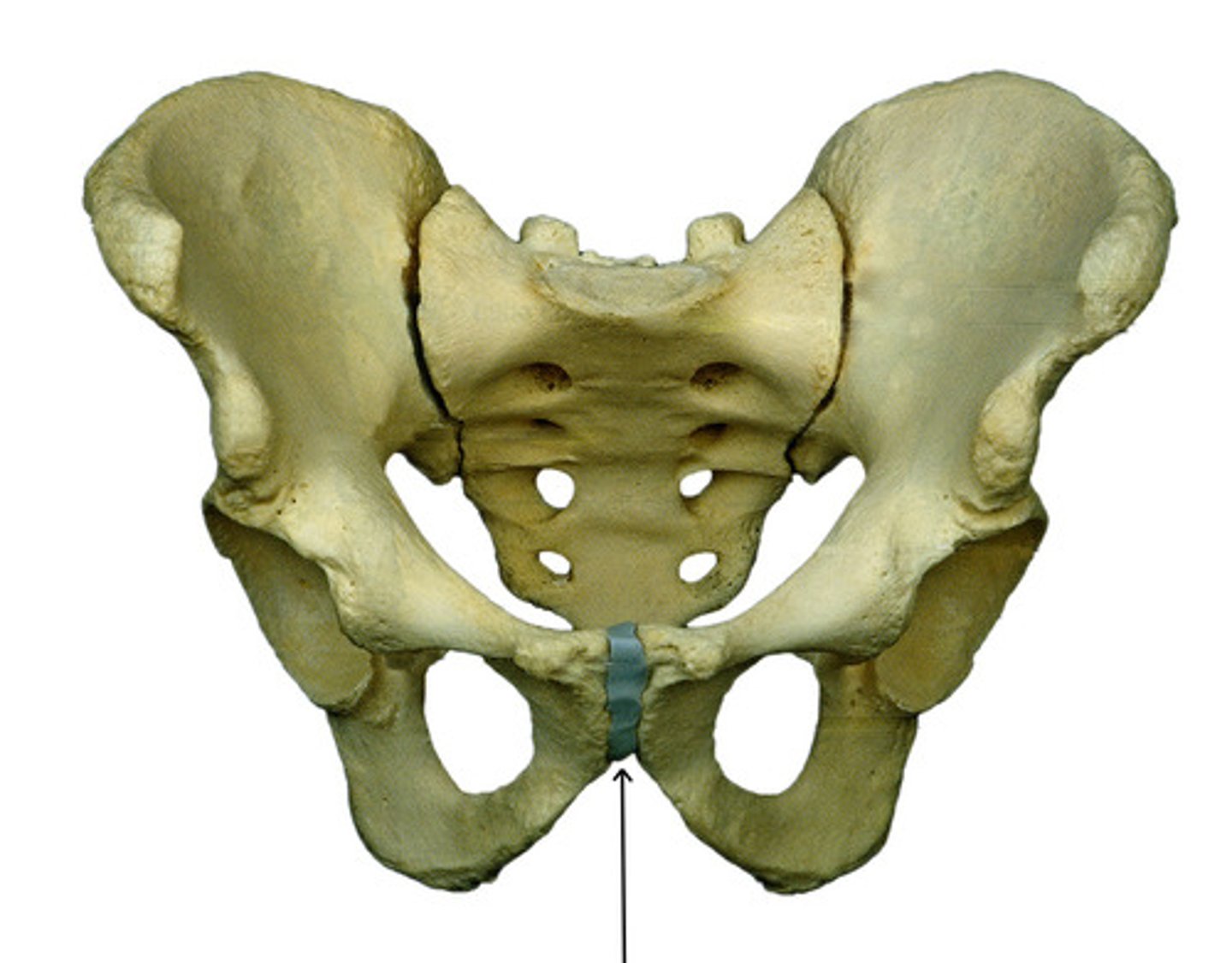
hyaline
The pubic symphysis is covered by which type of cartilage?
sacroiliac joint
auricular surface of ilia (fibrocartilage) and the first 3 sacral bones (fused and covered with hyaline cartilage)
*part synovial and part fibrous
**diarthrodial in childhood, modified synarthrodial in adulthood
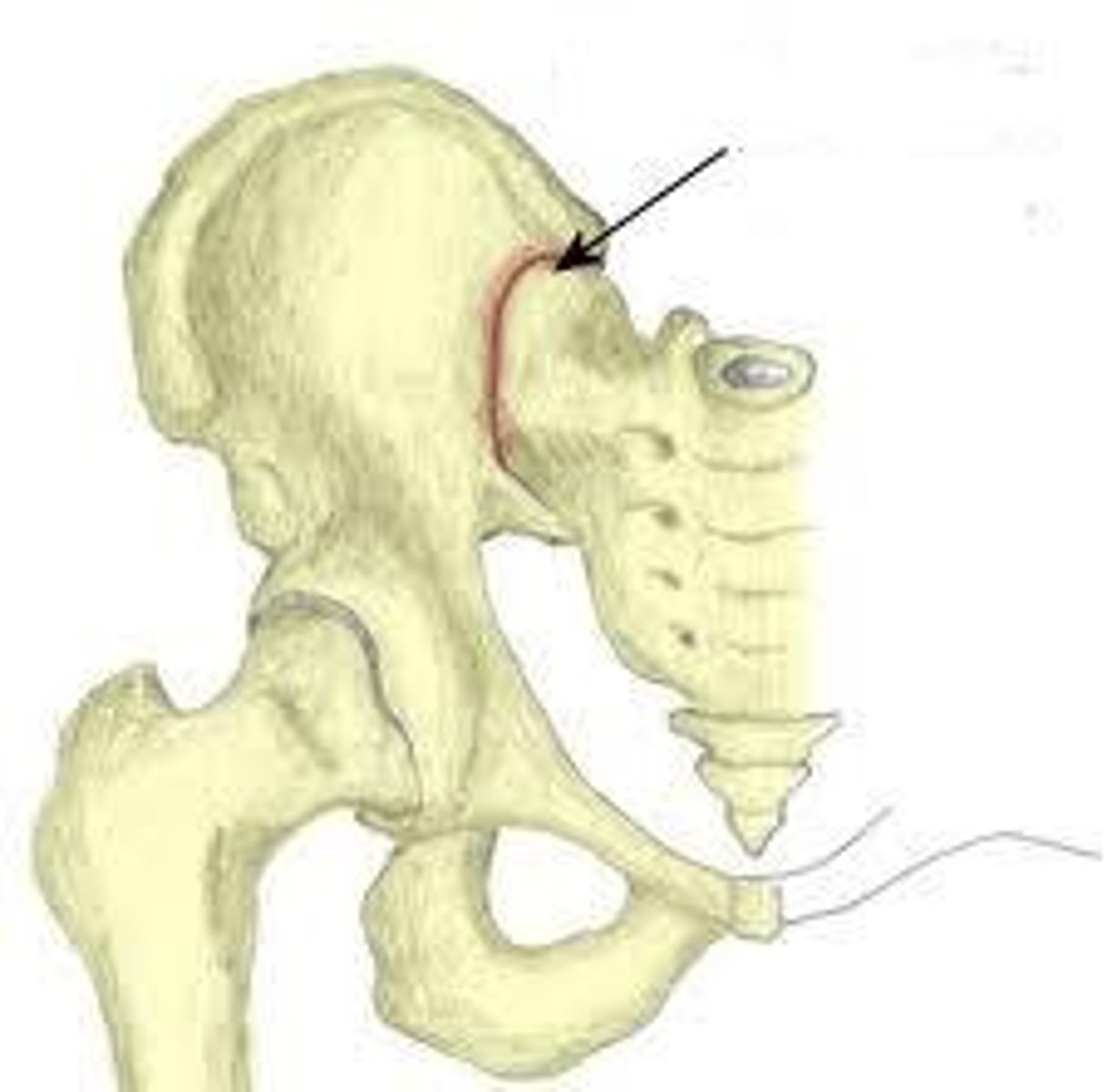
fibrocartilage, hyaline cartilage
In the SI joint, the ilia are covered by _______________________, while the sacrum is covered with ______________ ___________________.
coxofemoral joint
hip joint
ball and socket diarthrodial joint between the acetabulum of the innominate and the head of the femur
ilium, ischium, pubic
The acetabulum is 2/5 ____________, 2/5 ____________, and 1/5 __________ bone.
mechanical advantage
Because the greater trochanter is far from the head of the femur, it increases what?
articular cartilage
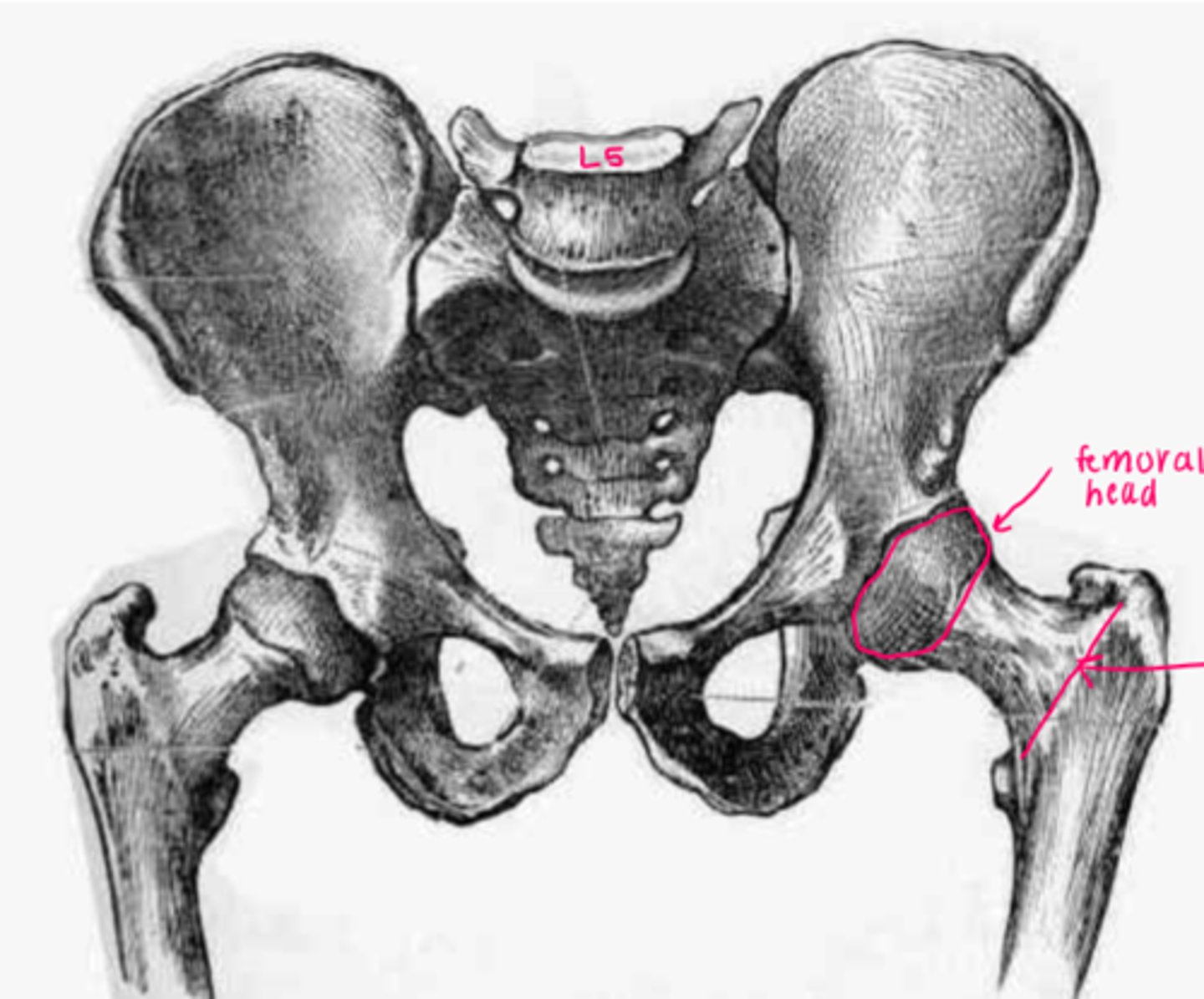
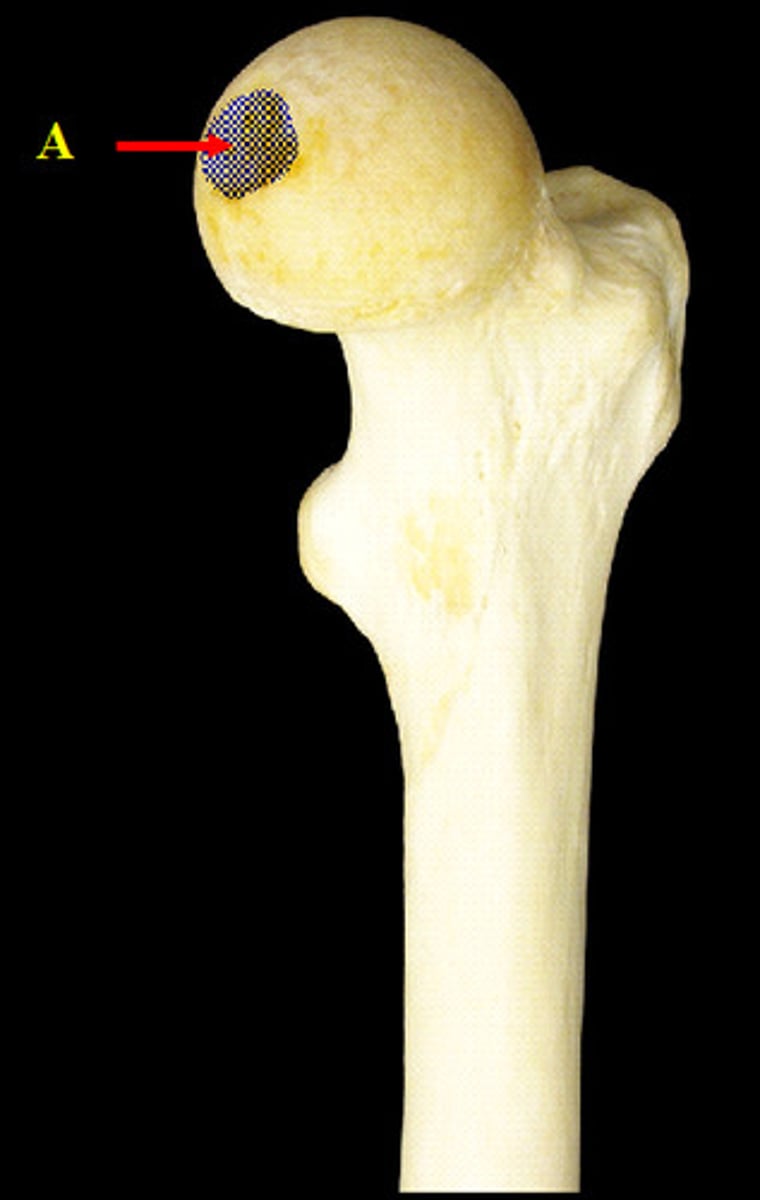
The head of the femur (excluding the fovea) is covered by what?
