Skeletal System Flashcards
1/141
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about the skeletal system
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Bones
Organs that make up the skeletal system.
Number of bones in an adult human
206
Framework function of the skeletal system
Support the body’s muscles, fat, and skin.
Protection function of the skeletal system
Surround organs, like the skull protecting the brain.
Levers for movement function of the skeletal system
Muscles pull on bones to facilitate this.
Storage function of the skeletal system
Minerals, including most of the body’s calcium.
Blood cell formation location
Red bone marrow in the medullary cavity.
Hemopoiesis or hematopoiesis
Red and white blood cells and platelets formation.
Compact bone (cortical bone)
Made of osteons, hard, dense, strong; outer portion of bone.
Cancellous bone (spongy bone)
Lacy, porous; inner portion of bone tissue.
Osteoblast
Building bone matrix, immature cells.
Osteoclast
Break down bone matrix to release minerals.
Osteocyte
Mature bone cell surrounded by bone matrix.
Shapes/Classifications of Bones
long, short, flat, irregular, sesamoid
Diaphysis
the long shaft of the long bones
Epiphysis
the two extremities or ends.
Medullary canal
cavity in the diaphysis.
Filled with yellow marrow which is mainly fat cells.
Endosteum
a membrane that lines the medullary canal and keeps the yellow marrow intact.
It also produces some bone growth.
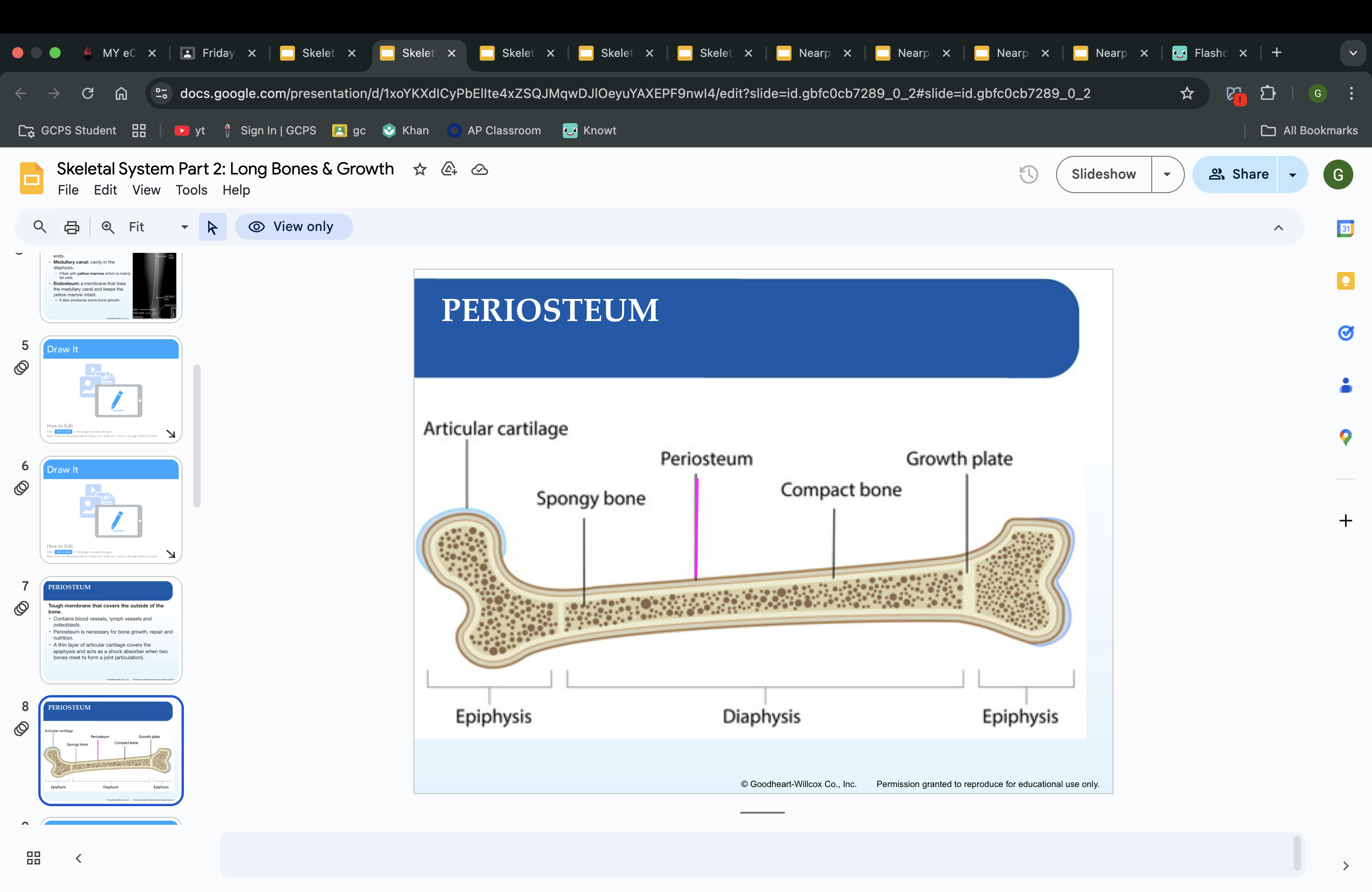
PERIOSTEUM
Tough membrane that covers the outside of the bone.
Contains blood vessels, lymph vessels and osteoblasts.
Periosteum is necessary for bone growth, repair and nutrition.
A thin layer of articular cartilage covers the epiphysis and acts as a shock absorber when two bones meet to form a joint (articulation).
Red Bone Marrow
a type of tissue found within certain bones that produces blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
longitudinal growth
epiphyseal plate - length
circumferential growth