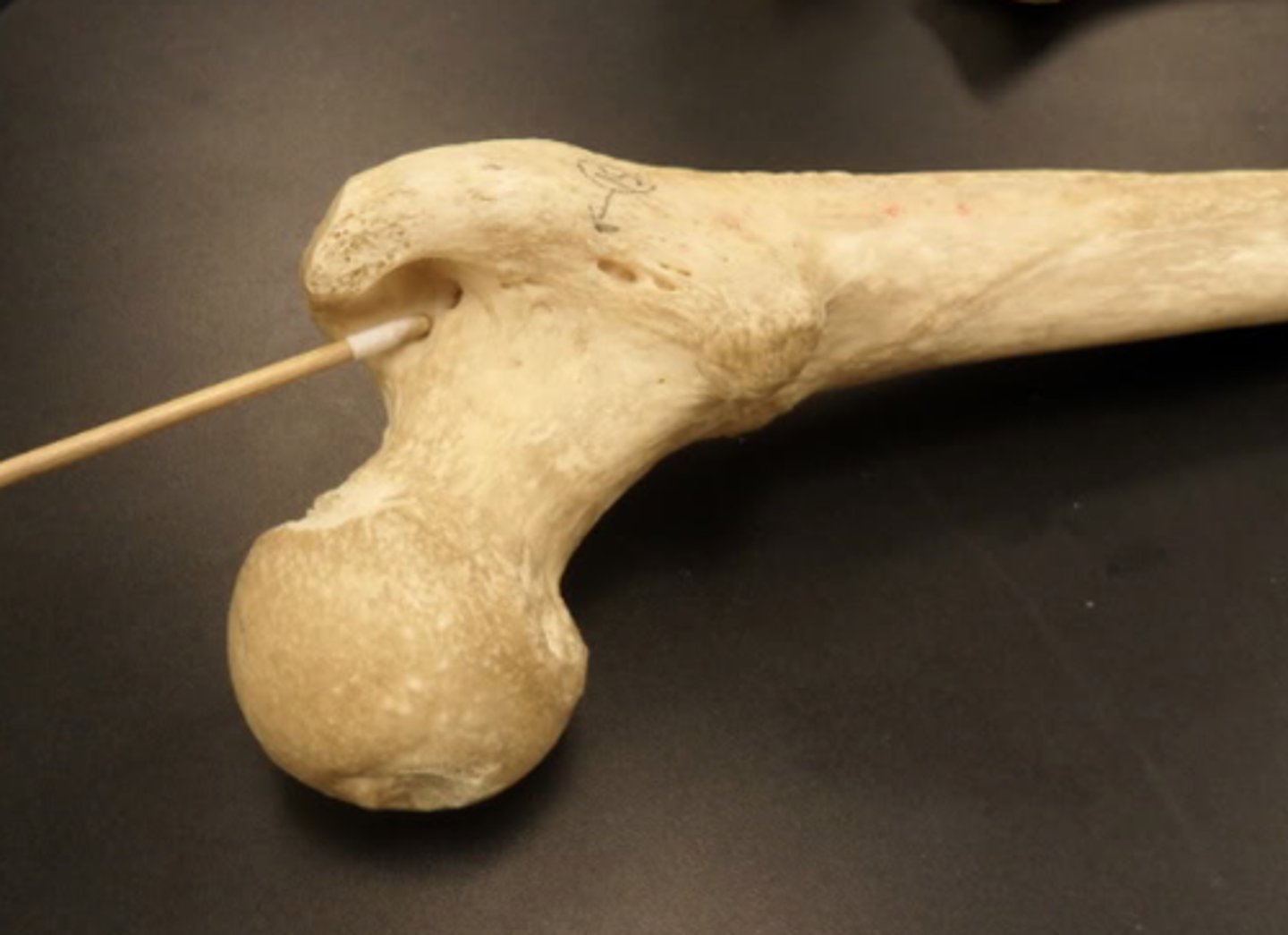
femoral head
1/2 to 2/3 of a sphere, almost completely covered by articular cartilage
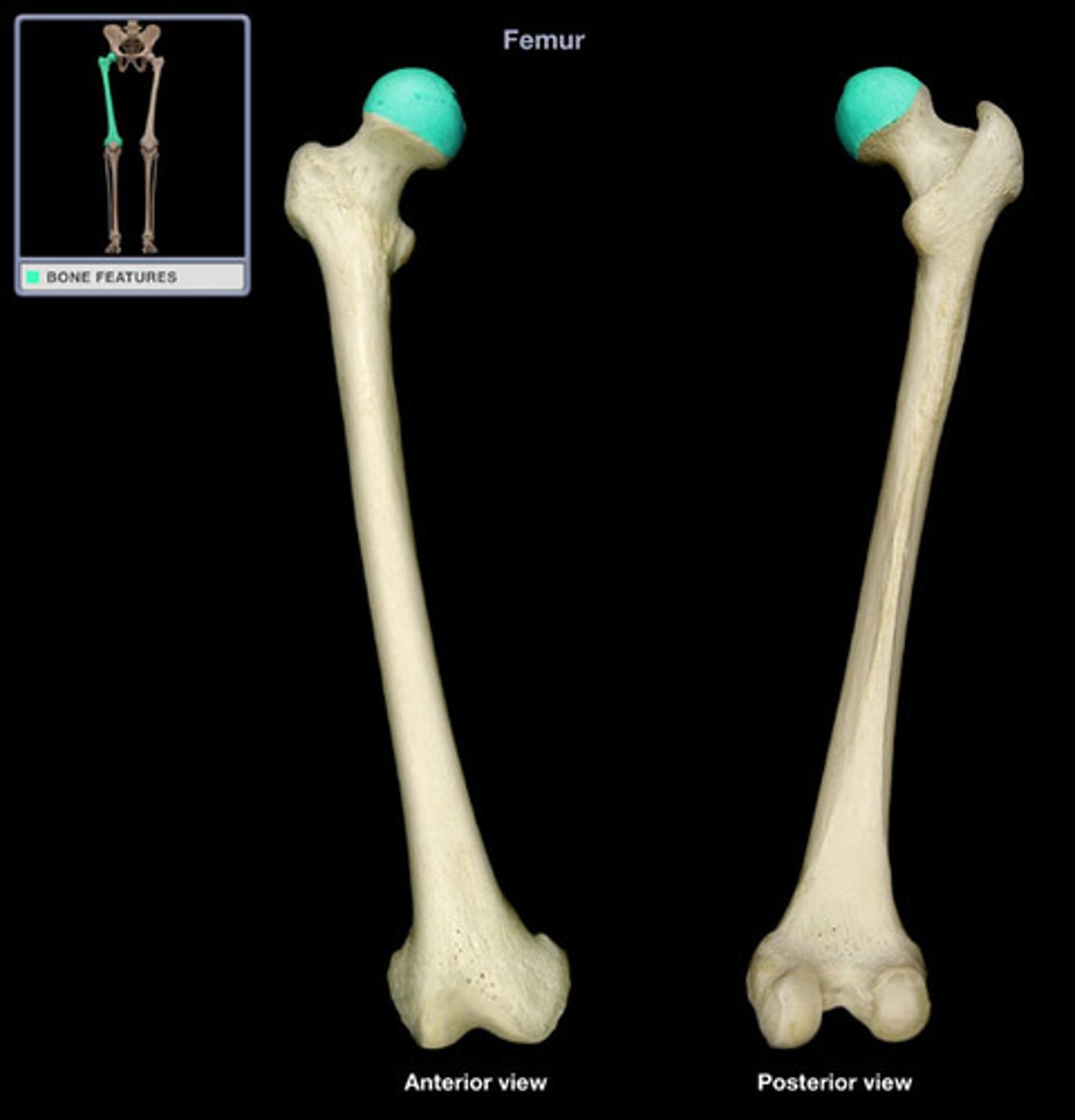
fovea
small depression on the femoral head that serves as an attachment for the ligamentum teres
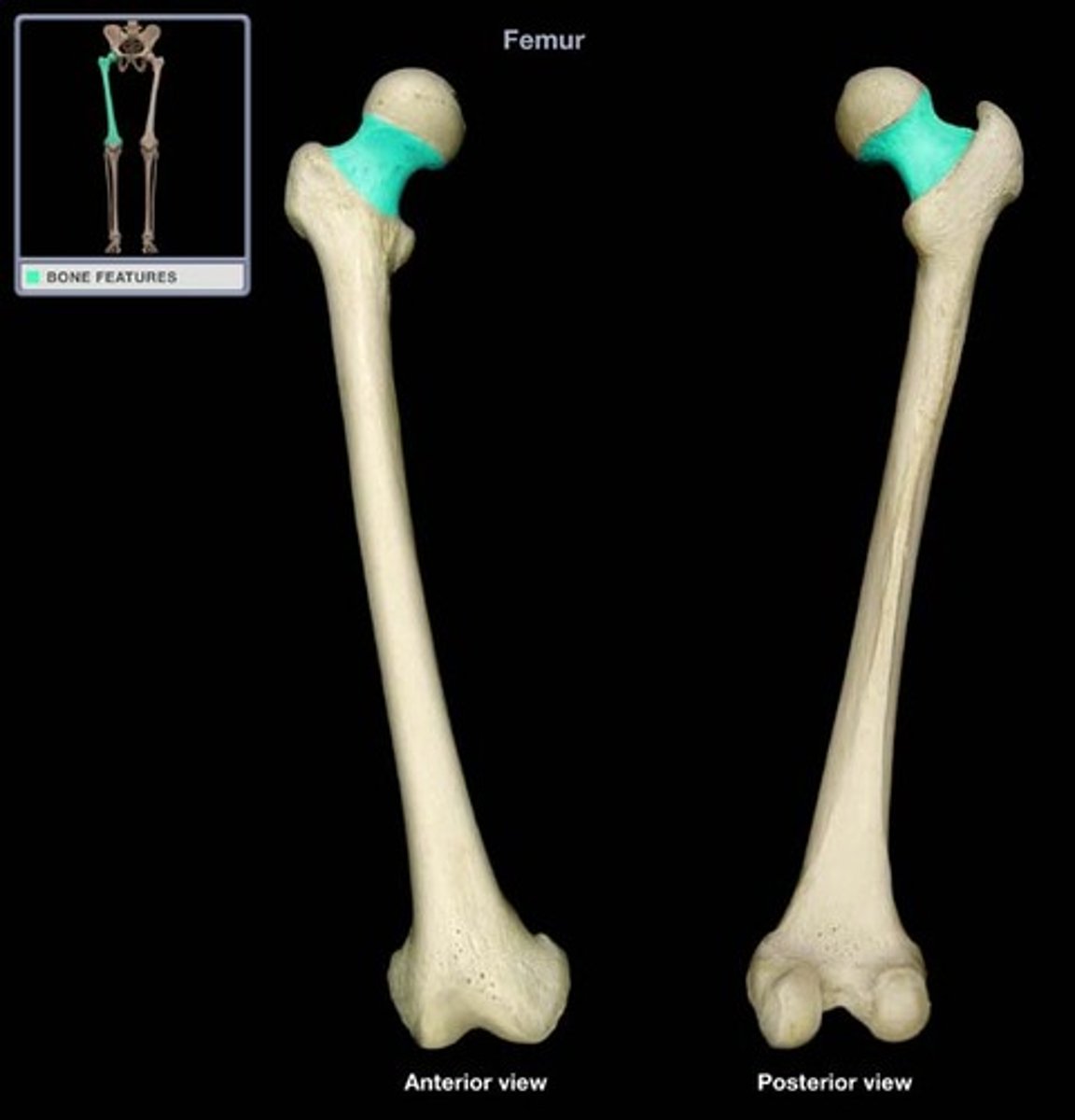
femoral neck
3/4 the diameter of the head
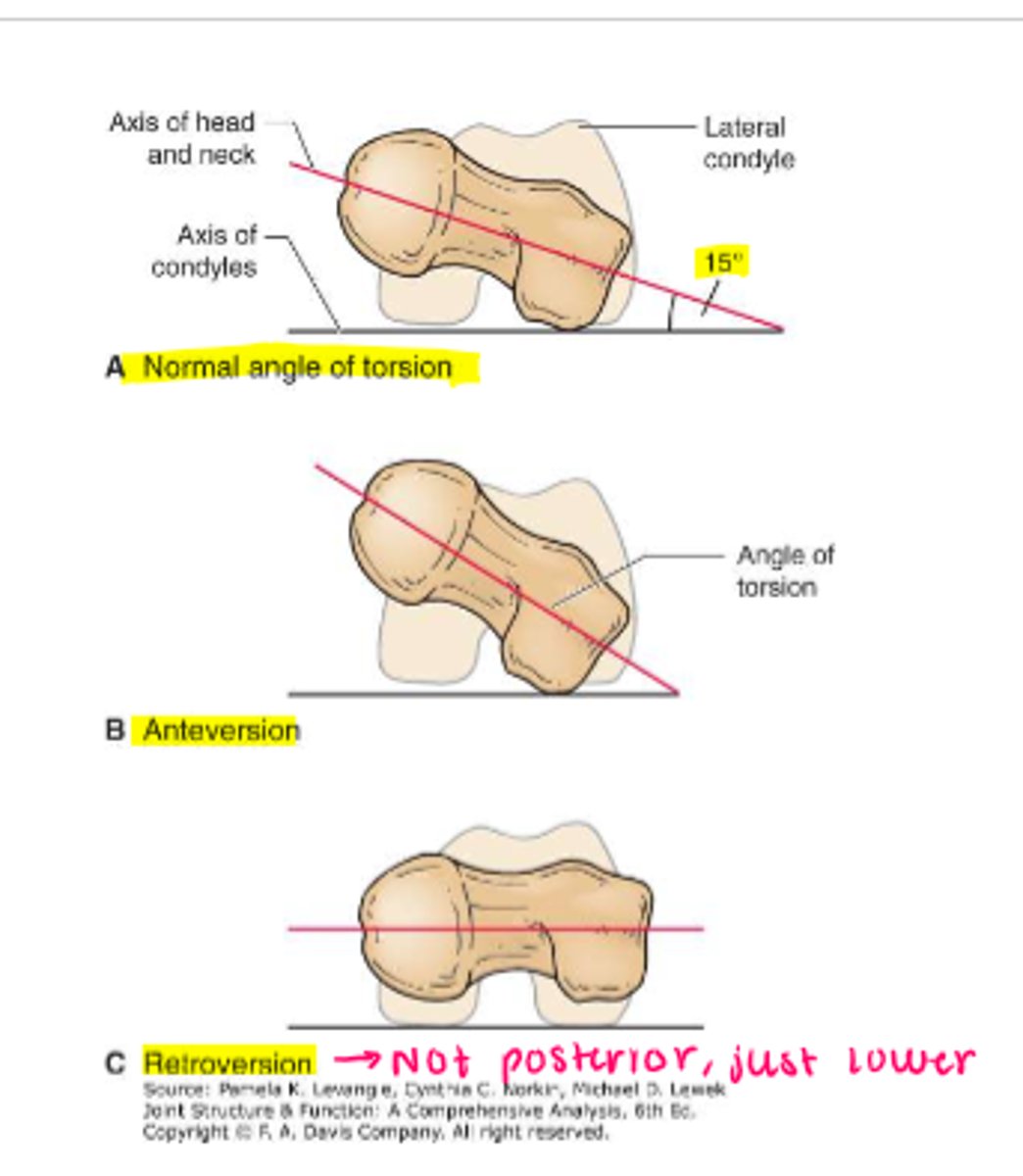
*angle of inclination
*angle of torsion
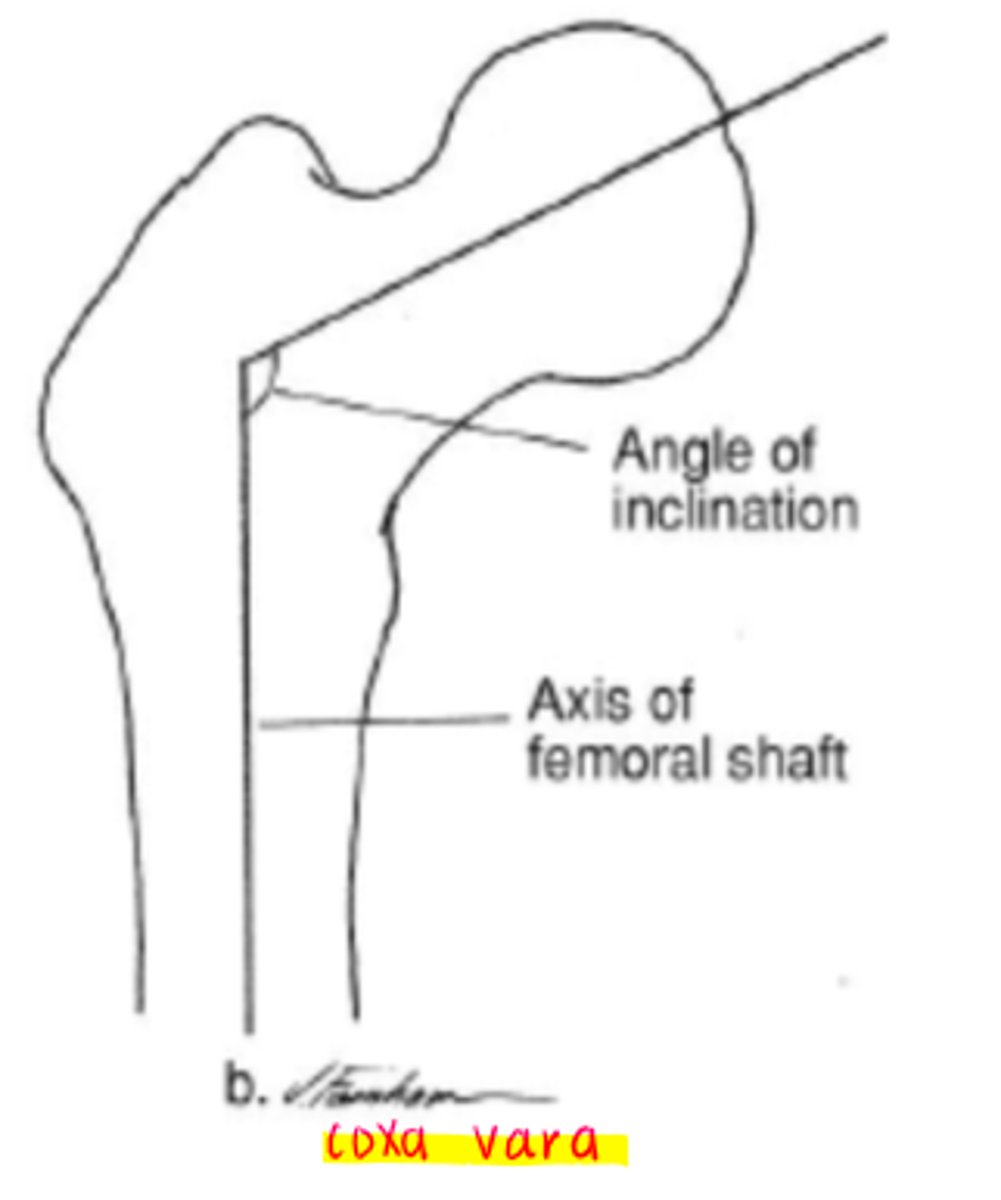
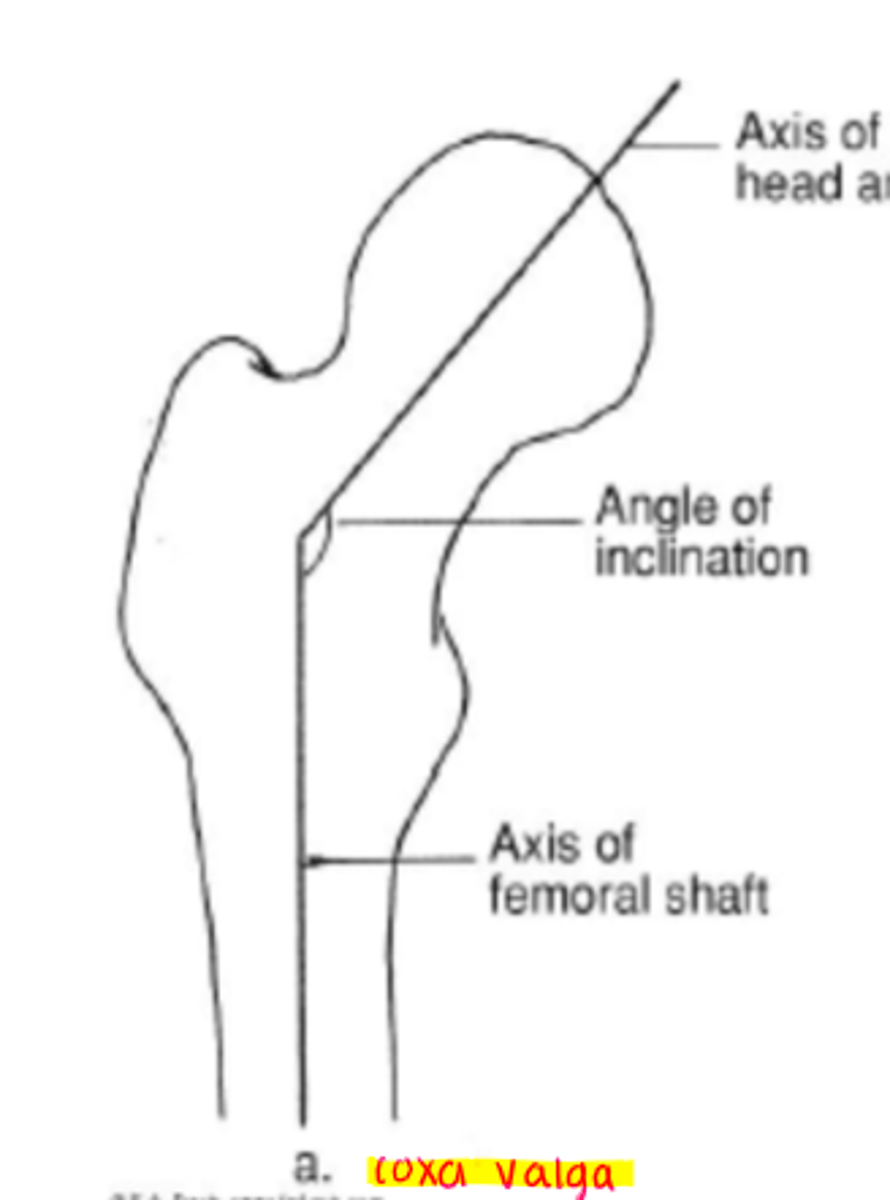
angle of inclination
angle between the femoral neck/head and the femoral shaft (frontal plane)
infant = 150-175 degrees
adult = 125 degrees (110-144 range)
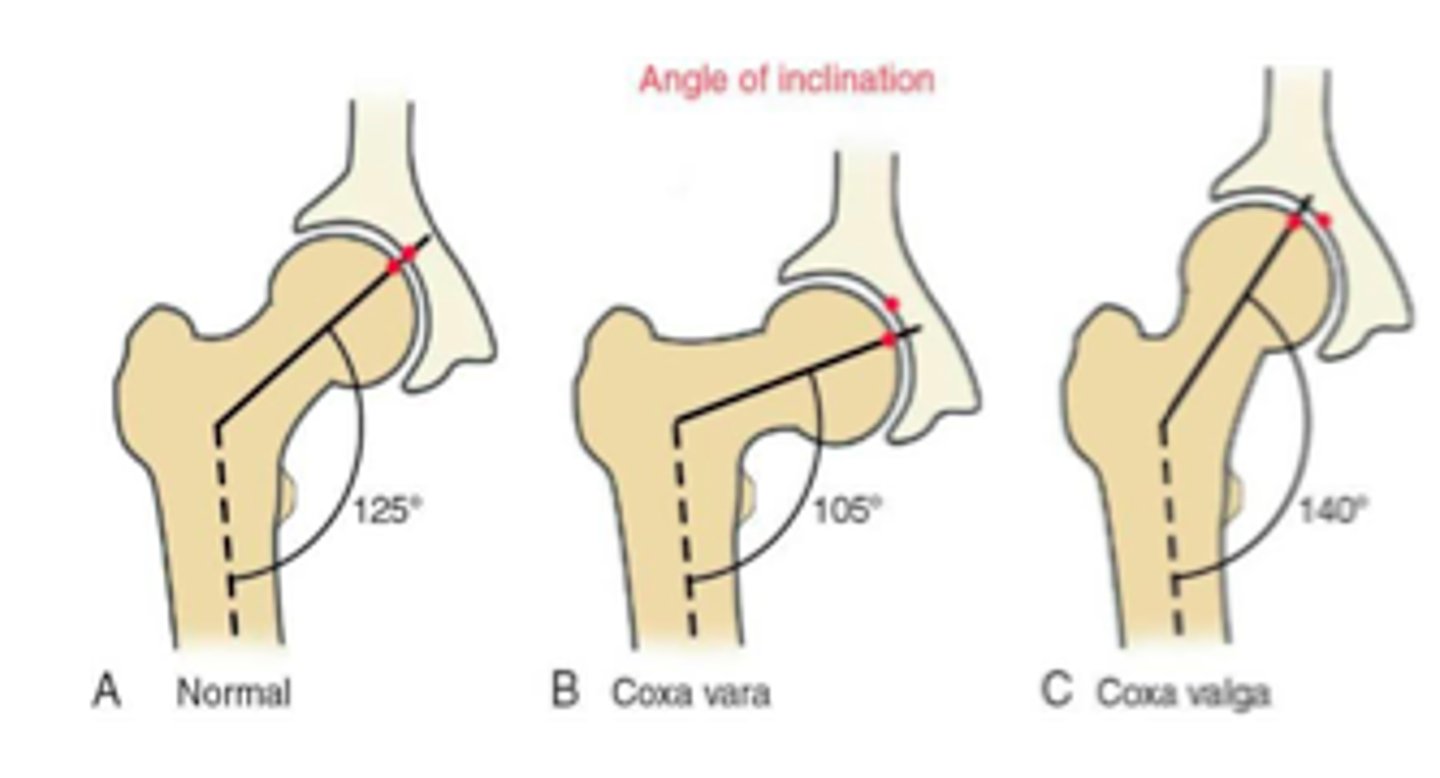
coxa vara
decreased angle of inclination
*less than 110 degrees
coxa valga
increased angle of inclination
*greater than 144 degrees
angle of torsion
angle of the head/neck of the femur with a line through the femoral condyles
*rotation in transverse plane
infant = 30-40 degrees
adult = 10-15/20 degrees
(M=15, F=18)
anteversion
turning forward
>15/20 degrees
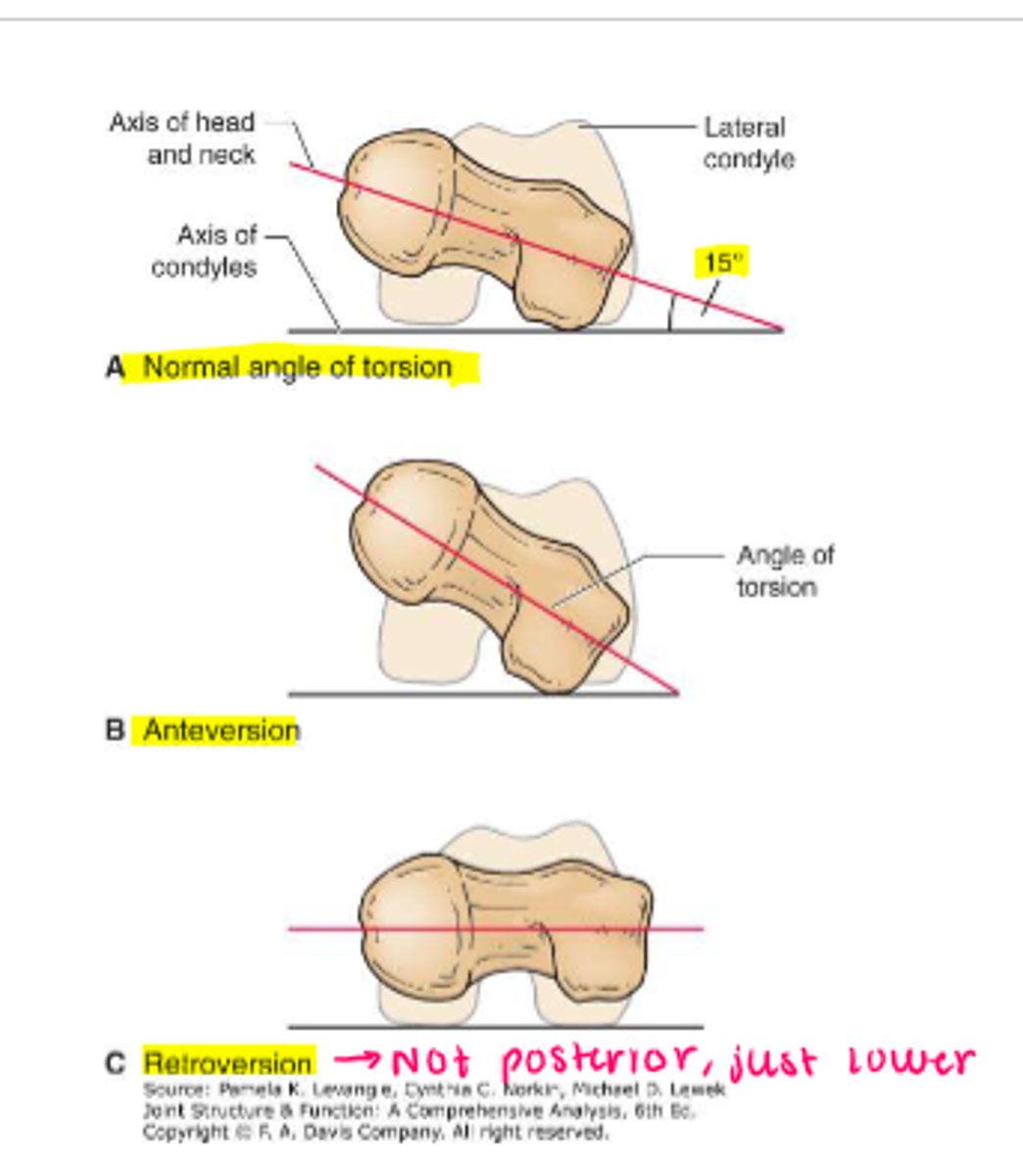
retroversion
turning backward
<15/20 degrees
greater trochanter
attachment for:
1. glut med
2. glut min
3. piriformis
4. gemellus sup
5. obturator internus
6. gemellus inf
7. vastus lateralis
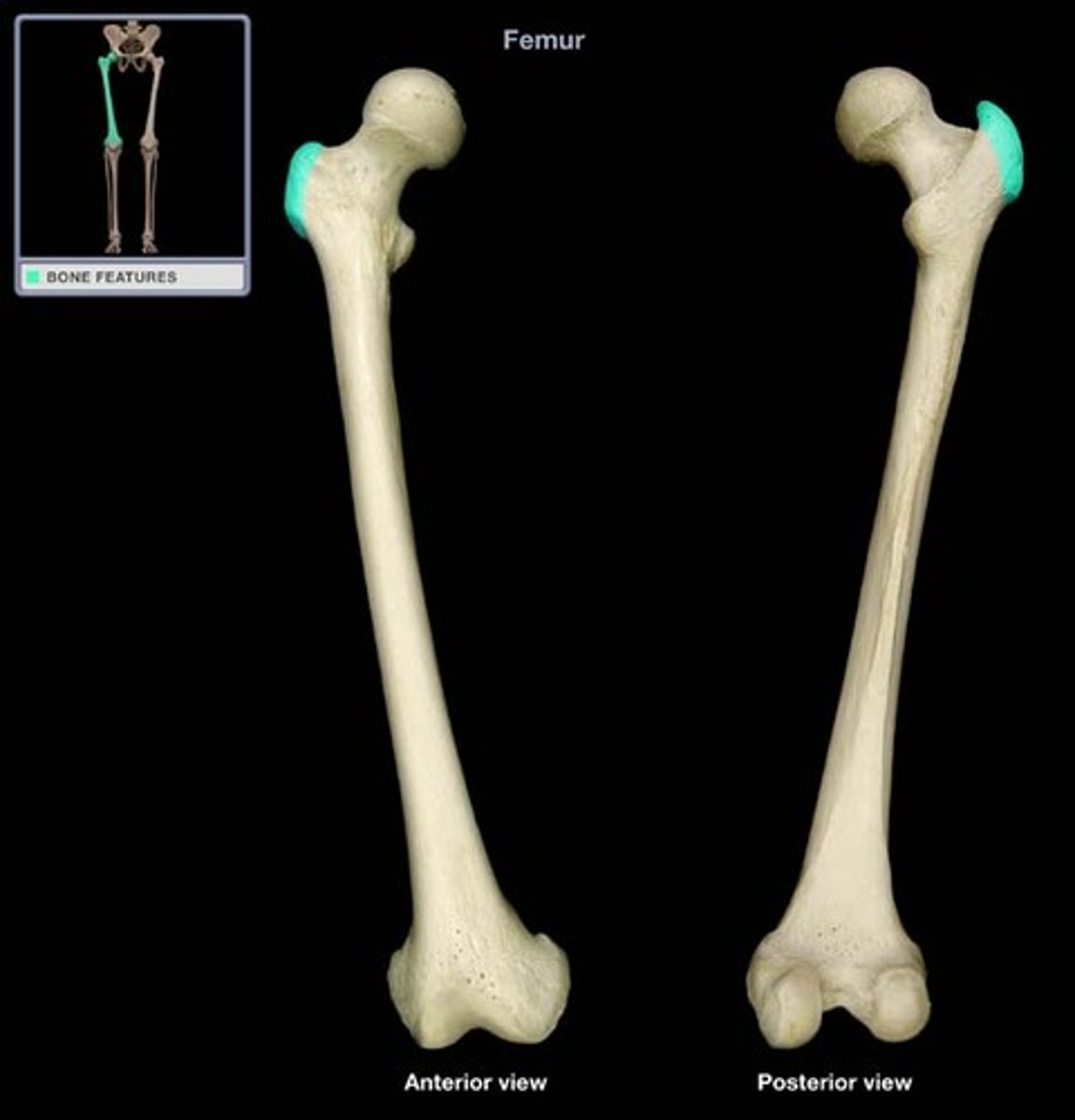
lesser trochanter
attachment for:
1. iliacus
2. psoas
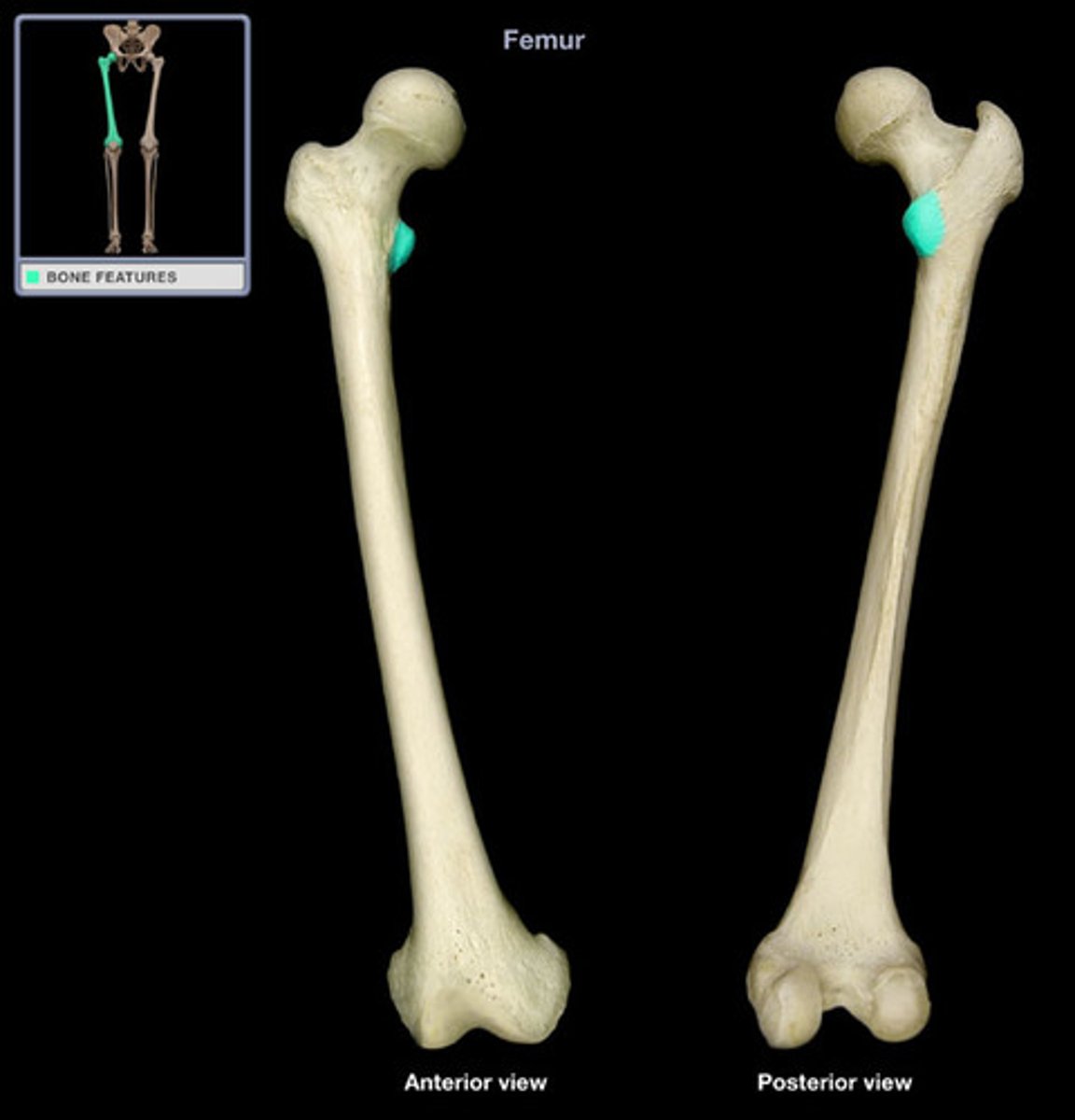
insertion of obturator externus
trochanteric fossa of femur
linea aspera
proximally becomes the pectineal line and gluteal tuberosity
attachment for:
1. 3 vasti muscles
2. 3 adductors
3. short head of biceps fem
4. glut max
5. pectineus
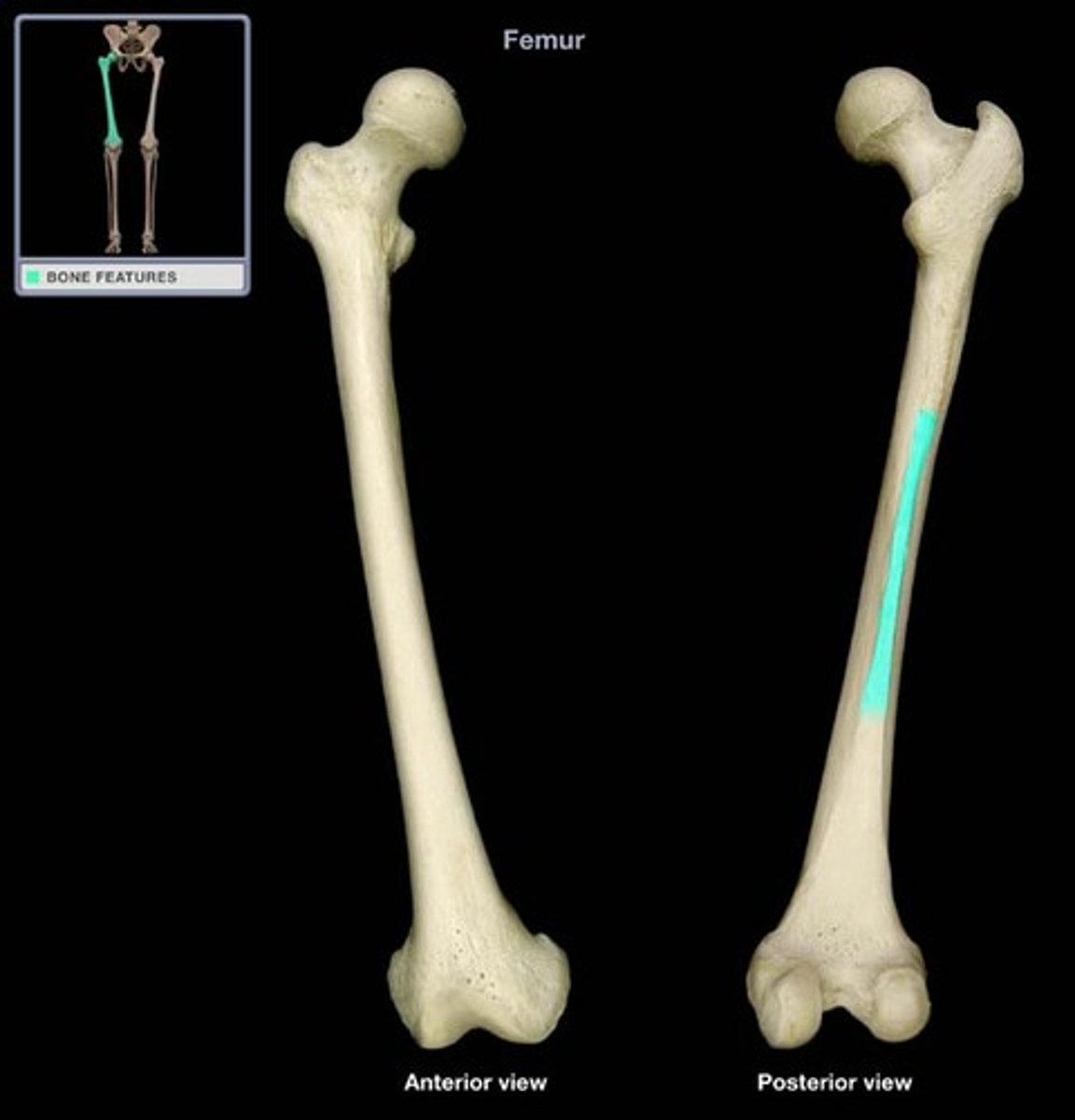
shaft
bows with posterior concavity/anterior convexity
*b/c of weight bearing
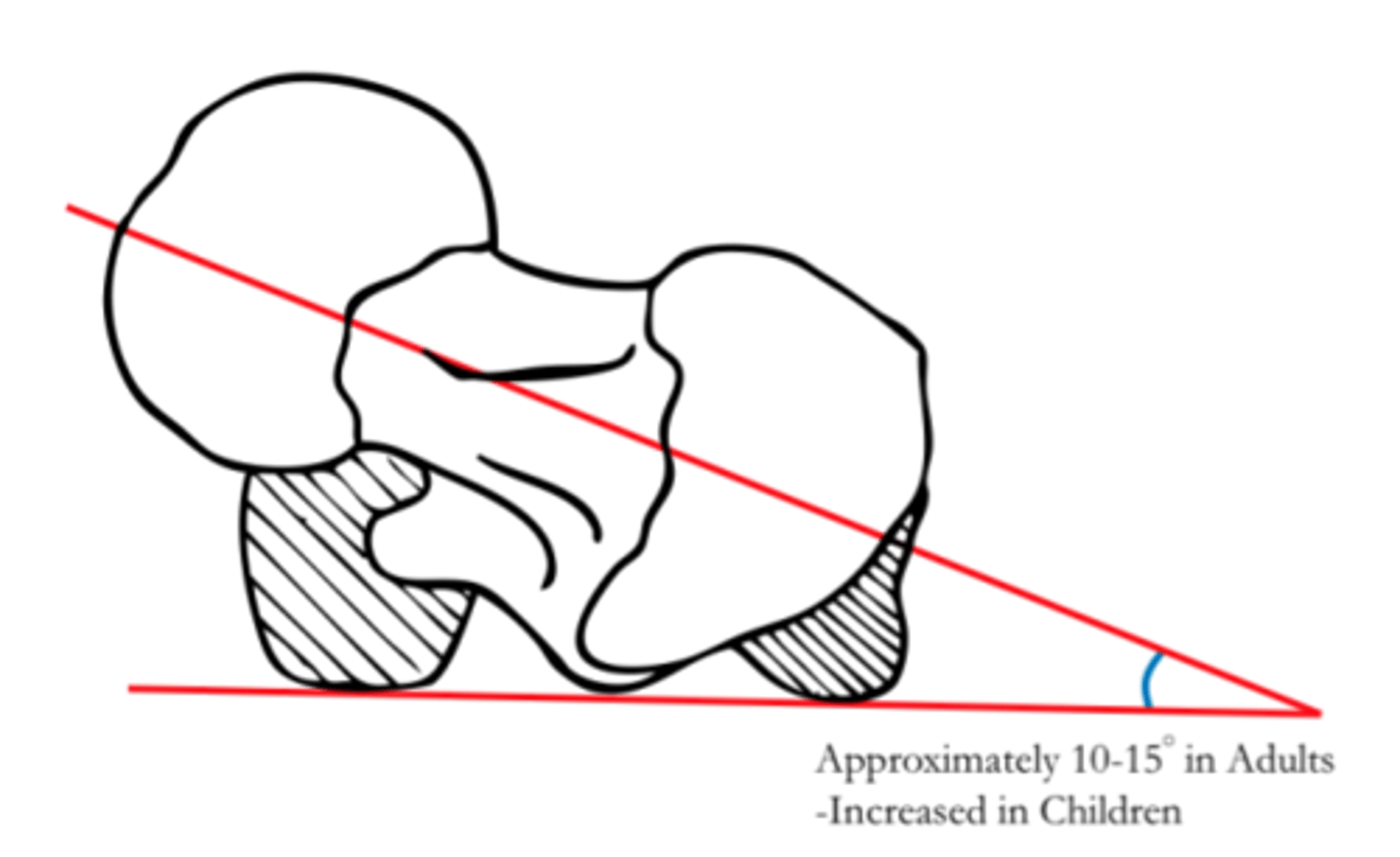
center edge angle
the degree to which the acetabulum covers the femoral head
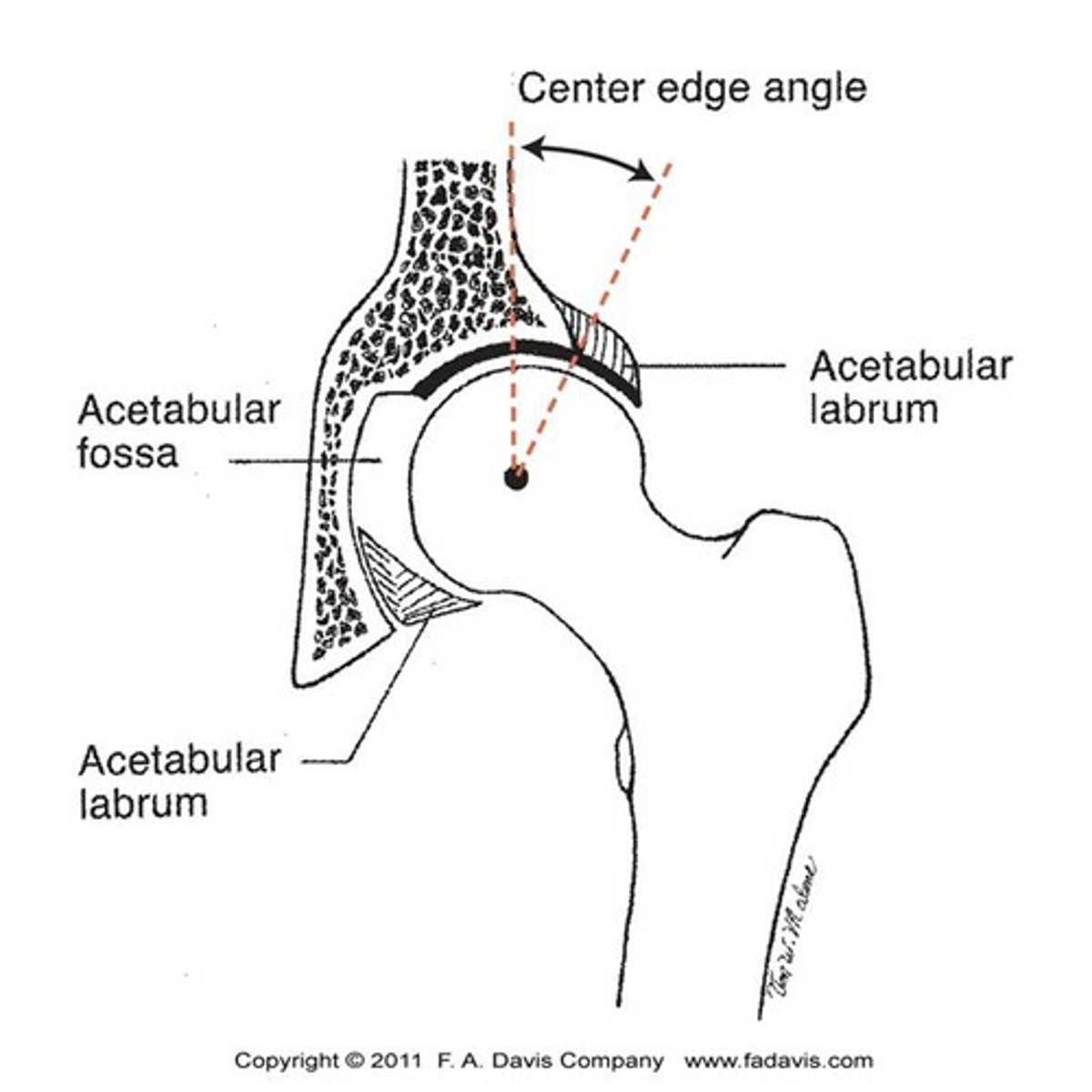
deeper acetabulum
What does a LARGE center edge angle indicate?