change in diameter
appositional growth
growth that maintains correct proportions during growth
adult bone development
aging causes loss of bone mass
Epiphyseal plates:
growth plates
Separate the diaphysis from the epiphysis
Cartilage cells at the epiphysis (chondrocytes) reproduce rapidly and die rapidly.
Becomes calcified cartilage and blood vessels begin to grow, building up new bone.
hypertrophy of bones
stronger bones
atrophy of bones
weaker bones
SKELETAL SYSTEM IS DIVIDED INTO TWO SECTIONS: what are they called
Axial skeleton and Appendicular skeleton
Axial skeleton
forms the main trunk of the body and is composed of the skull, spinal column, ribs and breastbone.
Appendicular skeleton
forms the extremities and is composed of the shoulder girdle, arm bones, pelvic girdle and leg bones
what is included in the axial skeleton
the skull
the vertebral column
the thoracic cage
what is included in the appendicular skeleton
shoulder & arms
hips & legs
pelvis
The Skull
the cranium
surround the brain
the facial bones
protect the front of the head
The Cranium has 8 bones, name them
frontal bone
parietal bones (2)
temporal bones (2)
occipital bones
ethmoid bone
sphenoid bone
The Facial Bones – 14 TOTAL
maxillary bones (2) —— upper jaw
palatine bones (2) —— hard palate
zygomatic bones (2) ——- cheek bones
lacrimal bones (2) —— medial eye area
nasal bones (2) —— bridge of nose
vomer —— vertical bone in nasal area
inferior concha bones (2) —- lateral bone in nasal area
mandible —— lower jaw
Sutures
areas where the cranial bones have joined together.
Sinuses
air spaces in the bones of the skull that act as resonating chambers for the voice. They are lined with mucous membranes.
Foramina
openings in bones that allow nerves and blood vessels to enter or leave the bone.
fontanels
soft spots, allow for the enlargement of the skull as brain growth occurs. (soft spot on baby heads)
Paranasal Sinuses
frontal
ethmoid
sphenoid
maxillary
Spinal Column
Made of 26 bones called vertebrae.