increased chance of dislocation
What does a SMALL center edge angle indicate?
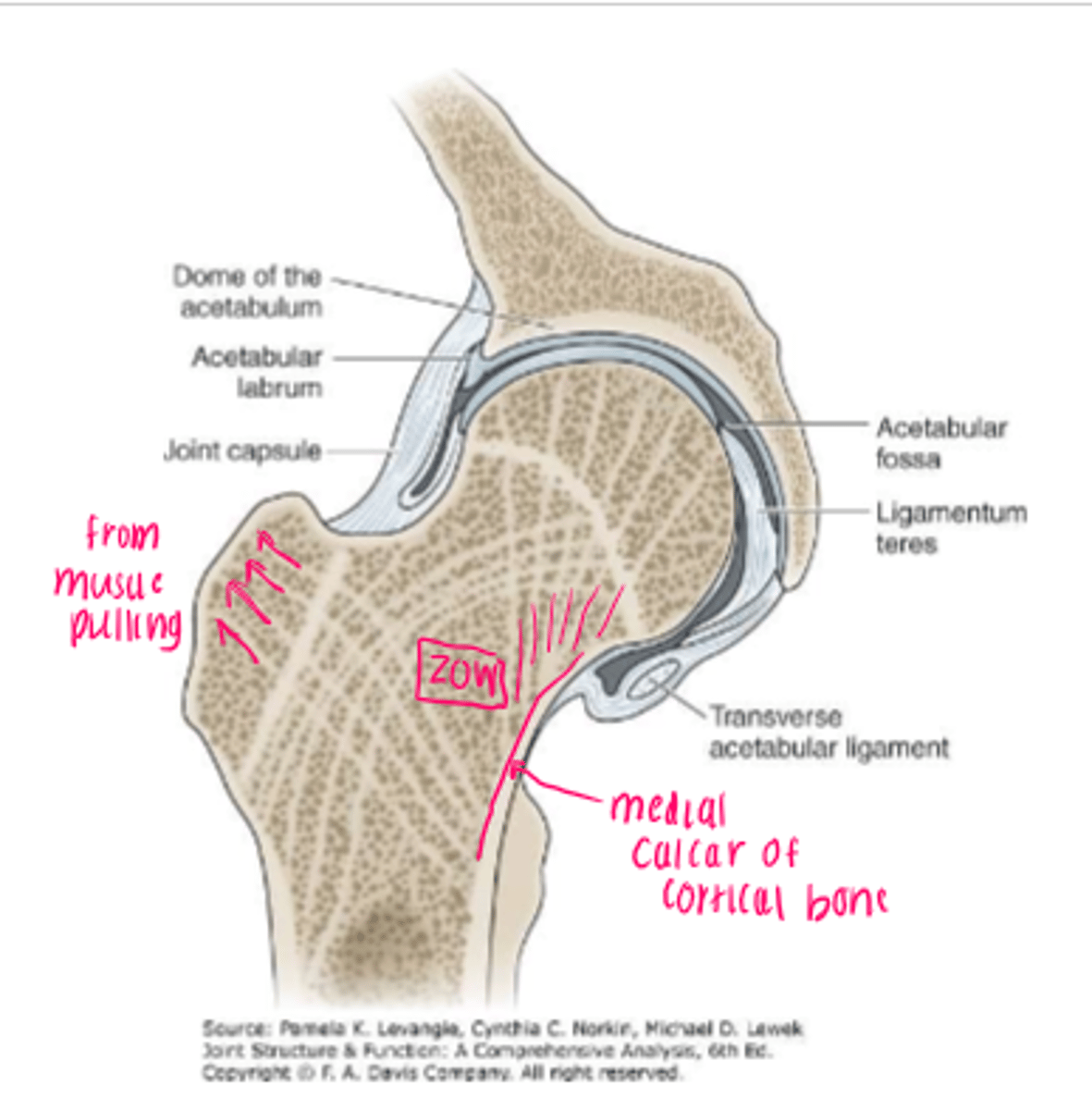
labrum
deepens acetabulum
*increases stability
**increases contact area between the femur and acetabulum
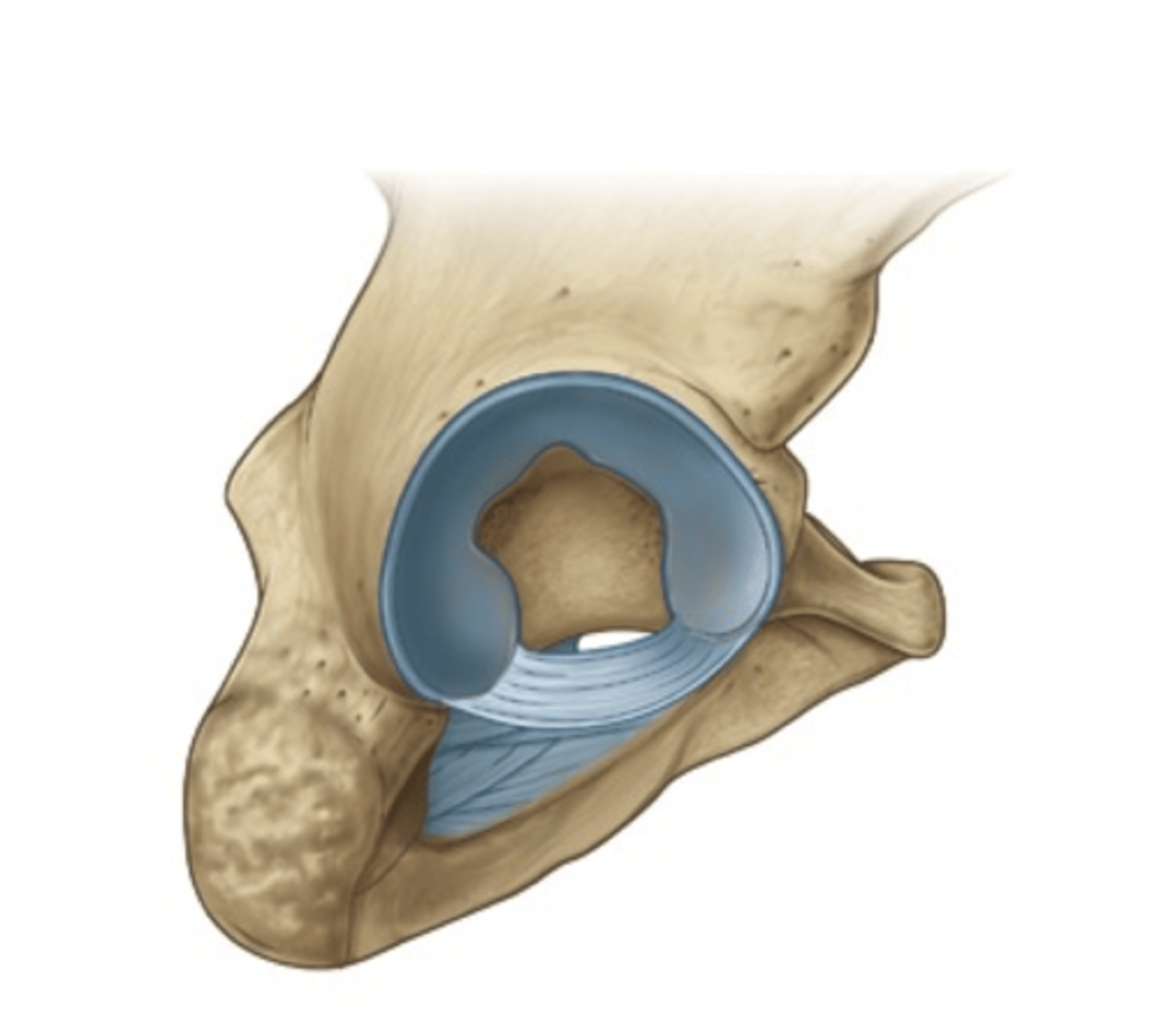
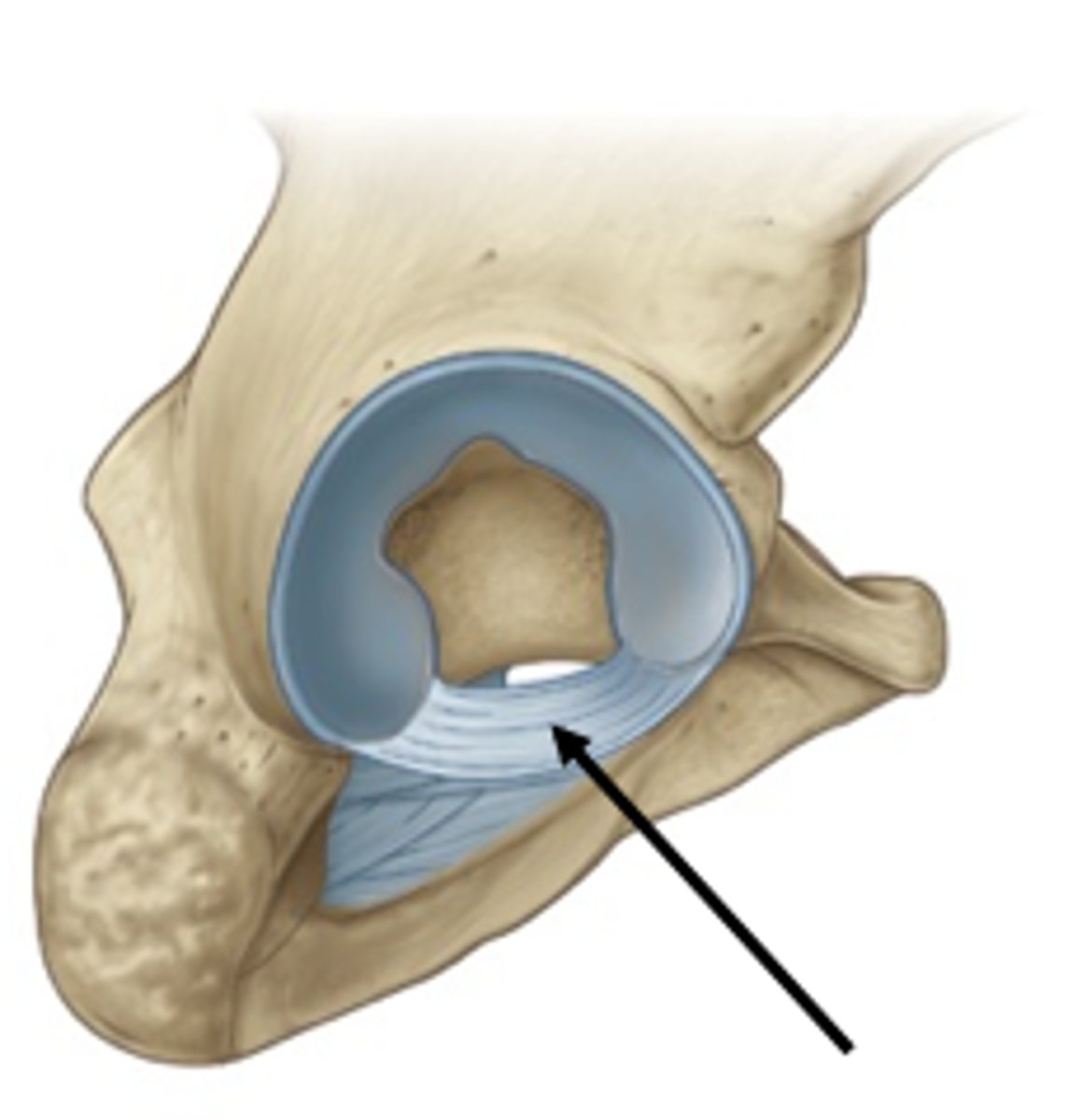
transverse acetabular ligament
bridges a gap in the inferior margin of the acetabular labrum
joint capsule
encloses head and proximal neck, attaches to intertrochanteric line anteriorly and 1.5 cm above the intertrochanteric crest posteriorly
zona orbicularis
deep fibers of the capsule which run circular around the neck of femur
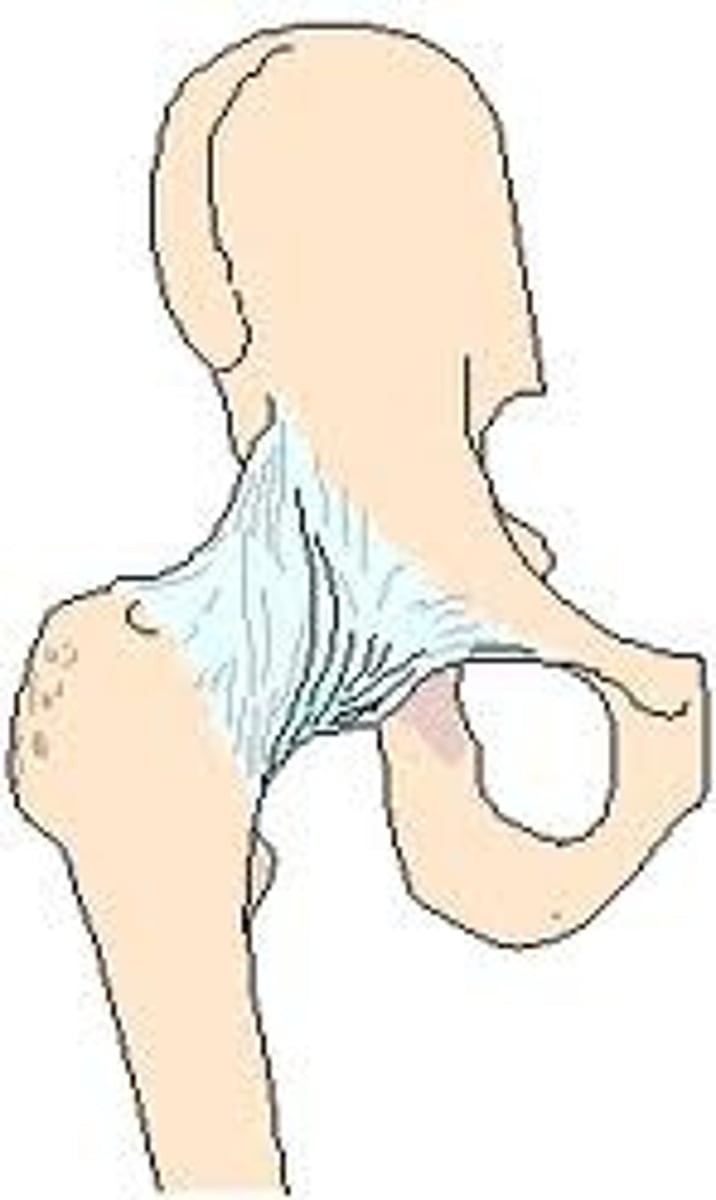
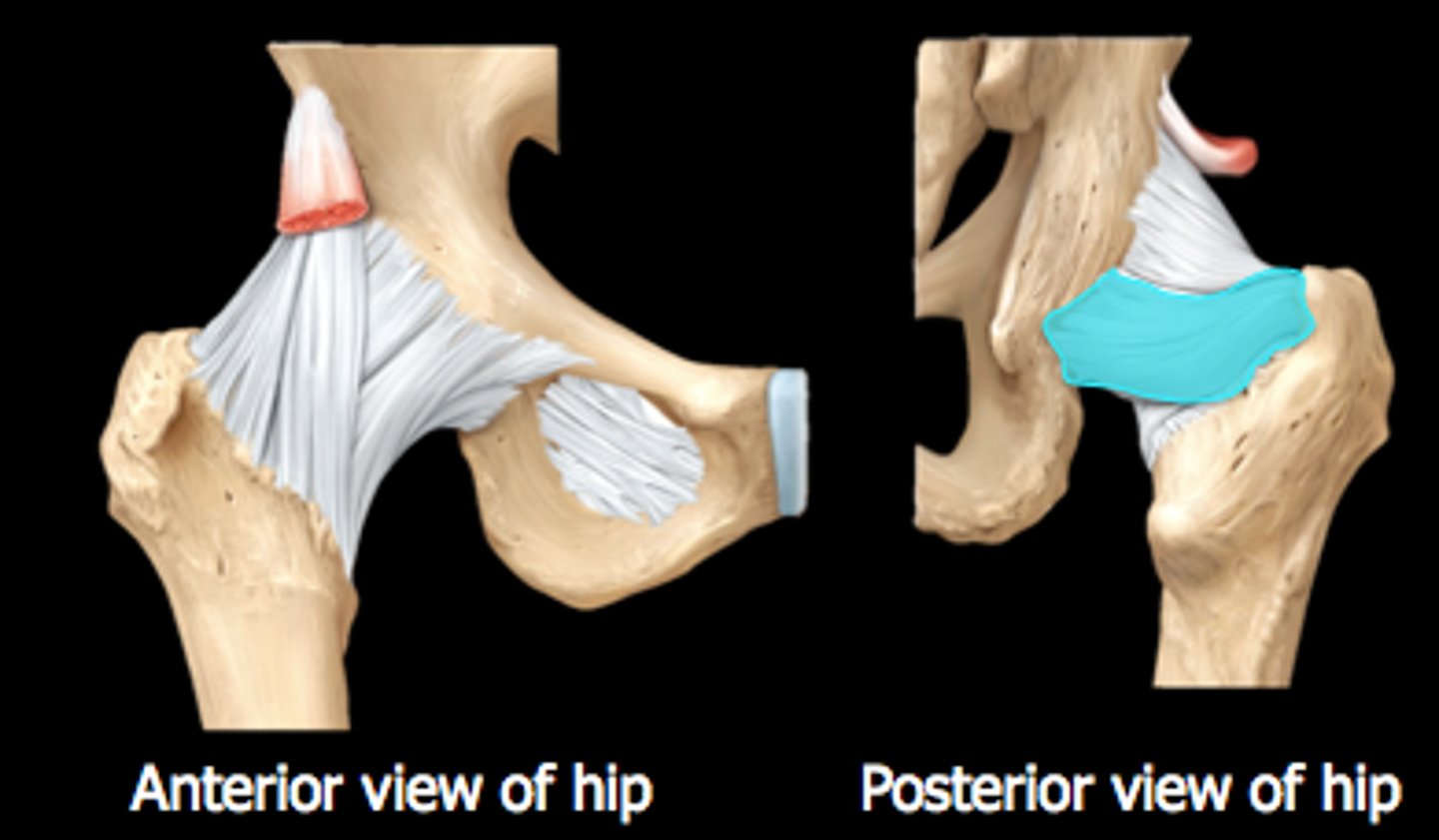
iliofemoral ligament
Y ligament from AIIS to intertrochanteric line
*fan-shaped/inverted Y
(A IN IMAGE)
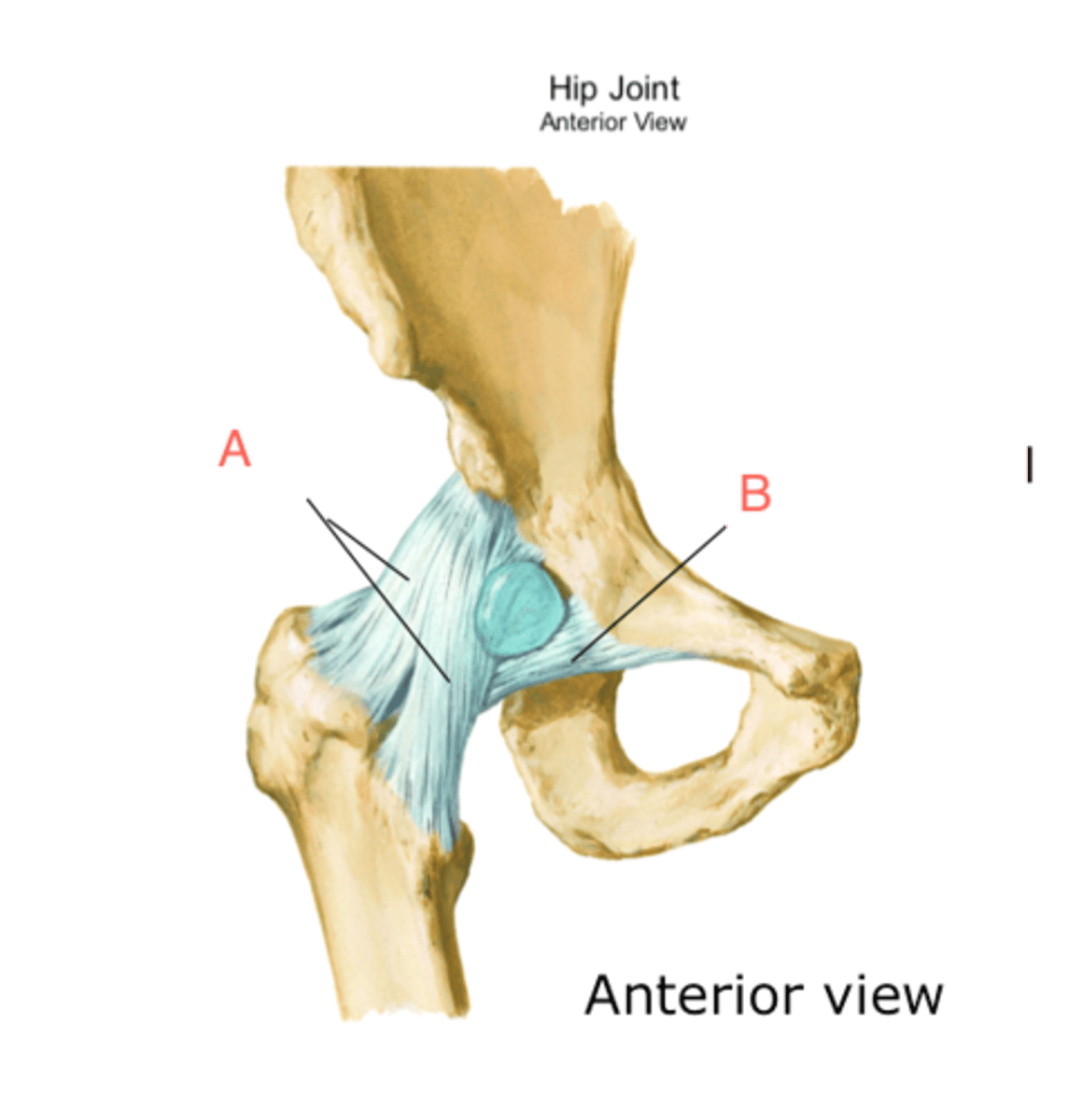
pubofemoral ligament
connects pubic bone to underside of femoral neck
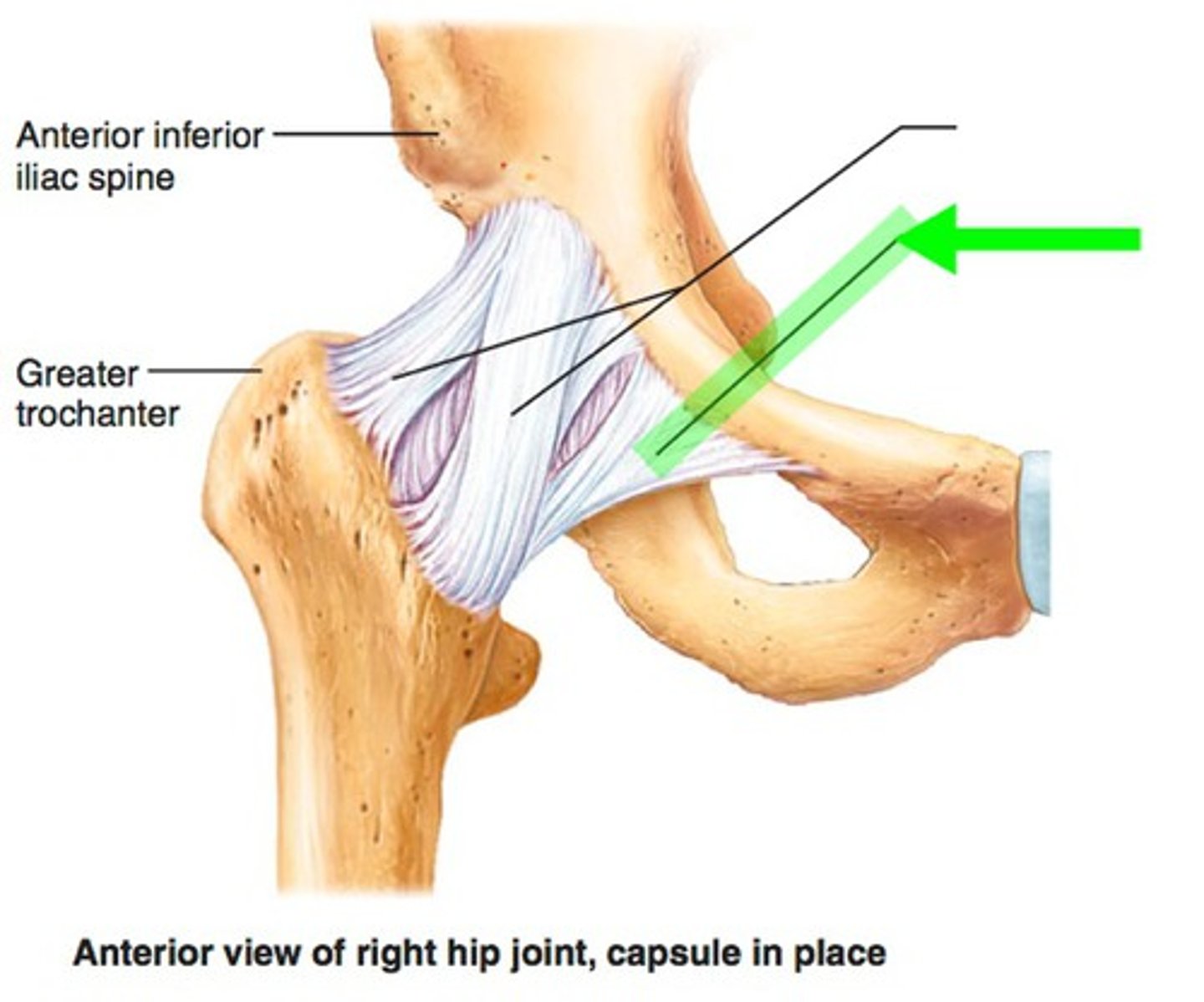
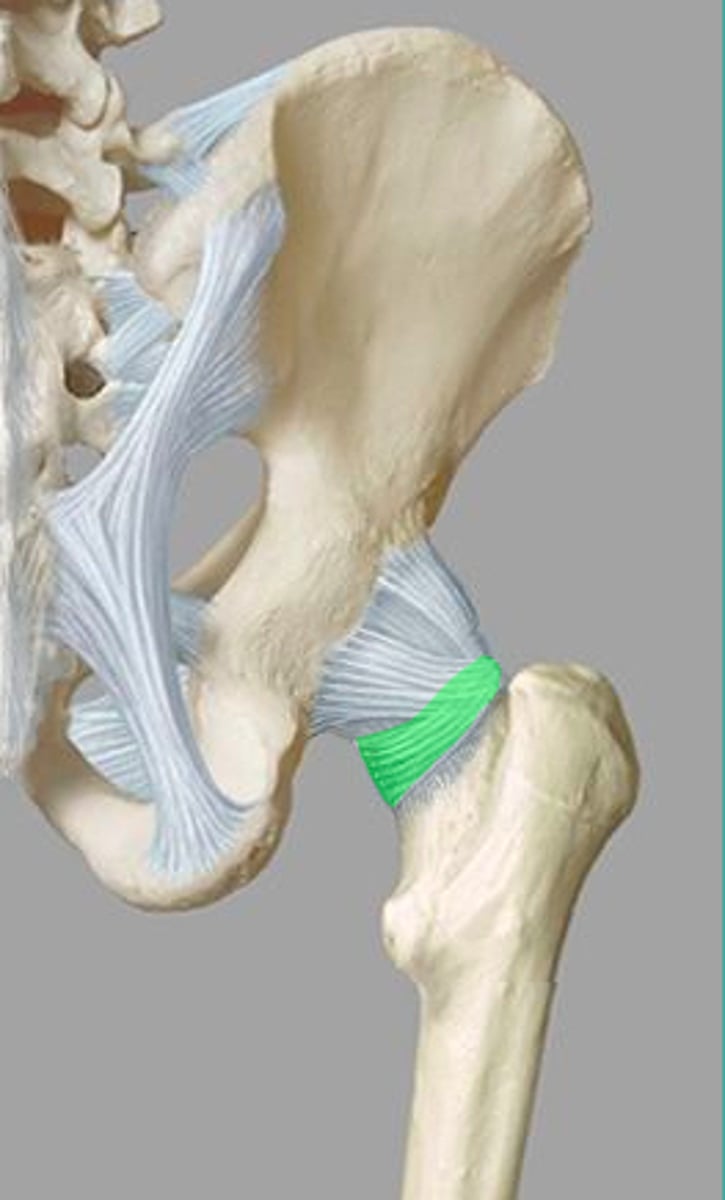
ischiofemoral ligament
connects ischial portion of acetabulum to greater trochanter
extension, flexion
The iliofemoral, pubofemoral, and ischiofemoral ligaments are all tense in __________________ and slack in _______________.
ligamentum teres
ligament of the head of the femur
*NOT really strong, but does increase hip stability
**protects artery to head of femur
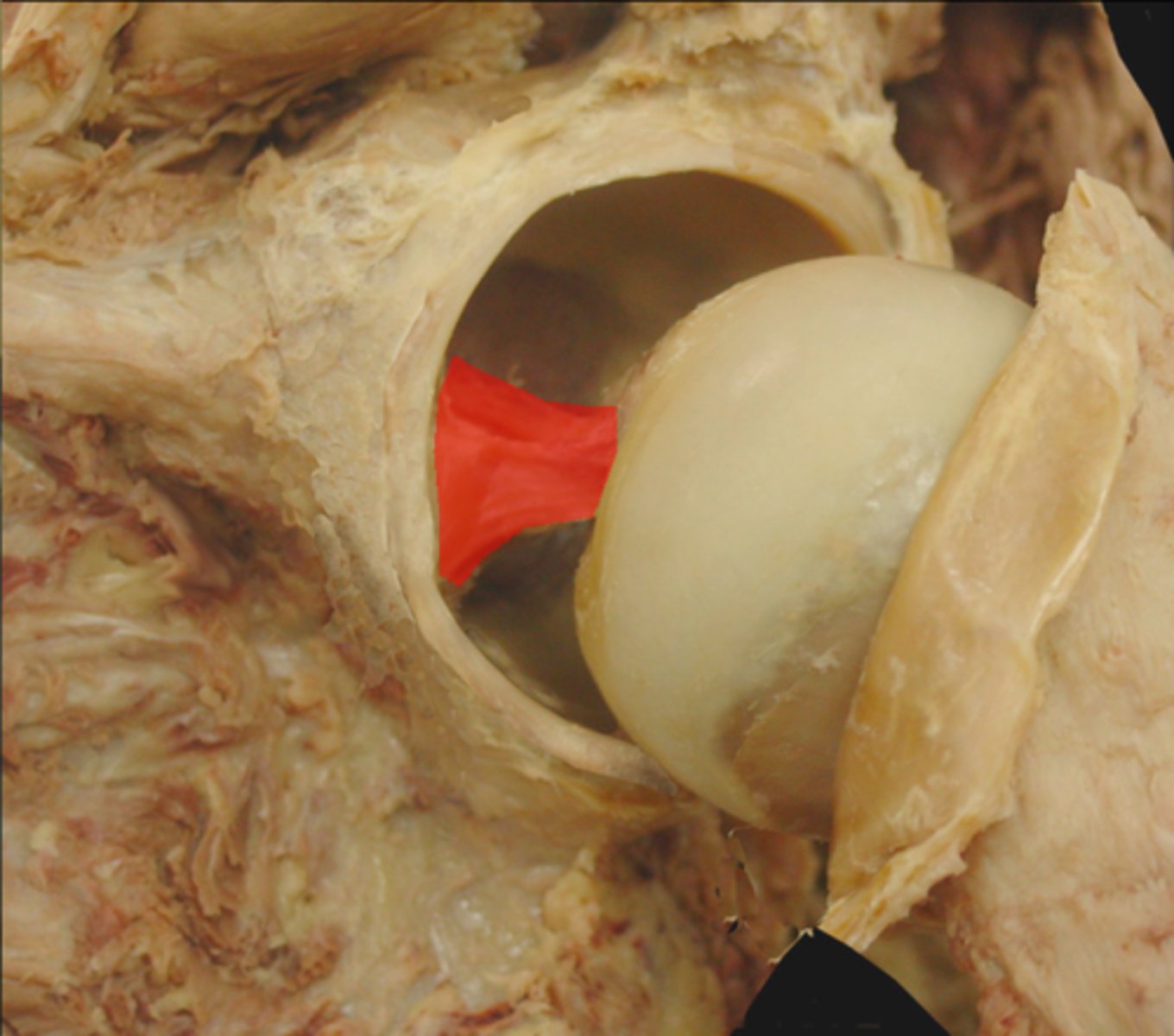
interarticular, extrasynovial
The ligamentum teres can be described as _____________________ and __________________.
bursae
fluid filled sacs that reduce friction
*about 20 in the hip
**iliopectineal & trochanteric
30 degrees flexion, 30 degrees abduction, slight ER
What is the open pack position for the coxofemoral joint?
HINT: frog leg
full extension, medial rotation
What is the close pack position for the coxofemoral joint?
90 degrees of flexion, mod. abduction, slight lateral rotation
What is the position of greatest joint congruency of the hip?