These bones protect the spinal cord and provide support for the head and trunk.
what is included in the spinal column
7 cervical (neck)
12 thoracic (chest)
5 lumbar (waist)
1 sacrum (back of pelvic girdle)
1 coccyx (tailbone)
Intervertebral Disks
Pads of cartilage
located between vertebrae
shock absorbers
allow flexibility
Lordosis
Sway back
Kyphosis
hump back
Scoliosis
Curve side to side
The Upper Extremity
humerus
radius
ulna
the shoulder girdle
scapula
clavicle
the wrist and hand
carpals (8)
metacarpals (5)
phalanges (14)
The Lower Extremity
the pelvic girdle
ilium
ischium
pubis
the leg
femur
tibia
fibula
patella
the ankle and foot
tarsals (7)
metatarsals (5)
phalanges (14)
synarthroses
immovable joints
aka skull
amphiarthrosis
slightly movable joints
diarthrosis/synovial
freely movable joints
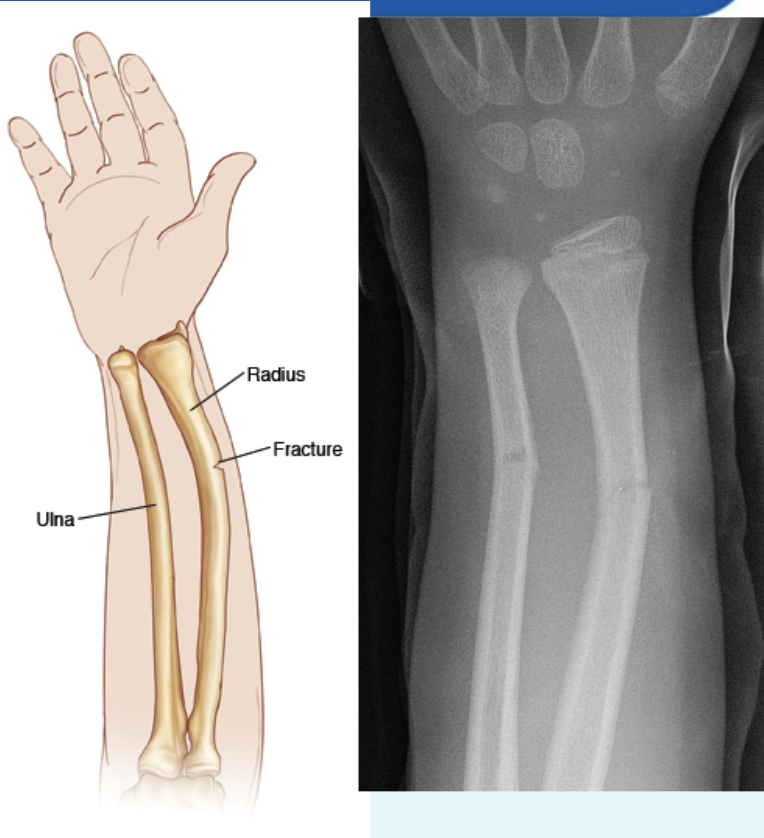
Fracture
is a crack or a break in a bone
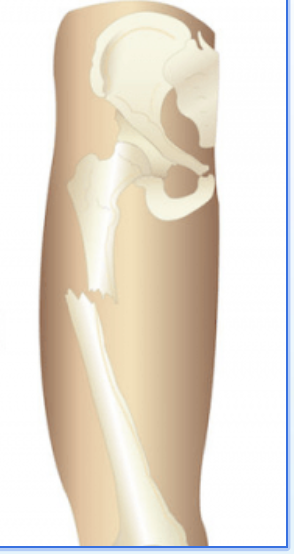
Greenstick Fx
bone is bent and splints, causing a crack or incomplete break; common in Children
Simple or Closed Fx
a complete break of the bone with no damage to the skin
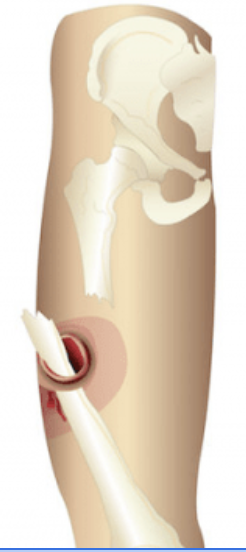
Compound or Open Fx:
ruptures thru skin, increase in infections
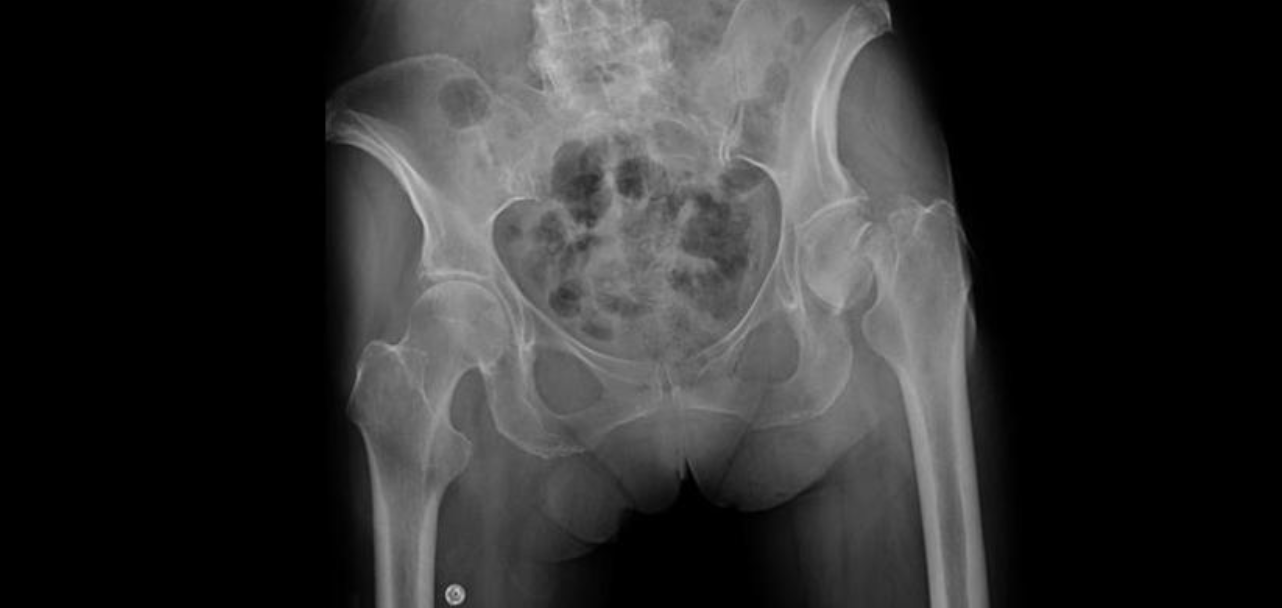
Impacted Fx
broken bones are pushed into each other.
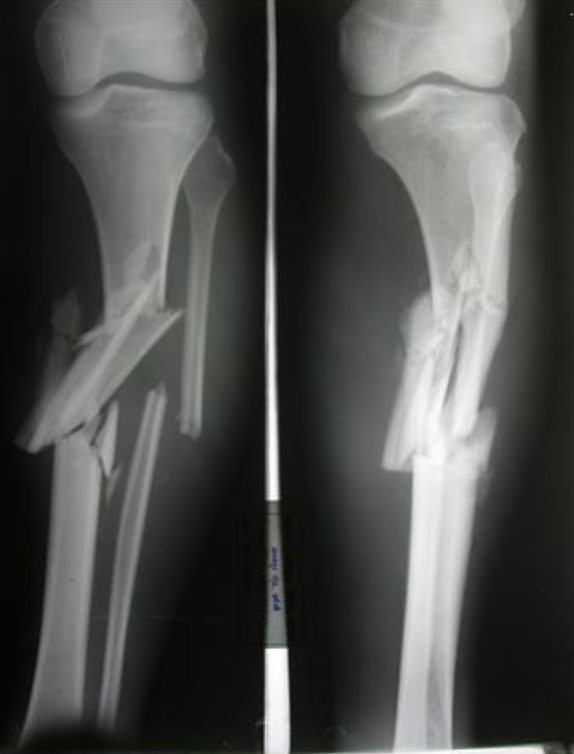
Comminuted
Bone displaces or splinters into more than 2 pieces.