HINT: NOT closed pack position
anteversion, angle of inclination, center edge angle
What 3 things does coxofemoral congruency depend on?
mechanical axis
adductors IR femur (despite posterior insertion)
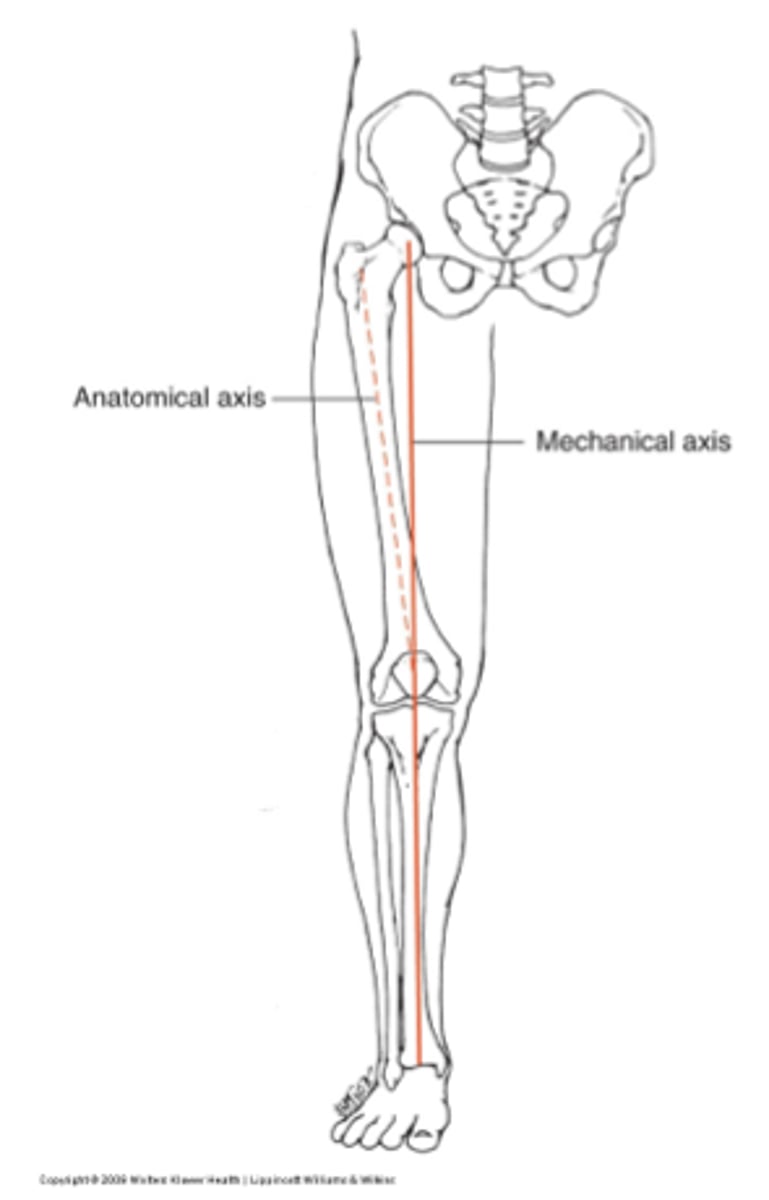
anatomical axis
through the shaft of femur
*head of femur to center of knee
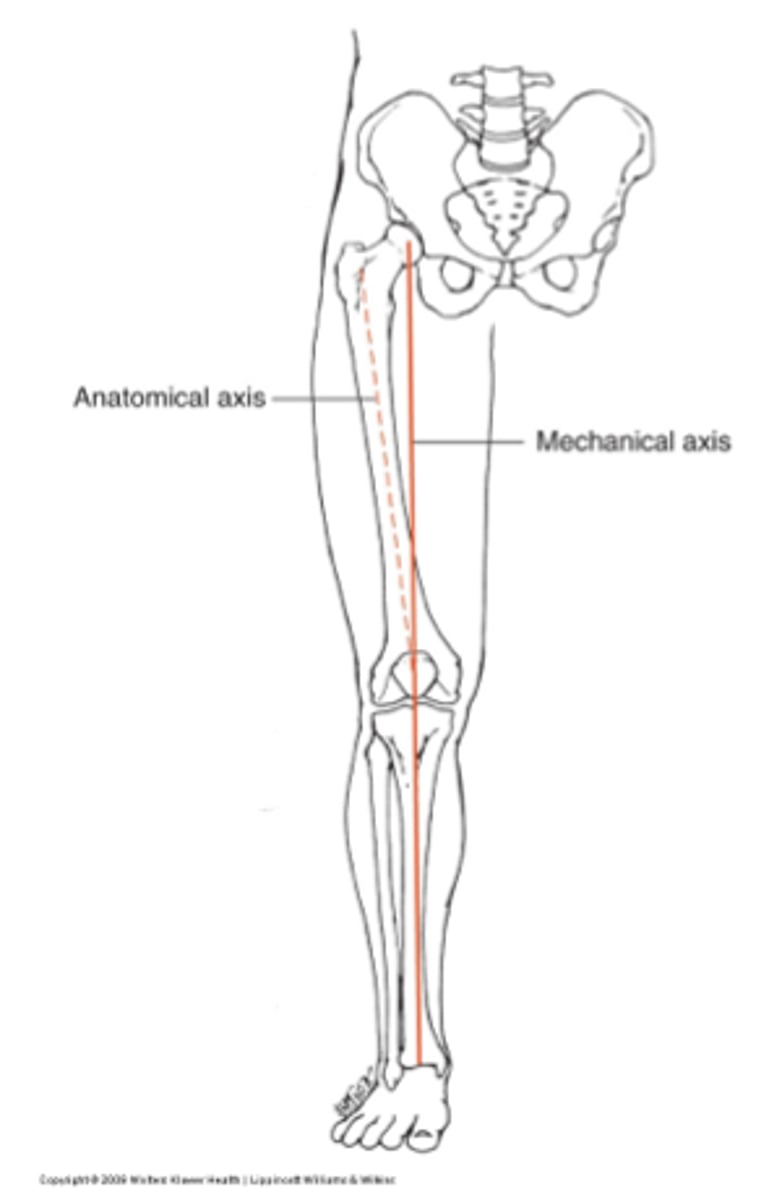
anteriorly, superiorly
In anatomical position, there is exposure of the femoral head ________________ and ________________ due to the directions the acetabulum and femoral head face.
quadruped
In the _________________ position, there is increased congruency.
flexion
There is the most congruency during which hip motion?
iliofemoral ligament, iliopsoas muscle
What 2 structures contribute to the ANTERIOR aspect of the hip joint stability?
HINT: 1 ligament, 1 muscle
glutes, ischiofemoral ligament
What 2 structures contribute to the POSTERIOR aspect of the hip joint stability?
HINT: 1 muscle group, 1 ligament
HAT, ground reaction force, muscular contraction
Force transmission at the hip occurs from what 3 places?
HINT: above, below, within
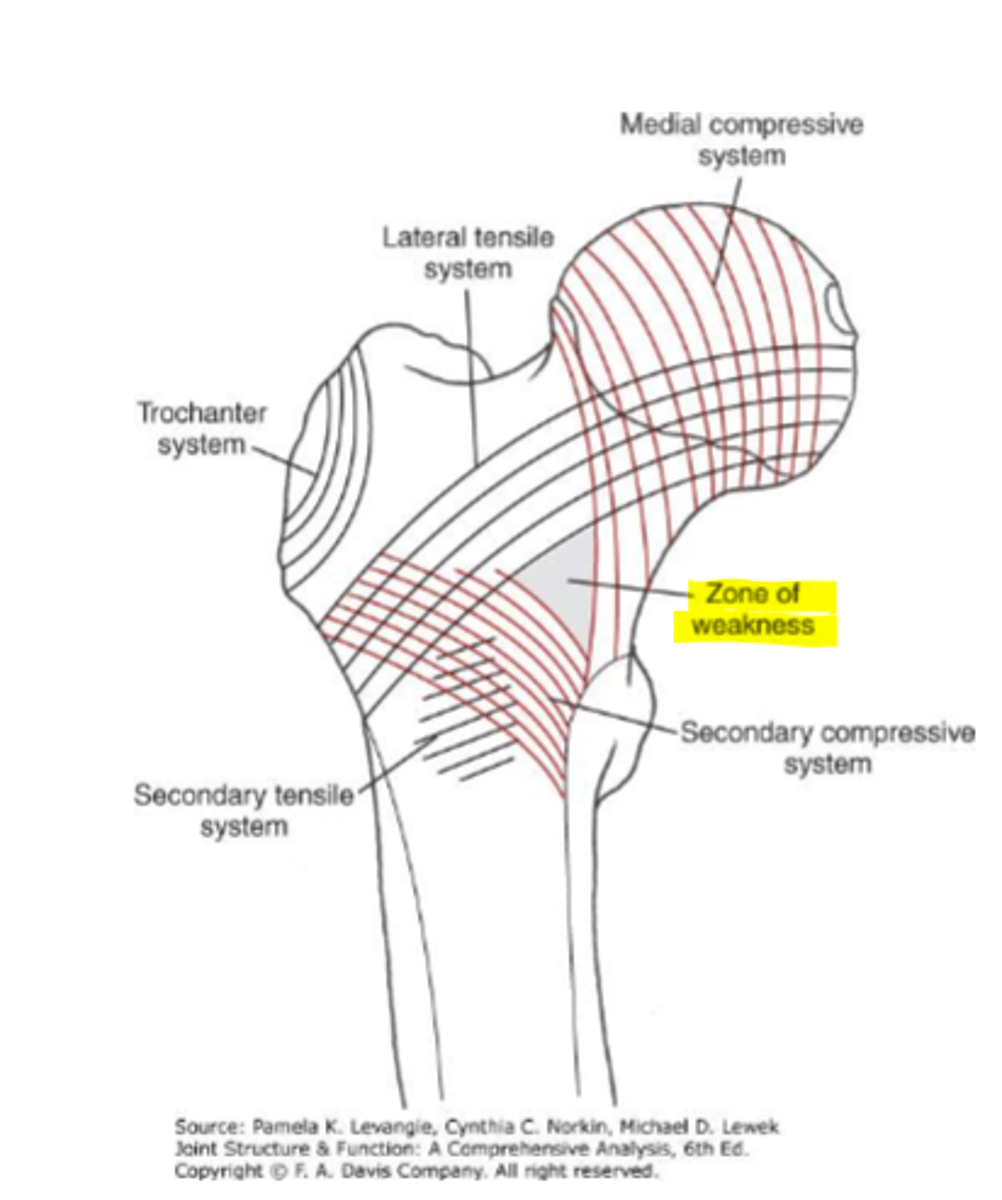
cantilever configuration
bending relationship between femoral head/neck vs shaft
*results in trabecular patterns within head/neck
zone of weakness
area in the femoral neck have fewer trabecular fibers
3 (F/E, IR/ER, AB/AD)
How many degrees of freedom does the hip have?
0-120 degrees
What is the normal ROM for hip FLEXION?
0-20 degrees
What is the normal ROM for hip EXTENSION?
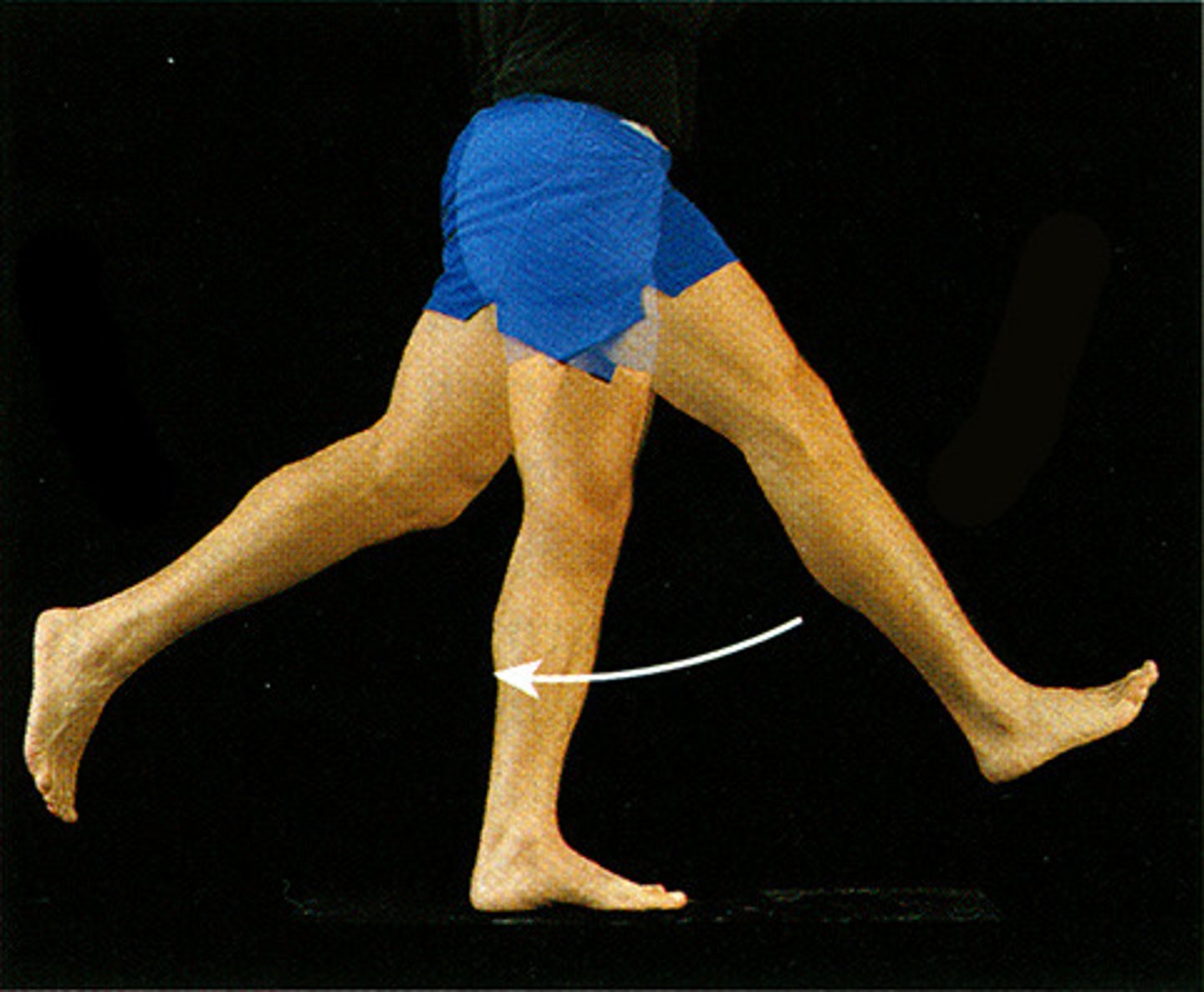
0-45 degrees
What is the normal ROM for hip ABDUCTION?
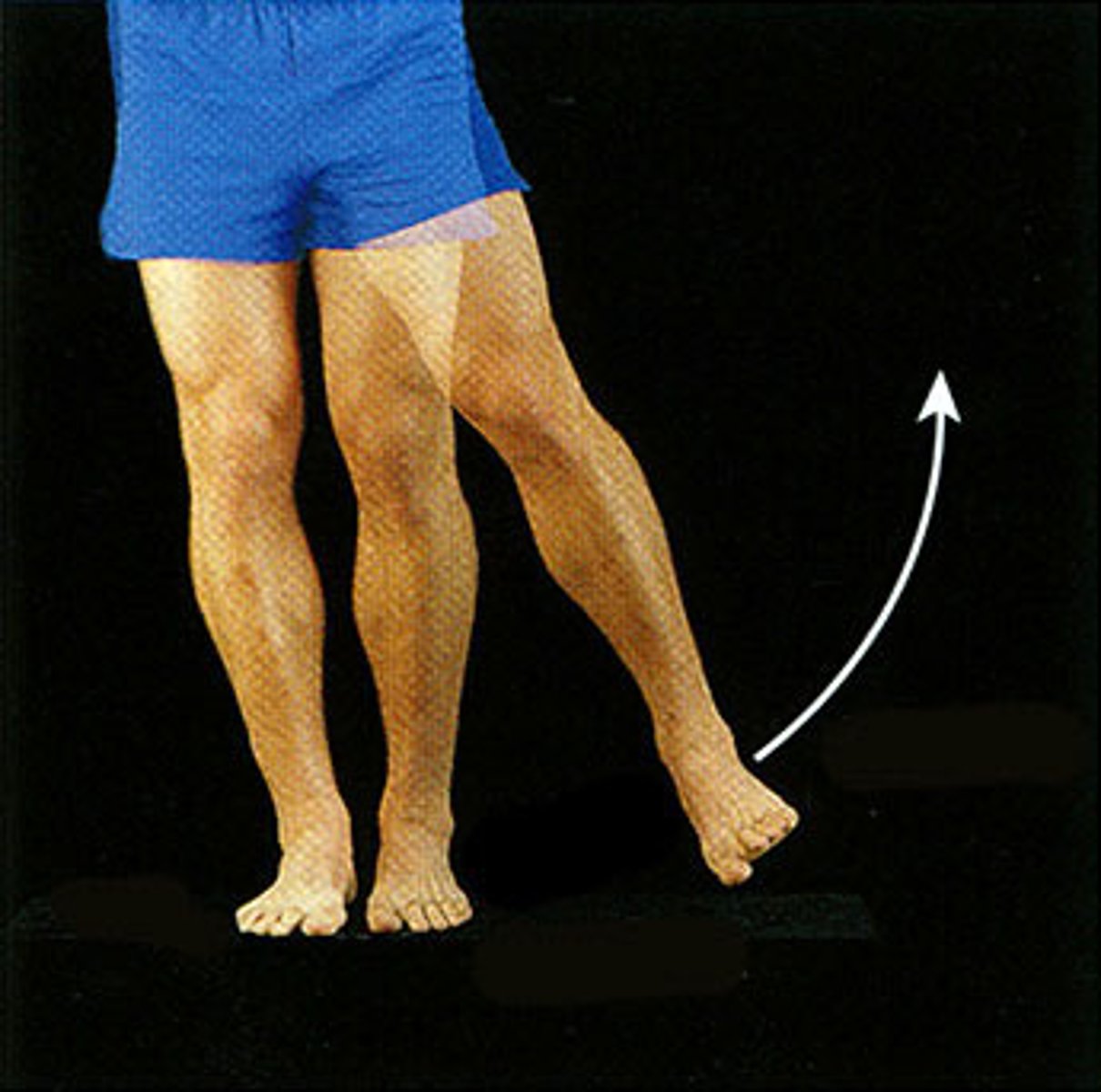
0-30 degrees
What is the normal ROM for hip ADDUCTION?
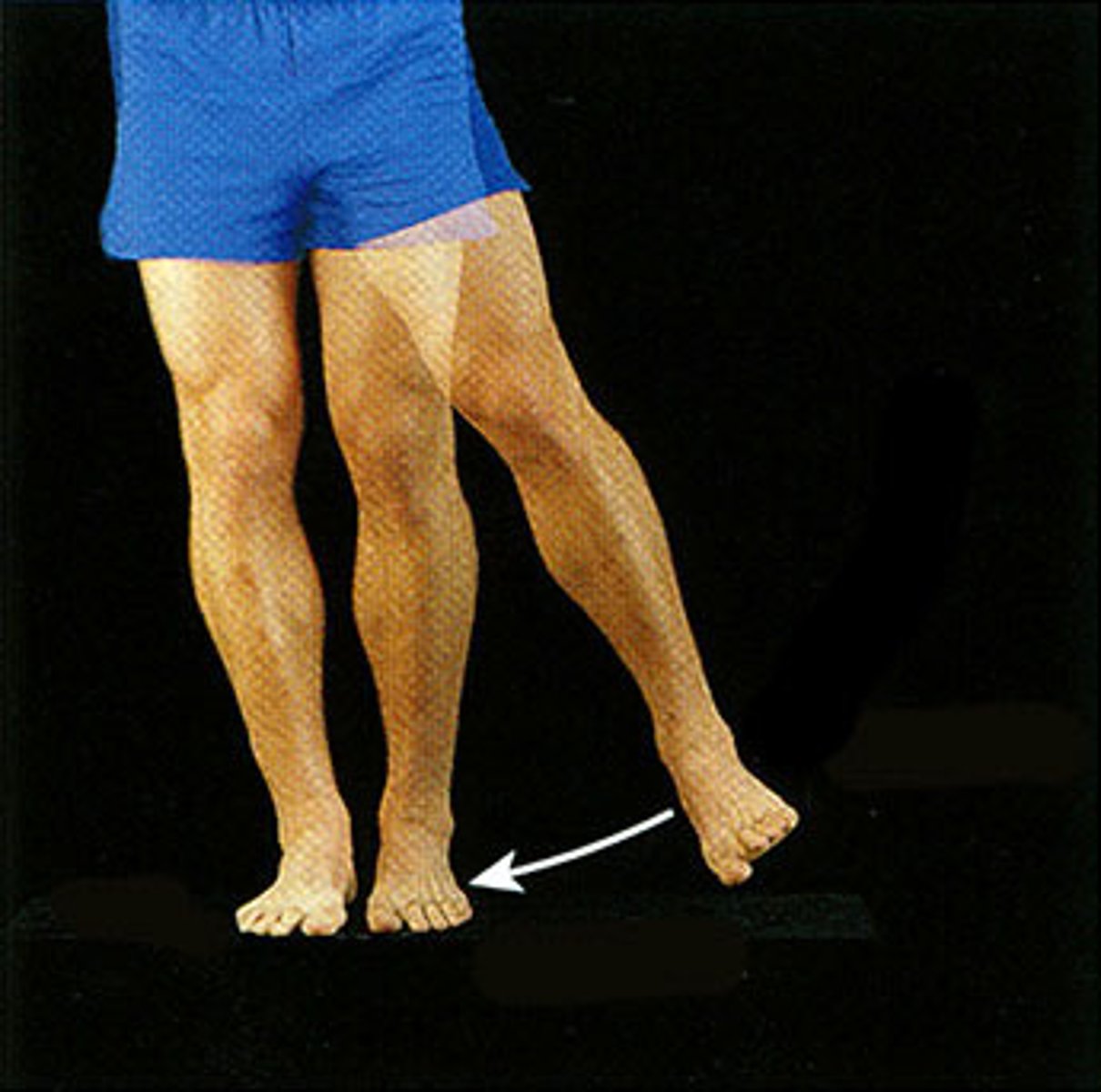
0-45 degrees
What is the normal ROM for hip INTERNAL ROTATION?
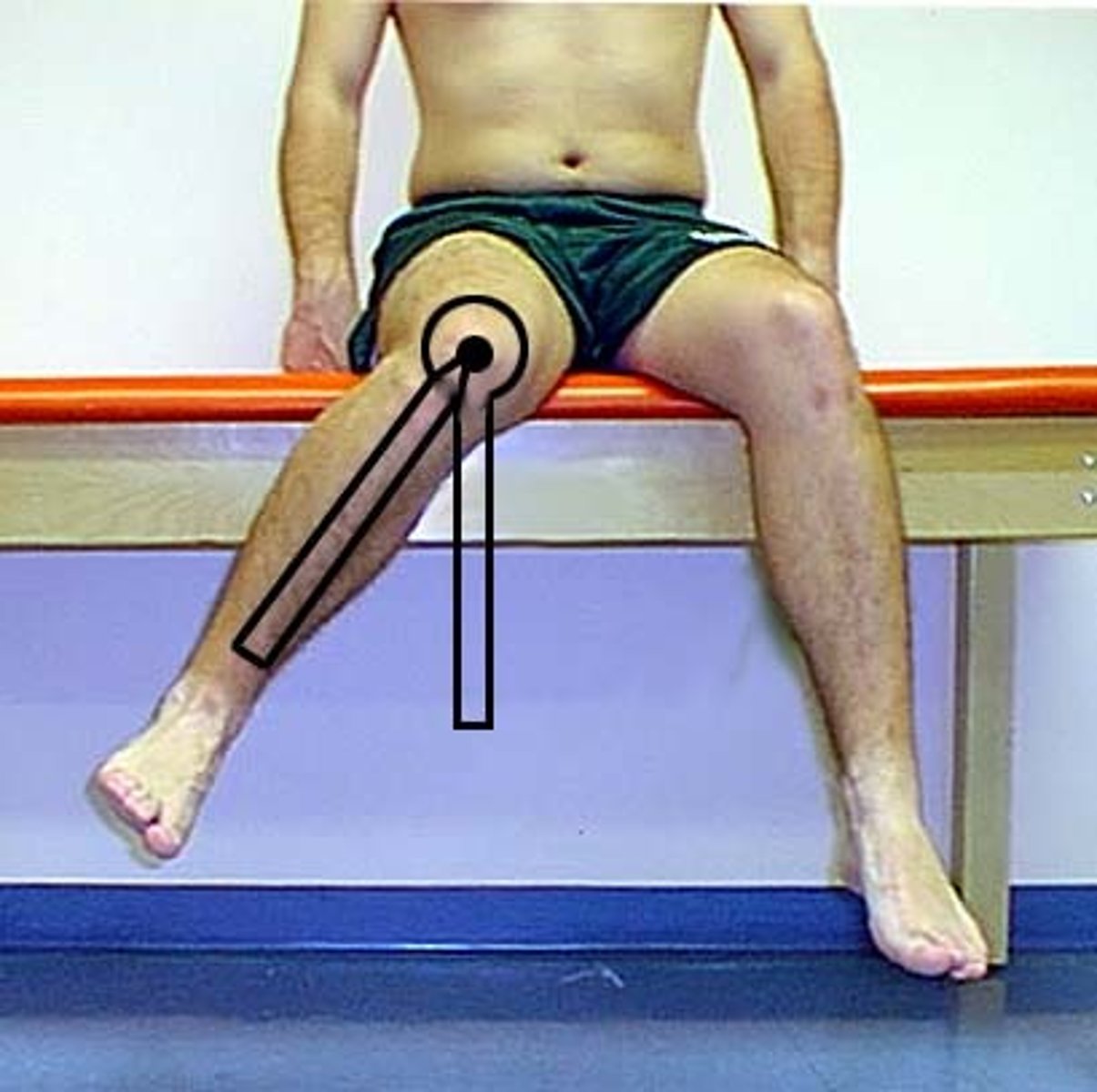
0-45 degrees
What is the normal ROM for hip EXTERNAL ROTATION?
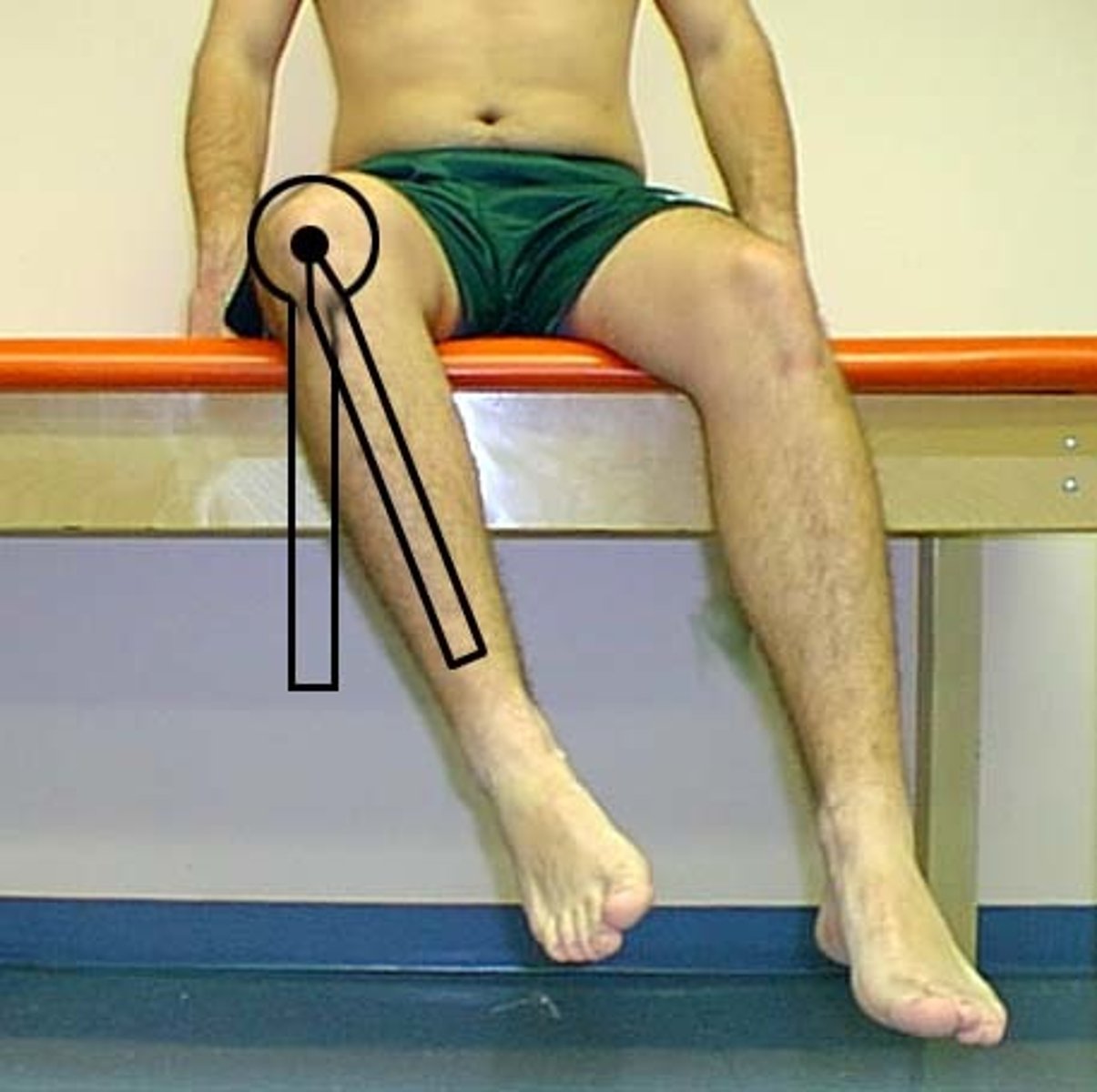
30 degrees flexion, 10 degrees extension, 5 degrees abduction
What is the functional ROM needed for WALKING?
60 degrees flexion
What is the functional ROM needed for STAIRS?
90 degrees flexion (could be less than 90 if lumbar spine is rounded)
What is the functional ROM needed for SITTING?
pelvis, femur
In most activities the _____________ moves over a fixed ___________.
HINT: closed chain
sagittal
Anterior and posterior pelvic tilting occurs in what plane?
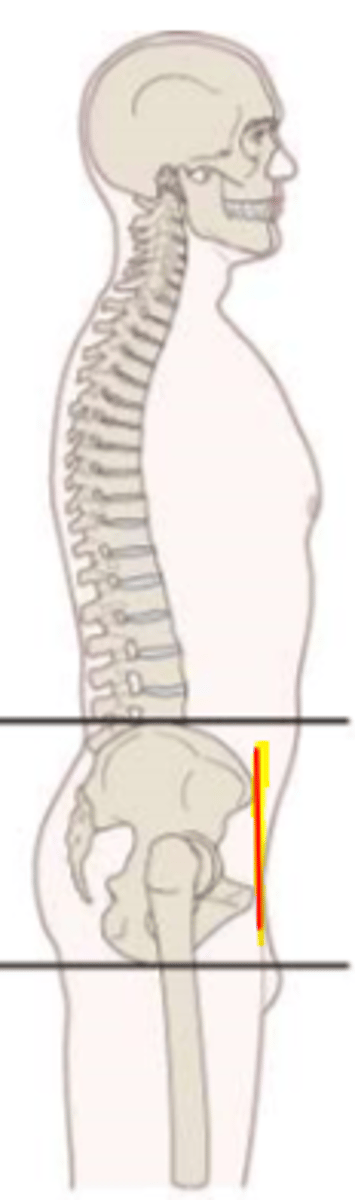
neutral position (of pelvis)
ASIS and pubic symphysis are oriented vertically
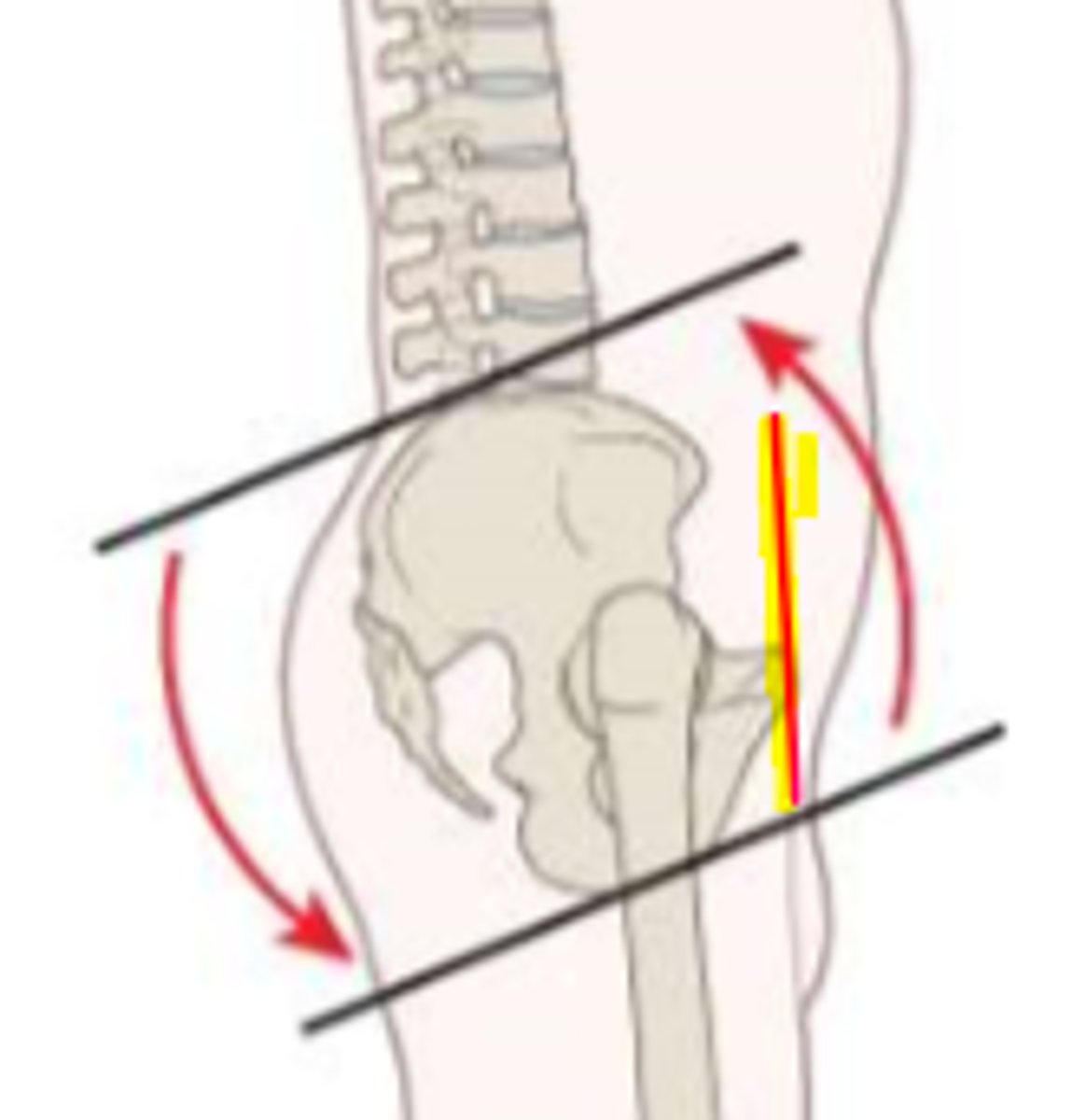
anterior tilt
force couple of hip flexors and back extensors
*ASIS is anterior to PS = hip flexion
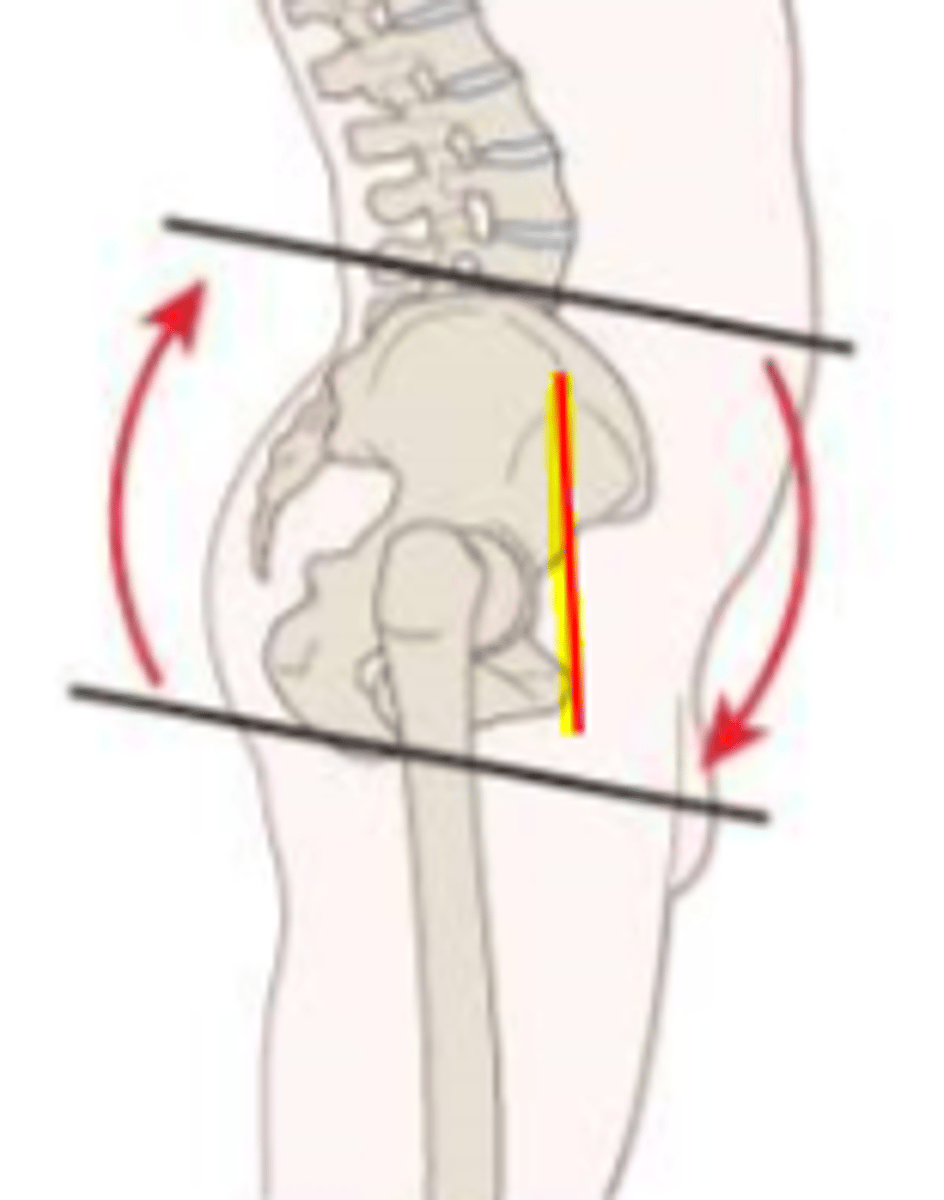
posterior tilt
force couple of hip extensors and trunk flexors
*ASIS is posterior to PS = hip extension
lateral tilt
frontal plane motion of pelvis around one supporting limb
*named according to motion of opposite side from the supporting limb
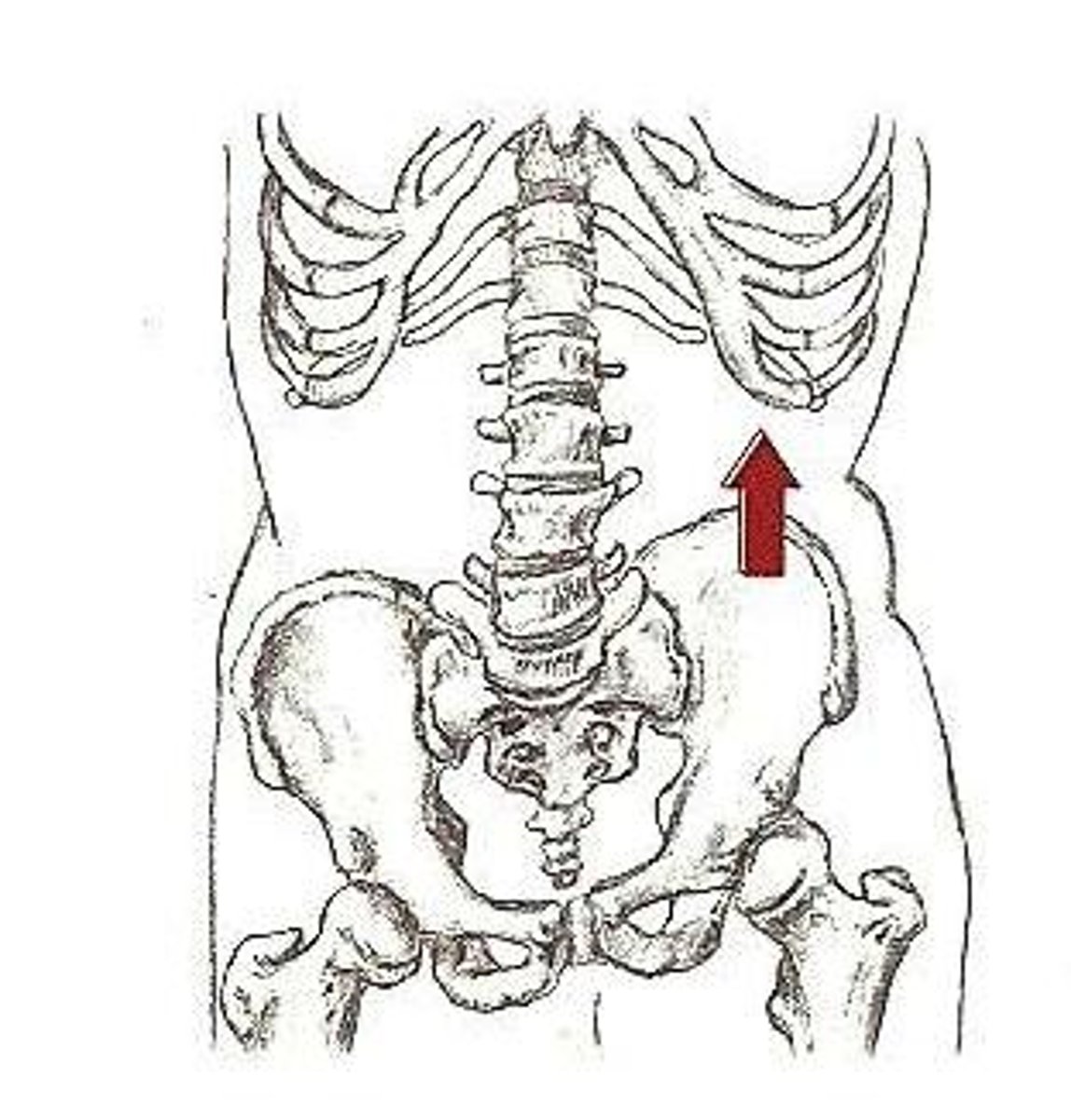
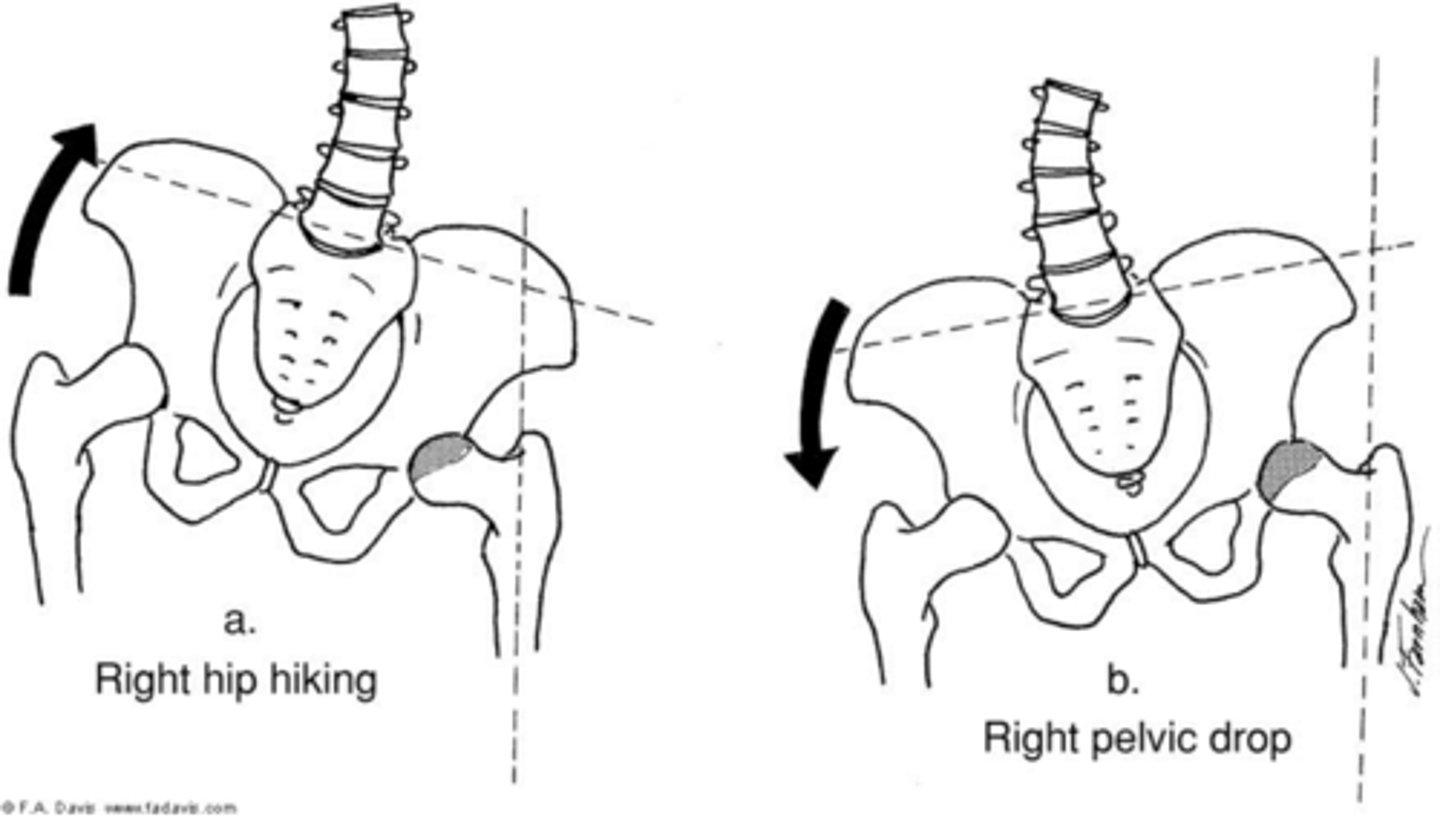
hip elevation (hike)
abduction of stance limb
(A IN IMAGE)
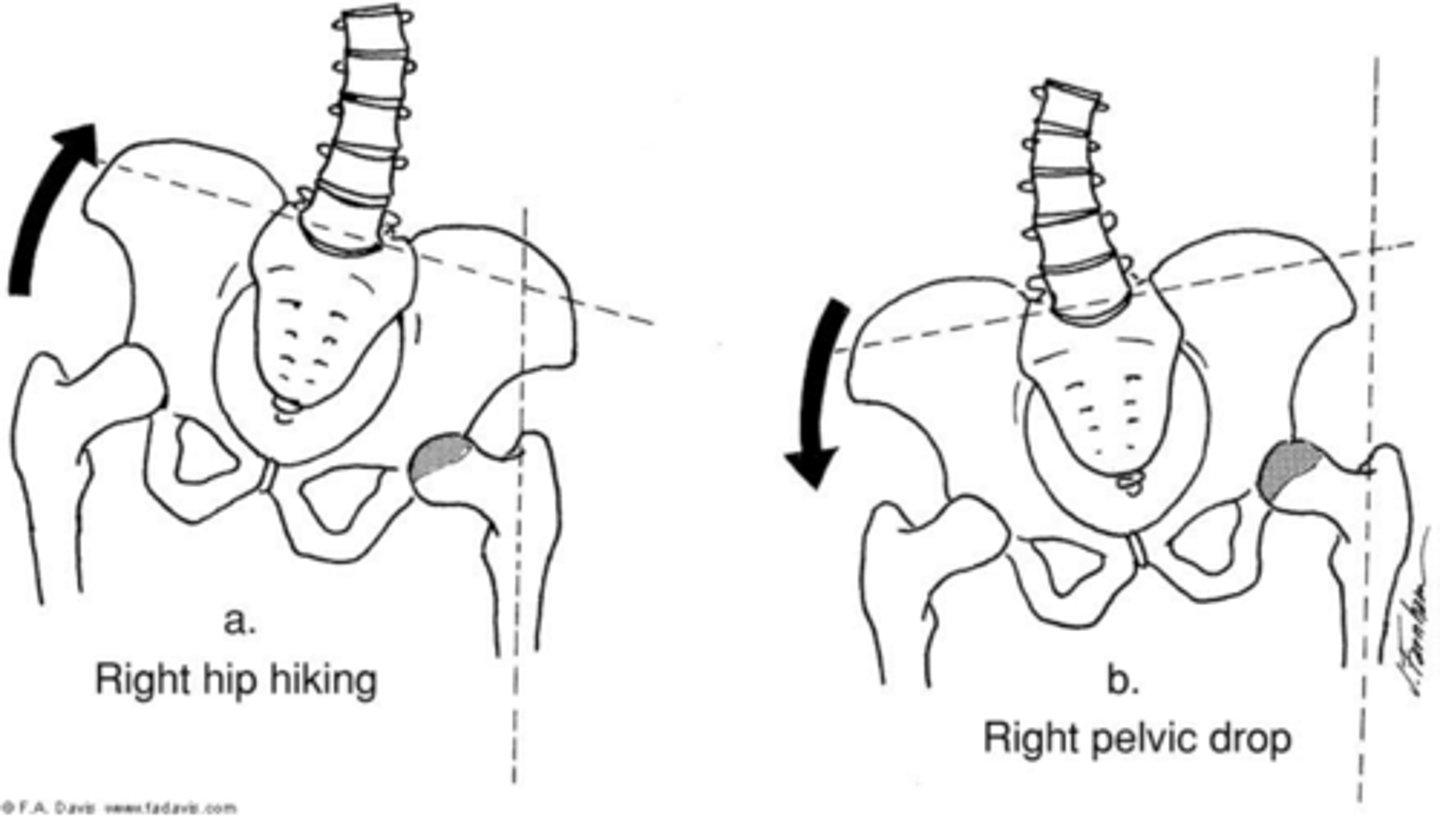
hip depression (drop)
adduction of stance limb
(B IN IMAGE)
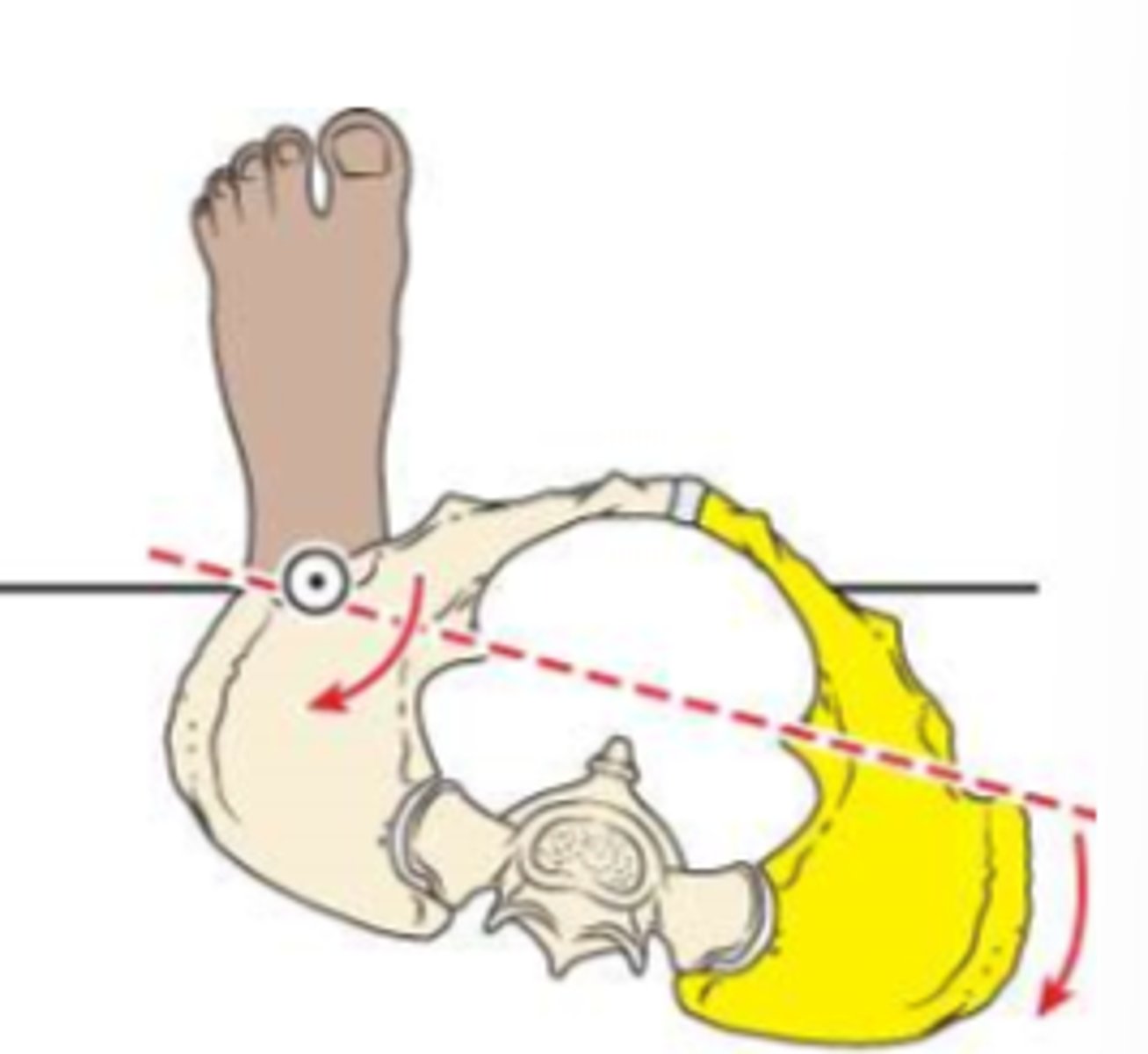
rotation
transverse plane motion of the pelvis around one supporting limb
*named according to motion of opposite side from supporting limb
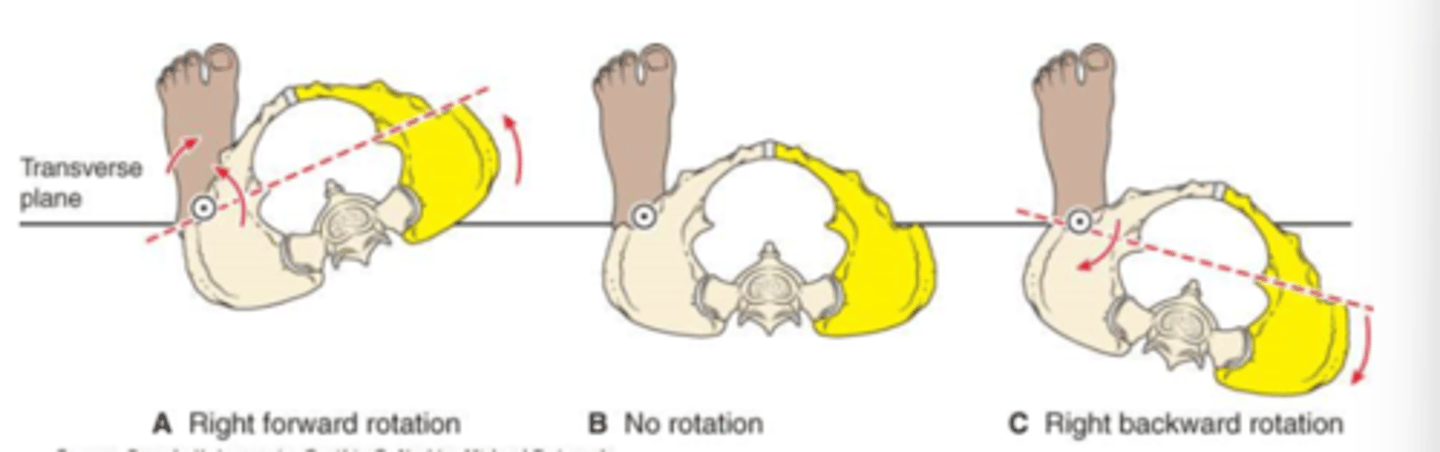
anterior pelvic rotation
IR of stance limb
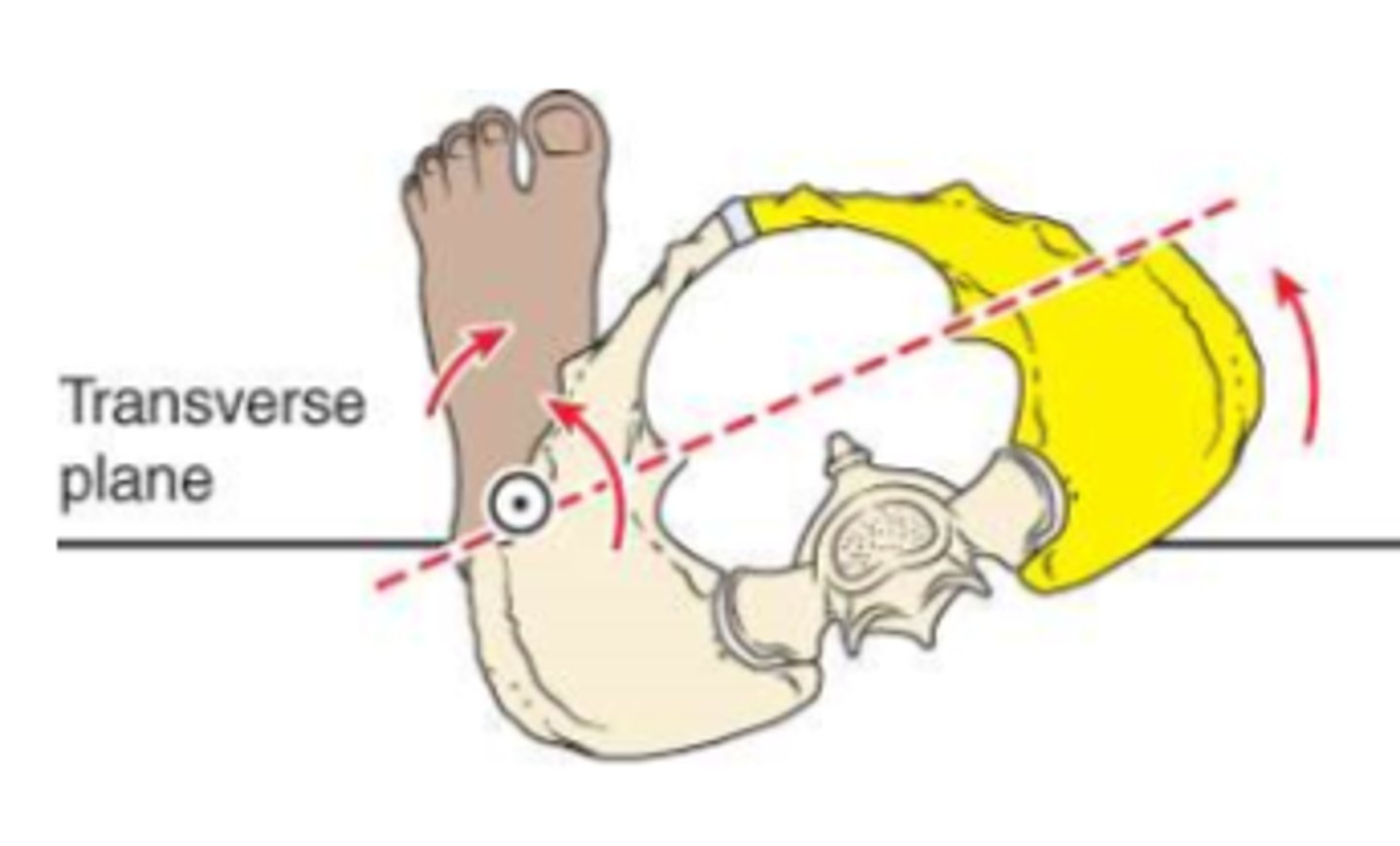
posterior pelvic rotation
ER of stance limb
open chain arthrokinematics