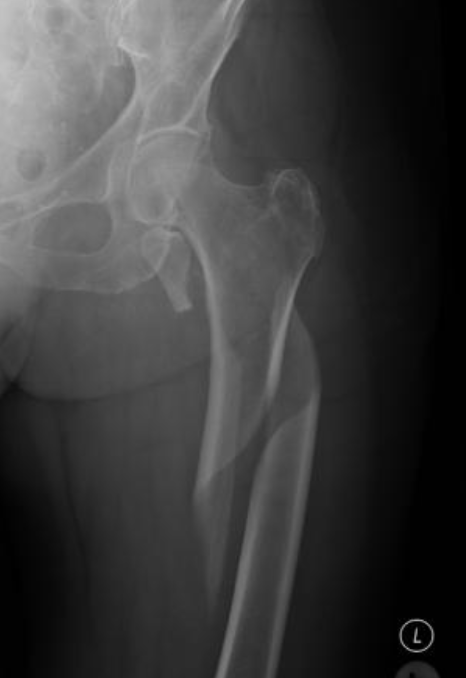
Spiral
bone twists resulting in one or more breaks and radiates up bone.
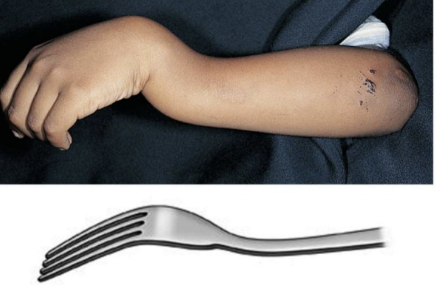
Colles Fx
breaking and dislocation of the distal radius and ulna that causes a characteristic bulge at the wrist; caused by falling with outstretched hands.
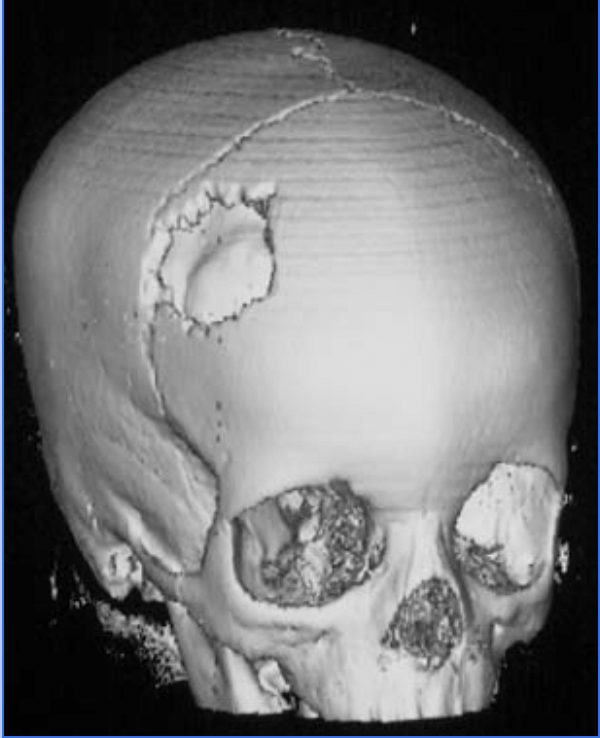
Depression Fx
a broken piece of skull bone moves internally, common with severe head injuries.
Fracture Reduction
Aligning the bone in proper position for healing.
Closed Reduction
uses traction, casting or splint to maintain proper position while the bone heals
Open Reduction
uses surgical repair of the bone. may include the use of special pins, screws, plates or other devices to maintain position
Dislocation
When a bone is forcefully displaced from a joint.
Frequently occurs in shoulders, fingers, knees and hips.
After ______ is reduced, the dislocation is immobilized with a splint, cast, or traction.