1. flexion
2. extension
3. abduction
4. adduction
5. internal rotation
6. external rotation
anterior/superior, posterior/inferior
During hip FLEXION, the convex femoral head rolls ____________/_____________ and glides ______________/____________.
posterior/inferior, anterior/superior
During hip EXTENSION, the convex femoral head rolls ____________/_____________ and glides ______________/____________.
superior/lateral, inferior/medial
During hip ABDUCTION, the convex femoral head rolls ____________/_____________ and glides ______________/____________.
inferior/medial, superior/lateral
During hip ADDUCTION, the convex femoral head rolls ____________/_____________ and glides ______________/____________.
anterior/medial, posterior/lateral
During hip IR, the convex femoral head rolls ____________/_____________ and glides ______________/____________.
posterior/lateral, anterior/medial
During hip ER, the convex femoral head rolls ____________/_____________ and glides ______________/____________.
closed chain arthrokinematics
1. anterior tilt
2. posterior tilt
3. upward lateral tilt
4. downward lateral tilt
5. anterior rotation
6. posterior rotation
anterior, anterior
During pelvic ANTERIOR TILT, the concave acetabulum rolls _____________ and glides _______________.
posterior, posterior
During pelvic POSTERIOR TILT, the concave acetabulum rolls _____________ and glides _______________.
lateral, lateral
During pelvic UPWARD LATERAL TILT, the concave acetabulum rolls _____________ and glides _______________.
medial, medial
During pelvic DOWNWARD LATERAL TILT, the concave acetabulum rolls _____________ and glides _______________.
anterior, anterior
During pelvic ANTERIOR ROTATION, the concave acetabulum rolls _____________ and glides _______________.