Sprain
When a twisting action tears the ligaments at at joint.
most common in wrists and ankles
symptoms: pain, swelling, discoloration, and limited range of motion.
Osteomyelitis
Bone inflammation caused by a pathogenic organism.
Accumulation of pus in the medullary canal
Infection impedes circulation of blood causing bone death
Osteoporosis
Softening of the bones caused by hormone deficiency (estrogen), lack of calcium in the diet, sedentary lifestyle.
Bones become porous, brittle
Bone Density Tests: early detection
Arthritis
A group of diseases involving inflammation of the joints.
Rheumatoid arthritis
autoimmune system attacks joints
Chronic, inflammatory disease affecting the connective tissues and joints
Three times more common in women than n men
Onset often occurs between the ages of 35-45.
Progressive attacks can cause scar tissue formation and atrophy of bone and muscle tissue, which result in permanent deformity and immobility.
Osteoarthritis
degeneration of articular cartilage
Most common form of arthritis
Chronic disease that usually occurs as a result of aging.
Frequently affects the hips and knees.
Symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, aching and limited range of motion.
No cure
Symptoms relieved by: rest, applications of heat and cold, anti-inflammatory medications, aspirin, injection of steroids into the joints and special exercises.
BURSITIS
inflammation of the bursae- small, fluid-filled sacs surrounding the joints.
Frequently affects the shoulders, elbows, hips or knees.
RUPTURED DISC
Also called herniated or slipped disc.
Occurs when an intervertebral disc (pad of cartilage separating the vertebrae) ruptures or protrudes out of place and causes pressure on the spinal nerve.
Most common site is at the lumbar-sacral area, but can occur anywhere on the spinal column.
how many muscles are in the human body
640
what are the functions of the muscular system
Provide body movement
Help Maintain body posture
Protect internal organs
Produce body heat & maintain core body temp.
Provide body shape
Tendon
strong, tough connective cords
attaches muscle to bone.
Ligament
attaches bone to bone.
Fascia
tough, sheet-like membrane cover/protect muscle cells
Skeletal Muscle
Called striated (striped) because they have striations of alternating light and dark bands.
Makes up the fleshy body parts of our body.
Provide movements to the limbs by acting as levers.
Origin
the point a muscle tendon attaches to the stationary bone.
Insertion
the point a muscle’s tendon attaches to the moveable bone.
Belly
the largest part of the muscle containing muscle cells.
Synergist
muscles working together in the same direction for motion
Prime Mover
when one muscle is more important in the motion than another for motion.
Antagonist
relaxes
Agonist
contracts
EXCITABILITY
irritability, the ability to respond to a stimulus such as a nerve impulse.
CONTRACTIBILITY
muscle fibers that are stimulated by nerves contract, or become short and thick, which causes movement.
EXTENSIBILITY
the ability to be stretched
ELASTICITY
allows the muscle to return to its original shape after it has contracted or stretched.
skeletal muscle
voluntary
striated (stripes)
Attached to bones and causes body movement.
Voluntary movement: a person has control over its action.
smooth muscle
involuntary
no striations
Found in the internal organs of the body such as those of the digestive and respiratory systems and the blood vessels and eyes.
cardiac muscle
involuntary
striated
intercalated disks
Forms the walls of the heart and contracts to circulate blood.
Involuntary movement- they function without conscious thought or control.
muscle tone
the state of partial contraction is called, described as a state of readiness to act.
Muscles are partially contracted at all times, even when not in use.
Loss of muscle tone can occur in severe illness such as paralysis.
muscle fatigue
the buildup of lactic acid caused by vigorous exercise where blood is unable to be transported
Sarcomeres
sarcomeres are the area in the muscle cells that shorten in the muscle fibers
Chemical reactions between actin filaments sliding along myosin filaments generate a muscle contraction.
sternocleidomastoid
side of neck
turns and flexes head
trapezius
upper back and neck
extends head, moves shoulder
Deltoid
shoulder
abducts arm, injection site
biceps brachii
upper arm
flexes lower arm
triceps brachii
upper arm
extends lower arm